- Где находится android_sdk_root? И как его установить?
- How to install Android SDK and setup AVD Emulator without Android Studio
- Understanding the Android SDK
- Installing the Android SDK
- Step 1 — Download the tools package
- Step 2— You need Java 8!
- Step 3 — Download the essential packages
- Step 4 — Set your environmental variables
- Step 5 — Download the platform specific packages you want
- Step 5 — Create a AVD device
- Step 6 — Run the Android Emulator
- How To Install Android SDK Tools On Windows
- Step 1 — Download SDK Tools
- Step 2 — Install Command Line Tools
- Step 3 — Install Platform Tools
- Step 4 — Configure Environment Variable
- Step 5 — Configure Commands
- Step 6 — Using the SDK Manager
- Step 7 — Using the Emulator and AVD Manager
- Summary
Где находится android_sdk_root? И как его установить?
Я установил android_sdk_home, чтобы мое приложение могло найти .android при попытке запустить. Теперь я получаю сообщение об ошибке, указывающее, что android_sdk_root не определен. Я запускаю win 7, новую установку Android-студии, внутри параллелей на macbook pro.
Благодарю за ваш ответ. Я проверил местоположение, и он идентифицирован как то же место, что и путь среды ANDROID_SDK_HOME. Он все еще говорит, что root не определен. Я создал путь окружения ANDROID_SDK_ROOT к тому же местоположению, и он все еще не определен.
Android_sdk_root – системная переменная, указывающая на корневую папку инструментов android sdk. Вероятно, вы получите ошибку, потому что переменная не установлена. Чтобы установить его в Android Studio, перейдите по ссылке:
- Файл -> Структура проекта в структуре проекта
- Слева -> местоположение SDK
- Местоположение SDK выберите местоположение Android SDK
Если вы установили SDK для Android, обратитесь к этому ответу, чтобы найти путь к нему: https://stackoverflow.com/a/15702396/3625900
Я получил ту же ошибку после установки студии Android и попытался запустить мир привет. Я думаю, вам нужно использовать SDK Manager внутри Android Studio, чтобы сначала установить некоторые вещи.
Откройте Android Studio и нажмите на Диспетчер SDK на панели инструментов.
Теперь установите необходимые инструменты SDK.
- Инструменты -> Android SDK Tools
- Инструменты -> Android SDK Platform-tools
- Инструменты -> Android SDK Build-tools (самая высокая версия)
Для каждого выпуска Android, на который настроен таргетинг, нажмите соответствующую папку Android XX и выберите (как минимум):
- Платформа SDK
- Системное изображение для эмулятора, такое как ARM EABI v7a System Image
Менеджер SDK будет запускаться (это может занять некоторое время) и загрузить и установить различные SDK.
Внутри Android Studio, File-> Project Structure покажет вам, где установлены ваши Android-устройства. Как вы видите, мой – это c: \ users \ Joe \ AppData \ Local \ Android \ sdk1.
Если я перейду к C: \ Users \ Joe \ AppData \ Local \ Android \ sdk1 \ sources, вы сможете увидеть различные Android SDK, установленные там …
Источник
How to install Android SDK and setup AVD Emulator without Android Studio
If you are trying to develop to Android, you probably will end up installing the Android Studio to get the Android SDK and the AVD Emulator working properly.
But if you are using another code editor, like Sublime Text or VSCode, installing the Android Studio will just mess up with your setup and consume your precious RAM for no good reason.
I had a hard time figuring out how to properly do this setup due the lack of documentation about it, so i hope this article helps you. 🙂
Recommended previous knowledge:
- SDK (Standard Development Kit); Read about on Wikipedia;
- AVD (Android Virtual Device); Read about on docs;
- CLI (Command Line Interface); Read about on Wikipedia;
- Android API levels; Read about on Vanderbilt University;
- How to open, navigate and execute files in your OS terminal;
- Know what are environmental variables;
Understanding the Android SDK
Basically, the Android SDK is a bunch of packages necessary to develop for Android.
These packages stays in subfolders of a folder called “sdk” (or “android-sdk” sometimes). You do not need to know how these packages really work, just what they do.
The picture below is my Android SDK folder, these are the basic packages you will need in order to get everything working properly.
Here is a brief explanation of each package:
- tools: This package is mainly used to manage the other packages and to create AVD’s;
- emulator: As the name suggest, this is the Android emulator;
- platform-tools: Some tools to communicate with Android devices when you plug then in your computer;
- patcher: This package is automatically downloaded by the SDK. I didn’t find what exactly this is for, so just leave it as it is;
The folders bellow contain sub-folders with the packages for each Android API level.
- platforms: The platform packages are required to compile your app for the specified API level.
- system-images: These are the android images used in the emulator.
- build-tools: These are necessary to build your Android apps
Installing the Android SDK
In order to install the SDK we will use the Command Line Tools. These are some quite simple CLI’s used to manage the Android SDK. You can read the documentation here for more details.
Step 1 — Download the tools package
First, you need to download the tools package. And with this package you can download the others.
- First, go to the Android Studio download page: https://developer.android.com/studio;
- Then click in “ Download Options”;
- There you will find a table named “ Command line tools only”;
- This table contain some zip files. Download the appropriate file for your system ( Windows, Mac or Linux);
- Extract this zip and you will get a folder called tools: This is the tools package i explained earlier;
Create a folder anywhere you prefer to place your SDK. I recommend you to stick with one of these commonly used places:
- Globally: C:\Android\sdk or C:\android-sdk (this is not default, but i usually set my SDK here on Windows)
- One user only: C:\Users\ \AppData\Local\Android\sdk
- Globally: /Library/Android/sdk
- One user only: /Users/ /Library/Android/sdk
And move the tools folder to this new sdk folder. Make sure you have admin access to this folder and any sub-folders inside it, or the tools package will fail to download new packages.
Note: You can also download a pre-build package for your SO (like the one available on Ubuntu repository). But i do not recommend you do to so, because they probably will not be updated and will be harder to manage, since it was automatically installed.
Step 2— You need Java 8!
The Android SDK packages require Java 8. If you do not have it, you need to download. If you are using a newer version, you have to downgrade to Java 8 or you will eventually get some errors, because it is not compatible.
If you do not have the Java 8 SDK, here is how you can install it:
On Ubuntu run these commands:
- # sudo apt-get update
- # sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk
Sorry for MacOS users, i don’t know how to install it on this OS.
Step 3 — Download the essential packages
Now, download the platform-tools and the emulator packages, because they contain some CLI binary files you will need later. I decided to download these packages first in order to set all the necessary environment variables at once and make the rest of the process easier.
Open a terminal window (you need to use a terminal, not the file explorer), go to your sdk folder and navigate to the /tools/bin directory.
This folder contain the SDKManager binary: this is a CLI used to list the available packages in the Google’s repository and download, update or remove them from your SDK folder.
The bellow command will list all packages installed (the first items on the list) and all packages available to download:
To download the packages, simply copy the package names and pass it as a parameter to the SDKManager CLI using the terminal:
# ./sdkmanager platform-tools emulator
If you open your sdk folder you should see these packages folders there.
Step 4 — Set your environmental variables
You need to set the below environmental variables containing the path to our SDK, so any running program can find it in your pc:
ANDROID_SDK_ROOT = Path to your SDK folder
ANDROID_HOME = The same as ANDROID_SDK_ROOT. This variable is now deprecated, but i recommend setting it because some programs still using it to locate your sdk.
And add these folders to the PATH variable, making their binary files accessible from everywhere:
To add the environment variables on WIndows, just follow these steps:
- Open the “Control Panel”;
- Go to “ System and Security” option in the side menu;
- In the window “ System Properties” open the tab “ Advanced”;
- Click in the button “ Environment Variables” in the bottom of the page;
- In the “ Environment Variables” window you will see two tables: “User Variables” and ” System Variables”.
- If you created your sdk folder for one user only, set the variables in the “ User Variables” table;
- But, if you create your sdk folder globally, set the variables in the “ System Variables” table instead;
On Linux, you can set your environment variables in many places. So i choose the ones I found the most appropriate:
- If you created your sdk folder for one user only, set your environment variables in the file
/.bashrc;
Here is how i set these variables in my Ubuntu, using the file /etc/environment:
And sorry again, no MacOS instructions for this task.
You can find more about these environmental variables in the oficial docs here.
Now your SDK is ready! If you do not need to run the emulator there’s no need to follow the next steps.
Step 5 — Download the platform specific packages you want
You need more three packages: The platform, the system-image and the build-tools. You can download these packages for any Android version you prefer. In this article, i will download the packages for the API Level 28.
Use the “ sdkmanager — list” command to find these packages and download them using the command “ sdkmanager
Here’s an example:
Step 5 — Create a AVD device
Creating a AVD device is a simple task: run the AVDManager command (this is a binary file located in the tools/bin folder of your sdk) with the create avd option, a name for the new AVD and the image you want to use.
Here is a example:
# avdmanager create avd — name android28 — package “system-images;android-28;default;x86”
You will be asked if you want to alter some configurations. You can also modify these configurations later in the file config.ini, located in the avd folder (this folder usually is created in your user folder, under the android directory). The currently active configurations can be find in the file hardware-qemu.ini (this file just will be created after the emulator runs for the first time).
Step 6 — Run the Android Emulator
Now you just need to run the emulator command (remember that we added this package to the environmental variables?):
The emulator take some time to init for the first time. But if you done everything correctly you should see this screen:
Источник
How To Install Android SDK Tools On Windows
It provides all the steps required to install Android Platform Tools and SDK Manager on Windows 10 without using Android Studio.
In this tutorial, we will discuss all the steps required to install Android Platform Tools and SDK Manager on Windows 10. This tutorial provides the steps for Windows 10, though the steps should be the same on other versions of Windows.
This post is useful for the developers using Android Platform Tools and SDK manager without installing Android Studio for the use cases including hybrid app development using Ionic. It also assumes that a valid JAVA_HOME environment variable exists pointing to the installation directory of Java.
You can follow How To Install Java 8 On Windows 10, How To Install Java 11 On Windows, How To Install Java 15 On Windows, or How To Install OpenJDK 15 On Windows to install Java on Windows. In case you are interested in developing Android applications using Android Studio, you can also follow How To Install Android Studio On Windows.
Step 1 — Download SDK Tools
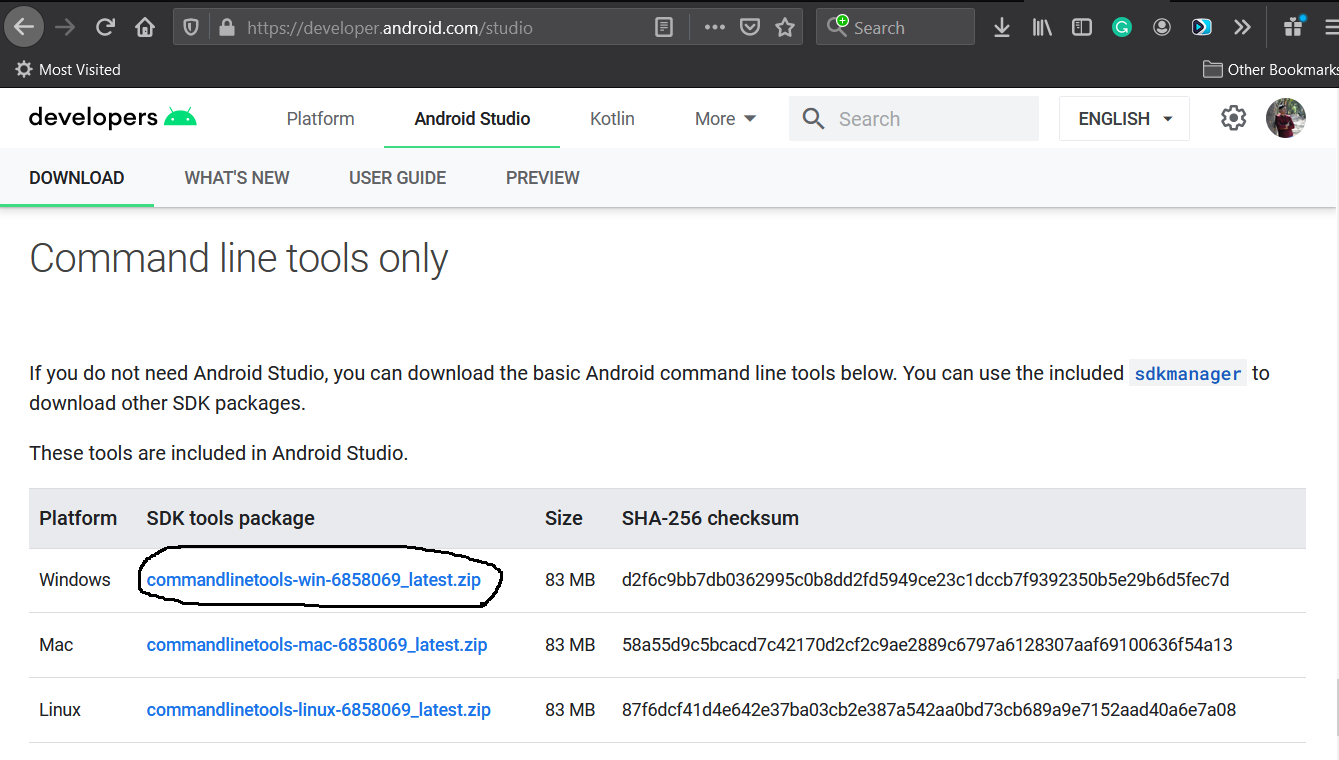
Open the download tab of Android Studio and scroll down to the Command line tools only section. This section shows various options to download the SDK tools as shown in Fig 1.
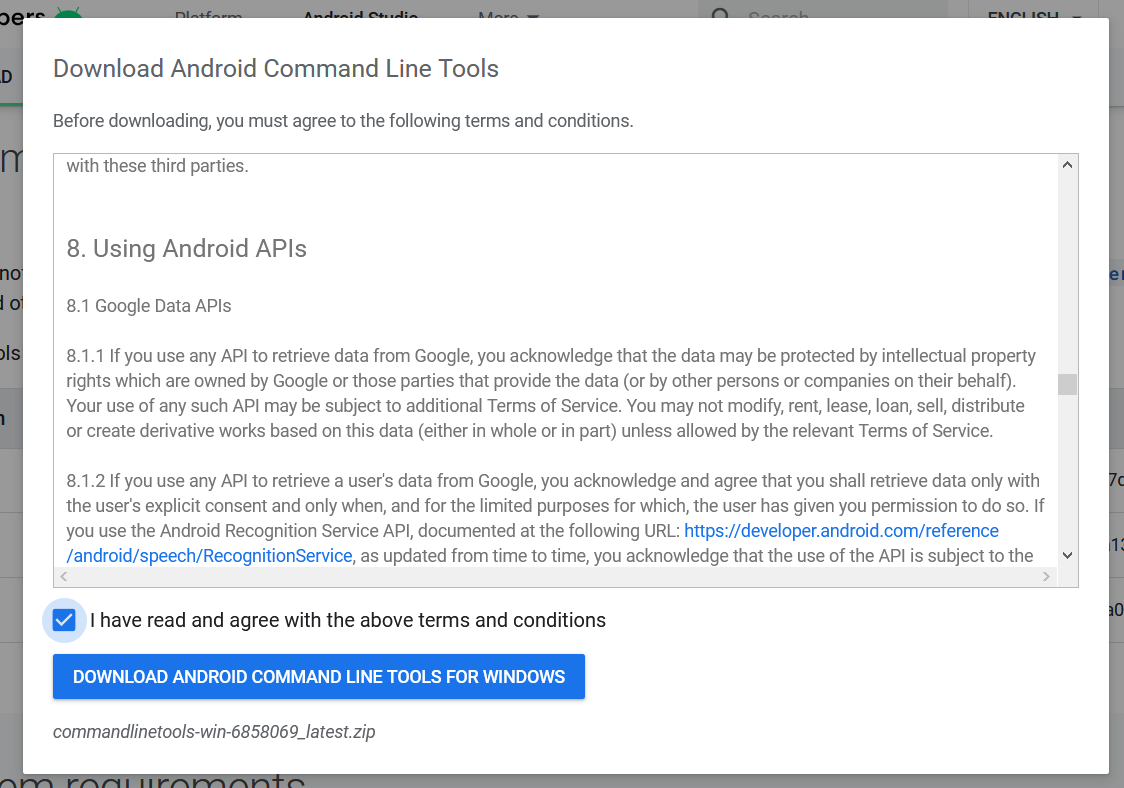
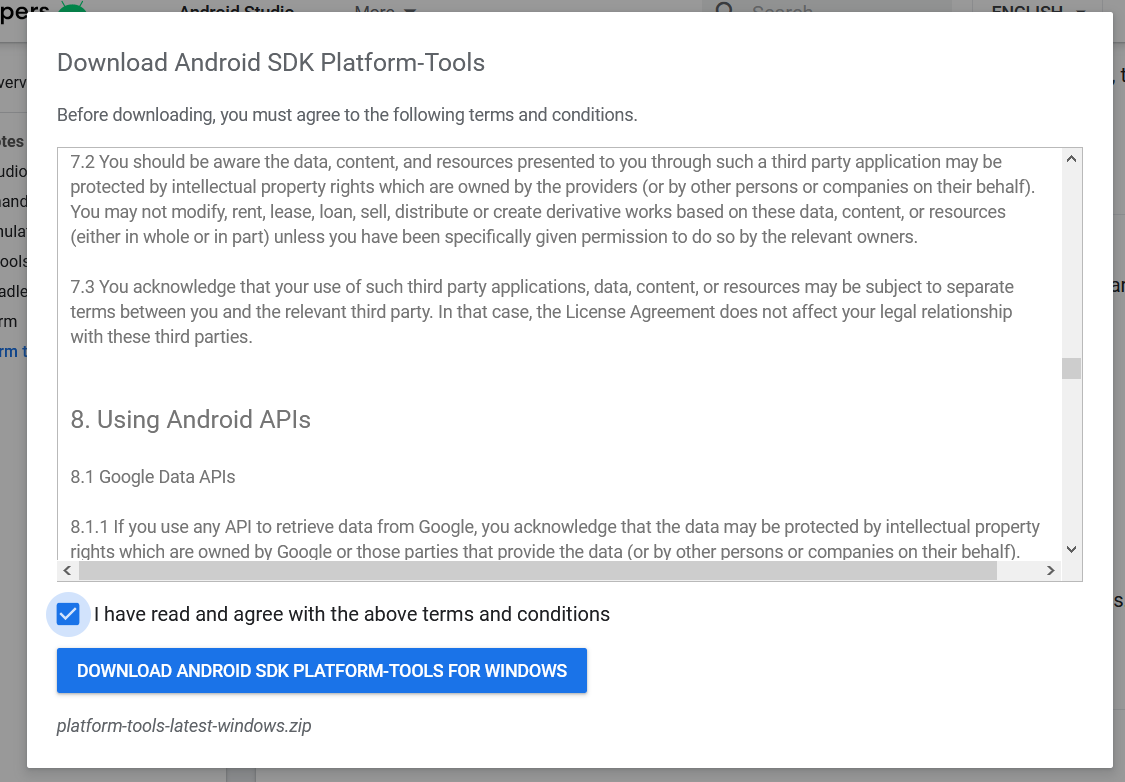
Click the first link having the download option for Windows as highlighted in Fig 1. It will ask to accept to terms and conditions as shown in Fig 2.
Go through the details, agree on the terms and conditions and click the Download Button to start the download.
Step 2 — Install Command Line Tools
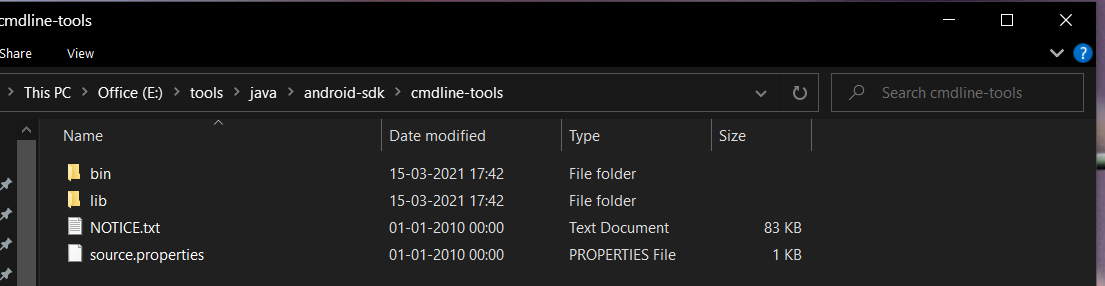
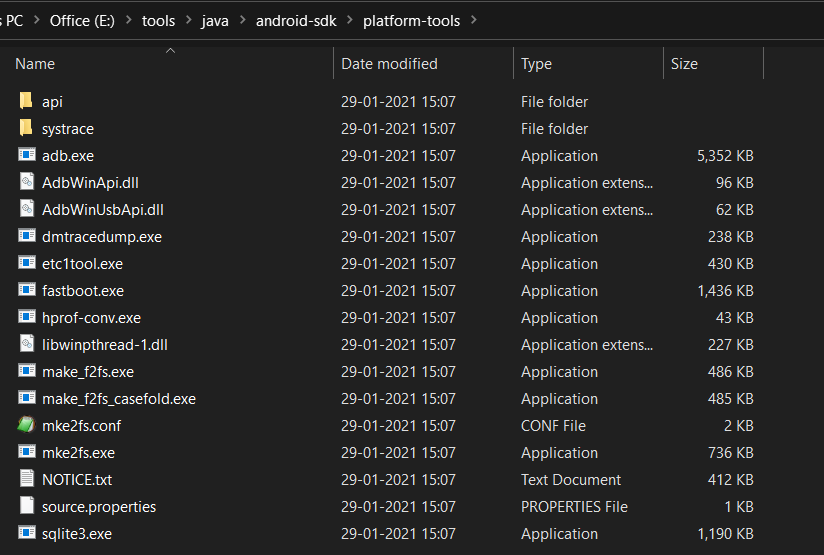
In this step, we will install the Android Command Line Tools on Windows 10. Create the directory android-sdk at your preferred location and extract the content of the downloaded SDK Tools zip to this directory. Make sure that the extracted content is available within the android-sdk directory created by us as shown in Fig 3.
Step 3 — Install Platform Tools
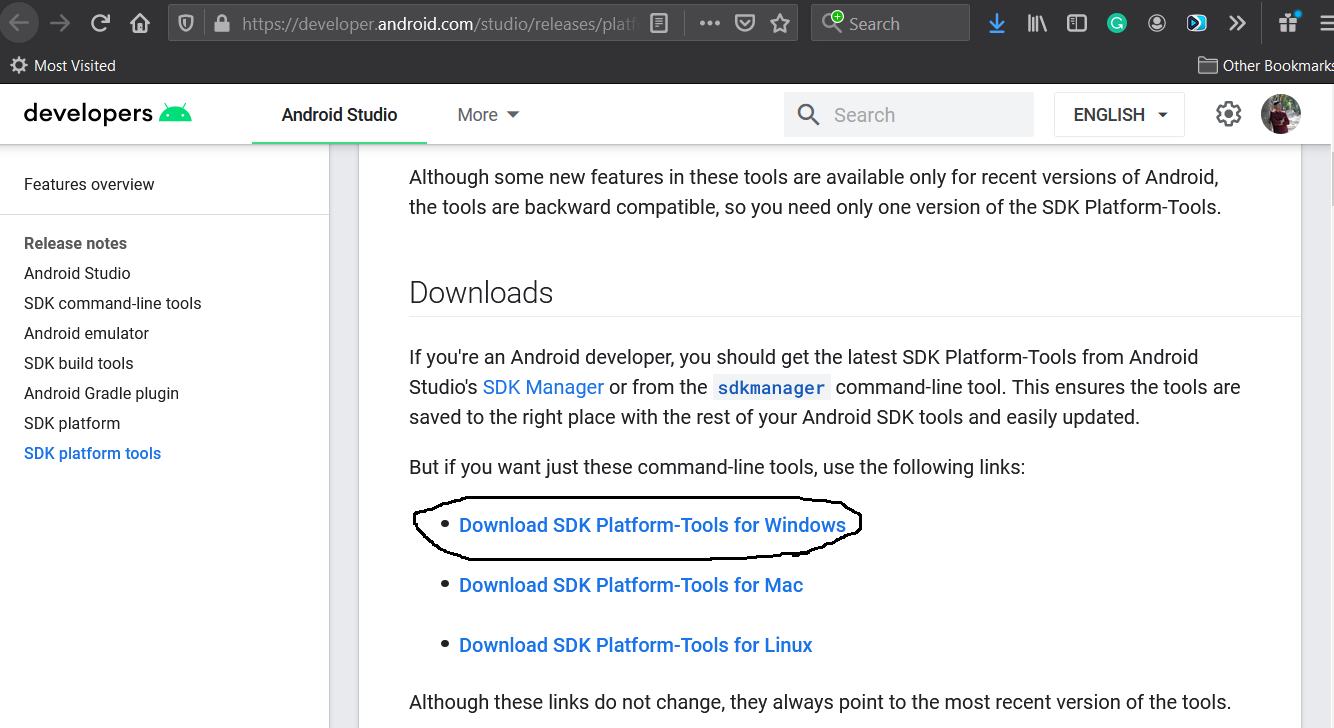
In this step, we will install the Android Platform Tools on Windows 10. Follow the same steps similar to Android SDK Tools to install Android Platform Tools using the download link as shown in Fig 4, Fig 5, and Fig 6.
Step 4 — Configure Environment Variable
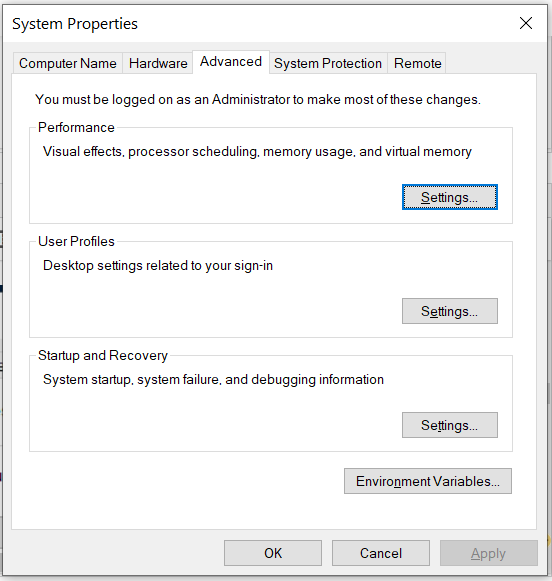
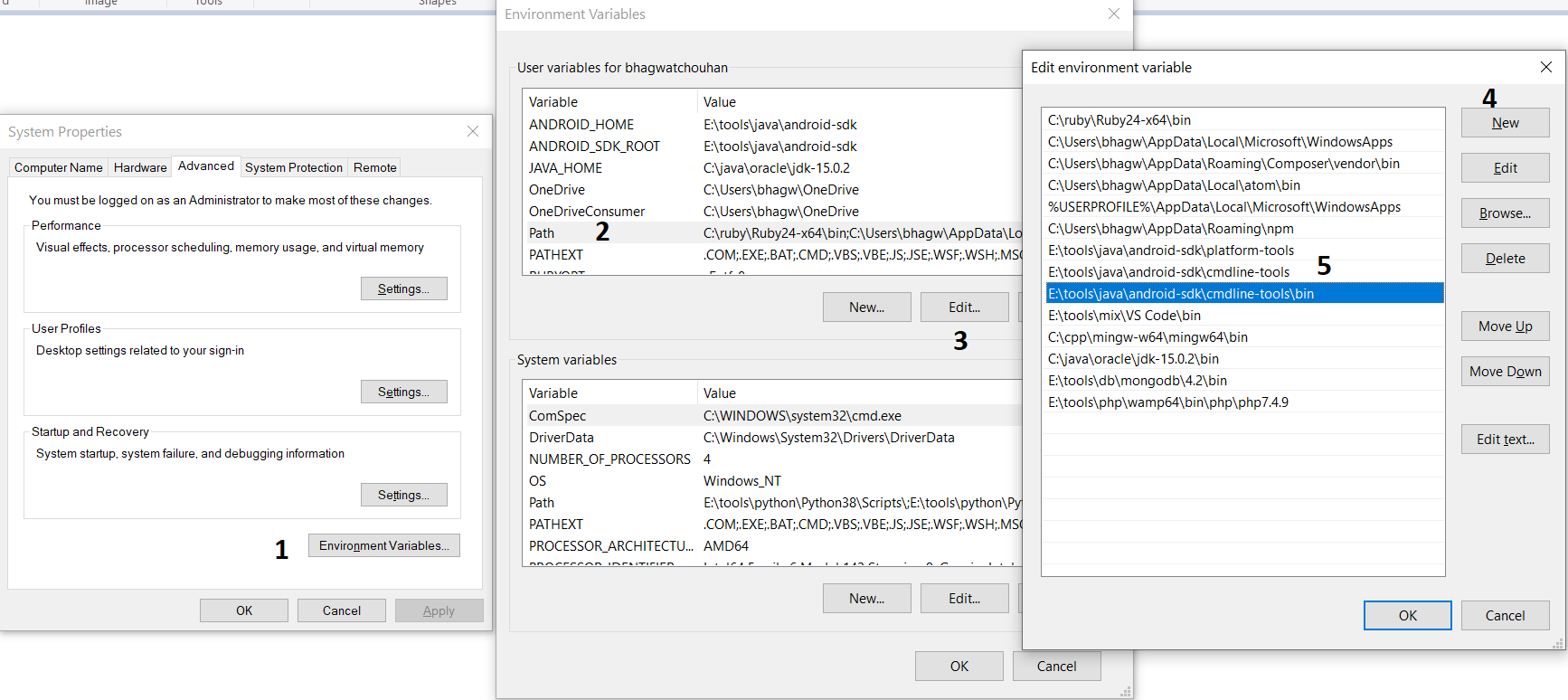
Right-click the My Computer or This PC on the desktop and click the Properties Option. Now click the Advanced system settings. It will show the System Properties dialog having Advanced Tab options as shown in Fig 7.
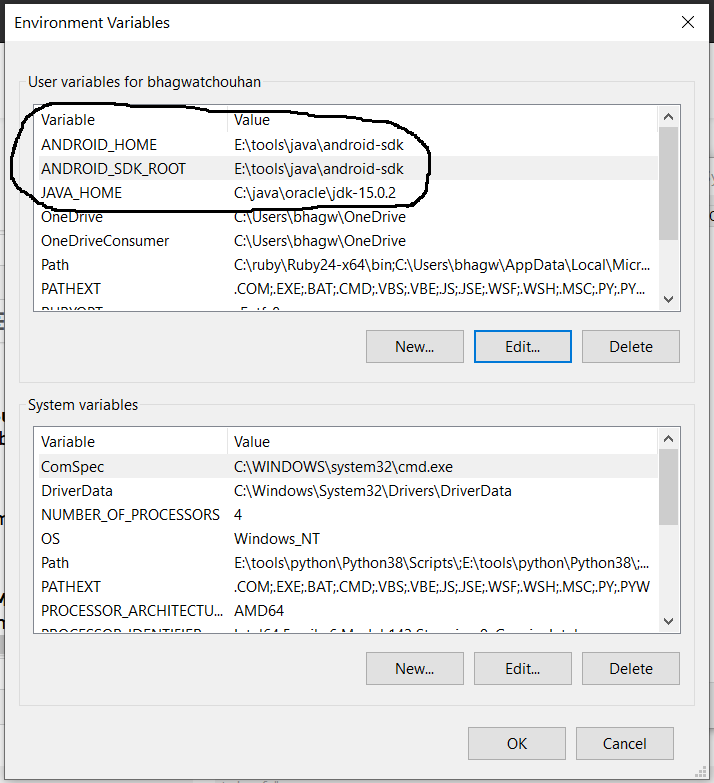
Click the Environment Variables Button and click the New Button in the first section. Set the Variable Name field to ANDROID_HOME and Variable Value to the android-sdk directory created by us in the previous step.
Similarly, also configure the environment variable ANDROID_SDK_ROOT to the android-sdk directory.
Also , make sure that the JAVA_HOME environment variable is set to the JDK installation directory. It must not end with the bin as we do with the system path variable.
Step 5 — Configure Commands
In previous steps, we have downloaded and extracted the Command Line Tools and Platform Tools to the android-sdk directory. Both the tools provide several command-line utilities which we need to run by going to the appropriate directory having the executable files.
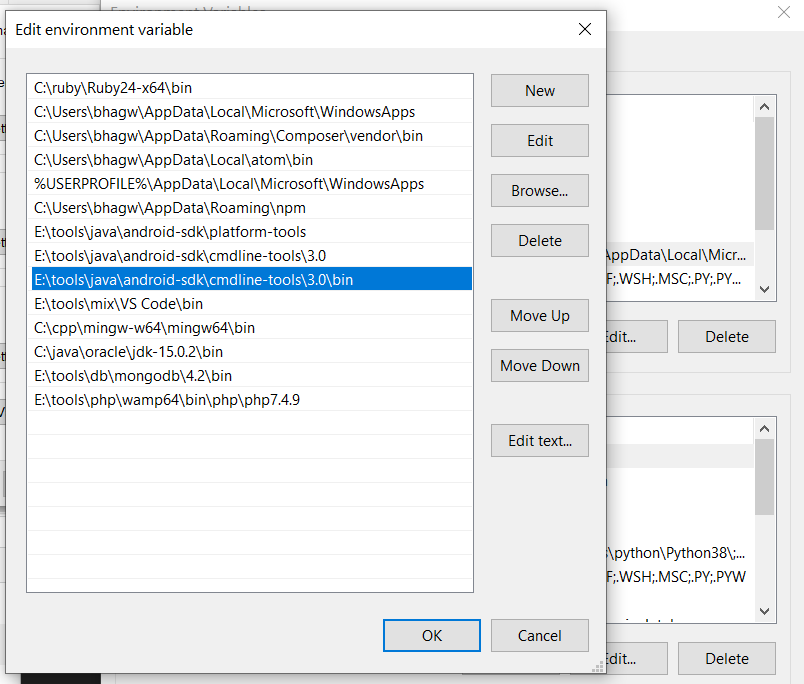
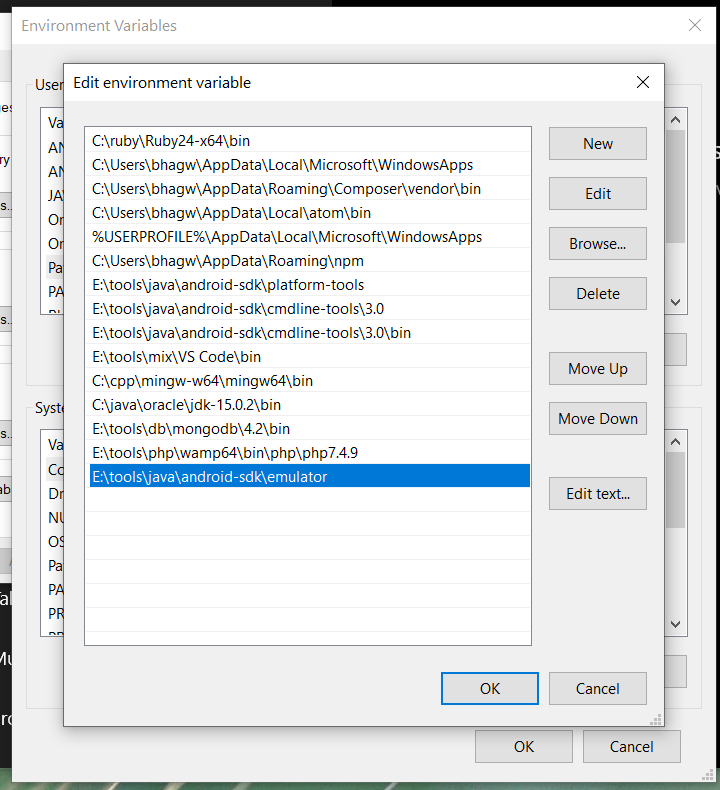
We can make these commands available at the system level without going to these directories by adding the path to tools, tools\bin, and platform-tools to the system path as shown in Fig 9. Make sure that these executables do not break other commands having the same name before adding these paths to the PATH environment variable.
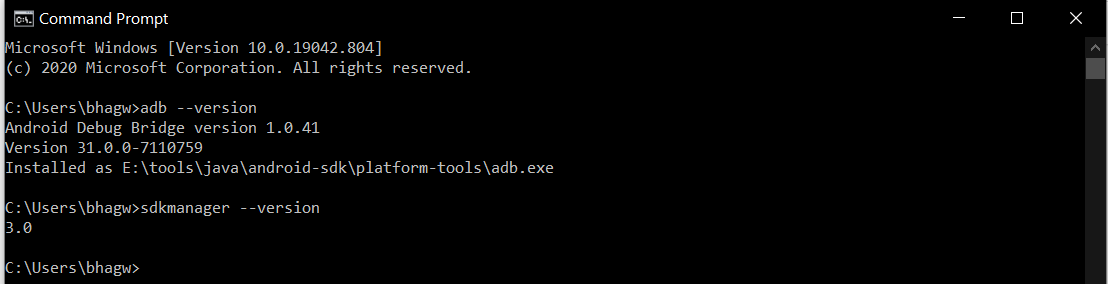
Now open the Command Prompt and check the ADB and SDK Manager versions as shown in Fig 10. You might be required to restart the system to apply the environment variables set by us.
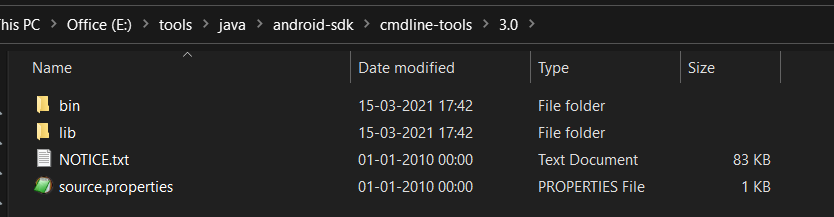
We can see that the ADB command works well and shows the version details, but the sdkmanager shows an error — «error: could not determine sdk root. error: either specify it explicitly with —sdk_root= or move this package into its expected location: \cmdline-tools\latest\» since it expects the Command Line Tools in a version-specific directory. Now open the source.properties file from the cmdline-tools directory to check the version. It will show the version details as shown below.
Now move all the files to the directory cmdline-tools/3.0 as shown in Fig 10.
Also, update the system path as shown in Fig 11.
Now close and open the Command Prompt. Also, check the ADB and SDK Manager versions as shown in Fig 12.
Step 6 — Using the SDK Manager
List — We can list the installed and available packages and images using the list command as shown below.
Install Platform — Use the below-mentioned command to install the Android 10 (API level 30) using the SDK manager.
It will ask to accept the terms and conditions as shown in Fig 13. Enter y and hit Enter Key to accept the terms and conditions. This command creates the directory platforms within android-sdk and installs the package android-30 having all the required files to run the emulator for Android 10.
If we again check the installed packages, the list command shows the installed options as shown below.
Update SDK Manager — Update the SDK manager using the below-mentioned command.
Add System Image — We can add system images from available images shown by the list command using the SDK manager as shown below. We are adding the most recent default 64-bit system image.
Accept the License Agreement to complete the download.
There are several projects which need Google Play Services. We need system images specific to Google Play Services as shown below.
Accept the License Agreement to complete the download.
Install Emulator — We need to install the emulator before creating the AVD using SDK Manager.
Accept the License Agreement to complete the download.
Install Build Tools — Install the most recent build tool listed by the list command.
Step 7 — Using the Emulator and AVD Manager
Create Android Emulator — Create the emulator using the system image downloaded in the previous step as shown below. Replace with the actual name preferred by you.
The above commands ask a bunch of questions to configure the AVD if we choose the custom hardware profile option. We have excluded the details of these options from this tutorial since these configuration details depend on the actual needs. After completing all the configurations, it creates the AVD using the name provided by us while configuring it.
Similarly, we can also install the AVD of older versions as shown below.
List Android Emulators — Now go to the tools directory on the command line and check the installed platform as shown below.
Notes: Add Emulator to the system path as shown in Fig 14.
Close and re-open the Command Prompt to check the AVDs created by us in the previous steps.
It will list all the AVDs installed by us.
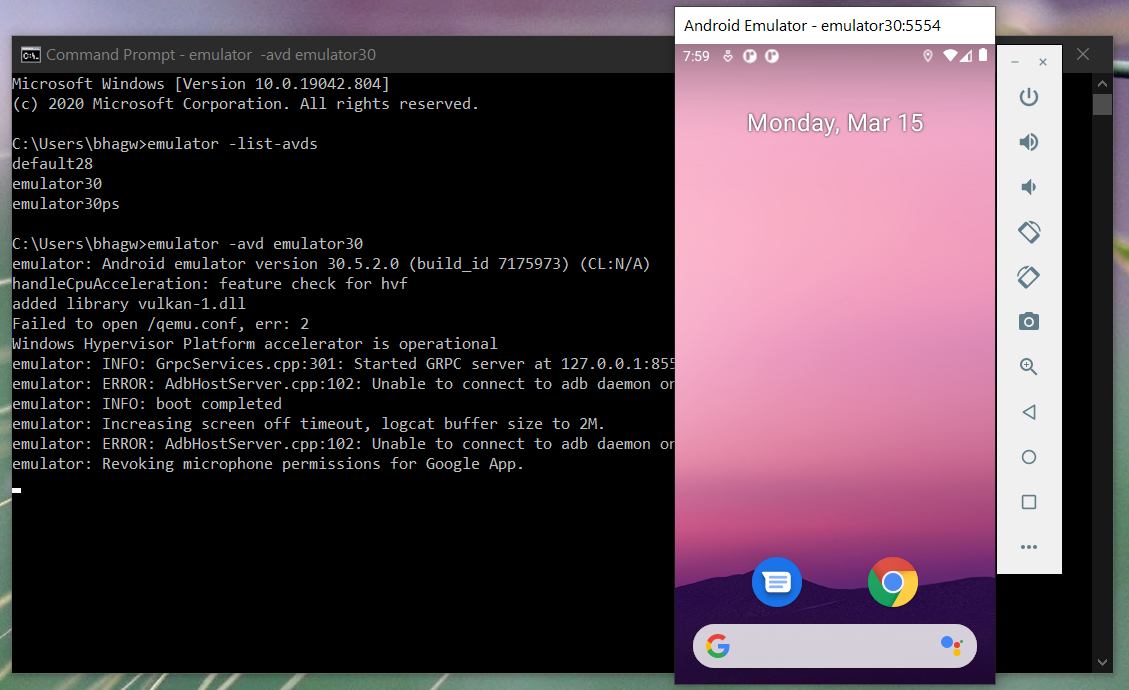
Run Emulator — We can run the emulator created by us as shown below.
The emulator will take some time to completely launch the AVD. The final results should look similar to Fig 15.
Delete Emulator — We can also delete an existing emulator as shown below.
Summary
This tutorial provided all the steps required to install Android Platform Tools and Android SDK Manager on Windows 10. It also provided the steps required to create and launch the AVDs using the Emulator.
Источник