- Работа с XML в Android
- Шаг 1.
- Шаг 2.
- Шаг 3.
- Шаг 4.
- Parsing XML data in Android Apps
- Creating a simple User Interface
- Defining XML data to parse
- Creating a Player POJO
- Preparing the XML Parser
- Parsing the XML data
- Displaying the XML data
- Our App in Action
- Learning to Parse XML Data in Your Android App
- Introduction
- The classes for XML parsing in Android
- Instantiating your parser
- Parsing the XML
- Other Parsers used for XML
- SAX Parsers
- Conclusion
- Работа с XML
- Ресурсы XML и их парсинг
Работа с XML в Android
Очень часто приходится хранить информацию форм и для этого можно использовать xml файлы. В данном уроке мы это и рассмотрим, как можно работать с файлами XML.
Библиотеки Android имеют набор классов для работы с XML-документами с произвольной структурой и содержанием.
Шаг 1.
Для того чтобы упаковать статический XML файл вместе с вашим приложением, вам нужно поместить его в папку: res/xml/
В каталоге res/ создайте подкаталог xml/ в котором будет располагаться наш ХМL-файл.
После чего вы получите возможность обращаться в коде программы к этому документу.
Шаг 2.
Рассмотрим загрузку XML-документа произвольной структуры из ресурсов в код программы.
Создадим приложения, которое будет уметь способность читать список имен, фамилий и телефонов, определенных в XML-файле.
Теперь создадим XML файл который будет хранить Имена, Фамилии и номера телефонов сотрудников фирмы и сохраним его в res/xml/ под именем contacts.xml.
Вот как будут выглядеть XML файл contacts.xml
Шаг 3.
Создадим View состоять она будет с LinearLayout и ListView и назовем main.xml:
Шаг 4.
Загружаем файл contacts.xml, созданный ранее:
Метод getXml() возвращает XmlPullParser, используя который можно прочитать загруженный XML-документ в цикле while:
В конечном итоге ваше приложение должно выглядеть так:

Обратите внимание что наследуется MyActivity не от Activity а от ListActivity.
Источник
Parsing XML data in Android Apps
Jun 28, 2018 · 4 min read
JSON is become a very widespread format for the Web Services but in some cases, you would have to parse data in the good old XML format. In that tutorial, you are going to learn how to parse a XML file on Android.
Note that there are various XML parses available in the Android SDK in standard. Thus, you can use the following solutions :
- XMLPullParser API
- DOM Parser API
- SAX Parser API
As usual, each parser has its advantages and drawbacks.
The recommendation on Andr o id is to use the XMLPullParser API which consumes less memory than the DOM Parser API which loads the complete XML file in memory before parsing it.
So, in this tutorial, we will use the XMLPullParser API. Note that you can also discover this tutorial in video on YouTube :
Creating a simple User Interface
To display the parsed XML data, we need to create a simple User Interface. It will consist in a simple TextView centered on the screen :
Defining XML data to parse
Then, we define some XML data to parse inside a file under the assets directory of our Android project. This file will be named data.xml and will contain some NBA players with data like name, age and position played :
Creating a Player POJO
To map the data for each player, we create a Player POJO (Plain Old Java Object) :
Preparing the XML Parser
The first step is to load the XML file from the assets of our Android Application. For that, we define a parseXML method. We create a new instance of the XMLPullParserFactory class. Then, we create a new XMLPullParser instance by calling the newPullParser method of the XMLPullParserFactory got previously.
We got an InputStream on the XML file by calling the open method of the AssetManager instance. With that instance, we can set the input on the XMLPullParser instance. It gives us the following code :
Parsing the XML data
Now, we need to parse the XML data. The parsing will be processed in the processParsing method. We start by getting the current event type from the parser by calling the getEventType method.
Then, we enter in a loop while the event type is different of the XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT constant. In the loop, when we meet a XmlPullParser.START_TAG event type, we get the name of the current tag by calling the getName method.
When we have a player tag, we create a new Player instance and we add it in an ArrayList of Player. This list will be used to store all the players read from the XML file.
If the current player is not null, we are reading data for a player. We have to check if the tag is name, age or position. For each case, we call the nextText method of the parser to get the value associated to the tag. Then, we set the value on the current player.
At the end of the loop, we have stored all the players from the XML file on the ArrayList of Player. Note that just before the end of the loop, you need to call the next method of the parser to pass to the following event.
It gives us the following code :
Displaying the XML data
The last step is also the simplest. We need to display the players in our TextView via the printPlayers called at the end of the processParsing method.
In that method, we iterate on the ArrayList of Player and for each player we add its properties (name, age and position) on a StringBuilder instance. Finally, we display the text on the TextView by calling its setText method with the value of the StringBuilder instance.
It gives us the following complete code for the MainActivity :
Our App in Action
Best part of the tutorial is coming since it’s time to put our App in Action. When, you will launch the Application, you should have the following result :
That’s all for that tutorial.
To discover more tutorials on Android development, don’t hesitate to subscribe to the SSaurel’s Channel on YouTube :
Источник
Learning to Parse XML Data in Your Android App
Introduction
We are in an age where, typically, an application cannot work in total isolation and does not have all the data it needs to do its work. It generally has to communicate to some other application–maybe over the internet–and read or send some data to it.
However, the applications with which your app communicates might not be developed using the same technology as yours. For smooth data exchanges between your app and some other application you might be exchanging data in an open format like Extensible Markup language or XML.
An XML document is a human readable text document that contains some starting and ending tags with attributes and data in those tags. Most of the languages and platforms have support for parsing and creating XML documents in them. Android also provides us APIs so that we can work and process XML documents in our app with ease and flexibility. In this article, we are going to see how you can work effectively with XML documents in your Android app.
The classes for XML parsing in Android
There are various XML parsers we can use on the Android platform. For XML, Android recommends the use of the XMLPullParser . Android gives a multiple implementation of the XMLPullParser and you can use any of them in your program. Depending on the way you create your XMLPullParser , the implementation of the parser will be chosen.
Instantiating your parser
As stated above, there are multiple ways in Android you can create an XMLPullParser . The first way to do it is using the Xml class as shown below:
You have to just call newPullParser which will return you a reference to the XMLPull parser. Or you can get a reference from the XmlPullParserFactory as shown below.
Parsing the XML
Once we have the parser reference it’s now time to use it to parse an XML. We are going to use the following XML as the XML to parse. So now create a file called temp.xml in your assets folder with the content:
The code of the activity to read and parse is as follows:
In the above code we have created a small class called Product which has three members: name, quantity and color.
In the activity we first get the XMLPullParser instance then we open the temp.xml as an inputstream . Once that is done we set the inputstream as input to the parser. Then we parse the xml in our function parseXML .
In the function parseXML we create an ArrayList in which we will store all the products which we will parse from the XML. Once that is done we create a loop which will work till the end of the document is reached.
At the start of the document we created the ArrayList of products. If a tag starts and if the tag is product we know that now it’s a new product so we create a new product instance. Then if the other tags are read we will just read and add the values in our Product instance.
Once the Product tag is ended we add the product to the ArrayList . Once all the products are added we call the function printProducts in which we iterate over the ArrayList and then print the values on the screen.
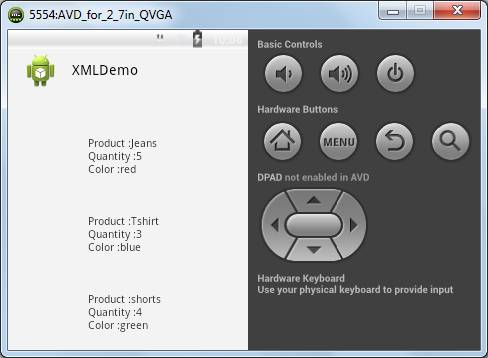
If we run the activity now we will see the output as follows:
Other Parsers used for XML
There are other parsers also that can be used to parse XML in Android. The DOM parser can be used which creates a complete memory model of the XML and can be used to either create or parse XML. DOM parsers generally consume a lot of memory.
You can get the instance of a DOMBuilder as shown below
SAX Parsers
The SAXParsers can also be used to parse XML and consume much lesser memory then DOM parsers. The SAXParsers can be used only to parse XMLs not to create them. You can get the reference of a SAXParser as shown below:
Conclusion
XML documents are becoming a standard way to exchange data between applications over the internet. With our Android apps becoming smarter and smarter it might be necessary for your Android app to communicate and exchange data between different applications over the internet. Android provides a rich set of APIs to work with XML documents in your Android app.
With the help of these APIs you can easily incorporate XML into your Android app. The XML parsers do the tedious work of parsing the XML and we have to just write the code to fetch the appropriate information from it and store it for further processing.
So, have fun processing XML in your next Android app.
And if you enjoyed reading this post, you’ll love Learnable; the place to learn fresh skills and techniques from the masters. Members get instant access to all of SitePoint’s ebooks and interactive online courses, like Beginning Android Development.
Comments on this article are closed. Have a question about developing Apps? Why not ask it on our forums?
Источник
Работа с XML
Ресурсы XML и их парсинг
Одним из распространенных форматов хранения и передачи данных является xml . Рассмотрим, как с ним работать в приложении на Android.
Приложение может получать данные в формате xml различными способами — из ресурсов, из сети и т.д. В данном случае рассмотрим ситуацию, когда файл xml хранится в ресурсах.
Возьмем стандартный проект Android по умолчанию и в папке res создадим каталог xml . Для этого нажмем на каталог res правой кнопкой мыши и в контекстном меню выберем New -> Android Resource Directory :
В появившемся окне в качестве типа ресурсов укажем xml :
В этот каталог добавим новый файл, который назовем users.xml и который будет иметь следующее содержимое:
Это обычный файл xml, который хранит набор элементов user. Каждый элемент характеризуется наличием двух подэлементов — name и age. Условно говоря, каждый элемент описывает пользователя, у которого есть имя и возраст.
В папку, где находится основной класс MainActivity, добавим новый класс, который назовем User :
Этот класс описывает товар, информация о котором будет извлекаться из xml-файла.
И в ту же папку добавим новый класс UserResourceParser :
Определим для класса UserResourceParser следующий код:
Данный класс выполняет функции парсинга xml. Распарсенные данные будут храниться в переменной users. Непосредственно сам парсинг осуществляется с помощью функции parse . Основную работу выполняет передаваемый в качестве параметра объект XmlPullParser . Этот класс позволяет пробежаться по всему документу xml и получить его содержимое.
Когда данный объект проходит по документу xml, при обнаружении определенного тега он генерирует некоторое событие. Есть четыре события, которые описываются следующими константами:
START_TAG : открывающий тег элемента
TEXT : прочитан текст элемента
END_TAG : закрывающий тег элемента
END_DOCUMENT : конец документа
С помощью метода getEventType() можно получить первое событие и потом последовательно считывать документ, пока не дойдем до его конца. Когда будет достигнут конец документа, то событие будет представлять константу END_DOCUMENT :
Для перехода к следующему событию применяется метод next() .
При чтении документа с помощью метода getName() можно получить название считываемого элемента.
И в зависимости от названия тега и события мы можем выполнить определенные действия. Например, если это открывающий тег элемента user, то создаем новый объект User и устанавливаем, что мы находимся внутри элемента user:
Если событие TEXT , то считано содержимое элемента, которое мы можем прочитать с помощью метода getText() :
Если закрывающий тег, то все зависит от того, какой элемент прочитан. Если прочитан элемент user, то добавляем объект User в коллекцию ArrayList и сбрываем переменную inEntry, указывая, что мы вышли из элемента user:
Если прочитаны элементы name и age, то передаем их значения переменным name и age объекта User:
Теперь изменим класс MainActivity, который будет загружать ресурс xml:
Вначале получаем ресурс xml с помощью метода getXml() , в который передается название ресурса. Данный метод возвращает объект XmlPullParser , который затем используется для парсинга. Для простоты просто выводим данные в окне Logcat :
Источник