- How to Add Image to Drawable Folder in Android Studio?
- Method 1
- Method 2
- Add images to your Android Project
- How To Add Image To Drawable Folder In Android Studio
- Adding Image To Drawable Folder In Android Studio
- ImageView
- Общая информация
- Метод setImageResource()
- Метод setImageBitmap()
- Метод setImageDrawable()
- Метод setImageURI()
- Другие методы
- Масштабирование через свойство Scale Type
- Атрибут android:adjustViewBounds=»true»
- Загрузка изображения из галереи
- Получить размеры ImageView — будьте осторожны
- Копирование изображений между ImageView
- Примеры
How to Add Image to Drawable Folder in Android Studio?
The resource folder is the most important folder because it contains all the non-code sources like images, XML layouts, UI strings for the android application. In Android Studio inside the res folder, one can find the drawable folder, layout folder, mipmap folder, values folder, etc. Among them, the drawable folder contains the different types of images used for the development of the application. We need to add all the images to the drawable folder for the application development. Images are used in android applications to provide more user-friendly behavior & functionality. So in this article, we are going to discuss how to add an image to the drawable folder with multiple methods being explained step by step.
Method 1
In method 1 we will do it through the way Android Studio provided to you.
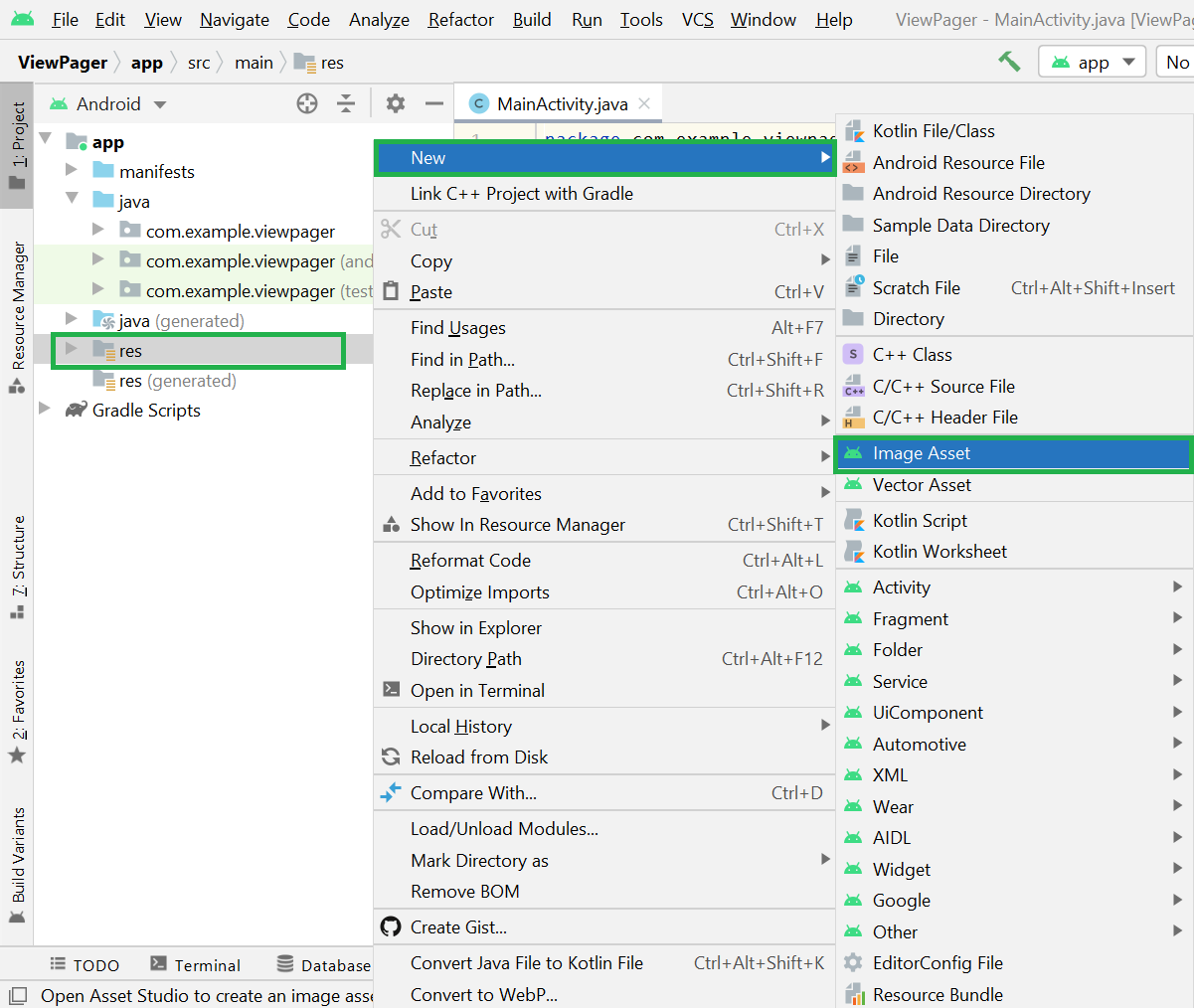
Step 1: Open Android Studio and go to the app > res > right-click > New > Image Asset as shown in the below figure.
Step 2: A pop-up screen will arise like below. Here choose Action Bar and Tab Icons in Icon Type.
Step 3: Then choose Asset Type as Image and enter the Path of your image. Enter the name of your image and click on Next.
Step 4: Now you can see the android studio automatically created the different-sized images. You can directly create the folder and drag image inside but you won’t have the different-sized icons if you do that and this the main advantage of following this method. And finally, click on the Finish button.
Now go to the app > res > drawable and you can find a folder named as image and the different sized images inside this folder as shown in the below image.
- drawable-ldpi (low-density): Lower images quality supported by the earlier sets of the android – 240×320 pixels
- drawable-mdpi (medium-density): For medium images support – 320×480 pixels
- drawable-hdpi (high-density): Images for the Android Broad Screen set or Android Phones with the Higher resolution – 480×800 pixels
- drawable-xhdpi (extra high-density): Devices with maximum resolution – 720×1280 pixels
Method 2
Method 2 is very easy but as we discussed above we can directly create the folder and drag image inside but you won’t have the different-sized icons if you do that and this the main advantage of method 1. So the developer must follow method 1. Below is the step by step implementation of method 2:
Step 1: In this method first of all in your system find your required images and copy the image as we do normally.
Step 2: Then open the Android Studio go to the app > res > drawable > right-click > Paste as shown in the below figure.
Step 3: Then a pop-up screen will arise like below. Here choose your directory where you want to store your image file. And click on OK.
Step 4: In this screen, you can rename your image file name and also choose your directory. And click on the Refactor button. And you are done.
Now go to the app > res > drawable and you can find a file named as method_2.jpg as shown in the below image.
Источник
Add images to your Android Project
We’re now going to add a picture to Android Studio. This picture will be used in an Image View.
First, download this picture: (Right click and select Save Image As.)
Save it to your own computer and remember where you saved it to.
We need to import this picture into the res > drawable folder. Open up your Project Explorer again by clicking its tab:
Now expand the res item and locate the drawable folder:
Right click the drawable folder, and select Show in Explorer from the menu:
This will open a window showing a list of folders. The image below is from Windows 10:
All of these folders are from your res directory. (The mipmap ones are used mainly for icons. You can create them in different sizes. We’ll do this much later in the course.)
What you need to do is to copy and paste your image from where you saved it on your computer into the drawable folder (we’re assuming you know how to copy and paste files from one folder to another):
Now go back to Android Studio and you should see it there:
We can now use this image in our app.
Go back to your blueprint. Locate the Image View control in the Palette, which is under Images in earlier versions of Android Studio:
In later versions of Android Studio, you can find the Image View control under the Common category of the Palette (and under Widgets):
Drag an Image View to just below your Text View. As soon as you do, you should the following dialogue box appear:
Expand the Project item of Drawable and select the bridge image and click OK. Your blueprint will then look like this:
As you can see, the Image View has ended up in the top left. We don’t want it there.
With the Image View selected, click anywhere inside of it with your left mouse button. Keep the left mouse button held down and drag it below the Text View:
(You won’t be able to see the image itself in Blueprint View.)
Now we’ll add a Constraint. We want to connect the top middle circle of the Image View to the bottom middle circle of the Text View. Hold your mouse over the top middle circle of the Image View. It will turn green. Now hold your left mouse button down. Keep it held down and drag to the bottom middle circle of the Text View:
You should see a blue arrow connecting the two:
Now add a constraint from the left of the Image View to the left edge of the screen, just like you did for the Text View. Likewise, connect the right edge of the Image View to the right edge of the screen. Your blueprint will then look like this:
It can be a little bit fiddly, so don’t forget you can undo with CTRL + Z.
If you have a look at the properties area again, you may be wondering what all those lines are for:
The straight lines indicate which sides of your view are constrained, and to where. They also tell you the size of the margins, 8 in the image above. Hold your mouse over one of the lines and you’ll see a dropdown list. You can change your margins from here:
The other lines to be aware of are the ones inside the square, pointy arrows in the image above. There are three different settings here:
Wrap Contents
Fixed
Match constraints
Click the arrows to see what they do. Watch what happens to the Image View when you click a set of arrows. In the image below, we’ve set the arrows to Fixed:
The arrows have turned into straight lines. Notice that layout_width value has changed to 200dp. It has changed to 200 because that was the width of the image we used. Notice that the Image View hasn’t changed its size. But move the horizontal slider from 50 to something else. Watch what happens to your Image View in the blueprint.
Click the straight lines inside the square to see the third of the settings, Match Constraints:
Notice that image has now stretched to the margins of the screen. Notice, too, that the layout_width has been reset to zero. Click again, though, to go back to Wrap Contents.
In the next lesson, you’ll learn about a different type of layout — LinearLayout.
Источник
How To Add Image To Drawable Folder In Android Studio
Images are used in android application to add-on more user friendly behavior & functionality. A image can be added in drawable folder with multiple methods being explained step by step.
Adding Image To Drawable Folder In Android Studio
Easier steps are to followed up for adding a image in drawable folder.
Step 1- In this you need to follow this path to reach the desired folder.
app-> res -> drawable

Step 2- Further you need to right click on the drawable folder and click on File_Path.

Step 4- Clicking on drawable open a window which containing the images used in your android application. Here you can easily add-on or remove the images.
Other way to add images is:
Step 1- Firstly follow path to reach the folder as explained above
app-> res -> drawable

Step 2- Copy the images you want to add and right click on drawable folder. Further click on paste, your images are inserted in the folder & use them as per requirement.
Источник
ImageView
Общая информация
Компонент ImageView предназначен для отображения изображений. Находится в разделе Widgets.
Для загрузки изображения в XML-файле используется атрибут android:src, в последнее время чаще используется атрибут app:srcCompat.
ImageView является базовым элементом-контейнером для использования графики. Можно загружать изображения из разных источников, например, из ресурсов программы, контент-провайдеров. В классе ImageView существует несколько методов для загрузки изображений:
- setImageResource(int resId) — загружает изображение по идентификатору ресурса
- setImageBitmap(Bitmap bitmap) — загружает растровое изображение
- setImageDrawable(Drawable drawable) — загружает готовое изображение
- setImageURI(Uri uri) — загружает изображение по его URI
Метод setImageResource()
Сначала нужно получить ссылку на ImageView, а затем используется идентификатор изображения из ресурсов:
Метод setImageBitmap()
Используется класс BitmapFactory для чтения ресурса изображения в объект Bitmap, а затем в ImageView указывается полученный Bitmap. Могут быть и другие варианты.
Метод setImageDrawable()
Если у вас есть готовое изображение, например, на SD-карте, то его можно использовать в качестве объекта Drawable.
Drawable можно получить и из ресурсов, хотя такой код выглядит избыточным, если можно сразу вызвать setImageResource().
Метод setImageURI()
Берётся URI файла изображения и используется в качестве источника изображения. Этот способ годится для работы с локальными изображениями.
Загружаем Drawable через URI.
Другие методы
Также вам часто придется использовать методы, связанные с размерами и масштабированием: setMaxHeight(), setMaxWidth(), getMinimunHeight(), getMinimunWidth(), getScaleType(), setScaleType().
Масштабирование через свойство Scale Type
Для масштабирования картинки в ImageView есть свойство Scale Type и соответствующий ему атрибут android:scaleType и перечисление ImageView.ScaleType.
- CENTER
- CENTER_CROP
- CENTER_INSIDE
- FIT_CENTER
- FIT_START
- FIT_END
- FIT_XY
- MATRIX
Чтобы увидеть разницу между разными режимами, желательно использовать большую картинку, превосходящую по ширине экрана устройства. Допустим, у нас есть простенькая разметка:
Для наглядности я задал красный цвет для фона ImageView.
Режим android:scaleType=»center» выводит картинку в центре без масштабирования. Если у вас будет картинка большего размера, то края могут быть обрезаны.
Режим android:scaleType=»centerCrop» также размещает картинку в центре, но учитывает ширину или высоту контейнера. Режим попытается сделать так, чтобы ширина (или высота) картинки совпала с шириной (или высотой) контейнера, а остальное обрезается.
Режим android:scaleType=»centerInside» масштабирует картинку, сохраняя пропорции. Можно увидеть задний фон контейнера, если его размеры отличаются от размера картинки.
Режим android:scaleType=»fitCenter» (по умолчанию) похож на предыдущий, но может не сохранять пропорции.
Если выбрать режим android:scaleType=»fitStart», то картинка прижимается к левому верхнему углу и таким образом заполняет верхнюю половину контейнера.
Значение android:scaleType=»fitEnd» сместит картинку в нижнюю часть контейнера.
Режим android:scaleType=»fitXY» растягивает/сжимает картинку, чтобы подогнать её к контейнеру. Может получиться вытянутая картинка, поэтому будьте осторожны.
Последний атрибут android:scaleType=»matrix» вывел картинку без изменений в левом верхнем углу с обрезанными краями.
Атрибут android:adjustViewBounds=»true»
При использовании атрибута scaleType=»fitCenter» из предыдущего примера Android вычисляет размеры самой картинки, игнорируя размеры ImageView. В этом случае ваша разметка может «поехать». Атрибут adjustViewBounds заставляет картинку подчиниться размеру компонента-контейнера. В некоторых случаях это может не сработать, например, если у ImageView установлен атрибут layout_width=»0dip». В таком случае поместите ImageView в RelativeLayout или FrameLayout и используйте значение 0dip для этих контейнеров.
Загрузка изображения из галереи
Предположим, у вас есть на экране компонент ImageView, и вы хотите загрузить в него какое-нибудь изображение из галереи по нажатию кнопки:
Намерение ACTION_PICK вызывает отображение галереи всех изображений, хранящихся на телефоне, позволяя выбрать одно изображение. При этом возвращается адрес URI, определяющий местоположение выбранного изображения. Для его получения используется метод getData(). Далее для преобразования URI-адреса в соответствующий экземпляр класса Bitmap используется специальный метод Media.getBitmap(). И у нас появляется возможность установить изображение в ImageView при помощи setImageBitmap().
На самом деле можно поступить ещё проще и использовать метод setImageURI.
Сравните с предыдущим примером — чувствуете разницу? Тем не менее, приходится часто наблюдать подобный избыточный код во многих проектах. Это связано с тем, что метод порой кэширует адрес и не происходит изменений. Рекомендуется использовать инструкцию setImageURI(null) для сброса кэша и повторный вызов метода с нужным Uri.
В последних версиях системных эмуляторов два примера не работают. Проверяйте на реальных устройствах.
Получить размеры ImageView — будьте осторожны
У элемента ImageView есть два метода getWidth() и getHeight(), позволяющие получить его ширину и высоту. Но если вы попробуете вызвать указанные методы сразу в методе onCreate(), то они возвратят нулевые значения. Можно добавить кнопку и вызвать данные методы через нажатие, тогда будут получены правильные результаты. Либо использовать другой метод активности, который наступает позже.
Копирование изображений между ImageView
Если вам надо скопировать изображение из одного ImageView в другой, то можно получить объект Drawable через метод getDrawable() и присвоить ему второму компоненту.
Примеры
В моих статьях можно найти примеры использования ImageView.
Источник