SDK Manager
The Android SDK separates tools, platforms, and other components into packages you can download using the SDK Manager. For example, when the SDK Tools are updated or a new version of the Android platform is released, you can use the SDK Manager to quickly download them to your environment.
You can launch the SDK Manager in one of the following ways:
- From Eclipse (with ADT), select Window >Android SDK Manager.
- From Android Studio, select Tools >Android >SDK Manager.
- On Windows, double-click the SDK Manager.exe file at the root of the Android SDK directory.
- On Mac or Linux, open a terminal and navigate to the tools/ directory in the location where the Android SDK is installed, then execute android sdk .
You can select which packages you want to download by toggling the checkboxes on the left, then click Install to install the selected packages.
Figure 1. The Android SDK Manager shows the SDK packages that are available, already installed, or for which an update is available.
There are several different packages available for the Android SDK. The table below describes most of the available packages and where they’re located in your SDK directory once you download them.
Recommended Packages
Here’s an outline of the packages required and those we recommend you use:
SDK Tools Required. Your new SDK installation already has the latest version. Make sure you keep this up to date. SDK Platform-tools Required. You must install this package when you install the SDK for the first time. SDK Platform Required.You must download at least one platform into your environment so you’re able to compile your application. In order to provide the best user experience on the latest devices, we recommend that you use the latest platform version as your build target. You’ll still be able to run your app on older versions, but you must build against the latest version in order to use new features when running on devices with the latest version of Android.
To get started, download the latest Android version, plus the lowest version you plan to support (we recommend Android 2.2 for your lowest version).
System Image Recommended. Although you might have one or more Android-powered devices on which to test your app, it’s unlikely you have a device for every version of Android your app supports. It’s a good practice to download system images for all versions of Android your app supports and test your app running on them with the Android emulator. Android Support Recommended. Includes a static library that allows you to use some of the latest Android APIs (such as fragments, plus others not included in the framework at all) on devices running a platform version as old as Android 1.6. All of the activity templates available when creating a new project with the ADT Plugin require this. For more information, read Support Library. SDK Samples Recommended. The samples give you source code that you can use to learn about Android, load as a project and run, or reuse in your own app. Note that multiple samples packages are available — one for each Android platform version. When you are choosing a samples package to download, select the one whose API Level matches the API Level of the Android platform that you plan to use.
Tip: For easy access to the SDK tools from a command line, add the location of the SDK’s tools/ and platform-tools to your PATH environment variable.
The above list is not comprehensive and you can add new sites to download additional packages from third-parties.
In some cases, an SDK package may require a specific minimum revision of another package or SDK tool. The development tools will notify you with warnings if there is dependency that you need to address. The Android SDK Manager also enforces dependencies by requiring that you download any packages that are needed by those you have selected.
Adding New Sites
By default, Available Packages displays packages available from the Android Repository and Third party Add-ons. You can add other sites that host their own Android SDK add-ons, then download the SDK add-ons from those sites.
For example, a mobile carrier or device manufacturer might offer additional API libraries that are supported by their own Android-powered devices. In order to develop using their libraries, you must install their Android SDK add-on, if it’s not already available under Third party Add-ons.
If a carrier or device manufacturer has hosted an SDK add-on repository file on their web site, follow these steps to add their site to the Android SDK Manager:
- Select Available Packages in the left panel.
- Click Add Add-on Site and enter the URL of the repository.xml file. Click OK.
Any SDK packages available from the site will now be listed under a new item named User Add-ons.
Troubleshooting
Problems connecting to the SDK repository
If you are using the Android SDK Manager to download packages and are encountering connection problems, try connecting over http, rather than https. To switch the protocol used by the Android SDK Manager, follow these steps:
Источник
Installing the Android SDK
Android Studio provides everything you need to start developing apps for Android, including the Android Studio IDE and the Android SDK tools.
If you didn’t download Android Studio, go download Android Studio now, or switch to the stand-alone SDK Tools install instructions.
Before you set up Android Studio, be sure you have installed JDK 6 or higher (the JRE alone is not sufficient)—JDK 7 is required when developing for Android 5.0 and higher. To check if you have JDK installed (and which version), open a terminal and type javac -version . If the JDK is not available or the version is lower than 6, go download JDK.
To set up Android Studio on Windows:
- Launch the .exe file you just downloaded.
- Follow the setup wizard to install Android Studio and any necessary SDK tools.
On some Windows systems, the launcher script does not find where Java is installed. If you encounter this problem, you need to set an environment variable indicating the correct location.
Select Start menu > Computer > System Properties > Advanced System Properties. Then open Advanced tab > Environment Variables and add a new system variable JAVA_HOME that points to your JDK folder, for example C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_21 .
The individual tools and other SDK packages are saved outside the Android Studio application directory. If you need to access the tools directly, use a terminal to navigate to the location where they are installed. For example:
To set up Android Studio on Mac OSX:
- Unzip the downloaded zip file, android-studio-ide- -mac.zip .
- Drag and drop Android Studio into the Applications folder.
- Open Android Studio and follow the setup wizard to install any necessary SDK tools.
Depending on your security settings, when you attempt to open Android Studio, you might see a warning that says the package is damaged and should be moved to the trash. If this happens, go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy and under Allow applications downloaded from, select Anywhere. Then open Android Studio again.
The individual tools and other SDK packages are saved outside the Android Studio application directory. If you need access the tools directly, use a terminal to navigate into the location where they are installed. For example:
To set up Android Studio on Linux:
- Unpack the downloaded Tar file, android-studio-ide- -linux.zip , into an appropriate location for your applications.
- To launch Android Studio, navigate to the android-studio/bin/ directory in a terminal and execute studio.sh .
You may want to add android-studio/bin/ to your PATH environmental variable so that you can start Android Studio from any directory.
If the SDK is not already installed, follow the setup wizard to install the SDK and any necessary SDK tools.
Note: You may also need to install the ia32-libs, lib32ncurses5-dev, and lib32stdc++6 packages. These packages are required to support 32-bit apps on a 64-bit machine.
Android Studio is now ready and loaded with the Android developer tools, but there are still a couple packages you should add to make your Android SDK complete.
The stand-alone SDK Tools package does not include a complete Android development environment. It includes only the core SDK tools, which you can access from a command line or with a plugin for your favorite IDE (if available).
If you didn’t download the SDK tools, go download the SDK now, or switch to the Android Studio install instructions.
To get started on Windows:
Your download package is an executable file that starts an installer. The installer checks your machine for required tools, such as the proper Java SE Development Kit (JDK) and installs it if necessary. The installer then saves the Android SDK Tools to a specified the location outside of the Android Studio directories.
- Double-click the executable ( .exe file) to start the install.
- Make a note of the name and location where you save the SDK on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later when using the SDK tools from the command line.
- Once the installation completes, the installer starts the Android SDK Manager.
To get started on Mac OSX:
Unpack the ZIP file you’ve downloaded. By default, it’s unpacked into a directory named android-sdk-mac_x86 . Move it to an appropriate location on your machine, such as a «Development» directory in your home directory.
Make a note of the name and location of the SDK directory on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later when using the SDK tools from the command line.
To get started on Linux:
Unpack the .zip file you’ve downloaded. The SDK files are download separately to a user-specified directory.
Make a note of the name and location of the SDK directory on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later when using the SDK tools from the command line.
Troubleshooting Ubuntu
- If you need help installing and configuring Java on your development machine, you might find these resources helpful:
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Java
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/JavaInstallation
- Here are the steps to install Java:
-
If you are running a 64-bit distribution on your development machine, you need to install additional packages first. For Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) and above, install the libncurses5:i386 , libstdc++6:i386 , and zlib1g:i386 packages using apt-get :
For earlier versions of Ubuntu, install the ia32-libs package using apt-get :
The Android SDK tools are now ready to begin developing apps, but there are still a couple packages you should add to make your Android SDK complete.
Then, select which SDK bundle you want to install:
Источник
How to Install Android SDK Tools
To Develop Android-based Apps, you will need to Install Android SDK. In this How to Install Android SDK Tools, we will learn what is Android SDK is and how to install the Android SDK using Android Studio. First, we will learn about the Android SDK Manager GUI to manage the SDK. We will find out how to find out the SDK location, various components of SDK like SDK Platforms, SDK Tools, Build Tools, Platform-tools, System Images, Emulators, etc. Finally, we will show you how to install the Android SDK.
Table of Contents
What is Android SDK
The Android Software Development Kit (SDK) is a set of development tools, which is needed to develop Android-based applications.
We can create Android Apps in many ways. You can make use of Java or Kotlin or use frameworks like Ionic, NativeScript or React Native. But whichever tools you use the Android SDK is a must.
The Android SDK comes with the required tools to build Android apps. Using the SDK you can install the app in the device and access the features provided by the OS. The SDK also comes with tools to debug the application. The Android emulator allows you to test apps in different types of devices, without needing to buy one.
The Android SDK comes in various versions. Each new release of Android OS is accompanied by a new SDK version or API Version. For Example, the latest Android Pie ( or Android 9 ) has a corresponding SDK API version of 28. You can refer to the SDK Platform release notes to find out the more details about each release
Android SDK Manager
The Android SDK Manager helps us download & manage the Android SDK. It makes it very easier to search for updates, install and remove the older unused SDK’s easily
The SDK Manager is part of the Android Studio and installed along with it. Hence, you need to install it first. Refer to our tutorial How to download & install the Android Studio tutorial.
You can open the SDK Manager by clicking on Menu Option Tools -> SDK Manager ( or Tools -> Android -> SDK Manager in older versions of Android Studio). You can also click on the
icon in the tool bar as shown in image below
Locating the Android SDK Manager in Android Studio
The Following is the image of the Android SDK Manager
Android SDK Manager
In the lefthand side pane, you have to select Android SDK under Appearance & behavior -> System Settings
Android SDK Location
The Android SDK path is usually C:\Users\ \AppData\Local\Android\sdk as shown in the image above. But you can change it by clicking on the edit link.
The SDK Location is very important if you are using NativeScript or ionic, For NativeScript to pick up the SDK you need to define the ANDROID_HOME environment variable. While the ionic expects ANDROID_SDK_ROOT environment variable to point to the SDK path.
The SDK Manager contains three tabs. They are SDK Platforms SDK Tools & SDK Update Sites.
SDK Platforms
This tab contains the list of Android SDKs. The SDKs are a must if you want to develop apps targeting the Android Platform. Each new version of Android comes with its own SDK version ( API level and a revision).
Under each API, there are a few different types of files, which are displayed only if you select show package details option. They are shown in the image below.
Android SDK Platform:
This file is required to compile and run the Android Application. At least one SDK Platform must be installed. Always use the latest SDK version, when developing the App. You are still able to run the App on the older versions of Android.Sources for Android package:
The source files for the platform, contain metadata about the SDK Platform and is helpful when debugging the android App. Always install the corresponding sources when installing the SDK PlatformSystem Image packages:
These are used by the Android Emulators to run the App in Emulator. Each SDK platform version contains a list of supported system images. You must select an image based on your computer Processor. You can also install them when you are creating the Android Virtual Devices (AVDs) using the AVD Manager.SDK Tools
This tab contains the set of development and debugging tools for the Android SDK
Android SDK Build-Tools: Required
This contains the tools required to build Android Apps. You must install this package. See the Android SDK Build tools release notes.Android SDK Platform-Tools: Required
This contains the tools required by the Android platform. The tools like ADB (Android Debug Bridge) are part of the Platform-tools. This package is required. See the Android SDK Platform Release notesAndroid SDK Tools: Required
This tool includes essential tools such as ProGuard etc. See the SDK Tools Release Notes.Android Emulator: Recommended
The Android Emulator was part of the Android SDK Tools up to version 25.2. Now they are available to install separately. You need an Emulator to debug and test your applications in an Emulated Android Runtime. See the Android Emulator release notes.SDK Update Sites
This tab lists the Android & third party sites, where Android Studio looks for the update. You can add other sites to the list and download the packages from those sites as well.
SDK Update sites. List of sites where Android Looks for Updates.
If you are behind a proxy server, then remember to setup the proxy server from the HTTP Proxy option.
How to install the Android SDK
To Install a new SDK click the checkbox, Similarly to update an SDK. Whenever an update is available a dash appears in the checkbox next to the package. The status field shows the current installation status of the SDK.
To remove or uninstall a package, unselect the checkbox
Click on the Apply or OK button to begin the installation.
Next, you may be asked to accept the License Terms and then the installation begins. Installation takes some time to complete depending on the no of packages you have selected.
Once done, click on Finish. Now the Android SDK is successfully installed.
Summary
In this How to Install Android SDK Tutorial, we learned what is Android SDK is and how to install/update it using Android SDK, We also learned a few things about SDK Platform, SDK Tools, SDK Platform build tools, SDK Build Tools, System Images, etc.
Источник
-

 icon in the tool bar as shown in image below
icon in the tool bar as shown in image below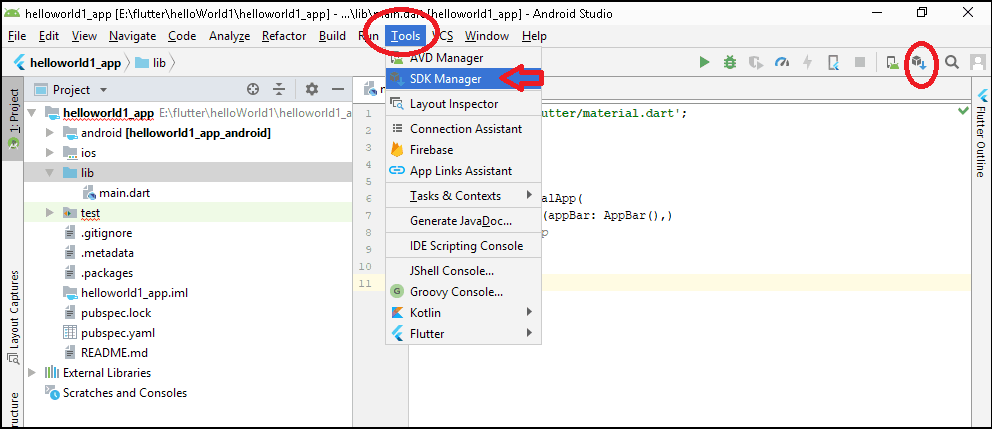 Locating the Android SDK Manager in Android Studio
Locating the Android SDK Manager in Android Studio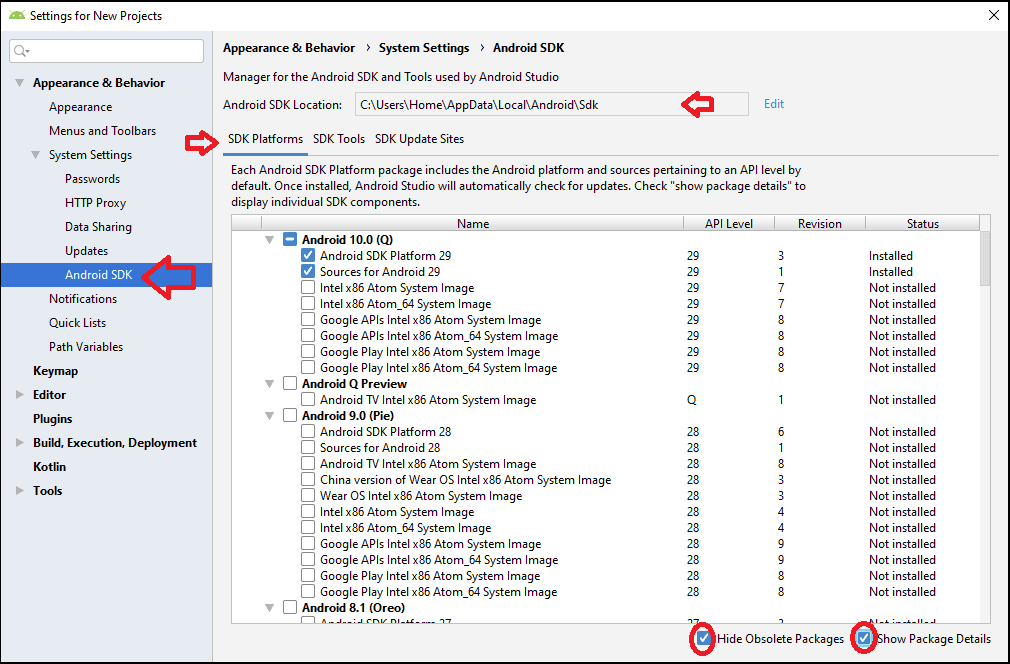 Android SDK Manager
Android SDK Manager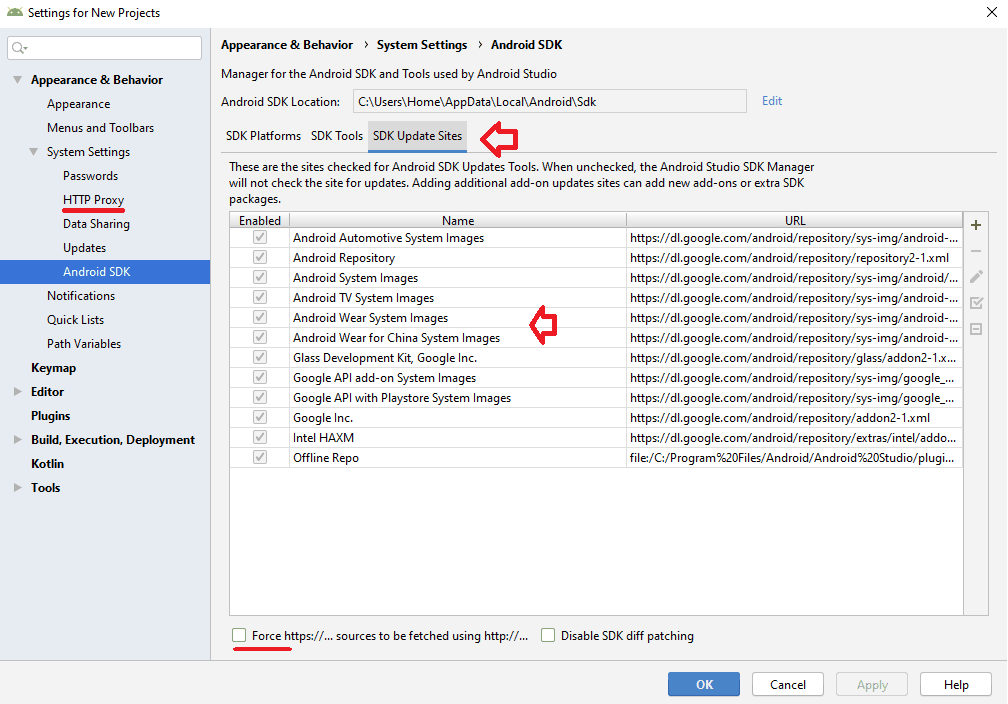 SDK Update sites. List of sites where Android Looks for Updates.
SDK Update sites. List of sites where Android Looks for Updates.


