- ImageView
- Общая информация
- Метод setImageResource()
- Метод setImageBitmap()
- Метод setImageDrawable()
- Метод setImageURI()
- Другие методы
- Масштабирование через свойство Scale Type
- Атрибут android:adjustViewBounds=»true»
- Загрузка изображения из галереи
- Получить размеры ImageView — будьте осторожны
- Копирование изображений между ImageView
- Примеры
- Android ImageView ScaleType: A Visual Guide
- Scale Types
- CENTER
- CENTER_CROP
- CENTER_INSIDE
- FIT_CENTER
- FIT_END
- FIT_START
- FIT_XY
- MATRIX
- Adjust View Bounds
- If you enjoyed this post, you might also like:
- Mobile design and development services for every stage of your app
- Understanding ImageView ScaleType in Android
- Adding an image to the project
- ImageView ScaleType in Android
- CENTER
- CENTER_CROP
- CENTER_INSIDE
- FIT_CENTER
- FIT_START
- FIT_END
- FIT_XY
- MATRIX
- Conclusion
ImageView
Общая информация
Компонент ImageView предназначен для отображения изображений. Находится в разделе Widgets.
Для загрузки изображения в XML-файле используется атрибут android:src, в последнее время чаще используется атрибут app:srcCompat.
ImageView является базовым элементом-контейнером для использования графики. Можно загружать изображения из разных источников, например, из ресурсов программы, контент-провайдеров. В классе ImageView существует несколько методов для загрузки изображений:
- setImageResource(int resId) — загружает изображение по идентификатору ресурса
- setImageBitmap(Bitmap bitmap) — загружает растровое изображение
- setImageDrawable(Drawable drawable) — загружает готовое изображение
- setImageURI(Uri uri) — загружает изображение по его URI
Метод setImageResource()
Сначала нужно получить ссылку на ImageView, а затем используется идентификатор изображения из ресурсов:
Метод setImageBitmap()
Используется класс BitmapFactory для чтения ресурса изображения в объект Bitmap, а затем в ImageView указывается полученный Bitmap. Могут быть и другие варианты.
Метод setImageDrawable()
Если у вас есть готовое изображение, например, на SD-карте, то его можно использовать в качестве объекта Drawable.
Drawable можно получить и из ресурсов, хотя такой код выглядит избыточным, если можно сразу вызвать setImageResource().
Метод setImageURI()
Берётся URI файла изображения и используется в качестве источника изображения. Этот способ годится для работы с локальными изображениями.
Загружаем Drawable через URI.
Другие методы
Также вам часто придется использовать методы, связанные с размерами и масштабированием: setMaxHeight(), setMaxWidth(), getMinimunHeight(), getMinimunWidth(), getScaleType(), setScaleType().
Масштабирование через свойство Scale Type
Для масштабирования картинки в ImageView есть свойство Scale Type и соответствующий ему атрибут android:scaleType и перечисление ImageView.ScaleType.
- CENTER
- CENTER_CROP
- CENTER_INSIDE
- FIT_CENTER
- FIT_START
- FIT_END
- FIT_XY
- MATRIX
Чтобы увидеть разницу между разными режимами, желательно использовать большую картинку, превосходящую по ширине экрана устройства. Допустим, у нас есть простенькая разметка:
Для наглядности я задал красный цвет для фона ImageView.
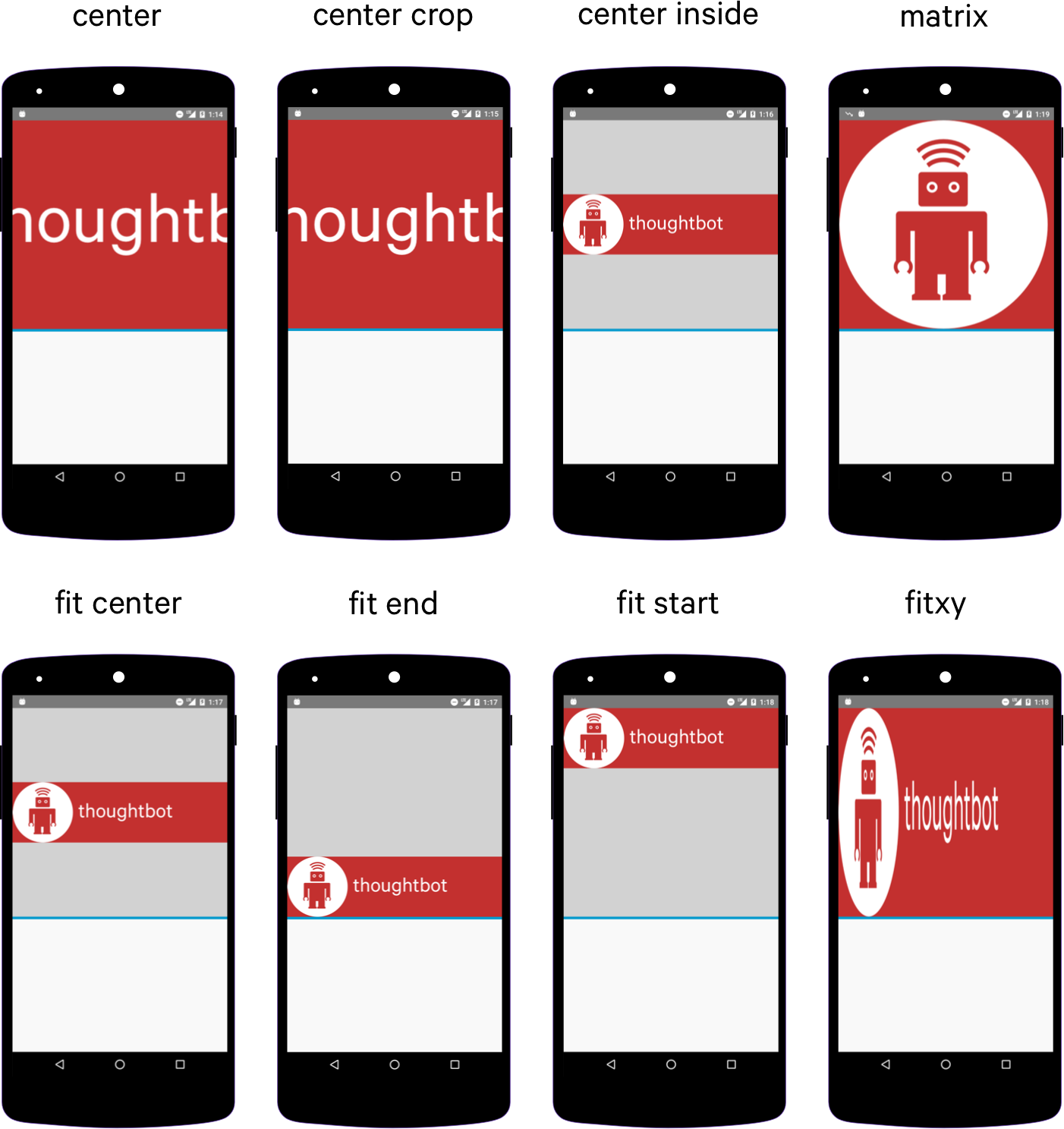
Режим android:scaleType=»center» выводит картинку в центре без масштабирования. Если у вас будет картинка большего размера, то края могут быть обрезаны.
Режим android:scaleType=»centerCrop» также размещает картинку в центре, но учитывает ширину или высоту контейнера. Режим попытается сделать так, чтобы ширина (или высота) картинки совпала с шириной (или высотой) контейнера, а остальное обрезается.
Режим android:scaleType=»centerInside» масштабирует картинку, сохраняя пропорции. Можно увидеть задний фон контейнера, если его размеры отличаются от размера картинки.
Режим android:scaleType=»fitCenter» (по умолчанию) похож на предыдущий, но может не сохранять пропорции.
Если выбрать режим android:scaleType=»fitStart», то картинка прижимается к левому верхнему углу и таким образом заполняет верхнюю половину контейнера.
Значение android:scaleType=»fitEnd» сместит картинку в нижнюю часть контейнера.
Режим android:scaleType=»fitXY» растягивает/сжимает картинку, чтобы подогнать её к контейнеру. Может получиться вытянутая картинка, поэтому будьте осторожны.
Последний атрибут android:scaleType=»matrix» вывел картинку без изменений в левом верхнем углу с обрезанными краями.
Атрибут android:adjustViewBounds=»true»
При использовании атрибута scaleType=»fitCenter» из предыдущего примера Android вычисляет размеры самой картинки, игнорируя размеры ImageView. В этом случае ваша разметка может «поехать». Атрибут adjustViewBounds заставляет картинку подчиниться размеру компонента-контейнера. В некоторых случаях это может не сработать, например, если у ImageView установлен атрибут layout_width=»0dip». В таком случае поместите ImageView в RelativeLayout или FrameLayout и используйте значение 0dip для этих контейнеров.
Загрузка изображения из галереи
Предположим, у вас есть на экране компонент ImageView, и вы хотите загрузить в него какое-нибудь изображение из галереи по нажатию кнопки:
Намерение ACTION_PICK вызывает отображение галереи всех изображений, хранящихся на телефоне, позволяя выбрать одно изображение. При этом возвращается адрес URI, определяющий местоположение выбранного изображения. Для его получения используется метод getData(). Далее для преобразования URI-адреса в соответствующий экземпляр класса Bitmap используется специальный метод Media.getBitmap(). И у нас появляется возможность установить изображение в ImageView при помощи setImageBitmap().
На самом деле можно поступить ещё проще и использовать метод setImageURI.
Сравните с предыдущим примером — чувствуете разницу? Тем не менее, приходится часто наблюдать подобный избыточный код во многих проектах. Это связано с тем, что метод порой кэширует адрес и не происходит изменений. Рекомендуется использовать инструкцию setImageURI(null) для сброса кэша и повторный вызов метода с нужным Uri.
В последних версиях системных эмуляторов два примера не работают. Проверяйте на реальных устройствах.
Получить размеры ImageView — будьте осторожны
У элемента ImageView есть два метода getWidth() и getHeight(), позволяющие получить его ширину и высоту. Но если вы попробуете вызвать указанные методы сразу в методе onCreate(), то они возвратят нулевые значения. Можно добавить кнопку и вызвать данные методы через нажатие, тогда будут получены правильные результаты. Либо использовать другой метод активности, который наступает позже.
Копирование изображений между ImageView
Если вам надо скопировать изображение из одного ImageView в другой, то можно получить объект Drawable через метод getDrawable() и присвоить ему второму компоненту.
Примеры
В моих статьях можно найти примеры использования ImageView.
Источник
Android ImageView ScaleType: A Visual Guide
If you’re anything like me, you are really, really, ridiculously good looking. But you’re also probably a tad forgetful. So when it comes time to scale an image in an ImageView , you cannot for the life of you remember what all the different ScaleType s actually look like on the screen. So, you spend the next 10-15 minutes building and rebuilding your app with each and every scale type to see what they all look like. Then you inevitably forget the difference between two of them and start the whole process all over again. As the kids say, “I gotchu fam”.
Below are screenshots of all the different ScaleType s placed side-by-side. And below that are all the ScaleType definitions copy and pasted directly from the official Android docs. And even further below those is a helpful tip for those brave souls who make it to the end of this post 🙂
Scale Types
The full descriptions of each ScaleType from the official Android documentation.
CENTER
Center the image in the view, but perform no scaling.
CENTER_CROP
Scale the image uniformly (maintain the image’s aspect ratio) so that both dimensions (width and height) of the image will be equal to or larger than the corresponding dimension of the view (minus padding).
CENTER_INSIDE
Scale the image uniformly (maintain the image’s aspect ratio) so that both dimensions (width and height) of the image will be equal to or less than the corresponding dimension of the view (minus padding).
FIT_CENTER
Scale the image using Matrix.ScaleToFit.CENTER
Matrix.ScaleToFit.CENTER : Compute a scale that will maintain the original src aspect ratio, but will also ensure that src fits entirely inside dst. At least one axis (X or Y) will fit exactly. The result is centered inside dst.
FIT_END
Scale the image using Matrix.ScaleToFit.END
Matrix.ScaleToFit.END : Compute a scale that will maintain the original src aspect ratio, but will also ensure that src fits entirely inside dst. At least one axis (X or Y) will fit exactly. END aligns the result to the right and bottom edges of dst.
FIT_START
Scale the image using Matrix.ScaleToFit.START
Matrix.ScaleToFit.START : Compute a scale that will maintain the original src aspect ratio, but will also ensure that src fits entirely inside dst. At least one axis (X or Y) will fit exactly. START aligns the result to the left and top edges of dst.
FIT_XY
Scale the image using Matrix.ScaleToFit.FILL
Matrix.ScaleToFit.FILL : Scale in X and Y independently, so that src matches dst exactly. This may change the aspect ratio of the src.
MATRIX
Scale using the image matrix when drawing.
Adjust View Bounds
While not technically an ImageView.ScaleType this will come in handy. If you notice with CENTER_INSIDE , FIT_CENTER , FIT_END and FIT_START the actual bounds of the ImageView are much larger than the scaled image. To set the bounds of the ImageView to the height of the image inside, use android:adjustViewBounds=»true” in your XML. It looks like this:
If you enjoyed this post, you might also like:
Mobile design and development services for every stage of your app
We design and build iOS, Android, and cross-platform React Native apps for startups and established businesses.
© 2021 thoughtbot, inc. The design of a robot and thoughtbot are registered trademarks of thoughtbot, inc. Privacy Policy
Источник
Understanding ImageView ScaleType in Android
Open your Android phone, look at the applications present in it and try to find if there is some application which doesn’t have any image. Did you get any? The answer will be a big NO (how do I know? No I don’t have the access to your phone 🙂 ). This is because every application uses an image in some or the other form to have a better user experience.
So, we as an Android developer are very fond of adding images or we can say adding ImageView to our application. But many times, we face various issues related to the scaling of the image i.e. either your image will be cropped or you will get your image left aligned and many other problems arise while scaling an image.
So, welcome to MindOrks! In this blog, we are going to learn ImageView ScaleType. Let’s get started.
Note: In this blog, I am going to use the MindOrks logo. You can download the below image and use this in your project.
Adding an image to the project
First of all, we need to add an image to our project. Copy the desired image and paste into the res > drawable directory . After that, add an ImageView to your XML file. Here is the code of my activity_main.xml file:
The following is the output of the above XML code:
We will use the above image for our reference to compare with the output image after applying some ScaleType .
ImageView ScaleType in Android
In Android, we can scale the bounds of an ImageView by using various ScaleType s. By using ScaleType , the bounds of the image are scaled to the bounds of the ImageView . The following are the ScaleType s used in Android:
- CENTER
- CENTER_CROP
- CENTER_INSIDE
- FIT_CENTER
- FIT_START
- FIT_END
- FIT_XY
- MATRIX
Let’s learn one by one.
CENTER
The CENTER ScaleType is used to place the image to the center of the ImageView in which that image is present by keeping the same aspect ratio. No scaling is done here and while centering the image, if the image is so big such that it is not fitting in the center, then some parts of the image will be cropped.
The below line of code is used to apply CENTER ScaleType:
The output will look something like this:
If you compare the above image with our original image then you will find that some parts of the image are cropped because the image is centered here.
CENTER_CROP
The CENTER_CROP ScaleType is used to place the image in the center of the ImageView and scale the image uniformly by maintaining the aspect ratio. So basically it scales in such a way that one of the width or height of the image becomes equal to the width and height of the ImageView. During scaling, if any of them becomes equal then the scaling will be stopped and the rest of the parts will be cropped. So, the dimensions of the image can be equal to or more than that of ImageView.
The below line of code is used to apply CENTER_CROP ScaleType:
The output will look something like this:
In the above image, while scaling when the width of the image becomes equal to the width of ImageView, then the scaling is stopped and the rest of the part is cropped.
CENTER_INSIDE
The CENTER_INSIDE ScaleType is used to place the image in the center of the ImageView and scale the image uniformly by maintaining the aspect ratio. So basically the scaling is done until both the width and height of the image become less than the width and height of the ImageView. So, the image will be put inside the ImageView irrespective of the size of the image and no cropping of the image will be performed.
The below line of code is used to apply CENTER_INSIDE ScaleType:
The output will look something like this:
In the above image, the scaling is done until both the width and height of the image become equal to the width and height of ImageView.
FIT_CENTER
The FIT_CENTER ScaleType is used to place the image in the center of the ImageView and scale the image uniformly by maintaining the aspect ratio and no cropping of image will be performed. The width and height of the image are scaled down or up based on the size of the image. So basically the scaling is done until both the width and height of the image become less than the width and height of the ImageView. Anyone of width or height must be the same with the width or height of the ImageView.
The below line of code is used to apply FIT_CENTER ScaleType:
The output will look something like this:
In the above image, the image is fitted in the center without any cropping.
FIT_START
The FIT_START ScaleType is used to place the image in the left-most and top part of the ImageView and scale the image uniformly by maintaining the aspect ratio and no cropping of image will be performed. The width and height of the image are scaled down or up based on the size of the image. So basically the scaling is done in the left part until both the width and height of the image become less than the width and height of the ImageView. Anyone of width or height must be the same with the width or height of the ImageView.
The below line of code is used to apply FIT_START ScaleType:
The output will look something like this:
In the above image, the image is scaled in the left-part of the ImageView.
FIT_END
The FIT_END ScaleType is used to place the image in the right-most bottom part of the ImageView and scale the image uniformly by maintaining the aspect ratio and no cropping of image will be performed. The width and height of the image are scaled down or up based on the size of the image. So basically the scaling is done until both the width and height of the image become less than the width and height of the ImageView. Anyone of width or height must be the same with the width or height of the ImageView.
The below line of code is used to apply FIT_START ScaleType:
The output will look something like this:
In the above image, the image is scaled to the right-part of ImageView.
FIT_XY
The FIT_XY ScaleType is used to scale the image throughout the ImageView. The aspect ratio of the image is not maintained here. The width and height of the image are the same as that of the width and height of the ImageView.
The below line of code is used to apply FIT_XY ScaleType:
The output will look something like this:
In the above image, the image is scaled to fit the width and height of the ImageView. So, the width and height of the image are the same as that of ImageView.
MATRIX
The MATRIX ScaleType is used to scale the image according to some user-defined MATRIX. Basically, we use a Matrix to manipulate the canvas while drawing some graphics. So, when using a Matrix with an ImageView, you can use it to flip, rotate, translate, etc with your image.
The below line of code is used to apply FIT_START ScaleType:
The output will look something like this:
Conclusion
In this blog, we learned about all the ScaleTypes that can be used in an ImageView. You can experiment more by making use of images of different size and also using the ImageView of different sizes.
Hope you enjoyed this blog. Do share this blog with your fellow developers to spread Android learning.
Источник