- Android check current version
- About
- How to check version of Android in your phone or tablet?
- This Android guide shows you how to check Android version in your phone and table, and how to read the build number and security patch level, which are always shown together with Android version.
- Why you may care about version of Android in your device?
- How to check version of Android in your phone or tablet?
- What is security patch level? is it related to Android versions?
- What is the build number?
- Do you know how to check version of Android in your phone or tablet?
- Android check current version
Android check current version
This is unofficial service-wrapper of Google Play Developer API for retrieving Android app version that currently located on Google Play Store in simple JSON (REST) response.
Just call GET request /?id=
Request to Google Play Developer API takes about 3 second. That’s why this service cached app version for 4 hour. So you will receive information from the delay up to 4 hours.
Table of contents
You have put your app on the Google Play Store. It has been installed by lots of customers. The users should check the auto-update check box in the Play Store app for each app they want to auto-update. However some users have unchecked it or not checked it in the first place.
So you may want to use some service to pragmatically check if there is an updated version of my app on the Play Store. If there is an updated version then the user could be directed to the Play Store.
Google Play does not provide any official APIs for retrieving metadata in simple way.
So I found several solution on stackoverflow. There are 2 types of them:
First services just wrapper for web page or hosted on google app engine which usually outage when daily free quota used up.
With Second solution you have to update hardcoded version number every release. For example we release a new version every week and forgot to update hardcoded version number saved on our backend.
Third. www.playstoreapi.com is not available anymore.
Fourth solution is pretty good. You have to get this value from your Google Play Store page.
But you have to update the app when something in html is changed. And this method have another side effect. Google don’t show app version number when you use several platforms (x86 and armeabi-v7a). For example https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.wipon.wipon page have not version number on it.
That’s why I’d like to use Google Play Developer API and fake deploy mechanism to get apk’s list. This method is the most stable in my opinion. It realised in this repo
pip install -r requirements.txt
Python 2.6 or 2.7 are fully supported. This requirement flew from google-api-python-client
Python 3.3+ is also now supported! However, this service has not yet been used as thoroughly with Python 3, so I’d recommend testing before deploying with Python 3 in production.
Configuration is simply copying the OAuth2 key to project folder.
- Go to the APIs Console and log in with your Google Play Developer Console account.
- Go to Settings → API access
- Turn the Google Play Android Developer API on if it’s not
- Create or link Google Developer Project with Google Play Developer Console account
- Go to Service Accounts and Grant Access to this account
- Click Add user on window above
- Generate OAuth service account in Google Developer Console
- Create JSON (NOT p12) keyfile and Save as key.json in the project directory
- That’s it
For development or local (5005 port)
For staging or testing (5005 port)
Optionally you can use supervisor/staging_android_version_checker.conf supervisor program config.
For production (Debian or Ubuntu + NGINX + Gunicorn)
For example I use /var/www/android-version-checker as project folder.
1. Install virtualenv
2. From project folder
3. Set up virtualenv
4. Update pip and install gunicorn
5. Install dependencies
7. If everything is good — test gunicorn
8. Create a systemd Unit File (don’t forget modify path). Group must be www-data otherwise nginx can not access to sock file.
9. Deactivate environment and start gunicorn process
9.5 [Ubuntu only] Open up port 5005 or another port
10. Configure nginx
Service API reference
By default API runs on 5005 port.
Returns app version by package id
- id — Required field. Android Package identifier
- mask — Optional field. Mask for version format. The following characters are recognized in the format parameter string: «H — Major, L- Minor, P-Patch, I-ignore». By default «HILPIII»
Example of version number: 2.5.3
Credentials file corrupted or empty (501 BAD REQUEST)
Look at configuration. Maybe you haven’t credential file.
Google don’t now about your package or you don’t upload any version yet (422 BAD REQUEST)
Look at Google Play Developer Console. You may have an error on it.
Your package has unusual version number convention (400 BAD REQUEST)
This service support apk version like 2005304 or 100004
The package id argument undefined (400 BAD REQUEST)
Check your Google Play Developer Console. Do you upload apk file?
The package id argument undefined (400 BAD REQUEST)
id — Required field.
Common error (400 BAD REQUEST)
Something else happened. Maybe your server don’t have stable internet connection.
All contributions are more than welcome.
Distributed under the MIT license
About
Robust Android Play Market App version checker. Using Google Play Developer Console API written in Python.
Источник
How to check version of Android in your phone or tablet?
This Android guide shows you how to check Android version in your phone and table, and how to read the build number and security patch level, which are always shown together with Android version.
Why you may care about version of Android in your device?
As you already know, Android has been updated consistently. Each new version of Android brought some new and enhanced features, in addition to bug fixes (and new bugs as well).
In recent years, Google has been tried to release one major update each year.
For example, Android Nougat (Android 7.0/7.1) in 2016, Android Marshmallow (Android 6.0) in 2015, and Android Lollipop (Android 5.0/5.1) in 2014, Android KitKat (Android 4.4) in 2013.
But for Android phones or tablets, most vendors only update the Android version for less than 2 years since the release of the product. And normally, only flagship (=expensive) models get such update. Please check this post on why some Android devices never receive any update.
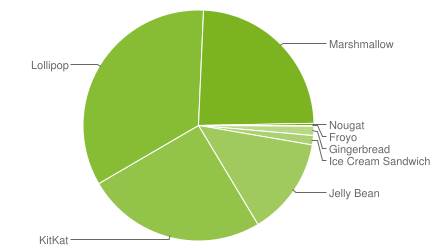
Therefore the majority of the Android phones and tablets in use are running old (not latest) versions of Android. For example, as shown in the chart below, by October 2016,
- 34.1% Android devices are running Android Lollipop (Android 5.0/5.1).
- 25.2% Android devices are running Android KitKat (Android 4.4).
- 24% Android devices are running Android Marshmallow (Android 6.0).
- 13.% Android devices are running Android Jelly Bean (Android 4.1/4.2/4.3).
- 1.3% Android devices are running Android Ice Cream Sandwich (Android 4.0).
- 1.3% Android devices are running Android Gingerbread (Android 2.3)
- 0.3% Android devices are running Android Nougat (Android 7.0/7/1), which is the latest version of Android.
- 0.1% Android devices are running Android Froyo (Android 2.2).
You may want to know the version of Android in your device so that you can check whether you have some special features of certain versions of Android.
How to check version of Android in your phone or tablet?
You can always check the version of Android in your phone or tablet in Settings —About phone (or Settings–About device) as shown below.
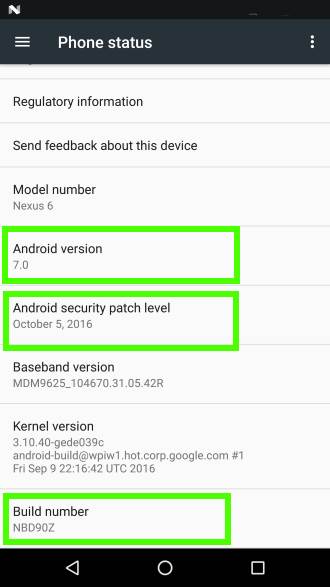
In Nexus and Google Pixel phones, the Android version is indicated below about phone as shown below. Other Android vendors seldom show the version of Android here.
Anyway, tap About phone as shown below, you will find the version of Android and other software info including:
- Android version.
- Build number.
- Android security patch level.
As explained in this guide, you can tap build number 7 times to unhide developer options in settings.
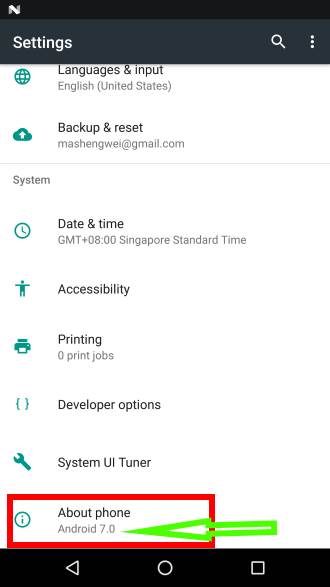
Please note, different Android vendors may choose different ways to show Android version and other software info.
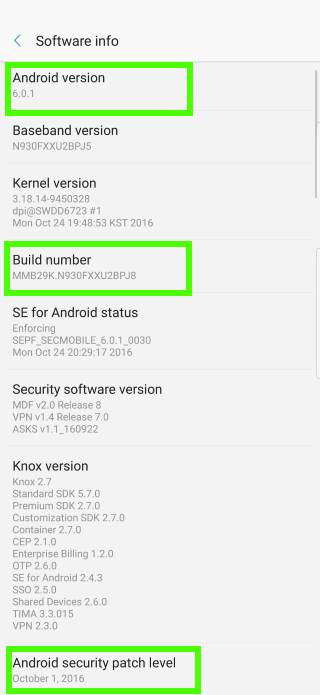
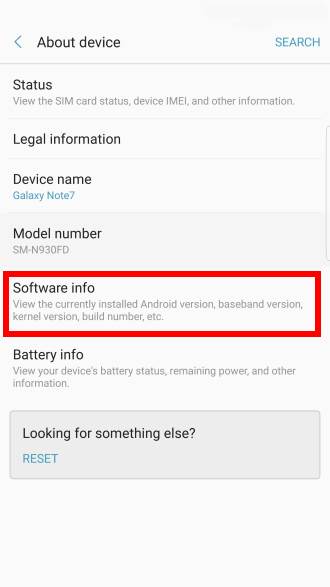
For example, as shown above, on Samsung devices (since Marshmallow update), the version of Android is not shown in About device screen as shown above.
Instead, you have to tap Software info after tapping About device as shown above.
In Software info page, you can find similar software info: Android version, build number and security patch level, as shown in the screenshot above..
What is security patch level? is it related to Android versions?
Since August 2015, Google has released monthly security patch. The date when a patch is published will be called as security patch level.
Some security issues may only affect specific versions of Android. But the security patch level, up to now, is not directly related to Android versions. In other words, most patches can (and should) be applied to several versions of Android.
For example, you may have a device running Lollipop with October 1, 2016 security patch level, and another device running Marshmallow with April 1, 2016 security patch level.
In this case, the vendor of the first device did not update the version of Android, but issued the security patch for it. This should be considered as a responsible vendor.
The vendor of the second device did not do a good job. They should issue new security patches if the device is still under maintenance.
Anyway, most Android vendors may stop maintaining the device after 12-18 months. In this case, you will not get the new version of Android and new security patches any more.
The security patch level usually tells you how responsive an Android vendor is (when the device is still under maintenance).
What is the build number?
As mentioned above, build number is always shown together with Android version. It indicates the version of base Android source code.
For Nexus devices, the build number incorporates:
- Android version. The first letter in build number is for major version of Android. As illustrated above, the N in NBD90Z indicates it is Android N (Nougat).
- Android branch. The second letter in build number is for branch identifier of the Android source.
- Date. The third latter in build number is for quarters. A is for Q1 2009. The two digits in the build number is for days in the quarter. As the maximum days in a quarter is 92 days, two digits are sufficient. Please note, this date is NOT the actual build (compiling) date. It is the date of the base source code. Minor revisions are NOT reflected. For example, D90 in NBD90Z indicates the source code is based on that on June 29, 2016.
- Date version identifier. The last letter in build number is for different versions of the same date code. Z in NBD90Z means it is based on the final version of that day.
Other Android vendors may or may not follow this convention.
For example, as shown above, Samsung devices have two build numbers. The first one follows the convention mentioned above. MMB29K indicates it is based on Android Marshmallow source code at October 29, 2015. The second one is for Samsung internal use.
Do you know how to check version of Android in your phone or tablet?
If you have any questions on checking version of Android in your phone or tablet, please let us know in the comment box below.
For questions on Android Nougat (Android 7.0 and 7.1), please check Android Nougat guides page.
For questions on Android Marshmallow (Android 6.0), please check Android Marshmallow guide page.
For question on Android Lollipop (Android 5.0 and 5.1), please check Android Lollipop guide page.
For other Android questions or problems, please check Android 101 page.
Источник
Android check current version


A version checker for react-native applications. This library gets the latest app version by parsing google play store, apple app store’s app information or custom url. Parsing code is referenced from here
Looking for maintainers!
I have almost zero experience in ios development, and I am no longer working on mobile app development(doing backend and devops works mainly and some web frontend). It makes it hard to maintain this library actively. Hope to have someone to help maintaining react-native-version-check!
— iOS — Link Manually
Add .xcodeproj file as library to XCode project.
- In project navigator, right click Libraries
- Select Add Files to [PROJECT_NAME]
- Add the node_modules/react-native-version-check/ios/RNVersionCheck.xcodeproj file
Add the libRNVersionCheck.a from the RNVersionCheck project to your project’s Build Phases > Link Binary With Libraries
iOS — CocoaPods Package Manager
- Add to your Podfile (assuming it’s in ios/Podfile ):
- Append the following lines to android/settings.gradle :
- Insert the following lines inside the dependencies block in android/app/build.gradle :
- Open up android/app/src/main/java/[. ]/MainApplication.java
# getCountry() (Promise ) — Returns device’s country code of 2 characters.
# getPackageName() (packageName: String) — Returns package name of app.
# getCurrentBuildNumber() (buildNumber: Number) — Returns current app build number.
# getStoreUrl([option: Object]) (Promise ) — Returns url of Play Market or App Store of app.
# getAppStoreUrl([option: Object]) (Promise ) — Returns url of App Store of app.
| Field | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| appID | string | App ID |
| ignoreErrors | boolean | true |
# getPlayStoreUrl([option: Object]) (Promise ) — Returns url of Play Store of app.
| Field | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| packageName | string | Package Name |
| ignoreErrors | boolean | true |
# getCurrentVersion() (currentVersion: String) — Returns current app version.
# getLatestVersion([option: Object]) (Promise ) — Returns the latest app version parsed from url. Returns null when parsing error occurs.
| Field | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| forceUpdate | boolean | false |
| provider | string or function | provider name or function that returns promise or value of the latest version |
| fetchOptions | object | isomorphic-fetch options (https://github.github.io/fetch/) |
| ignoreErrors | boolean | true |
# needUpdate([option: Object]) (Promise ) — Returns an object contains with boolean value whether update needed, current version and latest version. Current and the latest app versions are first split by delimiter, and check each split numbers into depth.
Источник