- About Apple ID security questions
- Set up or change your security questions
- iCloud security overview
- Data security
- End-to-end encryption
- Data types and encryption
- Additional information
- iCloud Data Recovery Service
- Messages in iCloud
- Health data
- Privacy
- Learn more
- Security and your Apple ID
- Use a strong password for your Apple ID
- Make the answers to your security questions hard to guess
- Protect your account with two-factor authentication
- Check for encryption and SSL
- Employee privacy and security policies
- Other tips for keeping your account secure
- Apple Platform Security
- Hardware security
- System security
- Encryption and Data Protection
- App security
- Services security
About Apple ID security questions
Learn about Apple ID security questions, including how to set up or change your questions.
Apple uses security questions to provide you with a secondary method to identify yourself online or when contacting Apple Support. Security questions are designed to be memorable to you but hard for anyone else to guess. When used in conjunction with other identifying information, they help Apple verify that you’re the person requesting access to your account.
You might be asked to answer one or more of your security questions before you can change your password or other account information, view your device details, or make an iTunes purchase from a new device.
If you don’t want security questions or you’re concerned about forgetting the answers, you can set up two-step verification or two-factor authentication. With two-step verification and two-factor authentication, you don’t need security questions to secure your account or verify your identity.
Set up or change your security questions
- Sign in to your Apple ID account page.
- In the Security section, click Edit.
- If you already have security questions, you’ll be asked to answer them before you continue. Forgot the answers?
- Click Change Questions. If you need to set them up, click Add Security Questions.
- Choose your new security questions, then enter the answers.
- Add and verify a rescue email address.
It’s very important to remember the answers to your security questions to avoid being locked out of your account. And make sure you add and verify your rescue email address. If you forget the answers to your security questions, you’ll need a rescue email address to help you reset them.
Источник
iCloud security overview
iCloud uses best-in-class security technologies, employs strict policies to protect your information, and leads the industry by adopting secure, privacy-preserving technologies like end-to-end encryption for your data.
Data security
iCloud secures your information by encrypting it when it’s in transit and storing it in iCloud in an encrypted format. Many Apple services use end-to-end encryption, which means that only you can access your information, and only on trusted devices where you’re signed in with your Apple ID.
In some cases, your iCloud data may be stored using third-party partners’ servers—such as Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud Platform—but these partners don’t have the keys to decrypt your data stored on their servers.
End-to-end encryption
End-to-end encryption provides the highest level of data security. On each of your devices, the data that you store in iCloud and that’s associated with your Apple ID is protected with a key derived from information unique to that device, combined with your device passcode which only you know. No one else, not even Apple, can access end-to-end encrypted information.
End-to-end encryption requires that you use two-factor authentication for your Apple ID and set a passcode on your device. Some features also require recent software, generally iOS 13 or later. With two-factor authentication, your account can be accessed only on devices you trust, like your iPhone, iPad, or Mac. Keeping your software up to date, using two-factor authentication for your Apple ID, and protecting your device with a passcode—or password on Mac—Face ID, or Touch ID are the most important things that you can do to maintain the security of your devices and data.
Data types and encryption
Here’s more detail on how iCloud protects your data.
| Data | Encryption | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Backup | In transit & on server | A minimum of 128-bit AES encryption |
| Calendars | In transit & on server | |
| Contacts | In transit & on server | |
| iCloud Drive | In transit & on server | |
| Notes | In transit & on server | |
| Photos | In transit & on server | |
| Reminders | In transit & on server | |
| Safari Bookmarks | In transit & on server | |
| Siri Shortcuts | In transit & on server | |
| Voice Memos | In transit & on server | |
| Wallet passes | In transit & on server | |
| iCloud.com | In transit | All sessions at iCloud.com are encrypted with TLS 1.2. Any data accessed via iCloud.com is encrypted on server as indicated in this table. |
| In transit | All traffic between your devices and iCloud Mail is encrypted with TLS 1.2. Consistent with standard industry practice, iCloud does not encrypt data stored on IMAP mail servers. All Apple email clients support optional S/MIME encryption. | |
| Apple Card transactions | End-to-end | |
| Health data | End-to-end | Additional info below |
| Home data | End-to-end | |
| Keychain | End-to-end | Includes all of your saved accounts and passwords |
| Maps Favorites, Collections and search history | End-to-end | |
| Memoji | End-to-end | |
| Messages in iCloud | End-to-end | Additional info below |
| Payment information | End-to-end | |
| QuickType Keyboard learned vocabulary | End-to-end | |
| Safari History, Tab Groups, and iCloud Tabs | End-to-end | |
| Screen Time | End-to-end | |
| Siri information | End-to-end | Includes Siri settings and personalization, and if you have set up Hey Siri, a small sample of your requests |
| Wi-Fi passwords | End-to-end | |
| W1 and H1 Bluetooth keys | End-to-end |
Additional information
iCloud Data Recovery Service
If you forget your password or device passcode, iCloud Data Recovery Service can help you decrypt your data so you can regain access to your photos, notes, documents, device backups, and more. Data types that are protected by end-to-end encryption—such as your Keychain, Messages, Screen Time, and Health data—are not accessible via iCloud Data Recovery Service. Your device passcodes, which only you know, are required to decrypt and access them. Only you can access this information, and only on devices where you’re signed in to iCloud.
Messages in iCloud
For Messages in iCloud, if you have iCloud Backup turned on, your backup includes a copy of the key protecting your messages. This ensures you can recover your messages if you lose access to your Keychain and your trusted devices. When you turn off iCloud Backup, a new key is generated on your device to protect future messages and isn’t stored by Apple.
Health data
If you back up your device on your Mac or iTunes, Health data is stored only if the backup is encrypted. Learn more about managing your Health data.
Privacy
Apple believes that privacy is a human right. Our Privacy Policy covers how we collect, use, disclose, transfer, and store your information. And in addition to adhering to the Apple Privacy Policy, Apple designs all iCloud features with your privacy in mind.
Learn more
Learn more about advanced security features in Apple products.
Information about products not manufactured by Apple, or independent websites not controlled or tested by Apple, is provided without recommendation or endorsement. Apple assumes no responsibility with regard to the selection, performance, or use of third-party websites or products. Apple makes no representations regarding third-party website accuracy or reliability. Contact the vendor for additional information.
Источник
Security and your Apple ID
Learn more about security and your Apple ID.
Your Apple ID is the account you use to access Apple services like the App Store, Apple Music, iCloud, iMessage, FaceTime, and more. It includes the email address and password you use to sign in as well as the contact, payment, and security details you use across Apple services. Apple takes the privacy of your personal information very seriously and employs industry-standard practices to safeguard your Apple ID.
Here are some of the best practices you can follow to maximize the security of your account.
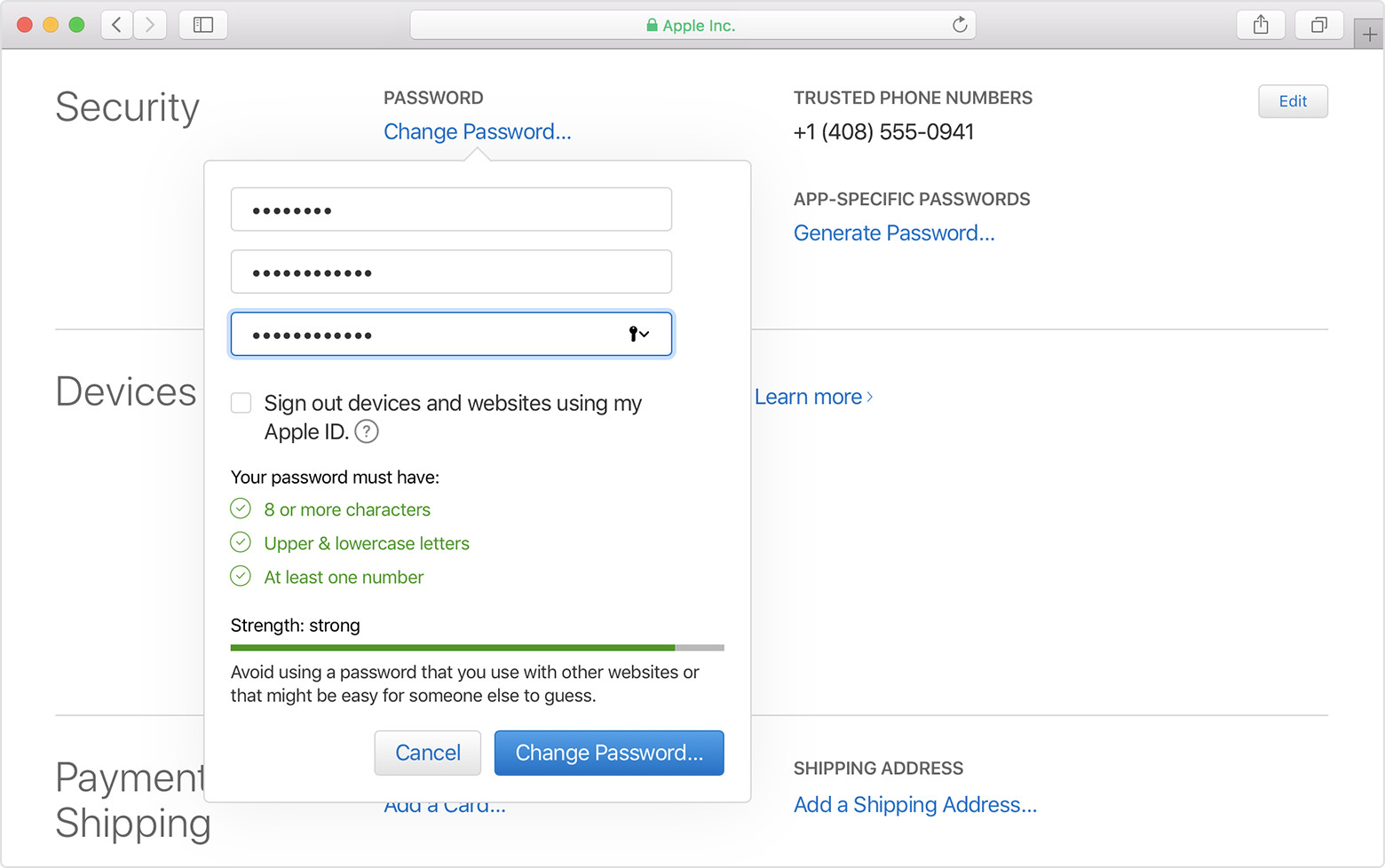
Use a strong password for your Apple ID
Apple policy requires you use strong passwords with your Apple ID. Your password must have eight or more characters and include upper and lowercase letters, and at least one number. You can also add extra characters and punctuation marks to make your password even stronger. Apple also uses other password rules to make sure your password isn’t easy to guess.
If you aren’t sure if you have a strong password, visit your Apple ID account page to reset your password as soon as possible.
Make the answers to your security questions hard to guess
Apple uses security questions to provide you with a secondary method to identify yourself online or when contacting Apple Support. Security questions are designed to be memorable to you but hard for anyone else to guess. When used in conjunction with other identifying information, they help Apple verify that you are the person who is requesting access to your account. If you haven’t selected your security questions, visit your Apple ID account page to set them up.
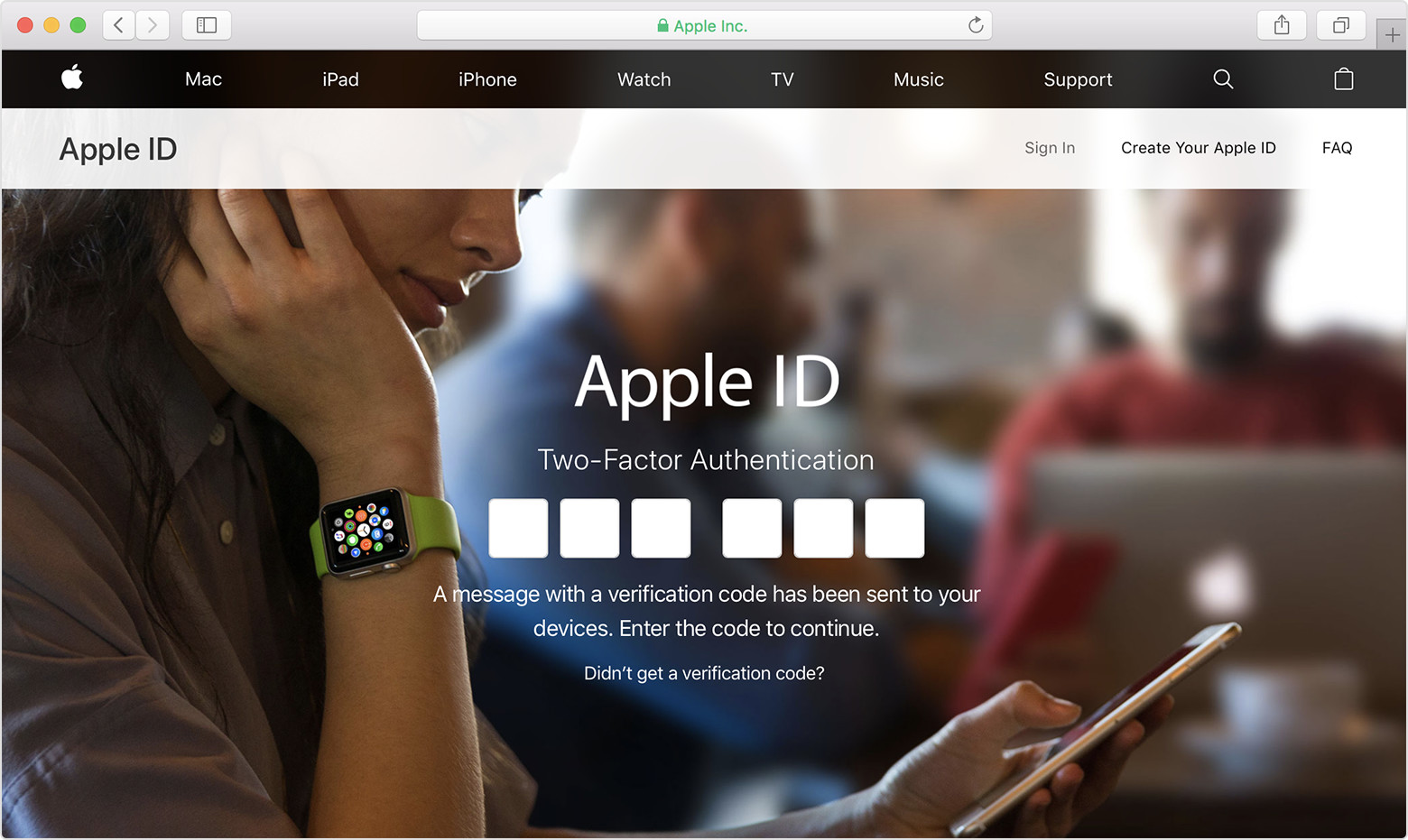
Protect your account with two-factor authentication
Apple offers an improved security method called two-factor authentication that’s designed to ensure that you’re the only person who can access your account, even if someone else knows your password. When you enter your Apple ID and password for the first time on a new device, we’ll ask you to verify your identity with a six-digit verification code. This code is displayed automatically on your other devices, or sent to a phone number you trust. Just enter the code to sign in and access your account on the new device. Never share your password or verification code with anyone else.
If you use iOS 11.3 or later on your iPhone, you might not need to enter a verification code. In some cases, your trusted phone number can be automatically verified in the background on your iPhone. It’s one less thing to do, and your account is still protected with two-factor authentication.
Two-factor authentication is built directly into iOS, macOS, tvOS, watchOS, and Apple’s websites. You can use two-factor authentication with your Apple ID if you have a device that’s using the latest iOS or macOS, or if you have access to a web browser and a phone number. Two-factor authentication is the default security method for some new Apple IDs created on iOS 10.3 or later and macOS 10.12.4 or later.
If you don’t have devices that can be updated to iOS 9 or later, or OS X El Capitan or later, you can set up two-step verification for your Apple ID instead.
You need two-factor authentication to use certain features that require improved security.
Check for encryption and SSL
All web pages where you can view or change your Apple ID use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to protect your privacy. In Safari, look for in your browser when accessing your account at your Apple ID account page to know your session is fully encrypted and secure.
Employee privacy and security policies
In addition to strong passwords, encryption, and other technology, Apple has strict policies and procedures in place to prevent unauthorized access to your account. Without proof of your identity via a temporary Support PIN and other carefully selected criteria, Apple Support can’t help you perform any actions on your account. These policies are audited and reviewed on a regular basis.
Other tips for keeping your account secure
Good online security requires a combination of practices by companies using Internet services and informed behavior by users. Below are some tips to follow to maximize your security when using your Apple ID and other online accounts.
- Always use a strong password.
- Never use your Apple ID password with other online accounts.
- Change your password regularly and avoid reusing old passwords.
- Choose security questions and answers that can’t be easily guessed. Your answers can even be nonsense as long as you can remember them. For example, Question: What is your favorite color? Answer: Mozart.
- If you abandon an email address or phone number associated with your Apple ID, be sure to update your Apple ID with current information as soon as possible.
- Set up two-factor authentication for your Apple ID to add an extra layer of security to your account and eliminate the need for security questions.
- Avoid phishing scams. Don’t click links in suspicious email or text messages and never provide personal information on any website you aren’t certain is legitimate. Learn how to identify phishing attempts.
- Don’t share your Apple ID with other people, even family members.
- When using a public computer, always sign out when your session is complete to prevent other people from accessing your account.
Never provide your password, security questions, verification codes, recovery key, or any other account security details to anyone else. Apple will never ask you for this information.
If Apple Support needs to verify your identity, we might ask you to generate a temporary Support PIN. We’ll only ask for this information over the phone after you contact Apple Support for help.
Источник
Apple Platform Security
Hardware security
Secure software requires a foundation of security built into hardware. That’s why Apple devices — using iOS, iPadOS, macOS, tvOS or watchOS — have security capabilities designed into silicon.
System security
Building on the unique capabilities of Apple hardware, system security is designed to maximise the security of the operating systems on Apple devices without compromising usability. System security encompasses the startup process, software updates and the ongoing operation of the operating system.
Encryption and Data Protection
Apple devices have encryption features to safeguard user data and enable remote wipe in the case of device theft or loss.
App security
Apple provides layers of protection designed to ensure that apps are free of known malware and haven’t been tampered with. Other protections help ensure that access from apps to user data is carefully mediated.
Services security
Apple has built a robust set of services to help users get even more utility and productivity out of their devices. These services include Apple ID , iCloud, Sign in with Apple , Apple Pay , iMessage, FaceTime and Find My .
To browse Apple Platform Security, click Table of Contents at the top of the page. To download a PDF, click or tap here.
Источник