- Set Up Device for Development
- Enable Debugging on the Device
- Android 9.0+
- Android 8.0 and Android 8.1
- Android 7.1 and lower
- Verify that USB debugging is enabled
- Android 9.0+
- Android 8.0 and Android 8.1
- Android 7.1 and lower
- Connect the device to the computer
- Alternate connection via Wifi
- Connecting over WiFi
- Troubleshooting
- Install USB Drivers
- Download the USB Drivers
- Installing the USB Driver
- Summary
- Build and run your app
- Change the run/debug configuration
- Change the build variant
- Build your project
- Monitor the build process
- Apply Changes
- Requirements
- Use Apply Changes
- Enable Run fallback for Apply Changes
- Platform-dependent changes
- Limitations of Apply Changes
- Code changes that require app restart
- Libraries and plugins
- Code that directly references content in an installed APK
Set Up Device for Development
This article explains how to setup an Android device and connect it to a computer so that the device may be used to run and debug Xamarin.Android applications.
After testing on an Android emulator, you will want to see and test your apps running on an Android device. You will need to enable debugging and connect the device to the computer.
Each of these steps will be covered in more detail in the sections below.
Enable Debugging on the Device
A device must be enabled for debugging in order to test an Android application. Developer options on Android have been hidden by default since version 4.2, and enabling them can vary based on the Android version.
Android 9.0+
For Android 9.0 and higher, debugging is enabled by following these steps:
- Go to the Settings screen.
- Select About Phone .
- Tap Build Number 7 times until You are now a developer! is visible.
Android 8.0 and Android 8.1
- Go to the Settings screen.
- Select System.
- Select About Phone
- Tap Build Number 7 times until You are now a developer! is visible.
Android 7.1 and lower
- Go to the Settings screen.
- Select About Phone.
- Tap Build Number 7 times until You are now a developer! is visible.
Verify that USB debugging is enabled
After enabling developer mode on your device, you must ensure that USB debugging is enabled on the device. This also varies based on the Android version.
Android 9.0+
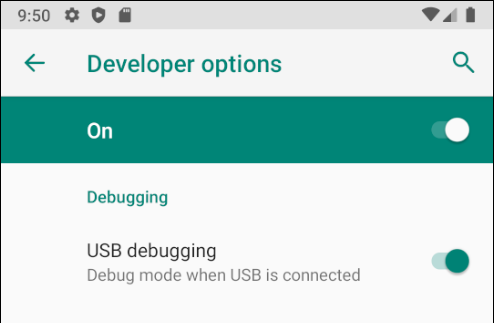
Navigate to Settings > System > Advanced > Developer Options and enable USB Debugging.
Android 8.0 and Android 8.1
Navigate to Settings > System > Developer Options and enable USB Debugging.
Android 7.1 and lower
Navigate to Settings > Developer Options and enable USB Debugging.
Once the Developer Options tab is available under Settings > System, open it to reveal developer settings:
This is the place to enable developer options such as USB debugging and stay awake mode.
Connect the device to the computer
The final step is to connect the device to the computer. The easiest and most reliable way is to do so over USB.
You will receive a prompt to trust the computer on your device if you have not used it for debugging before. You can also check Always allow from this computer to prevent requiring this prompt each time you connect the device.
Alternate connection via Wifi
It is possible to connect an Android device to a computer without using a USB cable, over WiFi. This technique requires more effort but could be useful when the device is too far from the computer to remain constantly plugged-in via cable.
Connecting over WiFi
By default, the Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is configured to communicate with an Android device via USB. It is possible to reconfigure it to use TCP/IP instead of USB. To do this, both the device and the computer must be on the same WiFi network. To setup your environment to debug over WiFi complete the following steps from the command line:
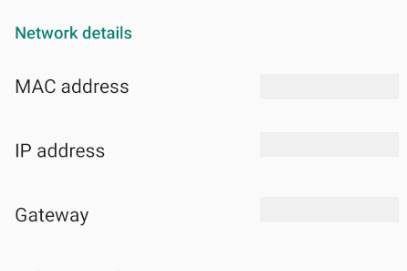
Determine the IP address of your Android device. One way to find out the IP address is to look under Settings > Network & internet > Wi-Fi, then tap on the WiFi network that the device is connected to, and then tap on Advanced. This will open a dropdown showing information about the network connection, similar to what is seen in the screenshot below:
On some versions of Android the IP address won’t be listed there but can be found instead under Settings > About phone > Status.
Connect your Android device to your computer via USB.
Next, restart ADB so that it using TCP on port 5555. From a command prompt, type the following command:
After this command is issued, your computer will not be able to listen to devices that are connected via USB.
Disconnect the USB cable connecting your device to your computer.
Configure ADB so that it will connect to your Android device on the port that was specified in step 1 above:
Once this command finishes the Android device is connected to the computer via WiFi.
When you’re finished debugging via WiFi, it’s possible to reset ADB back to USB mode with the following command:
It’s possible to request ADB to list the devices that are connected to the computer. Regardless of how the devices are connected, you can issue the following command at the command prompt to see what is connected:
Troubleshooting
In some cases you might find that your device cannot connect to the computer. In this case you may want to verify that USB drivers are installed.
Install USB Drivers
This step is not necessary for macOS; just connect the device to the Mac with a USB cable.
It may be necessary to install some extra drivers before a Windows computer will recognize an Android device connected by USB.
These are the steps to set up a Google Nexus device and are provided as a reference. Steps for your specific device may vary, but will follow a similar pattern. Search the internet for your device if you have trouble.
Run the android.bat application in the [Android SDK install path]\tools directory. By default, the Xamarin.Android installer will put the Android SDK in following location on a Windows computer:
Download the USB Drivers
Google Nexus devices (with the exception of the Galaxy Nexus) require the Google USB Driver. The driver for the Galaxy Nexus is distributed by Samsung. All other Android devices should use the USB driver from their respective manufacturer.
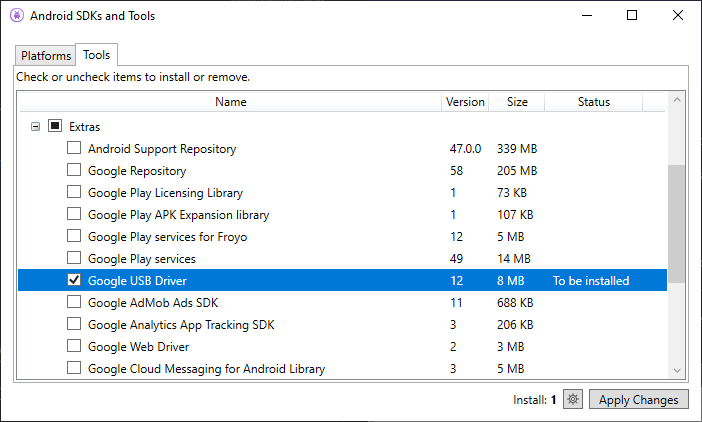
Install the Google USB Driver package by starting the Android SDK Manager, and expanding the Extras folder, as can be seen in the follow screenshot:
Check the Google USB Driver box, and click the Apply Changes button. The driver files are downloaded to the following location:
[Android SDK install path]\extras\google\usb\_driver
The default path for a Xamarin.Android installation is:
Installing the USB Driver
After the USB drivers are downloaded, it is necessary to install them. To install the drivers on Windows 7:
Connect your device to the computer with a USB cable.
Right-click on the Computer from your desktop or Windows Explorer, and select Manage .
Select Devices in the left pane.
Locate and expand Other Devices in the right pane.
Right-click the device name and select Update Driver Software . This will launch the Hardware Update Wizard.
Select Browse my computer for driver software and click Next .
Click Browse and locate the USB driver folder (the Google USB driver is located in [Android SDK install path]\extras\google\usb_driver).
Click Next to install the driver.
Summary
This article discussed how to configure an Android device for development by enabling debugging on the device. It also covered how to connect the device to a computer using either USB or WiFi.
Источник
Build and run your app
Android Studio sets up new projects to deploy to the Android Emulator or a connected device with just a few clicks. Once your app is installed, you can use Apply Changes to deploy certain code and resource changes without building a new APK.
To build and run your app, follow these steps:
- In the toolbar, select your app from the run configurations drop-down menu.
From the target device drop-down menu, select the device that you want to run your app on.
If you don’t have any devices configured, then you need to either connect a device via USB or create an AVD to use the Android Emulator.
Click Run .
Change the run/debug configuration
When you run your app for the first time, Android Studio uses a default run configuration. The run configuration specifies whether to deploy your app from an APK or an Android App Bundle, the module to run, package to deploy, activity to start, target device, emulator settings, logcat options, and more.
The default run/debug configuration builds an APK, launches the default project activity, and uses the Select Deployment Target dialog for target device selection. If the default settings don’t suit your project or module, you can customize the run/debug configuration, or even create a new one, at the project, default, and module levels. To edit a run/debug configuration, select Run > Edit Configurations. For more information, see Create and Edit Run/Debug Configurations.
Change the build variant
By default, Android Studio builds the debug version of your app, which is intended for use only during development, when you click Run.
To change the build variant Android Studio uses, select Build > Select Build Variant in the menu bar.
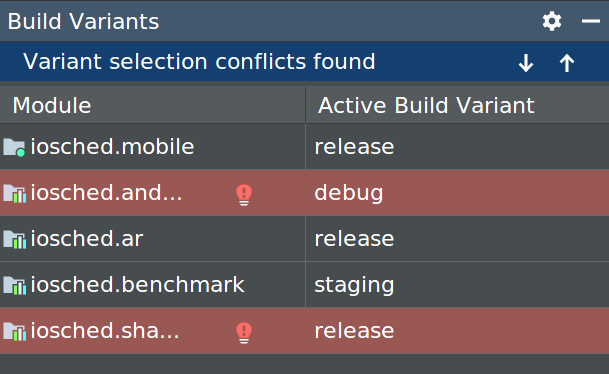
For projects without native/C++ code, the Build Variants panel has two columns: Module and Active Build Variant. The Active Build Variant value for the module determines which build variant the IDE deploys to your connected device and is visible in the editor.
Figure 1. The Build Variants panel has two columns for projects that do not have native/C++ code
To switch between variants, click the Active Build Variant cell for a module and choose the desired variant from the list field.
For projects with native/C++ code, the Build Variants panel has three columns: Module, Active Build Variant, and Active ABI. The Active Build Variant value for the module determines the build variant that the IDE deploys to your device and is visible in the editor. For native modules, the Active ABI value determines the ABI that the editor uses, but does not impact what is deployed.
Figure 2. The Build Variants panel adds the Active ABI column for projects with native/C++ code
To change the build variant or ABI, click the cell for the Active Build Variant or Active ABI column and choose the desired variant or ABI from the list. After you change the selection, the IDE syncs your project automatically. Changing either column for an app or library module will apply the change to all dependent rows.
By default, new projects are set up with two build variants: a debug and release variant. You need to build the release variant to prepare your app for public release.
To build other variations of your app, each with different features or device requirements, you can define additional build variants.
Conflicts in Android Studio’s Build Variants dialog
In Android Studio’s Build Variants dialog, you might see error messages indicating conflicts between build variants, such as the following:
This error does not indicate a build issue with Gradle – it is only indicating that the Android Studio IDE itself cannot resolve symbols between the variants of the selected modules.
For example, if you have a module M1 that depends on variant v1 of module M2 , but M2 has variant v2 selected in the IDE, you have unresolved symbols in the IDE. Let’s say that M1 depends on a class Foo which is only available in v1 . When v2 is selected, that class is not known by the IDE and it will fail to resolve it and show errors in the code of M1 .
These error messages appear because the IDE cannot load code for multiple variants simultaneously. In terms of your app’s build, however, the variant selected in this dialog will have no effect because Gradle builds your app with the source code specified in your Gradle build recipes, not based on what’s currently loaded in the IDE.
Build your project
The Run button builds and deploys your app to a device. However, to build your app to share or upload to Google Play, you’ll need to use one of the options in the Build menu to compile parts or all of your project. Before you select any of the build options listed in table 1, make sure you first select the build variant you want to use.
Table 1. Build options in the Build menu.
| Menu Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Make Module | Compiles all source files in the selected module that have been modified since the last build, and all modules the selected module depends on recursively. The compilation includes dependent source files and any associated build tasks. You can select the module to build by selecting either the module name or one of its files in the Project window. |
| Make Project | Makes all modules. |
| Clean Project | Deletes all intermediate/cached build files. |
| Rebuild Project | Runs Clean Project for the selected build variant and produces an APK. |
| Build Bundle(s) / APK(s) > Build APK(s) | |
| Build Bundle(s) / APK(s) > Build Bundle(s) | |
| Brings up a dialog with a wizard to set up a new signing configuration, and build either a signed app bundle or APK. You need to sign your app with a release key before you can upload it to the Play Console. For more information about app signing, see Sign your app. |
Note: The Run button builds an APK with testOnly=»true» , which means the APK can only be installed via adb (which Android Studio uses). If you want a debuggable APK that people can install without adb, select your debug variant and click Build Bundle(s) / APK(s) > Build APK(s).
For details about the tasks that Gradle executes for each command, open the Build window as described in the next section. For more information about Gradle and the build process, see Configure Your Build.
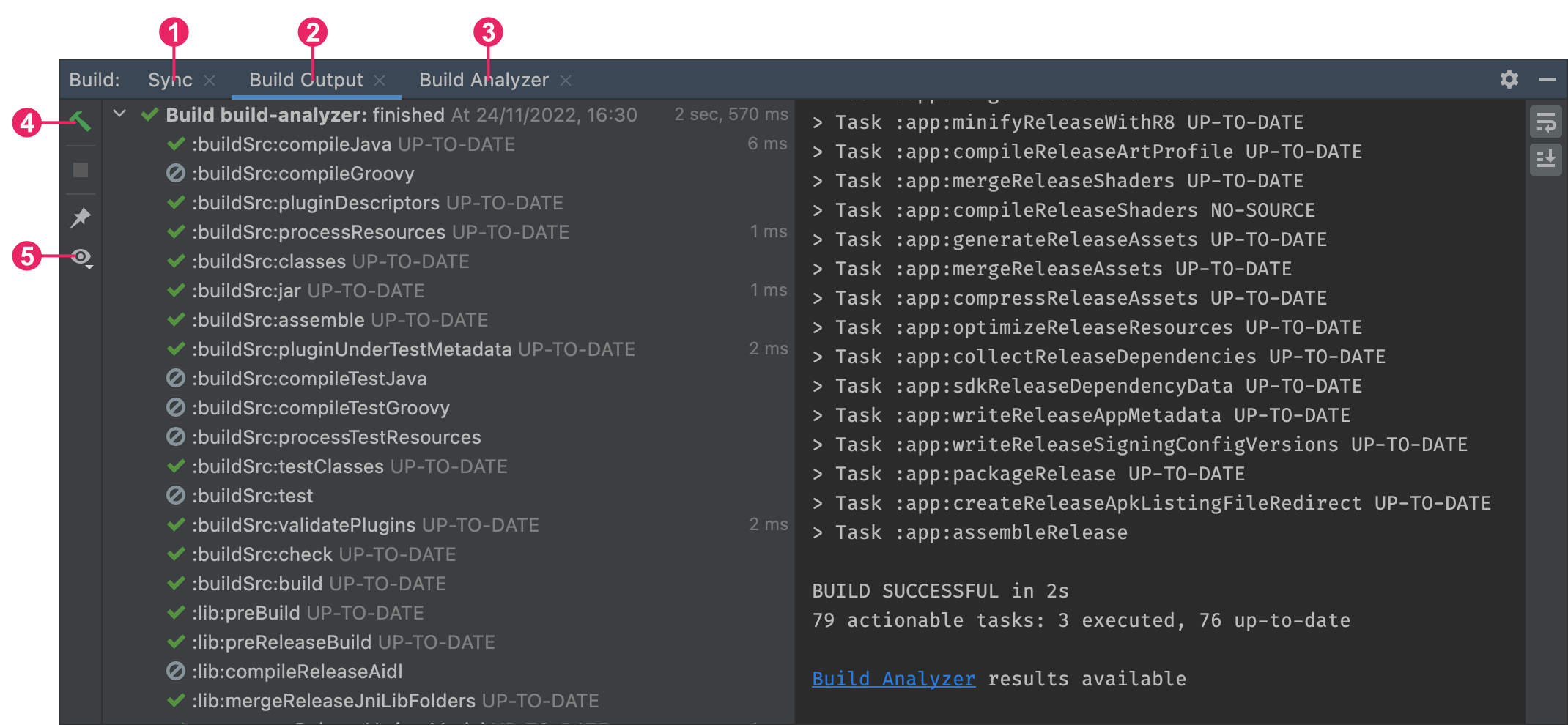
Monitor the build process
You can view details about the build process by clicking View > Tool Windows > Build (or by clicking Build in the tool window bar). The window displays the tasks that Gradle executes in order to build your app, as shown in figure 3.
Figure 3. The Build output window in Android Studio
- Build tab: Displays the tasks Gradle executes as a tree, where each node represents either a build phase or a group of task dependencies. If you receive build-time or compile-time errors, inspect the tree and select an element to read the error output, as shown in figure 4.
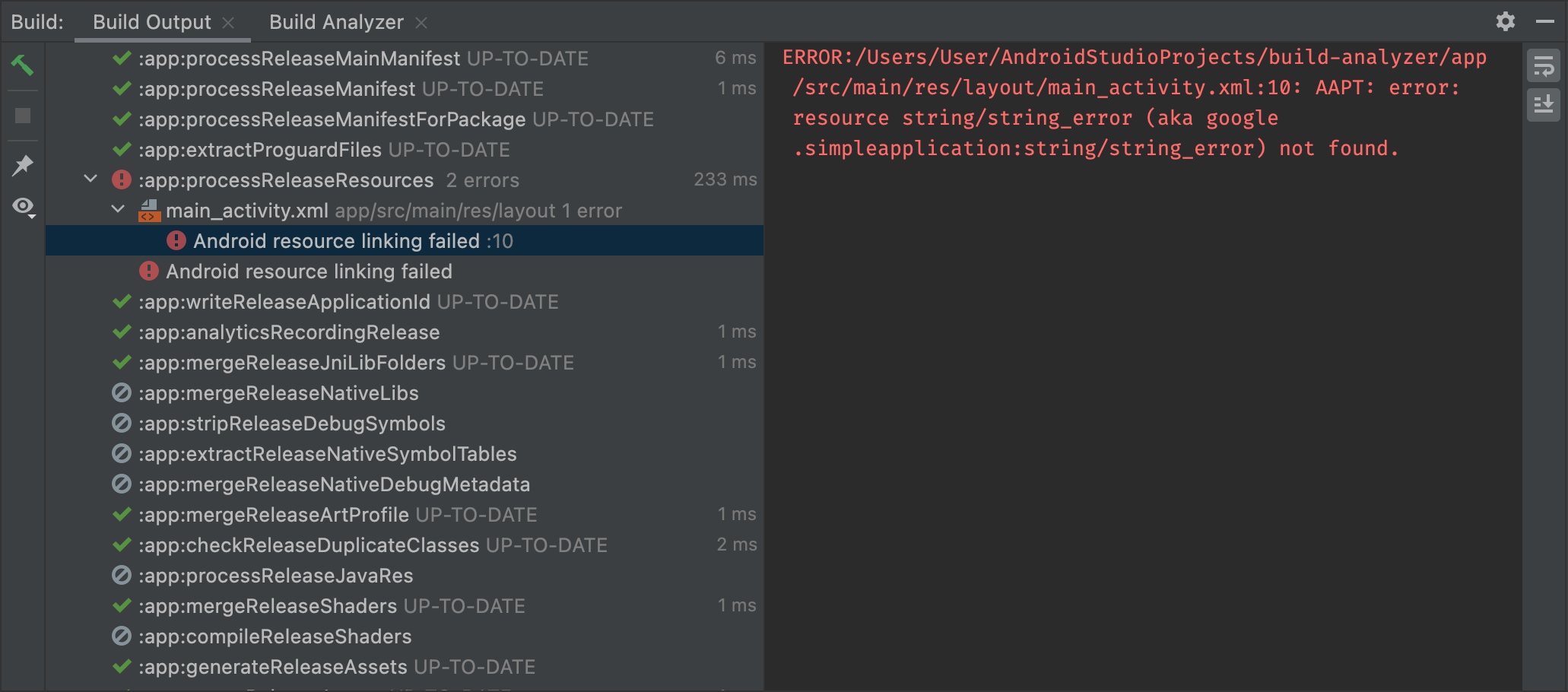
Figure 4. Inspect the Build output window for error messages
If your build variants use product flavors, Gradle also invokes tasks to build those product flavors. To view the list of all available build tasks, click View > Tool Windows > Gradle (or click Gradle in the tool window bar).
If an error occurs during the build process, Gradle may recommend some command-line options to help you resolve the issue, such as —stacktrace or —debug . To use command-line options with your build process:
- Open the Settings or Preferences dialog:
- On Windows or Linux, select File >Settings from the menu bar.
- On Mac OSX, select Android Studio >Preferences from the menu bar.
- Navigate to Build, Execution, Deployment >Compiler.
- In the text field next to Command-line Options, enter your command-line options.
- Click OK to save and exit.
Gradle applies these command-line options the next time you try building your app.
Apply Changes
In Android Studio 3.5 and higher, Apply Changes lets you push code and resource changes to your running app without restarting your app—and, in some cases, without restarting the current activity. This flexibility helps you control how much of your app is restarted when you want to deploy and test small, incremental changes while preserving your device’s current state. Apply Changes uses capabilities in the Android JVMTI implementation that are supported on devices running Android 8.0 (API level 26) or higher. To learn more about how Apply Changes works, see Android Studio Project Marble: Apply Changes.
Requirements
Apply Changes actions are only available when you meet the following conditions:
- You build the APK of your app using a debug build variant.
- You deploy your app to a target device or emulator that runs Android 8.0 (API level 26) or higher.
Use Apply Changes
Use the following options when you want to deploy your changes to a compatible device:
Apply Changes and Restart Activity
Attempts to apply both your resource and code changes by restarting your activity but without restarting your app. Generally, you can use this option when you’ve modified code in the body of a method or modified an existing resource.
You can also perform this action by pressing Ctrl+Alt+F10 (or Control+Shift+Command+R on macOS).
Apply Code Changes
Attempts to apply only your code changes without restarting anything. Generally, you can use this option when you’ve modified code in the body of a method but you have not modified any resources. If you’ve modified both code and resources, use Apply Changes and Restart Activity instead.
You can also perform this action by pressing Ctrl+F10 (or Control+Command+R on macOS).
Run
Deploys all changes and restarts the app. Use this option when the changes that you have made cannot be applied using either of the Apply Changes options. To learn more about the types of changes that require an app restart, see Limitations of Apply Changes.
Enable Run fallback for Apply Changes
After you’ve clicked either Apply Changes and Restart Activity or Apply Code Changes, Android Studio builds a new APK and determines whether the changes can be applied. If the changes can’t be applied and would cause Apply Changes to fail, Android Studio prompts you to Run your app again instead. However, if you don’t want to be prompted every time this occurs, you can configure Android Studio to automatically rerun your app when changes can’t be applied.
To enable this behavior, follow these steps:
Open the Settings or Preferences dialog:
- On Windows or Linux, select File > Settings from the menu bar.
- On macOS, select Android Studio > Preferences from the menu bar.
Navigate to Build, Execution, Deployment > Deployment.
Select the checkboxes to enable automatic Run fallback for either of the Apply Changes actions.
Click OK.
Platform-dependent changes
Some features of Apply Changes depend on specific versions of the Android platform. To apply these kinds of changes, your app must be deployed to a device running that version of Android (or higher).
| Type of change | Minimum platform version |
|---|---|
| Adding a method | Android 11 |
Limitations of Apply Changes
Apply Changes is designed to speed up the app deployment process. However, there are some limitations for when it can be used. If you encounter any issues while using Apply Changes, file a bug.
Code changes that require app restart
Some code and resource changes cannot be applied until the app is restarted, including the following:
- Adding or removing a field
- Removing a method
- Changing method signatures
- Changing modifiers of methods or classes
- Changing class inheritance
- Changing values in enums
- Adding or removing a resource
- Changing the app manifest
- Changing native libraries (SO files)
Libraries and plugins
Some libraries and plugins automatically make changes to your app’s manifest files or to resources that are referenced in the manifest. These automatic updates can interfere with Apply Changes in the following ways:
- If a library or plugin makes changes to your app’s manifest, you can’t use either Apply Code Changes or Apply Changes and Restart Activity and have to restart your app before you can see your changes.
- If a library or plugin makes changes to your app’s resource files, you can’t use Apply Code Changes , and you must use Apply Changes and Restart Activity to see your changes.
You can avoid these limitations by disabling all automatic updates for your debug build variants.
For example, Crashlytics updates app resources with a unique build ID during every build, which prevents you from using Apply Code Changes and requires you to restart your app’s activity to see your changes. You can disable this behavior so that you can use Apply Code Changes alongside Crashlytics with your debug builds.
Code that directly references content in an installed APK
If your code directly references content from your app’s APK that’s installed on the device, that code can cause crashes or misbehave after clicking Apply Code Changes . This behavior occurs because when you click Apply Code Changes, the underlying APK on the device is replaced during installation. In these cases, you can click Apply Changes and Restart Activity or Run , instead.
Content and code samples on this page are subject to the licenses described in the Content License. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Источник