- CheckBox (Флажок)
- Отслеживаем смену состояния флажка
- Собственные стили
- Собственный вид
- AnimatedStateListDrawable. Анимация между переключением состояния
- res/drawable/toggle.xml
- res/drawable/toggle_checked.xml
- res/drawable/toggle_unchecked.xml
- res/drawable-v21/toggle.xml
- res/drawable-v21/toggle_unchecked_checked.xml
- res/drawable-v21/toggle_checked_unchecked.xml
- Checkbox Basics with Example
- Android Checkbox Basics with Example
- Use Of Checkbox
- Adding Checkbox
- Changing Properties
- Method to take some action in Checkbox
- Android CheckBox with Examples
- Create CheckBox in XML Layout File
- Create CheckBox Control in Activity File
- Handle Android CheckBox Click Events
- Define CheckBox Click Event in XML Layout File
- Define CheckBox Click Event in Activity File
- Android CheckBox Control Attributes
- Android CheckBox Control Example
- activity_main.xml
- MainActivity.java
- Output of Android CheckBox Example
CheckBox (Флажок)
Компонент CheckBox является флажком, с помощью которого пользователь может отметить (поставить галочку) определённую опцию. Очень часто флажки используются в настройках, когда нужно выборочно выбрать определённые пункты, необходимые для комфортной работы пользователю.
Компонент находится в группе Buttons.
Для управления состояниями флажка используйте методы setChecked() или togglе(). Чтобы узнать текущее состояние флажка, вызовите свойство isChecked.
Для экспериментов воспользуемся программой «Счетчик ворон», которую писали при изучении щелчка кнопки.
Как вы помните, в программе была кнопка и текстовое поле. Добавим ещё два элемента CheckBox, а также четыре текстовые метки TextView. Нам нужно постараться, чтобы элементы были аккуратно сгруппированы. Для этой цели воспользуемся вложенными компоновками LinearLayout. Заодно применим интересный приём — мы не будем использовать текст у флажков CheckBox, а воспользуемся текстовыми метками с разными размерами шрифтов. Верхняя метка с крупным шрифтом будет указывать на основную функциональность флажка, а нижняя метка с мелким шрифтом будет использоваться в качестве своеобразной подсказки, в которой содержится дополнительная информация для пользователя.
На самом деле вы можете попробовать другие способы разметки, не воспринимайте как догму. А мы идём дальше. Флажки в нашем приложении нужны для того, чтобы пользователь мог менять вывод текста в текстовом поле. По желанию, можно выводить текст красным цветом и жирным стилем по отдельности или в совокупности. Для этого нам нужно добавить дополнительные строчки кода в обработчик щелчка кнопки.
Запустите проект и попробуйте снимать и ставить галочки у флажков в разных комбинациях, чтобы увидеть, как меняется текст после щелчка кнопки. Код очень простой — проверяется свойство isChecked. Если галочка у флажка установлена, то свойство возвращает true и мы меняем цвет (красный) или стиль текста (жирный). Если флажок не отмечен, то свойство возвращает false, и мы используем стандартные настройки текста.

Отслеживаем смену состояния флажка
С помощью слушателя-интерфейса OnCheckedChangeListener с его методом onCheckedChanged() можно отслеживать смену состояния флажка.
Собственные стили
Если вы используете стандартный проект, то флажок будет использовать цвета Material Design, в частности цвет colorAccent для фона флажка.
В файле res/values/styles.xml добавим строки:
Свойство colorControlNormal отвечает за прямоугольник в невыбранном состоянии, а colorControlActivated за закрашенный прямоугольник в выбранном состоянии.
Присваиваем созданный стиль атрибуту android:theme:
Теперь цвета флажков изменились.
Собственный вид
Если вас не устраивает стандартный вид элементов CheckBox, то не составит никакого труда реализовать свои представления о дизайне.
В папке res/drawable создаём файл checkbox_selector.xml:
Также необходимо подготовить два изображения для двух состояний флажков — выбран и не выбран. В нашем случае это две звезды — серая и жёлтая.
Осталось прописать селектор в компоненте CheckBox (атрибут android:button):
Готово! Можете запускать проект и проверять работу флажков. Ниже код для реагирования на смену состояния флажков:
AnimatedStateListDrawable. Анимация между переключением состояния
Когда мы создали собственный вид флажка, то переключение происходит сразу без анимации. В API 21 появилась возможность установить анимацию при помощи нового класса AnimatedStateListDrawable.
Создадим как прежде файл для собственного вида флажка.
res/drawable/toggle.xml
Далее нужные два значка. Они сделаны в векторном виде.
res/drawable/toggle_checked.xml
res/drawable/toggle_unchecked.xml
Присвоим созданный вид атрибуту android:button.
Код будет работать на устройствах, которые поддерживают векторную графику (API 14), но анимации не будет. Для анимации создадим альтернативный вариант файла в папке res/drawable-v21.
AnimatedStateListDrawable похож на обычный StateListDrawable, но позволяет указать анимацию перехода между двумя состояниями. Мы также указываем две картинки, но также добавляем элементы transition.
res/drawable-v21/toggle.xml
res/drawable-v21/toggle_unchecked_checked.xml
res/drawable-v21/toggle_checked_unchecked.xml
Если запустить пример на старом устройстве, то никакой анимации не увидим, но код будет работать без ошибок. На новых устройствах анимация будет работать.
Источник
Checkbox Basics with Example
Android Checkbox Basics with Example
Use Of Checkbox
So generally we use check boxes whenever we want to choose a list of items. For example, you are making a groceries shop app, you can use checkboxes to select the items. Or for example, you want to give the option to the user to select his favourite animals or his favourite dishes or favourite things. So basically whenever we want to select multiple items, we use checkboxes.
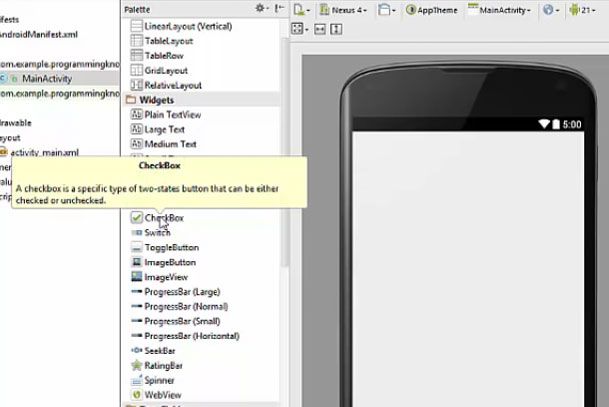
Adding Checkbox
We can add checkboxes by going to the palette and in the widget section and then drag and drop checkbox widget to Android activity. We must also take a button so that on the basis of button click, we can decide which checkboxes are checked and on the basis of checked checkboxes, we can take some action.
Changing Properties
In order to change the properties please select all the check boxes and in the properties go to layout_width and change it to fill_parent so that this width is filled in the width.
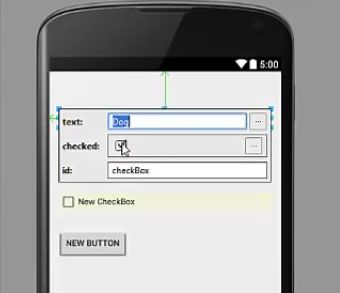
We can also change the name of these checkboxes, for example, we want to create a list of animals so that the user can choose his favourite animals such as dog and there you will see an option ‘checked’ so, if you choose this option checked, you can see whenever you run the application, it will be checked by default. Otherwise, when you uncheck this option, whenever you start your activity, the checkbox will be unchecked. So this is the default condition you want to check to your checkbox. The name to the checkbox according to user’s need.
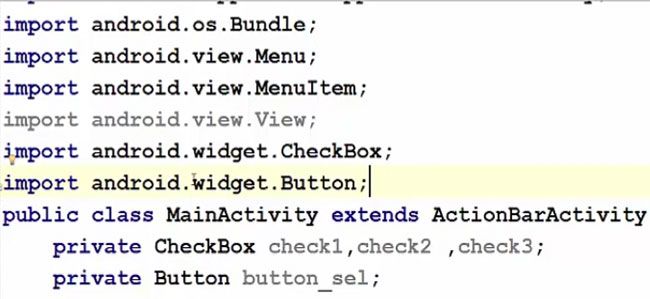
Now we will go to the code part of our activity, therefore, go to the MainActivity.java file and there we will declare three checkbox variables and one button variable.
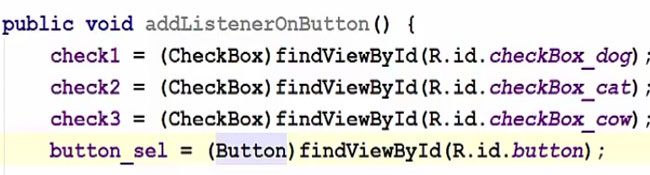
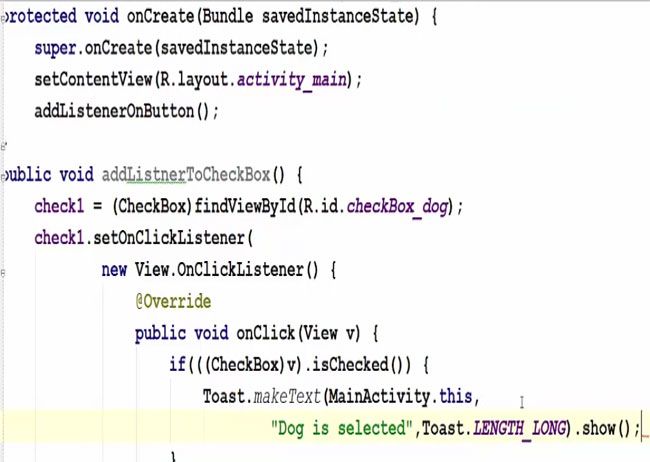
After declaring the variable we now have to create a method. This will be the public method and it’s not going to return anything and we are going to name our method as, for example, add a listener on the button and then it’s not going to take any argument and we will create or prepare the body of our function in these curly brackets. Inside our method, we have to cast our checkboxes and button for example, for the checkbox one we are going to cast it to the dog checkbox.
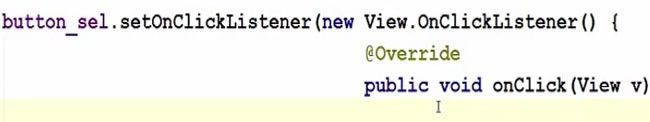
Now after casting all our widgets, we will have to add the listener so we are going to take our button variable and we will set the listener to it. Set on click listener and in here in the arguments, just press enter and we are going to create a new listener. So new on click listener and it will take three arguments.
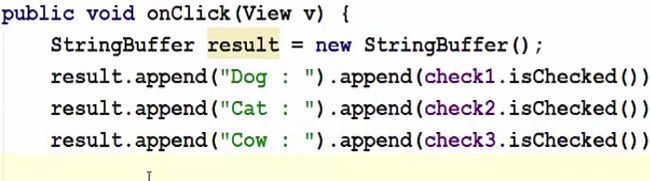
So we will create our String buffer and toast and in this result, we are going to append the checked items first. So first of all, take the result variable so in here Result.append and we can append any string to it, this will give you the binary option true or false or one or zero. If it’s checked it’s going to give you true or if it’s unchecked it’s going to give you false.
And now we can display this result to the toast.
Now once we have created this method we just need to call it in our onCreate method therefore just go below this function setContentView and just paste your method name.
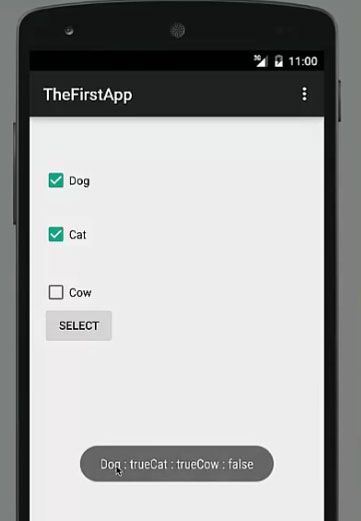
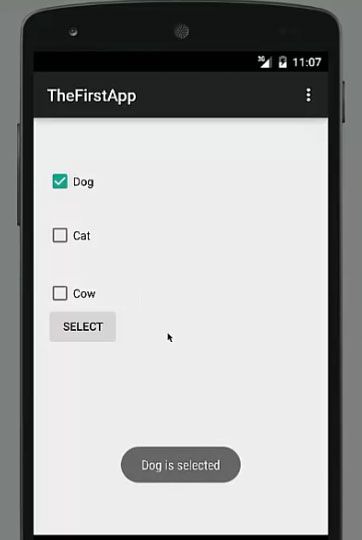
And now our application is running. for example, when we check box 1 and check box 2 and press this select button, the answer is a dog is equal to true and the cat is equal to true as you can see. Dog true cat true and cow false. So in this way you can choose your selection on the basis of is a select method here.
Method to take some action in Checkbox
Now let’s create a method on which we will allow the user to take some action on the checkbox click itself. So for example, once the user selects this dog checkbox, we are going to display some message that you selected dog without any button click event. So for that, we have is declare one more method, which will be public and cast our checkbox 1 variable because we want to take action on checkbox 1 and add a listener.
So as we added a listener to the dog checkbox only so whenever we check it, it shows dog is selected. But you can add the same kind of listener to these checkboxes also. So in this way, you can use checkboxes in your Android app.
Read More About Android Radio Button & Radio Groups Basics
Источник
Android CheckBox with Examples
In android, CheckBox is a two-states button that can be either checked (ON) or unchecked (OFF) and it will allow users to toggle between the two states (ON / OFF) based on the requirements.
Generally, we can use multiple CheckBox controls in android application to allow users to select one or more options from the set of values.
Following is the pictorial representation of using CheckBox control in android applications.
By default, the android CheckBox will be in the OFF (Unchecked) state. We can change the default state of CheckBox by using android:checked attribute.
In case, if we want to change the state of CheckBox to ON (Checked), then we need to set android:checked = “true” in our XML layout file.
In android, we can create CheckBox control in two ways either in the XML layout file or create it in the Activity file programmatically.
Create CheckBox in XML Layout File
Following is the sample way to define CheckBox control in XML layout file in android application.
If you observe above code snippet, here we defined CheckBox control and setting CheckBox state ON using android:checked attribute in xml layout file.
Create CheckBox Control in Activity File
In android, we can create CheckBox control programmatically in activity file based on our requirements.
Following is the example of creating a CheckBox control dynamically in an activity file.
LinearLayout layout = (LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id. l_layout );
CheckBox cb = new CheckBox( this );
cb.setText( «Tutlane» );
cb.setChecked( true );
layout.addView(cb);
This is how we can define CheckBox in XML layout file or programmatically in activity file based on our requirements.
Handle Android CheckBox Click Events
Generally, whenever the user clicks on CheckBox to Select or Deselect the CheckBox object will receive an on-click event.
In android, we can define the CheckBox click event in two ways either in the XML layout file or create it in the Activity file programmatically.
Define CheckBox Click Event in XML Layout File
We can define a click event handler for button by adding the android:onClick attribute to the element in our XML layout file.
The value of android:onClick attribute must be the name of method which we need to call in response to a click event and the Activity file which hosting XML layout must implement the corresponding method.
Following is the example of defining a CheckBox click event using android:onClick attribute in XML layout file.
android :onClick= «onCheckBoxClick»/>
LinearLayout >
In Activity that hosts our XML layout file, we need to implement click event method like as shown below.
public void onCheckboxClicked(View view) <
// Is the view now checked?
boolean checked = ((CheckBox) view).isChecked();
// Check which checkbox was clicked
switch (view.getId()) <
case R.id.chk1:
if (checked)
// Do your coding
else
// Do your coding
break ;
// Perform your logic
>
>
Define CheckBox Click Event in Activity File
In android, we can define CheckBox click event programmatically in Activity file rather than XML layout file.
To define checkbox click event programmatically, create View.OnClickListener object and assign it to the button by calling setOnClickListener(View.OnClickListener) like as shown below.
This is how we can handle CheckBox click events in android applications based on our requirements.
Android CheckBox Control Attributes
The following are some of the commonly used attributes related to CheckBox control in android applications.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| android:id | It is used to uniquely identify the control |
| android:checked | It is used to specify the current state of checkbox |
| android:gravity | It is used to specify how to align the text like left, right, center, top, etc. |
| android:text | It is used to set the text for a checkbox. |
| android:textColor | It is used to change the color of text. |
| android:textSize | It is used to specify the size of text. |
| android:textStyle | It is used to change the style (bold, italic, bolditalic) of text. |
| android:background | It is used to set the background color for checkbox control. |
| android:padding | It is used to set the padding from left, right, top and bottom. |
| android:onClick | It’s the name of the method to invoke when the checkbox clicked. |
| android:visibility | It is used to control the visibility of control. |
Android CheckBox Control Example
Following is the example of defining multiple CheckBox controls and one Button control in LinearLayout to get the selected values of CheckBox controls when we click on Button in the android application.
Create a new android application using android studio and give names as CheckBoxExample. In case if you are not aware of creating an app in android studio check this article Android Hello World App.
Now open an activity_main.xml file from \res\layout path and write the code like as shown below
activity_main.xml
xml version= «1.0» encoding= «utf-8» ?>
LinearLayout xmlns: android = «http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
android :orientation= «vertical» android :layout_width= «match_parent»
android :layout_height= «match_parent» >
CheckBox
android :id= «@+id/chkJava»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :padding= «10dp»
android :layout_marginTop= «150dp»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :text= «Java»
android :onClick= «onCheckboxClicked»/>
CheckBox
android :id= «@+id/chkPython»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :padding= «10dp»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :text= «Python»
android :onClick= «onCheckboxClicked»/>
CheckBox
android :id= «@+id/chkAndroid»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :padding= «10dp»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :text= «Android»
android :onClick= «onCheckboxClicked»/>
CheckBox
android :id= «@+id/chkAngular»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :padding= «10dp»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :text= «AngularJS»
android :onClick= «onCheckboxClicked»/>
Button
android :id= «@+id/getBtn»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :text= «Get Details»/>
LinearLayout >
If you observe above code we created a multiple CheckBox controls and one Button control in XML Layout file.
Once we are done with the creation of layout with required controls, we need to load the XML layout resource from our activity onCreate() callback method, for that open main activity file MainActivity.java from \java\com.tutlane.checkboxexample path and write the code like as shown below.
MainActivity.java
package com.tutlane.checkboxexample;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.CheckBox;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity <
CheckBox android , java , angular , python ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) <
super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout. activity_main );
android = (CheckBox)findViewById(R.id. chkAndroid );
angular = (CheckBox)findViewById(R.id. chkAngular );
java = (CheckBox)findViewById(R.id. chkJava );
python = (CheckBox)findViewById(R.id. chkPython );
Button btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id. getBtn );
btn.setOnClickListener( new View.OnClickListener() <
@Override
public void onClick(View v) <
String result = «Selected Courses» ;
if ( android .isChecked()) <
result += » \n Android» ;
>
if ( angular .isChecked()) <
result += » \n AngularJS» ;
>
if ( java .isChecked()) <
result += » \n Java» ;
>
if ( python .isChecked()) <
result += » \n Python» ;
>
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), result, Toast. LENGTH_SHORT ).show();
>
>);
>
public void onCheckboxClicked(View view) <
boolean checked = ((CheckBox) view).isChecked();
String str= «» ;
// Check which checkbox was clicked
switch (view.getId()) <
case R.id. chkAndroid :
str = checked? «Android Selected» : «Android Deselected» ;
break ;
case R.id. chkAngular :
str = checked? «AngularJS Selected» : «AngularJS Deselected» ;
break ;
case R.id. chkJava :
str = checked? «Java Selected» : «Java Deselected» ;
break ;
case R.id. chkPython :
str = checked? «Python Selected» : «Python Deselected» ;
break ;
>
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), str, Toast. LENGTH_SHORT ).show();
>
>
If you observe above code we are calling our layout using setContentView method in the form of R.layout.layout_file_name in our activity file. Here our xml file name is activity_main.xml so we used file name activity_main and we are getting the status of CheckBox controls when they Select / Deselect and getting the selected CheckBox control values on Button click.
Generally, during the launch of our activity, onCreate() callback method will be called by android framework to get the required layout for an activity.
Output of Android CheckBox Example
When we execute the above example using the android virtual device (AVD) we will get a result like as shown below.
If you observe above result, we are able to get the status of checkboxes while selecting / deselecting and getting all the selected CheckBox values on button click.
This is how we can use CheckBox control in android applications to allow users to select one or more options based on our requirements.
Источник