- com.google.android.packageinstaller — что это такое на Android? (GooglePackageInstaller)
- Можно ли удалить?
- По поводу ошибки
- Заключение
- What is com.google.android.packageinstaller?
- Google.Android.PackageInstaller
- What is the Android package installer used for?
- Package Installer vs Package Manager
- How do I stop the package installer?
- Where are APK files stored?
- Attributes of google.android.packageinstaller
- How to fix ‘Unfortunately, package installer has stopped’
- To fix package installer error on Android
- com.google.android.packageinstaller
- com.google.android.packageinstaller
- Difference between installer and manager
- Storage of APK files
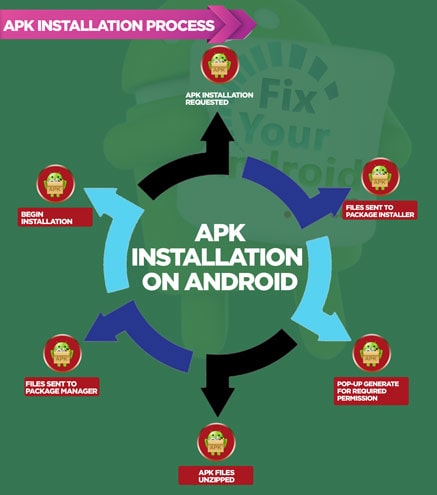
- Installation process
- Storage of data
- 1- packages.xml
- Ten attributes
- Subtags
- 2- package.list
- 3- Packages-stoped.xml
com.google.android.packageinstaller — что это такое на Android? (GooglePackageInstaller)
com.google.android.packageinstaller (GooglePackageInstaller) — отвечает за установку приложений Android, используется магазином Play Store для установки/удаления/обновления приложений на вашем устройстве.
Присутствует в стоковом Android начиная с версии 4.4.
Является системным/основным компонентом, соответственно удалять нельзя.
Другими словами com.google.android.packageinstaller может быть замечен при инсталляции приложений. Чтобы проверить, какие были установлены — откройте Google Play, перейдите в раздел Мои приложения и игры, выберите Все. Дальше можете просмотреть все последние приложения, установленные на ваш телефон. Может появляться в списке активности возможно из-за включенного обновления Google PlayStore.
В справочной информации Android сказано — в случае когда интернет-трафик платный, то можно заблокировать доступ в интернет для Google Play. Блокировать необходимо следующие пакеты:
- com.android.packageinstaller
- com.android.vending
- com.google.android.gms
- com.google.android.packageinstaller
Можно сделать вывод:
- com.google.android.packageinstaller точно относится к Google Play.
- Можно заблокировать доступ в интернет, но тогда пакет возможно будет чаще появляться в списке активности и пытаться установить коннект.
- Исходя из двух вышеперечисленных пунктов, возможно пакет можно и вовсе заморозить. Для этого можно использовать Titanium Backup, но необходимы root-права. Однако последствия — непредсказуемы, могут быть ошибки на этапе загрузки Андроида.
Можно ли удалить?
Нашел сообщение на форуме 4PDA:
Возможно правда, что пакет нужен для установки приложений именно из маркета. Будет ли устанавливаться apk-файлы без этого пакета? Нужно проверять, как раз для этого и можно использовать Titanium Backup — заморозить и протестировать.
Судя по этому сообщению — отключение/остановка пакета com.google.android.packageinstaller приведет к зависанию телефона при включении:
Вывод — не стоит отключать/морозить/удалять данное приложение!
По поводу ошибки
У одного пользователя была ошибка — он устанавливал Андроид 6, далее при установке любого apk — ошибка в приложении, вот комментарий человека:
Потом человек написал решение:
Так что если у вас также будет похожая ошибка — данное решение может помочь и вам.
При появлении Ошибка синтаксических пакетов, попробуйте:
- Зайти в меню Настройки > Приложения > Отобразить системные процессы > найти Программа установки пакета > Очистить кэш и данные.
- Второй вариант — попробовать заново установить гапсы из рекавери.
Заключение
- com.google.android.packageinstaller — отвечает за установку/удаление/обновление приложений, присутствует в стоковой версии Андроида.
- Удалять нельзя, заморозить можно (на свой страх и риск). Перед лучше сделать резервную копию Андроида.
Надеюсь информация оказалась полезной. Удачи и добра!
Источник
What is com.google.android.packageinstaller?
com.google.android.packageinstaller is another system app or app package on Android devices that helps Android OS to perform installation, uninstallation and update of apps on your Android. Know all about com.google.android.packageinstaller. A detailed overview

Google.Android.PackageInstaller
com.google.android.packageinstaller AKA package installer on Android is an app package responsible for installing new apps on Android devices.
In other words, it’s an analog to ZIP files used by Android OS to down apps on the device that includes the software update as well.
All the APK files are integrated into zip format and before you install the app on Android, it is required to unzip them.
In such com.google.android.packageinstaller comes on the surface that ensures the compressed apk files to properly unzipping and installed.
In addition, it also checks the sources APK files for compatibility, potential malware and other spyware injections.
What is the Android package installer used for?
Android package installer acts as a daemon app on Android devices and remains unnoticed. The only function of the packages is to assist your Android device to monitor and assist in installing new apps and apps update on the device.
In addition com.google.android.packageinstaller is also used for the installation of an APK file on Android.
It can monitor your device for software and apps in most of the case and keeps running in the background.
Package Installer vs Package Manager
So, here comes the question again- ‘What is the difference between a Package Installer and Package Manager?’.
As the name suggests itself the package installer is used for installing and uninstalling the apps on Android. While the Package manager is used to manage and distribute the app package files.
These are the core functions of an Android device and integrated with the Android OS database itself. They both work together to handle the distribution, installation and uninstallation of any app or APK file on Android.
Here is the detailed explanation between the Package installer and manager.
- Location: The package manager is broader than the package installer. It is used to monitor and performs all the task related to apps on Android including the system apps. Meanwhile, the package installer is limited for the installation and uninstallation of the APK files.
- Shipping: A package installer is shipped with the computer program. But a package manager is usually shipped with the operating system.
- Maintenance: the scope of the package installer’s maintenance is with which it was bundled, but for a package manager, it is, all the packages on the operating system.
- Development: A package installer is developed by numerous installer developers, whereas the package manager has only one vendor.
In a nutshell, the Package manager is a bit different from the package installer on the functional level.
The basic task of the Package manager is to analyze the apk files and display all necessary information to the user(confirmation, permission, etc) in form of a pop-up.
Once the user grants the permission, another java ‘installPackage‘ process is initiated and the package installer starts the installation process on the APK file by uncompressing and storing the files on the required storage location.
How do I stop the package installer?
As you read above the com.google.android.packageinstaller keeps running in the background on your Android and monitors all your app activity.
But, before you get panic and consider uninstalling com.google.android.packageinstaller, let me tell you, it is not possible to uninstall or disable com.google.android.packageinstaller on Android with or without root.
The app is the spine of your Android app and considering it as bloatware is a mistake.
As per safety, it is completely secure and doesn’t contain any spyware or malware. Secondly, it has nothing to do with your media and messages stored on your Android.
Where are APK files stored?
As we all know, not all apps are the same so neither the installation location is the same for all apps. To understand the APK storage location perfectly you need to understand the process of installation on an APK(Android Application Package)file on Android.
There are two types of apps on Android. one is pre-installed, camera, UI and some bloatware are the perfect examples of pre-installed apps.
While other apps are supposed to install from external sources like the Play store and manual APK files.
All the pre-installed apps on Android are stored under /data/app folder on the internal storage on Android.
No matter, what source you are using to install the app on your Android devices, the apps are installed in APK format on Android. All these third-party apps are stored under the /data/data/
Attributes of google.android.packageinstaller
There are few attributes used to name and identify the packages and files by google.android.packageinstaller on Android. Here are the few major attributes for Com google android packageinstaller are as follows.
ft – the hex format timestamp.
it – the hex format timestamp with the first installation.
ut – the hex format timestamp with the last update.
Flags – it stores the information on the flags of apps.
CodePath – it can be defined as the location of the installation of the APK file.
Native Library Path – it is the native library whose default path is /data/data/
SharedUserId – it is that the Linux UID which will be shared between different apps.
User Id – it is the ID/name of the Linux user.
Version – it is the code of the version of the file AndroidManifest.xml.
How to fix ‘Unfortunately, package installer has stopped’
improper cache distribution or some technical glitch may cause the packageinstaller to stop working and display the error while installing or uninstalling an app on Android.
In most cases, a simple restart can help you to fix the ‘unfortunately, packageinstaller has stopped’ error on Android. But, if you are still unable to install or uninstall an app on Android, follow the methods below.
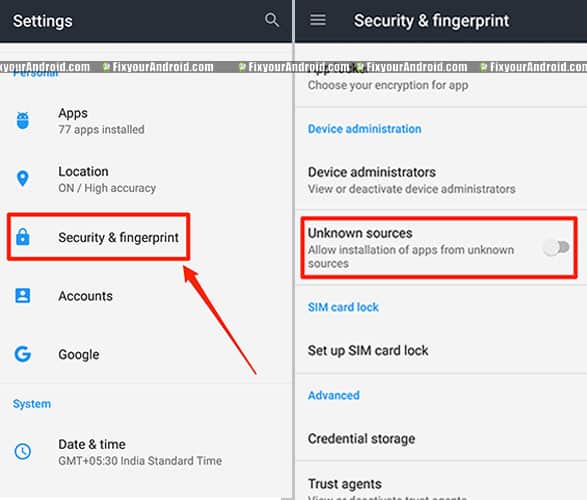
To fix package installer error on Android
- open Settings on Android
- Go to Biometric and security
- Find and open Unknown source and toggle it off
- Restart the device.
It is suggested to always keep the “unknown sources” toggled off as the setting ensures the safety of your Android by keeping an eye on the installation of external APK files.
Источник
com.google.android.packageinstaller
Com.google.android.packageinstaller: The package installer is precisely known as an Android package installer, which is mostly abbreviated as ‘APK‘ in common language. It is an analogue to the zip file and is used by the Android on your phone, to download or install all apps. The Android itself further compresses this zip file for ease in installation. For the installation of any particular app, the package installer first needs to extract the app. After the extraction is done, the app is ready on your phone or tablet anything. Maybe this installation can take a bit longer in many smartphones as after this, it may ask for security checks also.
In easy words, the package installer is not only used to install new applications on your phone but can also update the apps. It is too responsible for the un-installation of applications from your phone or tablet.
com.google.android.packageinstaller
Your smartphone may update your apps daily without your knowledge, and this happens with the help of the package installer. This can be viewed in the history of your apps. This Android package installer is a Google service, and this service provides support in two forms, one as a monolithic APK or else as split APK for apps. So basically, if you see any APK word in your phone history, don’t worry. Nothing wrong has happened to your phone.
Now, this APK downloads the app in small packages, and hence it got this name of package installer. This is a default application on your phone, and you cannot delete it from your device. The package installer gives the user a platform to manage the applications. The package installer asks for permission from the InstallAppProgress to receive the instructions given by the user that is us. Further, this InstallAppProgress again asks its head that is package manager service, to install the package/application. This process is done by installd.
Installd: The process “installd”, processes with a “d” at the end, is a daemon, which implies it operates in the background and manages system functions.
Now here comes to install daemon into the picture. This installd collects the request from the package manager through a Linux socket. These must already be present on your mobile phone. This installd has to follow a few necessary steps in order to install the APK.
Difference between installer and manager
Now you would ask what a package manager is. So, the package manager is precisely an application program interface (API). This interface actually manages the installation or updation of apps. The package manager is widely known as an install manager. Now you would say that this was the work of package installer. So what’s the difference? Often people misinterpret these two as the same things, but they aren’t. Let’s understand the difference.
- Location – the package manager is located in the central install database, whereas the package installer’s location is totally on the judgment of itself. It could be a file in the operating system of your phone or else a file in the app itself.
- Shipping– a package installer is shipped with each computer program, but a package manager is usually shipped with the operating system.
- Maintenance – the scope of package installer’s maintenance is with which it was bundled, but for a package manager, it is, all the packages on the operating system.
- Development – a package installer is developed by numerous installer developers, whereas the package manager has only one vendor.
Basically, the package manager is a bit different and is responsible for the distribution of data and software. Whenever we install any APK file on our device, this package manager analyses the file and pops you the confirmation. And as soon as you press the ‘OK’ button, the manager starts calling the ‘installPackage method.‘ This method has four parameters that are: Uri, Observer, installFlags, and installPackageName.
Now, the package manager initiates a ‘package’ service. Lookup for ‘InstallAppProgress.java’ in the installer source code to know what happens under this service.
Storage of APK files
Now the next question in our mind should be where do these files get stored? So there are multiple ways and answers to this. Not all apps work alike.
One category is the pre-install category that is there in our camera, calendar, browser. In these applications, APK is stored in /system/app/
Secondly, the category is the user install category, and the following are a few things that fall under this category: ApiDemo, any.do, etc. These files stored under /data/app.
The third category is in which package manager makes a directory for all types of data. These data include shared preferences, cache data, and native libraries. All of this is stored under /data/data/
/. Sometimes you may see your APK file ending with *.odex file. This is a bit different thing and currently not relevant to this topic.
Installation process
The package installation process occurs within the package manager’s service.
- The user will add a package/application for its installation on his phone in the queue.
- The next step is analyzing the location of the application or package.
- Then press install or update
- After that, you have to copy the APK file to someplace or directory.
- Now, locate the User ID of the app.
- Ask for the installd process.
- Prepare an application directory and then fix the permissions.
- After all, this extracts the dex code to another directory of the cache.
- Next step is to reflect the packages.list/system/data/packages.xml with its latest updated status.
- Then transmit it to the system with its name of the complete package.
- intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED
Storage of data
The package manager stores the data in three forms:
1- packages.xml
The XML file listed above can store two things:
- One is the permission
- Second is the package/application
These permissions are stored within the permissions tag in your device. And for each permission, there are basically three attributes. These attributes are name, protection, and the package. Let’s start with the first attribute, i.e., name, which has the name of the permission, which we use in AndroidManifest.xml. Next comes the protection attribute that is used to depict the security of the package. Third comes the package attribute, that shows permissions given to the package.
The package tag has around ten attributes within along with some subtags.
Ten attributes
- Name – it includes the package name.
- NativeLibraryPath – it is the native library whose default path is /data/data/
/lib/.
Subtags
1. Sigs: It stores the information about the signature. Also, the count keeps a check on the number of cert tags in a file.
2. Cert: The cert consists of many certification keys. Also, the index keeps a check on the index of the certification. This value increases when you install new certificates along with applications.
3. Perm: it provides the information about permissions that developers have set in AndroidManifest.xml file.
2- package.list
This can be defined as a simple text file that simply contains the names of the package, the userId, flags, etc. There’s no solid proof, but the only experience with which I can say that package. The list looks up for pre-installed packages faster. The only reason behind this is that it keeps the most important data only.
3- Packages-stoped.xml
This method includes the packages that are in stopped condition or state. These stopped-state apps do not get any signal. There are so many package installer apps also that are available online. Following is the list of the best package installers.
Источник