- Как преобразовать Drawable в Bitmap?
- Полный список
- Bitmap
- Layer List
- State List
- Практический опыт работы с Bitmap средствами Android
- Bitmap
- Summary
- Constants
- public static final int DENSITY_NONE
- Fields
- public static final Creator CREATOR
- Public Methods
- public boolean compress (Bitmap.CompressFormat format, int quality, OutputStream stream)
- public Bitmap copy (Bitmap.Config config, boolean isMutable)
- public void copyPixelsFromBuffer (Buffer src)
- public void copyPixelsToBuffer (Buffer dst)
- public static Bitmap createBitmap (DisplayMetrics display, int[] colors, int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config)
- public static Bitmap createBitmap (DisplayMetrics display, int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config)
- public void eraseColor (int c)
- public Bitmap extractAlpha ()
- public Bitmap extractAlpha (Paint paint, int[] offsetXY)
- public final int getAllocationByteCount ()
- public final int getByteCount ()
- public final Bitmap.Config getConfig ()
- public int getDensity ()
- public int getGenerationId ()
- public final int getHeight ()
- public byte[] getNinePatchChunk ()
- public int getPixel (int x, int y)
- public void getPixels (int[] pixels, int offset, int stride, int x, int y, int width, int height)
- public int getScaledHeight (DisplayMetrics metrics)
- public int getScaledHeight (int targetDensity)
- public int getScaledHeight (Canvas canvas)
- public int getScaledWidth (int targetDensity)
- public int getScaledWidth (DisplayMetrics metrics)
- public int getScaledWidth (Canvas canvas)
- public final int getWidth ()
- public final boolean hasAlpha ()
- public final boolean hasMipMap ()
- public final boolean isMutable ()
- public final boolean isPremultiplied ()
- public final boolean isRecycled ()
- public void prepareToDraw ()
- public void reconfigure (int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config)
- public void recycle ()
- public boolean sameAs (Bitmap other)
- public void setConfig (Bitmap.Config config)
- public void setDensity (int density)
- public void setHasAlpha (boolean hasAlpha)
- public final void setHasMipMap (boolean hasMipMap)
Как преобразовать Drawable в Bitmap?
Я хотел бы установить определенный Drawable в качестве обоев устройства, но все функции обоев принимают только Bitmap . Я не могу использовать WallpaperManager потому что я до 2.1.
Кроме того, мои чертежи загружаются из Интернета и не находятся в R.drawable .
Эта часть кода помогает.
Здесь версия, в которой загружается изображение.
Это преобразует BitmapDrawable в Bitmap.
Drawable можно нарисовать на Canvas , а Canvas может быть скопирован с помощью Bitmap :
(Обновлено для обработки быстрого преобразования для BitmapDrawable s и обеспечения того, что созданный Bitmap имеет допустимый размер)
Используйте этот код:
1. получить извлекаемую из ресурсов
2.get изображение из URL-адреса
Может быть, это поможет кому-то …
Из PictureDrawable в Bitmap используйте:
… реализованы как таковые:
Поэтому, посмотрев (и используя) другие ответы, кажется, что все они плохо обрабатывают ColorDrawable и PaintDrawable . (Особенно на леденец) казалось, что Shader s были настроены так, чтобы сплошные блоки цветов обрабатывались неправильно.
Теперь я использую следующий код:
В отличие от других, если вы вызываете setBounds на Drawable прежде чем просить превратить его в растровое изображение, он будет рисовать растровое изображение в правильном размере!
Вот лучшее разрешение
Код из инструкции Как читать биты с битами в качестве InputStream
Android предоставляет не прямое решение: BitmapDrawable . Чтобы получить битмап, нам нужно предоставить идентификатор ресурса R.drawable.flower_pic для BitmapDrawable а затем BitmapDrawable его в Bitmap .
Используйте этот код.it поможет вам достичь своей цели.
Следующий код преобразует Drawable в Bitmap
Источник
Полный список
— изучаем drawable теги: , ,
Продолжаем разбирать типы Drawable, которые можно описывать с помощью XML-разметки. Проектов в этом уроке создавать не будем. Я просто буду в своем проекте создавать XML-файлы в папке drawable и ставить их фоном для View. А в тексте урока приведу код и скрины. Иногда буду вешать дополнительно серый фон, чтобы был виден реальный размер View.
Чтобы программно добраться до Drawable, который вы для View повесили как фон, надо просто вызвать метод getBackground.
Bitmap
Тег позволяет получить Drawable обертку для Bitmap. У тега есть несколько атрибутов.
В атрибуте src указываем нужный нам файл-изображение.
Атрибут gravity указывает, как bitmap будет располагаться внутри Drawable. Можно использовать несколько значений, разделенных знаком | . Значения тут стандартные, и некоторые из них мы часто используем при работе с layout. Рассмотрим пример.
Значение атрибута gravity сдвигает изображение влево-вверх
Далее ставим следующие значение атрибута gravity:
fill_horizontal — растянуть по горизонтали
fill — растянуть (используется по умолчанию)
Насколько я понял, значения clip_vertical и clip_horizontal идентичны значениям fill_vertical и fill_horizontal в случае когда Bitmap по размеру больше, чем предоставляемое ему пространство. Т.е. clip_vertical сожмет его по вертикали, так чтобы он влез. А clip_horizontal — по горизонтали.
Атрибут tileMode — это режим «плитки». Позволяет замостить вашим изображением все доступное пространство. По умолчанию он имеет значение disabled.
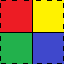
Для примера я создам такой bitmap.
Четыре разных цвета, внутренние границы — сплошные, внешние — пунктиром.
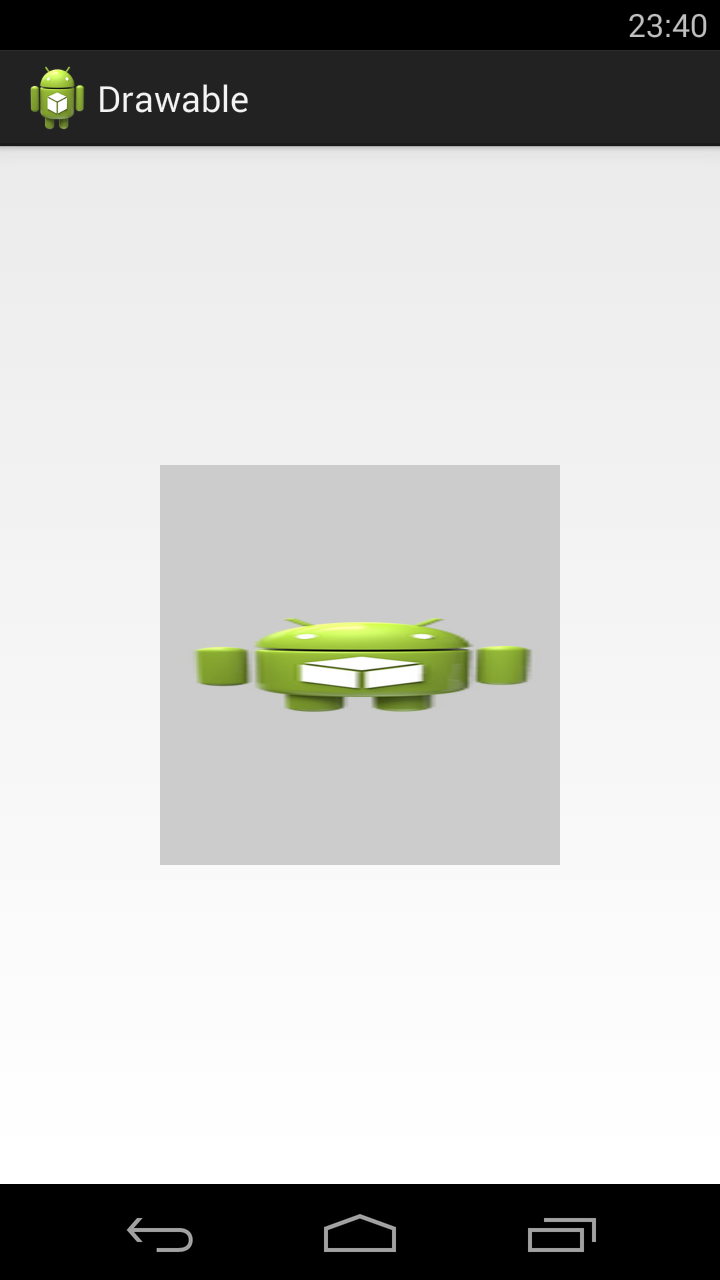
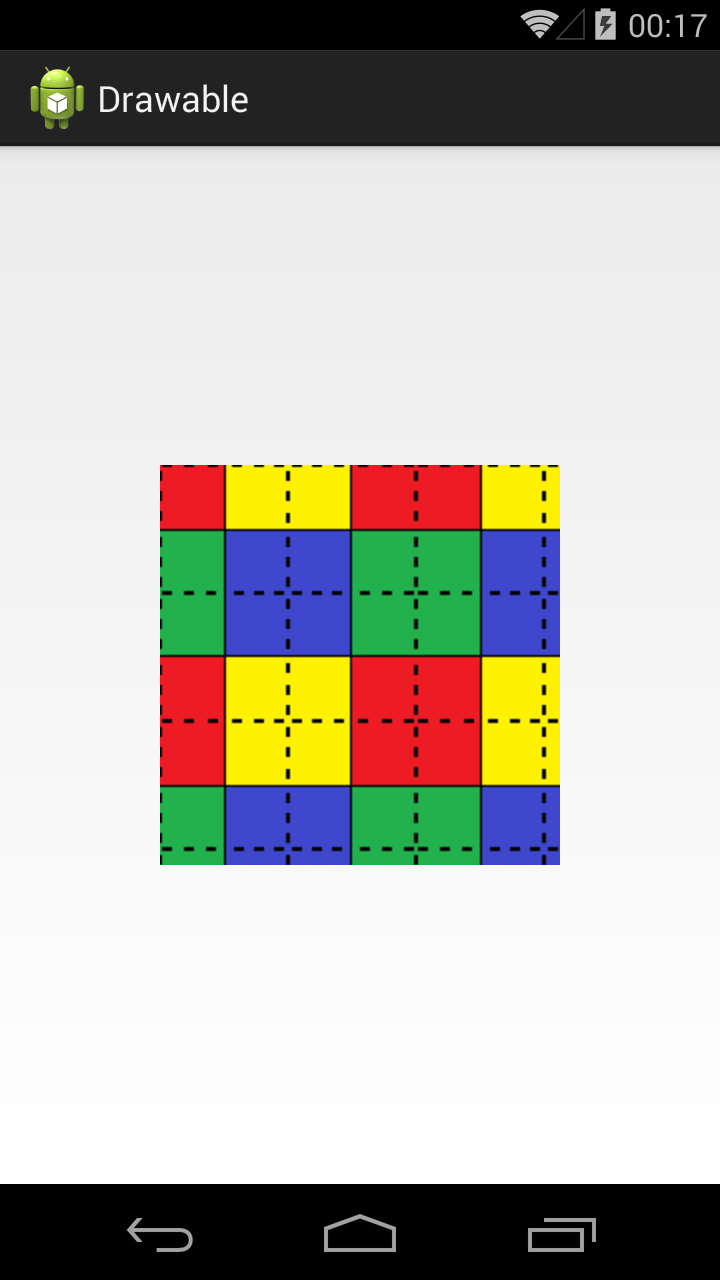
Если tileMode = repeat, то Bitmap будет размножен и займет все доступное пространство
Далее меняем значение атрибута tileMode.
mirror – Bitmap также будет размножен, но при этом он будет чередоваться со своим отражением
clamp – растягивает края картинки на все свободное пространство
Прочие атрибуты тега :
antialias – сглаживание линий
dither – преобразование цветов, если текущей палитры недостаточно для отображения
filter – фильтр при сжатии или растягивании (пример результата использования есть в Уроке 158)
mipMap – использование mip-текстурирования. Про него можно почитать в википедии. Используйте этот режим, если планируете в процессе отображения уменьшать bitmap более чем в два раза.
Мы рассмотрели XML-описание, но вы всегда можете создать этот объект и программно. Java-реализация – класс BitmapDrawable.
Layer List
Мы можем описать Drawable, который будет состоять из нескольких Drawable-слоев. Для этого используется тег , а внутри него теги .
У нас 4 слоя. Три bitmap со стандартной иконкой и одна фигура. Атрибуты left, top, right, bottom позволяют указывать отступы. А в атрибуте id можно указать id этого Drawable-слоя.
Обратите внимание, что важен порядок тегов item. Каждый последующий слой рисуется поверх предыдущего. Например, на получившемся изображении видно, что прямоугольник проходит «над» верхней иконкой, но «под» нижней.
Мы можем в коде получать доступ к отдельным Drawable внутри LayerDrawable. Для этого сначала получаем LayerDrawable.
А затем вызываем метод findDrawableByLayerId(int id) и указываем id, который вы указывали в атрибуте id тега item. На выходе получим Drawable.
Также у LayerDrawable есть еще несколько интересных методов
getDrawable(int index) — возвращает Drawable по индексу, а не по id
getId(int index) — возвращает id по индексу
getNumberOfLayers() — возвращает кол-во Drawable-слоев
State List
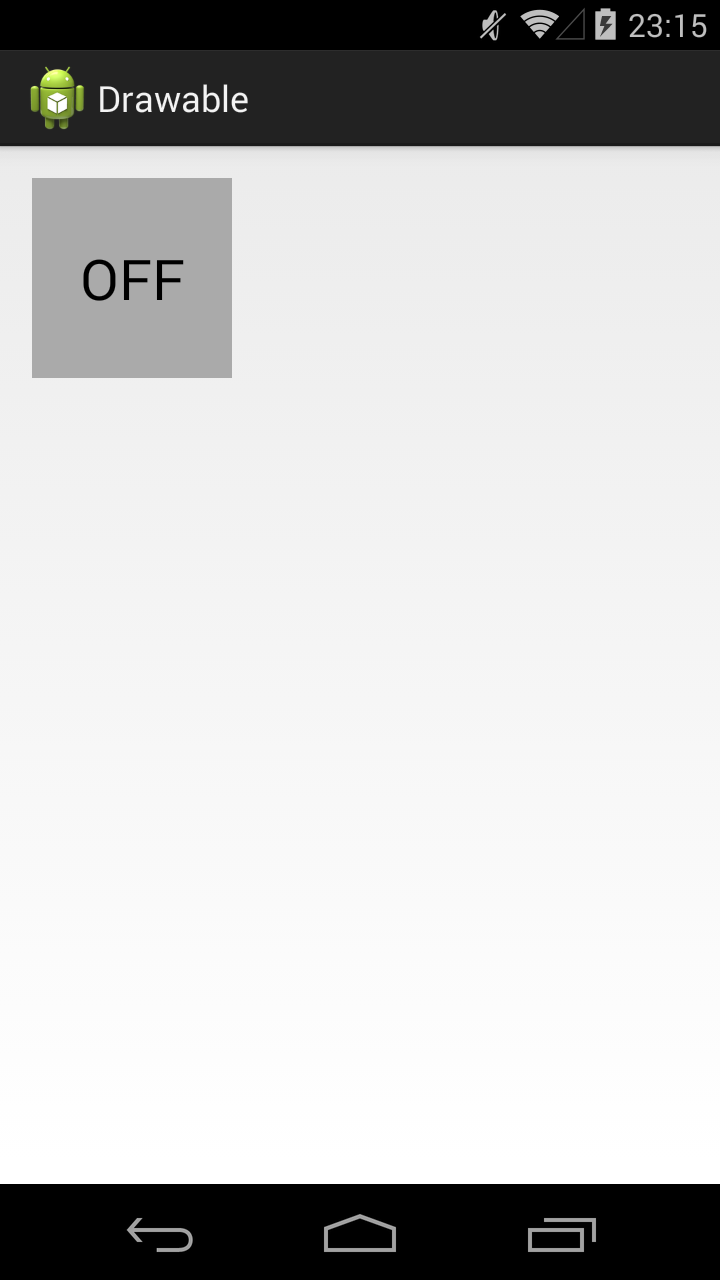
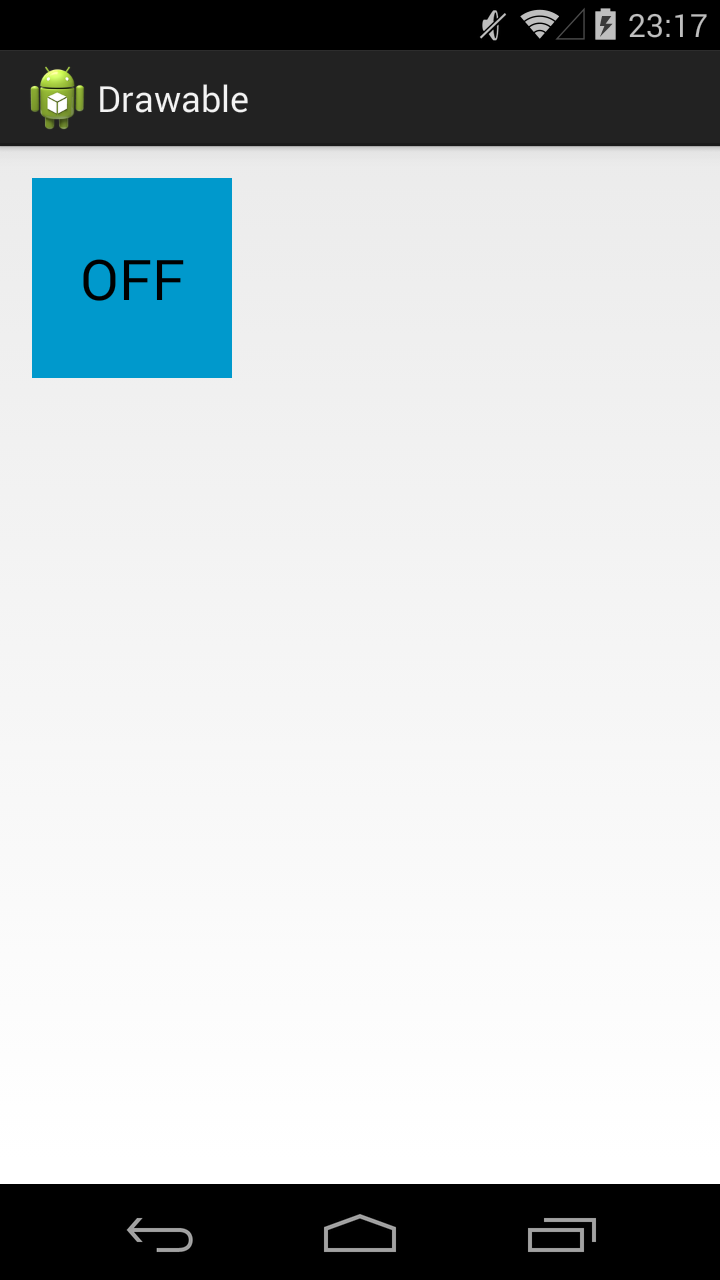
Тег позволяет отображать Drawable в зависимости от состояния View. Возможные состояние View можно посмотреть в хелпе. Рассмотрим пример с двумя из них: checked и pressed. На экране будет ToogleButton. Эта кнопка переходит в состояние checked и обратно, если на нее нажимать. А во время нажатия, пока палец касается экрана, кнопка находится в состоянии pressed.
State List позволит нам использовать три разных Drawable для отображения кнопки в трех состояниях: обычное, checked, pressed. Для этого создадим три файла в папке drawable.
Прямоугольник темно-серого цвета. Этот Drawable будем отображать в обычном состоянии кнопки.
Прямоугольник темно-синего цвета. Этот Drawable будем отображать в нажатом состоянии кнопки.
Прямоугольник светло-синего цвета. Этот Drawable будем отображать когда кнопка находится в состоянии checked.
И еще один файл, button_selector.xml:
Этот последний Drawable является селектором. В нем мы используем теги item, в которых указываем для какого состояния какой Drawable использовать
В первом item мы указали state_pressed=true, а значит этот item будет выбран системой когда кнопка будет в состоянии pressed. И экране мы увидим Drawable из этого item, т.е. toogle_button_pressed.
В втором item мы указали state_checked=true, а значит этот item будет выбран системой когда кнопка будет в состоянии checked. И экране мы увидим toogle_button_checked.
В третьем item мы не указали никакого состояния, этот item будет выбран при обычном состоянии кнопки. И экране мы увидим toogle_button.
Учтите, что здесь важен порядок расположения item внутри selector. Т.е. система идет по ним по порядку и выбирает первый подходящий. Если вы третий item, который без явного указания состояния, поставите первым, то система всегда будет останавливаться на нем.
Состояния можно комбинировать, т.е. в одном item вы можете указать несколько разных состояний.
Ставим этот Drawable, как фон для ToogleButton:
В результате, сначала видим обычное состояние
Нажимаем и держим, т.е. состояние pressed
Отпускаем – включился checked
Еще раз нажмем-отпустим — выключится checked и будет снова обычное состояние. Для каждого состояния отображается свой Drawable.
У View, кстати, есть методы, которые позволяют программно управлять состоянием. Это, например: setPressed и setSelected.
Присоединяйтесь к нам в Telegram:
— в канале StartAndroid публикуются ссылки на новые статьи с сайта startandroid.ru и интересные материалы с хабра, medium.com и т.п.
— в чатах решаем возникающие вопросы и проблемы по различным темам: Android, Kotlin, RxJava, Dagger, Тестирование
— ну и если просто хочется поговорить с коллегами по разработке, то есть чат Флудильня
— новый чат Performance для обсуждения проблем производительности и для ваших пожеланий по содержанию курса по этой теме
Источник
Практический опыт работы с Bitmap средствами Android

Не так давно по долгу службы я столкнулся с одной задачей: нужно было придумать и реализовать дизайн медиа-плеера для Android. И если продумать и организовать более или менее сносное размещение элементов управления и информации оказалось делом не хитрым, то чтобы привнести в дизайн какую-то изюминку, пришлось хорошенько подумать. К счастью, в запасе у меня был такой элемент, как картинка с обложкой альбома проигрываемой мелодии. Именно он должен был добавить красок всей картинке.
Однако, будучи просто выведенной среди кнопок и надписей, обложка выглядела бумажным стикером, наклеенным на экран. Я понял, что без обработки изображения здесь не обойтись.
Некоторые раздумья насчёт того, что можно было бы тут придумать увенчались решением сделать для изображения обложки эффект отражения и тени. Сразу оговорюсь, что практическая реализация отражения не является моей оригинальной идеей. Её я подсмотрел в найденной англоязычной статье. В настоящем посте я лишь хочу привести некоторое осмысление производимых над изображением манипуляций, свои дополнения к процессу обработки и отметить некоторые нюансы работы с Bitmap в Android.
Итак, на входе я имел Bitmap с картинкой. Для начала я создал пустой Bitmap размером с оригинальную картинку, который позже должен был стать той же обложкой, но с нанесённой на неё тенью.
Этот метод создаёт изменяемый (что важно) Bitmap.
Здесь обязательно нужно отметить, что при работе с Bitmap’ами необходимо внимательно следить за памятью. Придётся ловить исключения. И ещё один момент: изучение профайлером показало, что перед вызовом метода createBitmap() работает сборщик мусора. Учтите это, если в вашем приложении скорость работы критична.
Далее я создал холст и нанёс на него исходное изображение.
В этом месте отмечу, что всегда, как только Bitmap становится не нужен, его нужно уничтожать методом recycle(). Дело в том, что объект этого типа представляет собой всего лишь ссылку на память с самим изображением и выглядит для сборщика мусора очень маленьким (хотя на самом деле памяти занято много). Это может привести к тому, что память закончится в самый неподходящий момент.
После всей подготовки я нанёс на холст краску с тенью.
RadialGradient в моём случае представляет тень, падающую по полукругу из правого верхнего угла изображения в центр нижней грани. Ему нужно установить центр (может выходить за пределы картинки), радиус, последовательность цветов и расстояния от центра по радиусу для каждого цвета. Для тени использовалось изменение альфы в цветах на радиусе.
LinearGradient использовался для фэйда краёв картинки. Его применение очень похоже на RadialGradient. Нужно задать начало и конец линии, вдоль которой пойдёт градиент, цвета и их позиции на этой линии.
Наконец, я приступил к рисованию отражения. К этому моменту у меня уже был Bitmap с нанесёнными тенями gradBitmap. Опять надо было создавать холст, создавать пустое изображение (на этот раз на треть длиннее оригинального), помещать его на холст и наносить на верх него Bitmap с тенями.
После недолгих приготовлений начиналось самое интересное. Я создал матрицу, переворачивающую изображение снизу вверх. С её помощью создал Bitmap из трети исходного и нанёс его на холст под оригинальным изображением.
Кстати, краткое замечание: в классе Bitmap существует несколько методов createBitmap, и лишь один из них создаёт изменяемые Bitmap’ы, на которых можно рисовать. Остальные для рисования НА них не годятся.
И наконец, нанесение прозрачного градиента для придания эффекта отражения.
Краска наносится на ту часть рисунка, которая является отражением.
Всё. Я получил refCover — Bitmap, на котором изображена обложка альбома с тенью, сглаженными краями и отражением.
P.S. В данной статье для меня был важен не сам факт достижения визуальных эффектов, а способы их получения и нюансы, с ними связанные. Если для кого-то вещи, описанные здесь, очевидны — прекрасно. Всем остальным, я надеюсь, статья поможет в написании своих приложений под Android.
UPD: картинки ДО и ПОСЛЕ
Источник
Bitmap
Summary
| Nested Classes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitmap.CompressFormat | Specifies the known formats a bitmap can be compressed into | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bitmap.Config | Possible bitmap configurations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Constants | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| int | DENSITY_NONE | Indicates that the bitmap was created for an unknown pixel density. | |||||||||
[Expand]
Copy the pixels from the buffer, beginning at the current position, overwriting the bitmap’s pixels. Copy the bitmap’s pixels into the specified buffer (allocated by the caller). Returns the density for this bitmap. Indicates whether pixels stored in this bitmaps are stored pre-multiplied. Modifies the bitmap to have a specified width, height, and Bitmap.Config , without affecting the underlying allocation backing the bitmap. Convenience method for calling reconfigure(int, int, Config) with the current height and width. Specifies the density for this bitmap. Convenience method for calling reconfigure(int, int, Config) with the current width and config. Write the specified Color into the bitmap (assuming it is mutable) at the x,y coordinate. Replace pixels in the bitmap with the colors in the array. Convenience method for calling reconfigure(int, int, Config) with the current height and config. Constantspublic static final int DENSITY_NONEIndicates that the bitmap was created for an unknown pixel density. See AlsoFieldspublic static final Creator CREATORPublic Methodspublic boolean compress (Bitmap.CompressFormat format, int quality, OutputStream stream)Write a compressed version of the bitmap to the specified outputstream. If this returns true, the bitmap can be reconstructed by passing a corresponding inputstream to BitmapFactory.decodeStream(). Note: not all Formats support all bitmap configs directly, so it is possible that the returned bitmap from BitmapFactory could be in a different bitdepth, and/or may have lost per-pixel alpha (e.g. JPEG only supports opaque pixels). Parameters
Returns
public Bitmap copy (Bitmap.Config config, boolean isMutable)Tries to make a new bitmap based on the dimensions of this bitmap, setting the new bitmap’s config to the one specified, and then copying this bitmap’s pixels into the new bitmap. If the conversion is not supported, or the allocator fails, then this returns NULL. The returned bitmap initially has the same density as the original. Parameters
Returns
public void copyPixelsFromBuffer (Buffer src)Copy the pixels from the buffer, beginning at the current position, overwriting the bitmap’s pixels. The data in the buffer is not changed in any way (unlike setPixels(), which converts from unpremultipled 32bit to whatever the bitmap’s native format is. After this method returns, the current position of the buffer is updated: the position is incremented by the number of elements read from the buffer. If you need to read the bitmap from the buffer again you must first rewind the buffer. public void copyPixelsToBuffer (Buffer dst)Copy the bitmap’s pixels into the specified buffer (allocated by the caller). An exception is thrown if the buffer is not large enough to hold all of the pixels (taking into account the number of bytes per pixel) or if the Buffer subclass is not one of the support types (ByteBuffer, ShortBuffer, IntBuffer). The content of the bitmap is copied into the buffer as-is. This means that if this bitmap stores its pixels pre-multiplied (see isPremultiplied() , the values in the buffer will also be pre-multiplied. After this method returns, the current position of the buffer is updated: the position is incremented by the number of elements written in the buffer. public static Bitmap createBitmap (DisplayMetrics display, int[] colors, int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config)Returns a immutable bitmap with the specified width and height, with each pixel value set to the corresponding value in the colors array. Its initial density is determined from the given DisplayMetrics . Parameters
Throws
Returns a immutable bitmap with the specified width and height, with each pixel value set to the corresponding value in the colors array. Its initial density is determined from the given DisplayMetrics . Parameters
Returns an immutable bitmap from the specified subset of the source bitmap. The new bitmap may be the same object as source, or a copy may have been made. It is initialized with the same density as the original bitmap. Parameters
Returns
Throws
Returns an immutable bitmap from the source bitmap. The new bitmap may be the same object as source, or a copy may have been made. It is initialized with the same density as the original bitmap. public static Bitmap createBitmap (DisplayMetrics display, int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config)Returns a mutable bitmap with the specified width and height. Its initial density is determined from the given DisplayMetrics . Parameters
Throws
Returns an immutable bitmap from subset of the source bitmap, transformed by the optional matrix. The new bitmap may be the same object as source, or a copy may have been made. It is initialized with the same density as the original bitmap. If the source bitmap is immutable and the requested subset is the same as the source bitmap itself, then the source bitmap is returned and no new bitmap is created. Parameters
Returns
Throws
Returns a mutable bitmap with the specified width and height. Its initial density is as per getDensity() . Parameters
Throws
Returns a immutable bitmap with the specified width and height, with each pixel value set to the corresponding value in the colors array. Its initial density is as per getDensity() . Parameters
Returns a immutable bitmap with the specified width and height, with each pixel value set to the corresponding value in the colors array. Its initial density is as per getDensity() . Parameters
Throws
Creates a new bitmap, scaled from an existing bitmap, when possible. If the specified width and height are the same as the current width and height of the source bitmap, the source bitmap is returned and no new bitmap is created. Parameters
Returns
Throws
No special parcel contents. Returns
public void eraseColor (int c)Fills the bitmap’s pixels with the specified Color . Throwspublic Bitmap extractAlpha ()Returns a new bitmap that captures the alpha values of the original. This may be drawn with Canvas.drawBitmap(), where the color(s) will be taken from the paint that is passed to the draw call. Returns
public Bitmap extractAlpha (Paint paint, int[] offsetXY)Returns a new bitmap that captures the alpha values of the original. These values may be affected by the optional Paint parameter, which can contain its own alpha, and may also contain a MaskFilter which could change the actual dimensions of the resulting bitmap (e.g. a blur maskfilter might enlarge the resulting bitmap). If offsetXY is not null, it returns the amount to offset the returned bitmap so that it will logically align with the original. For example, if the paint contains a blur of radius 2, then offsetXY[] would contains -2, -2, so that drawing the alpha bitmap offset by (-2, -2) and then drawing the original would result in the blur visually aligning with the original. The initial density of the returned bitmap is the same as the original’s. Parameters
Returns
public final int getAllocationByteCount ()Returns the size of the allocated memory used to store this bitmap’s pixels. This can be larger than the result of getByteCount() if a bitmap is reused to decode other bitmaps of smaller size, or by manual reconfiguration. See reconfigure(int, int, Config) , setWidth(int) , setHeight(int) , setConfig(Bitmap.Config) , and BitmapFactory.Options.inBitmap . If a bitmap is not modified in this way, this value will be the same as that returned by getByteCount() . This value will not change over the lifetime of a Bitmap. See Alsopublic final int getByteCount ()Returns the minimum number of bytes that can be used to store this bitmap’s pixels. As of KITKAT , the result of this method can no longer be used to determine memory usage of a bitmap. See getAllocationByteCount() . public final Bitmap.Config getConfig ()If the bitmap’s internal config is in one of the public formats, return that config, otherwise return null. public int getDensity ()Returns the density for this bitmap. The default density is the same density as the current display, unless the current application does not support different screen densities in which case it is DENSITY_DEFAULT . Note that compatibility mode is determined by the application that was initially loaded into a process — applications that share the same process should all have the same compatibility, or ensure they explicitly set the density of their bitmaps appropriately. Returns
See Alsopublic int getGenerationId ()Returns the generation ID of this bitmap. The generation ID changes whenever the bitmap is modified. This can be used as an efficient way to check if a bitmap has changed. Returns
public final int getHeight ()Returns the bitmap’s height public byte[] getNinePatchChunk ()Returns an optional array of private data, used by the UI system for some bitmaps. Not intended to be called by applications. public int getPixel (int x, int y)Returns the Color at the specified location. Throws an exception if x or y are out of bounds (negative or >= to the width or height respectively). The returned color is a non-premultiplied ARGB value. Parameters
Returns
Throws
public void getPixels (int[] pixels, int offset, int stride, int x, int y, int width, int height)Returns in pixels[] a copy of the data in the bitmap. Each value is a packed int representing a Color . The stride parameter allows the caller to allow for gaps in the returned pixels array between rows. For normal packed results, just pass width for the stride value. The returned colors are non-premultiplied ARGB values. Parameters
Throws
Return the number of bytes between rows in the bitmap’s pixels. Note that this refers to the pixels as stored natively by the bitmap. If you call getPixels() or setPixels(), then the pixels are uniformly treated as 32bit values, packed according to the Color class. As of KITKAT , this method should not be used to calculate the memory usage of the bitmap. Instead, see getAllocationByteCount() . Returns
public int getScaledHeight (DisplayMetrics metrics)Convenience for calling getScaledHeight(int) with the target density of the given DisplayMetrics . public int getScaledHeight (int targetDensity)Convenience method that returns the height of this bitmap divided by the density scale factor. Parameters
Returns
public int getScaledHeight (Canvas canvas)Convenience for calling getScaledHeight(int) with the target density of the given Canvas . public int getScaledWidth (int targetDensity)Convenience method that returns the width of this bitmap divided by the density scale factor. Parameters
Returns
public int getScaledWidth (DisplayMetrics metrics)Convenience for calling getScaledWidth(int) with the target density of the given DisplayMetrics . public int getScaledWidth (Canvas canvas)Convenience for calling getScaledWidth(int) with the target density of the given Canvas . public final int getWidth ()Returns the bitmap’s width public final boolean hasAlpha ()Returns true if the bitmap’s config supports per-pixel alpha, and if the pixels may contain non-opaque alpha values. For some configs, this is always false (e.g. RGB_565), since they do not support per-pixel alpha. However, for configs that do, the bitmap may be flagged to be known that all of its pixels are opaque. In this case hasAlpha() will also return false. If a config such as ARGB_8888 is not so flagged, it will return true by default. public final boolean hasMipMap ()Indicates whether the renderer responsible for drawing this bitmap should attempt to use mipmaps when this bitmap is drawn scaled down. If you know that you are going to draw this bitmap at less than 50% of its original size, you may be able to obtain a higher quality This property is only a suggestion that can be ignored by the renderer. It is not guaranteed to have any effect. Returns
See Alsopublic final boolean isMutable ()Returns true if the bitmap is marked as mutable (i.e. can be drawn into) public final boolean isPremultiplied ()Indicates whether pixels stored in this bitmaps are stored pre-multiplied. When a pixel is pre-multiplied, the RGB components have been multiplied by the alpha component. For instance, if the original color is a 50% translucent red (128, 255, 0, 0) , the pre-multiplied form is (128, 128, 0, 0) . This method always returns false if getConfig() is RGB_565 . The return value is undefined if getConfig() is ALPHA_8 . This method only returns true if hasAlpha() returns true. A bitmap with no alpha channel can be used both as a pre-multiplied and as a non pre-multiplied bitmap. Only pre-multiplied bitmaps may be drawn by the view system or Canvas . If a non-pre-multiplied bitmap with an alpha channel is drawn to a Canvas, a RuntimeException will be thrown. Returns
See Alsopublic final boolean isRecycled ()Returns true if this bitmap has been recycled. If so, then it is an error to try to access its pixels, and the bitmap will not draw. Returns
public void prepareToDraw ()Rebuilds any caches associated with the bitmap that are used for drawing it. In the case of purgeable bitmaps, this call will attempt to ensure that the pixels have been decoded. If this is called on more than one bitmap in sequence, the priority is given in LRU order (i.e. the last bitmap called will be given highest priority). For bitmaps with no associated caches, this call is effectively a no-op, and therefore is harmless. public void reconfigure (int width, int height, Bitmap.Config config)Modifies the bitmap to have a specified width, height, and Bitmap.Config , without affecting the underlying allocation backing the bitmap. Bitmap pixel data is not re-initialized for the new configuration. This method can be used to avoid allocating a new bitmap, instead reusing an existing bitmap’s allocation for a new configuration of equal or lesser size. If the Bitmap’s allocation isn’t large enough to support the new configuration, an IllegalArgumentException will be thrown and the bitmap will not be modified. The result of getByteCount() will reflect the new configuration, while getAllocationByteCount() will reflect that of the initial configuration. Note: This may change this result of hasAlpha(). When converting to 565, the new bitmap will always be considered opaque. When converting from 565, the new bitmap will be considered non-opaque, and will respect the value set by setPremultiplied(). WARNING: This method should NOT be called on a bitmap currently used by the view system. It does not make guarantees about how the underlying pixel buffer is remapped to the new config, just that the allocation is reused. Additionally, the view system does not account for bitmap properties being modifying during use, e.g. while attached to drawables. See Alsopublic void recycle ()Free the native object associated with this bitmap, and clear the reference to the pixel data. This will not free the pixel data synchronously; it simply allows it to be garbage collected if there are no other references. The bitmap is marked as «dead», meaning it will throw an exception if getPixels() or setPixels() is called, and will draw nothing. This operation cannot be reversed, so it should only be called if you are sure there are no further uses for the bitmap. This is an advanced call, and normally need not be called, since the normal GC process will free up this memory when there are no more references to this bitmap. public boolean sameAs (Bitmap other)Given another bitmap, return true if it has the same dimensions, config, and pixel data as this bitmap. If any of those differ, return false. If other is null, return false. public void setConfig (Bitmap.Config config)Convenience method for calling reconfigure(int, int, Config) with the current height and width. WARNING: this method should not be used on bitmaps currently used by the view system, see reconfigure(int, int, Config) for more details. See Alsopublic void setDensity (int density)Specifies the density for this bitmap. When the bitmap is drawn to a Canvas that also has a density, it will be scaled appropriately. Parameters
See Alsopublic void setHasAlpha (boolean hasAlpha)Tell the bitmap if all of the pixels are known to be opaque (false) or if some of the pixels may contain non-opaque alpha values (true). Note, for some configs (e.g. RGB_565) this call is ignored, since it does not support per-pixel alpha values. This is meant as a drawing hint, as in some cases a bitmap that is known to be opaque can take a faster drawing case than one that may have non-opaque per-pixel alpha values. public final void setHasMipMap (boolean hasMipMap)Set a hint for the renderer responsible for drawing this bitmap indicating that it should attempt to use mipmaps when this bitmap is drawn scaled down. If you know that you are going to draw this bitmap at less than 50% of its original size, you may be able to obtain a higher quality by turning this property on. Note that if the renderer respects this hint it might have to allocate extra memory to hold the mipmap levels for this bitmap. This property is only a suggestion that can be ignored by the renderer. It is not guaranteed to have any effect. Источник |
|---|