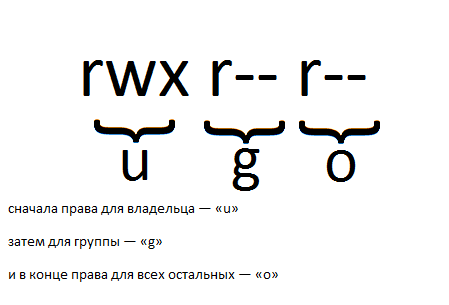- How to Manage and Fix Permissions on Android File System
- Things You Need to Fix File Permissions on Android
- Understanding Android File Permissions
- Fix File Permissions on Android Devices
- Quick Steps to Fix File Permissions on Android
- Detailed Steps to Manage Permissions on Android
- Права доступа (permission) в Android
- Права доступа (permission) на папки и файлы в Андроид
How to Manage and Fix Permissions on Android File System
On any UNIX or Linux based file system like Android, all files and folders have a set of permissions associated with them. These permissions which are also called ‘attributes’ determine the level of accessibility/permission given to a user or a group of users. Being based on Linux, Android is no exception. Today, we will see what permissions (Read-Write-Execute) mean and how we can set or fix file permissions on Android using a root file manager app.
You cannot taste the real flavor of the Lollipop, Marshmallow, Nougat, Oreo or Pie and the whole of Android kitchen unless you have root access on your phone or tablet. The power vested onto you after rooting your device unlocks the doors of a new world, far away from millions of apps found at the Google Play and sluggish and faulty firmware updates, where customization and possibilities breath and grow to give you the next-level experience with your Android device.
Being the owner of a rooted Android device puts you in a privileged position from where you can exact the best performance out of your device. You can choose from a wide range of custom ROMs, mods, ports, Kernels, themes, and patches for your Android device and thus have things as you want them to be.
The Open Source attribute of Android allows thousands of developers across the world to contribute to its development. They work hard to produce stuff that makes our mobile experience richer and convenient. It’s because of their efforts that we are able to enjoy various mods and ported apps on our Android devices.
In several cases, such mods and ports require a little effort from us too. Fixing file permission our setting an app’s Read, Write and Execute rules to get a mod or ported app to work, thus becomes a piece of knowledge all Android lovers must be familiar with. In the present tutorial, I’ll be showing you how you can set or fix a specific file’s permissions rules on Android devices.
Things You Need to Fix File Permissions on Android
Since fixing permissions of an app involves entering the system of your device, the first and foremost requirement is to have root access on it. If you have rooted your Android device, you are good to go.
The next requirement is to install a good root file manager on your device. Below, you’ll find a list of some of the best root file explorers for Android devices. Personally, I prefer Solid Explorer File Manager and Root Explorer apps.
[googleplay url=”https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=pl.solidexplorer2″] [googleplay url=”https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.jrummy.root.browserfree”] [googleplay url=”https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.speedsoftware.rootexplorer”]
Also, install the BusyBox app on your device:
Open the app when installed and then tap the install button to finish the setup.
Understanding Android File Permissions
On any UNIX or Linux based file system, every single file and folder stored on the hard drive has a set of permissions associated with it. These permissions which are also called attributes, determine the level of accessibility/permission given to a user or a group of users.
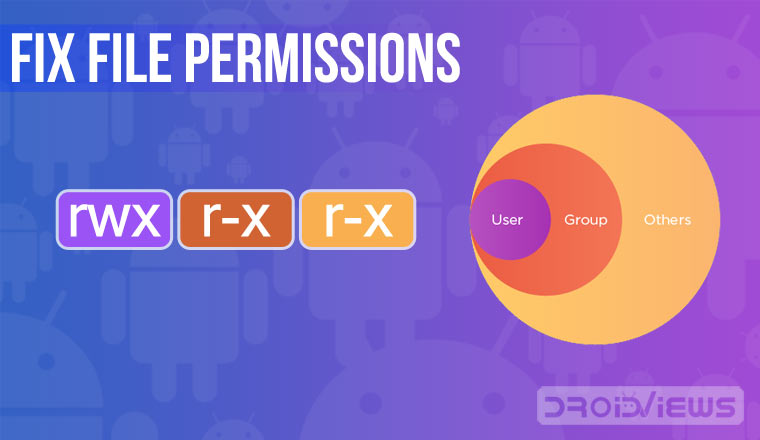
The Read-Write-Execute attributes tell the system or server who is allowed to do what with a particular file. In the same way, every file and directory also has an Owner, Group, and Others associated with it. By changing these permission rules, you can direct a system or server what kind of accessibility it allows to different types of peoples.
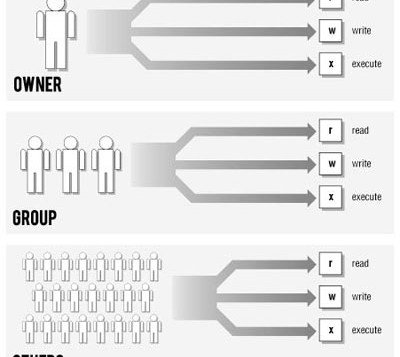
Android, being a Linux-based platform for mobile devices, also relies on this kind of permission rules in its system files. And therefore, you might need to fix/manage or edit them in certain situations.
Fix File Permissions on Android Devices
Follow the steps described below to manage Read, Write and Execute permissions of a file on Android devices.
Quick Steps to Fix File Permissions on Android
- Copy the file/APK that you want to fix permissions of and copy it to your devices’ internal or external SD Card.
- Now copy and paste the file/apk to the location suggested by the developer. If it is an app, push it to system/app directory.
- Set permissions to rw-r–r–
- Finally, reboot your phone or tablet device.
Please note that if you assign the wrong set of file permissions while copying an app or file on your rooted Android device, your phone might stick on a bootloop. To fix this error, do as follows:
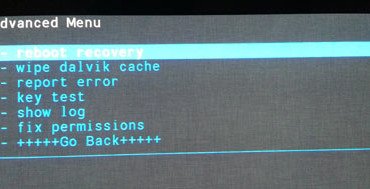
- Pull out your device’s battery and boot it into CWM or TWRP recovery mode.
- Go to the “advanced” option in recovery and select “fix permissions“.
- Then “wipe dalvik cache“.
- Go back to the main menu and select “reboot system now“.
Detailed Steps to Manage Permissions on Android
If you are new to Android and are gradually learning things, you might want a detailed guide on editing file permission on Android devices. Please be warned that playing with the permission rules of system files unnecessarily and without understanding, might produce bizarre results. So here are the steps to do it:
- Copy the file to the internal or external SD card storage on your device by connecting it to the computer using the USB cable.
- Now open the root file explorer app from the app drawer.
- Here you will see a list of directories and files.
- If you copied the file to the internal storage on your device, you can find it by opening the “sdcard” directory. To access the external storage, tap on “storage/extSdcard”.
- To fix or set Read-Write-Execute (R-W-E) permissions of the file, you must copy it to a root directory (like system, data, etc.) first. You cannot fix permissions while the file is stored on SD or ExtSD card on your device.
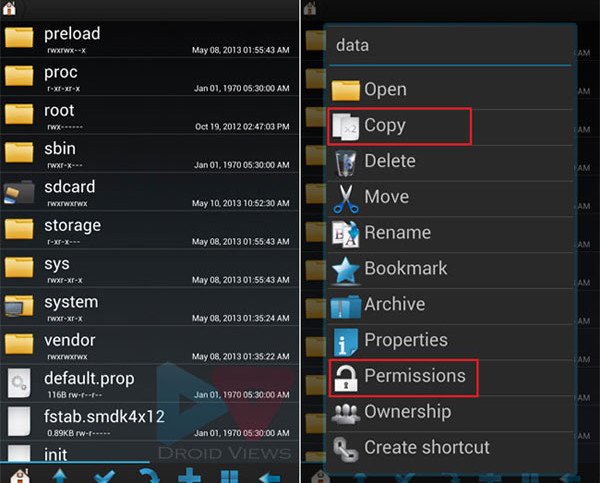
- To copy the file, navigate to it and then tap and hold it. You will see a pop-up window with all the available options.
- Select “Copy” option and go to the target directory by tapping on the Home or Up icon from the bottom bar.
- Navigate to the location/directory when you wish to paste the file and tap on “Paste” button.
- Now you can easily manage the permission rules of that file. Just press and hold it and from the popup option panel, select “Permissions”.
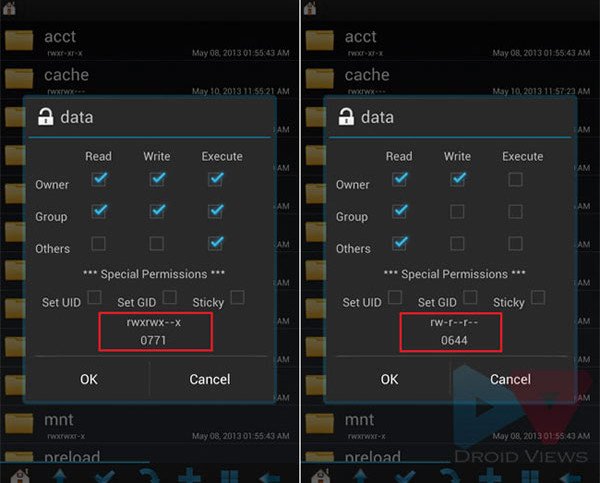
- You will see a new window showing the current permission attributes or read (r),write (w) and execute(x) rules for that file. In short, we mention this rule simply as rw- r– r– where each blank space shows unmarked attribute. You can edit it by checking and unchecking the boxes. The most used set of permissions that various files on Android need are
- Owner= Read+Write,
- Group=Read and
- Others= Read.
- In case, you have a permissions rule prescribed by a developer, edit them accordingly.
So this was our simple and detailed guide about fixing permission on Android file system using a root file manager. I hope it might prove useful to you in understanding not only the term “Permissions” but also how to manipulate it. Cheers, and keep visiting!
Источник
Права доступа (permission) в Android
Одним из интереснейших методов безопасности операционной системы Андроид является система разрешений (permissions), используемых приложениями. Когда OS ANDROID только появилась, её разработчики придумали – выделить все возможные функции, доступ к которым необходим приложению, и позволить пользователю их контролировать. Было это реализовано довольно интересно. Список возможных разрешений создан разработчиками Google и зафиксирован в документации. Он очень гибкий, в нем есть всё, что нужно для обеспечения какого угодно сложного функционала. Вместе с тем он грамотно разграничен.
Например, если программа работает с СМС, то ему можно дать права только на чтение сообщений, или только на их отправку, или только на уведомление о событии, которое связано с СМС. Это разграничение очень хорошо позволяет избегать злоупотребления привилегиями со стороны приложений. Ещё во время создания программы разработчик выделяет все функции, которые потребуются его программе. Этот список прописывается в файле AndroidManifest.xml, который на этапе сборки программы помещается в его APK-файл. Когда пользователь Андроид устройства будет устанавливать очередное приложение, то вышеупомянутый список, заданный его создателем, будет отображаться на экране. И только после того, как пользователь согласится дать все эти права устанавливаемому приложению, оно будет установлено. Считается, что именно на этом этапе большинство пользователей избежит вирусов, заподозрив программу в плохом поведении и отклонив установку.
С технической точки зрения, обойти существующий механизм прав доступа приложений к функциональности системы Андроид очень непросто. Так как менеджмент разрешений осуществляется на самом низком уровне ядром Linux, программе обязательно нужны права рут , чтобы повлиять на это. Хорошо формализованная система permissions облегчает реализацию инструментов безопасности сторонними разработчиками. Перспективным направлением является создание программ, которые позволяют пользователям тонко настраивать права доступа каждого отдельного приложения, предотвращая любые утечки информации с устройства.
Права доступа (permission) на папки и файлы в Андроид
Права доступа разделяются на две группы зто:
1.Права доступа к файлам
2.Права доступа к папке (директории)
Права доступа к файлам могут иметь такие атрибуты:
r — право на чтение данных. (read)
w — право на изменение содержимого или запись, но не удаление. (write)
x — право на исполнение файла. (xxxxxx)
Права доступа к папке (директории):
r — право на чтение папки (директории).
w — право на изменение содержимого директории можно создавать и удалять объекты в этой директории.
x — право, которое позволяет вам войти в директорию.
Сами права доступа подразделяются на три категории:
«user» — u владелец файла.
«group» — g член той же группы, к которой принадлежит владелец.
«world» — o все остальные.
Порядок записи прав доступа:
сначала права для владельца — «u»
затем для группы — «g»
и в конце права для всех остальных — «o»
Например: предположим что у вас на работе есть компьютер, вы его владелец, он состоит в локальной сети (группа) а есть пользователи, которые хотят что либо на вашем компьютере сделать. По всем этим категориям задаются права на файлы и папки в виде RWX которые дают какие либо права на выполнение чего либо, если в заданных правах RWX присутствует знак «-» то это означает что право отсутствует.
Например: rwx r— r— означает что владелец файла имеет все права: право на чтение, запись в него и исполнение, а все остальные пользователи только право на чтение.
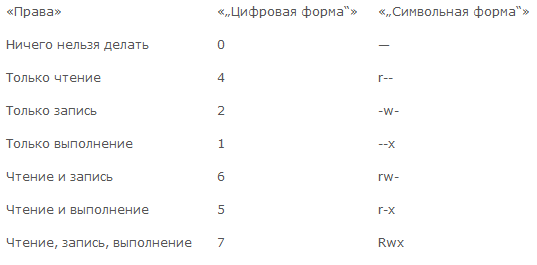
Помимо буквенных выражений есть числовые выражения:
r — (читать) это 4
w (запись) это 2
x (исполнение) это 1
«—» ничего не делать тоесть знак дефиса, 0
И их сумма означает конечные права
7 (rwx) = 4 + 2 +1 (полные права)
5 (r-x)= 4 + 0 + 1 (чтение и выполнение)
6 (rw-) = 4 + 2 + 0 (чтение и запись)
4 (r—) =4 + 0 + 0 (только чтение)
Часто используемые параметры:
400 (-r———) — владелец будет иметь право чтения, никто кроме него не имеет права выполнять никакие действия.
644 (-rw-r—r—) — все пользователи имеют право чтения, а владелец может редактировать.
660 (-rw-rw—-) — владелец и группа могут читать и редактировать, все остальные не имеют никаких прав.
664 (-rw-rw-r—) — все пользователи имеют право чтения, а владелец и группа могут редактировать.
666 (-rw-rw-rw-) — все пользователи могут читать и редактировать.
700 (-rwx——) — владелец может читать, записывать и запускать на выполнение, у других нет права выполнять никакие действия.
744 (-rwxr—r—) — все пользователи могут читать, а владелец имеет право редактировать и запускать на выполнение.
755 (-rwxr-xr-x) — каждый пользователь может читать и запускать на выполнение, владелец может редактировать.
777 (-rwxrwxrwx) — каждый пользователь может читать, редактировать и запускать на выполнение.
sudo passwd root — пароль суперпользователя root.
Здесь представлен онлайн калькулятор , и программа которая может задавать права на файл Root Explorer
Бывает что права состоят из 4х цифр это означает что помимо владельца, группы, остальных есть еще и SUPERUser (Супер Админ)
тогда список будет выглядеть вот так:
«SuperUser» — SuperUser
«user» — u владелец файла
«group» — g член той же группы, к которой принадлежит владелец
«world» — o все остальные
Источник