- Documentation of Operating Systems and Developers
- Android operating system
- Android OS
- Android Operating System
- What Is the Android Operating System?
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding the Android Operating System
- Android Operating System vs. Apple iOS
- Limitations of the Android Operating System
- What is Android operating system? A beginners read!
- Android operating system
- What is Android?
- The Android system consists of 3 layered stacks:
- Application Layer
- The System Libraries
- The Linux Kernel
- Related Posts
- Outlook notifications are not working on Android phone
- OneDrive Camera Upload not working on Android; How to Enable or Turn it On?
- Play Android games in the cloud on Windows with BlueStacks X
- [email protected]
- Android (operating system)
- Contents
- History
- Foundation
- Acquisition by Google
- Post-acquisition development
- Open Handset Alliance
- Version history
- Licensing
- Design
- Linux
- Features
- Applications
- Android Market
- Application security
- Privacy
- Marketing
- Market share
- Usage share
- Intellectual property infringement claims
Documentation of Operating Systems and Developers
Android operating system
Android OS

The Eclipse IDE with an official plugin is used for the development. The operating system Android for Smartphones is supported by the Open Handset Alliance. Including more than 30 communication provider, equipment and semiconductor manufacturers as well as software companies. Because Android is an open platform in the meaning of the software and product development the source code shall be available completely at a later time and is in opposite with the market leading closed operating systems Symbian, Palm OS and Windows Mobile.
Android include C/C++ function libraries used by different parts of the operating system.
- Surface manager for 2D and 3D even overlay display
- System C library, specialized for Linux-based devices (BSD implementation)
- SGL, 2D graphic system
- 3D libraries, based on OpenGL ES 1.0 APIs with hardware or software accelerated 3D display
- Media libraries for playback and record of audio, graphic and video formats (MPEG4, H.264, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, PNG)
- LibWebCore, Android internet browser
- FreeType, for representing of bitmap and vector fonds
- SQLite, an efficient and slim relational database for all applications
The Android SDK is available for Linux, MacOS and Windows. It contains an emulator with the surface of Android to try applications. After unpacking the SDK the emulator can be found in the subdirectory » oolsemulator.exe» that shows a HTC Smartphone with keyboard.
Standard programs for e-mail, SMS, contacts, calendar, road maps, internet browser and others are preinstalled.
The first Google Android Developer Challenge (ADC) started in April 2008 for engaged programmers to realize and present ideas. Approximately 1,800 programmes were submitted and 20 honoured with a price money under the best 50. Part of the best applications are for example cab4me by combination of Google Maps, GPS signal and a database to send a taxi in the simplest mode by click to the current position on the map. Or GoCart which reads the bar code of goods with the mobile telephone camera and looks over onlineshops and registered shops in the circumference for the best price.
Google creates a sales platform for Smarthone applications with Android Market. At first the market place is provided free of charge. The first Android mobile telephone cames from the taiwanese manufacturer HTC with the T-Mobile G1 smartphone starting at October 22nd, 2008 in the USA and at the beginning of 2009 in Germany. The Android Market was renamed in Google Play on 6th March 2012.
The market research group Gartner, Inc. released a press news about the worldwide market share of smartphone ventors and operating systems on 19th August 2016. In the 2nd quarter 2016, 296.9 million Android units have been sold, this represents a market share of 86.2%. The Android operating system increased his share, in 2nd quarter 2015 the market share was 82.2% with 271.6 million units sold.
Источник
Android Operating System
James Chen, CMT is an expert trader, investment adviser, and global market strategist. He has authored books on technical analysis and foreign exchange trading published by John Wiley and Sons and served as a guest expert on CNBC, BloombergTV, Forbes, and Reuters among other financial media.
Thomas J Catalano is a CFP and Registered Investment Adviser with the state of South Carolina, where he launched his own financial advisory firm in 2018. Thomas’ experience gives him expertise in a variety of areas including investments, retirement, insurance, and financial planning.
What Is the Android Operating System?
The Android operating system is a mobile operating system that was developed by Google (GOOGL) to be primarily used for touchscreen devices, cell phones, and tablets. Its design lets users manipulate the mobile devices intuitively, with finger movements that mirror common motions, such as pinching, swiping, and tapping. Google also employs Android software in televisions, cars, and wristwatches—each of which is fitted with a unique user interface.
Key Takeaways
- The Android operating system was developed by Google (GOOGL) for use in all of its touchscreen devices, tablets, and cell phones.
- This operating system was first developed by Android, Inc., a software company located in Silicon Valley before it was acquired by Google in 2005.
- While the Android source code is released in an open-source format to help advance open standards across mobile devices, it is still packaged with proprietary software when sold on handset devices.
Understanding the Android Operating System
The Android operating system was first developed by Android, Inc., a software company located in Silicon Valley before Google acquired it in 2005. Investors and electronics industry analysts have questioned Google’s true intentions for entering the mobile market space since that acquisition. But in any case, soon thereafter, Google announced the impending rollout of its first commercially available Android-powered device in 2007, although that product actually hit the marketplace in 2008.
Since then, software and application developers have been able to use Android technology to develop mobile apps, which are sold through app stores, such as Google Play. And because it is developed as a Google product, Android users are given the opportunity to link their mobile devices to other Google products, such as cloud storage, email platforms, and video services.
The Android source code is released in an open-source format to help advance open standards across mobile devices. However, despite being released as “open,” Android is still packaged with proprietary software when sold on handset devices.
According to research from Trend Micro, premium service abuse is the most common type of Android malware, in which text messages are sent from infected phones to premium-rate telephone numbers with neither the knowledge nor the consent of the user.
Android Operating System vs. Apple iOS
The emergence of Android created a new rivalry between smartphone manufacturers, with Apple (AAPL) serving as Google’s chief competitor. To some, this competitive dynamic mirrors that of the “cola wars” between Coca-Cola (KO) and Pepsi (PEP) over the past 30 years, where no clear winner or loser has emerged. Android was the most popular operating system on mobile devices as of the end of 2020, with 84.8% of the global market share while Apple’s iOS was in second place with 15.2%, according to International Data Corporation.
The increased popularity of the system has also led to a number of patent-related lawsuits, including a lawsuit brought forth by Oracle (ORCL). In 2010, the company alleged that Google unlawfully used Java APIs to develop its Android software. The case was pending as of October 2020.
Limitations of the Android Operating System
While Android offers users a viable alternative to other mobile operating systems, several limitations still remain. On the developer side, coding complex user experiences and interfaces is an often difficult task that demands a greater reliance on Java than Objective-C. For users, the apps on the Android Market tend to have lower standards than comparable app stores.
In other words, the apps have lower security profiles and make users more susceptible to data breaches. Meanwhile, Android’s lack of a voice-controlled assistant and its heavy dependence on advertising can repel some users.
Источник
What is Android operating system? A beginners read!
Today, the name Android operating system has become synonymous with a handheld device that can show movies, allow one to talk to another person, send messages, pictures, emails, play games and let you stay in touch with everybody.
Android operating system
Android is perhaps one of the most used Operating System plus framework available for what we call smartphones today. And it is poised to become an all-encompassing framework that will be used not only on a simple handheld device like smartphones but its uses will also be on HDTV’s, Automotive Infotainment systems. Any system which will require a simple, elegant, and easy to develop User Interface might be built on the Android framework.
What is Android?
Android is a Mobile Operating System, developed By Android Inc. and now, marketed by Google. Google and other members of Open Handset Alliance collaborated on Android development and release. Its software stack and framework is built on Linux kernel, which has been very instrumental in its seamless acceptance as an OS of choice in Mobile phones. Android OS consists of over 12 million lines of code written in C / C++ / Java and XML.
Android can be visualized basically as a framework of C C++ and Java libraries based on a Linux kernel. Because of this and the fact that Java apps can be effortlessly built through SDK’s the applications are portable on all mobile devices.
The Android system consists of 3 layered stacks:
- An application built in Java running on Dalvik Runtime Engine
- System Library is written in C and C++
- Kernel-based on Linux
Application Layer
Java language was chosen as the development language. There are a lot of mobile developers who are well versed in Java and hence can have a seamless transition to writing Mobile apps and widgets on Android-powered Smartphones
Java is a proven technology, portable on different software and hardware platform. Java is already available on the majority of mobile phones. Current Java on mobile (J2ME) has a lot of limitations, so major mobile phone companies add in their own extension to the Java library, this makes portability of Java application on mobile more difficult. Normally Java was used to create Java games on mobile; many other applications are still built on the native OS and not on the Java layer.
Sun has been pushing Java technology on mobiles for years, it was successfully deployed on most of the mobile phones, but lack of standardization made it difficult to reach the depths of the Mobile phone market.
Android has a very reach and standardized set of API’s and libraries, developers can use those API to develop games and applications, integrate well into mobile phones, and Java will make Android application portable on all (Android) mobile phones.
The Java program doesn’t run directly on Android; it is converted into Dalvik byte code. Basically Android can make any app run as long as it can be converted to Dalvik byte code.
The System Libraries
The system libraries on Android mainly built on C and C++, so they are fast and efficient. Since the library runs on top of the Linux kernel, there are a lot of drivers and libraries available which can be customized as per the vendor’s requirement.
The Linux Kernel
The Linux kernel was chosen because it was proven to be stable and powerful. Linux has good memory management, process management and already built in with many other functions like TCP/IP networking which is necessary for an operating system (especially you need it to connect to data network on your mobile).
For a new hardware mobile manufacturer, the first thing to do for building an Android platform is to build the device driver on the Linux kernel; there should be a lot of developers around who have the know-how to build the software stack from scratch or customize it from the available software.
There were a lot of companies trying to build a mobile phone operating system based on Linux kernel before Android did, but have not been very successful.
Even Motorola and Nokia had released some mobile and internet devices which run on the Linux operating system, but they were not very successful as well, like the Motorola A series phone started with A760. Nokia has an Internet Table device (N770) which was built using the Linux operating system too. From a technical point of view, Android using Java over Linux is a smart move. Both Java and Linux are proven the technology and provide portability for mobile applications on the Android platform.
Date: January 12, 2017 Tags: Android, Open Source
Related Posts
Outlook notifications are not working on Android phone
OneDrive Camera Upload not working on Android; How to Enable or Turn it On?
Play Android games in the cloud on Windows with BlueStacks X
[email protected]
Nitin Agarwal is an MVP alumni and a Pro Blogger. He was awarded as Most Valuable Professional for 3 times by Microsoft in Windows Expert — Consumer category. He is immensely inspired by Bill Gates, Steve Jobs and APJ Abdul Kalam.
Источник
Android (operating system)
 | |
|---|---|
 Home screen displayed by Samsung Galaxy Nexus, running Android 4.0 «Ice Cream Sandwich» | |
| Company / developer | Google Inc, Open Handset Alliance |
| Programmed in | C (core), [ 1 ] Java (UI), C++ |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model | Open Source [ 2 ] |
| Initial release | 20 September 2008 ( 2008-09-20 ) |
| Latest stable release | 4.0.1 (Ice Cream Sandwich) [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 6 ] / 14 November 2011 ; 8 days ago ( 2011-11-14 ) |
| Package manager | APK |
| Supported platforms | ARM, MIPS, [ 7 ] x86 [ 8 ] |
| Kernel type | Monolithic (Linux kernel) |
| Default user interface | Graphical |
| License | Apache License 2.0 Linux kernel patches under GNU GPL v2 [ 9 ] |
| Official website | www.android.com |
Android is an operating system for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. It is developed by the Open Handset Alliance led by Google. [ 10 ] [ 11 ]
Google purchased the initial developer of the software, Android Inc., in 2005. [ 12 ] The unveiling of the Android distribution on November 5, 2007 was announced with the founding of the Open Handset Alliance, a consortium of 84 hardware, software, and telecommunication companies devoted to advancing open standards for mobile devices. [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 16 ] Google released most of the Android code under the Apache License, a free software license. [ 17 ] The Android Open Source Project (AOSP) is tasked with the maintenance and further development of Android. [ 18 ]
Android consists of a kernel based on the Linux kernel, with middleware, libraries and APIs written in C and application software running on an application framework which includes Java-compatible libraries based on Apache Harmony. Android uses the Dalvik virtual machine with just-in-time compilation to run Dalvik dex-code (Dalvik Executable), which is usually translated from Java bytecode. [ 19 ]
Android has a large community of developers writing applications («apps») that extend the functionality of the devices. Developers write primarily in a customized version of Java. [ 20 ] There are currently approximately 300,000 apps available for Android, from a total of 500,000 apps over the life of Android. [ 21 ] [ 22 ] [ 23 ] Apps can be downloaded from third-party sites or through online stores such as Android Market, the app store run by Google.
Android was listed as the best-selling smartphone platform worldwide in Q4 2010 by Canalys [ 24 ] [ 25 ] with over 190 million Android devices in use by October 2011. [ 26 ]
Contents
History
Foundation
Android, Inc. was founded in Palo Alto, California, United States in October, 2003 by Andy Rubin (co-founder of Danger), [ 27 ] Rich Miner (co-founder of Wildfire Communications, Inc.), [ 28 ] Nick Sears (once VP at T-Mobile), [ 29 ] and Chris White (headed design and interface development at WebTV) [ 30 ] to develop, in Rubin’s words «. smarter mobile devices that are more aware of its owner’s location and preferences». [ 31 ] Despite the obvious past accomplishments of the founders and early employees, Android Inc. operated secretly, revealing only that it was working on software for mobile phones. [ 31 ]
That same year, Rubin ran out of money. Steve Perlman brought him $10,000 in cash in an envelope and refused a stake in the company. [ 32 ]
Acquisition by Google
Google acquired Android Inc. in August 2005, making Android Inc. a wholly owned subsidiary of Google Inc. Key employees of Android Inc., including Andy Rubin, Rich Miner and Chris White, stayed at the company after the acquisition. [ 12 ] Not much was known about Android Inc. at the time of the acquisition, but many assumed that Google was planning to enter the mobile phone market with this move. [ 12 ]
Post-acquisition development
At Google, the team led by Rubin developed a mobile device platform powered by the Linux kernel. Google marketed the platform to handset makers and carriers on the premise of providing a flexible, upgradable system. Google had lined up a series of hardware component and software partners and signaled to carriers that it was open to various degrees of cooperation on their part. [ 33 ] [ 34 ] [ 35 ]
Speculation about Google’s intention to enter the mobile communications market continued to build through December 2006. [ 36 ] Reports from the BBC and The Wall Street Journal noted that Google wanted its search and applications on mobile phones and it was working hard to deliver that. Print and online media outlets soon reported rumors that Google was developing a Google-branded handset. [ 37 ] Some speculated that as Google was defining technical specifications, it was showing prototypes to cell phone manufacturers and network operators.
In September 2007, InformationWeek covered an Evalueserve study reporting that Google had filed several patent applications in the area of mobile telephony. [ 38 ] [ 39 ]
Open Handset Alliance
On November 5, 2007, the Open Handset Alliance, a consortium of several companies which include Broadcom Corporation, Google, HTC, Intel, LG, Marvell Technology Group, Motorola, Nvidia, Qualcomm, Samsung Electronics, Sprint Nextel, T-Mobile and Texas Instruments unveiled itself. The goal of the Open Handset Alliance is to develop open standards for mobile devices. [ 15 ] On the same day, the Open Handset Alliance also unveiled their first product, Android, a mobile device platform built on the Linux kernel version 2.6. [ 15 ]
On December 9, 2008, 14 new members joined, including ARM Holdings, Atheros Communications, Asustek Computer Inc, Garmin Ltd, Huawei Technologies, PacketVideo, Softbank, Sony Ericsson, Toshiba Corp, and Vodafone Group Plc. [ 40 ] [ 41 ]
Version history
Android has seen a number of updates since its original release, each fixing bugs and adding new features. Each version is named, in alphabetical order, after a dessert. [ 42 ]
Recent releases
- 2.3 Gingerbread refined the user interface, improved the soft keyboard and copy/paste features, improved gaming performance, added SIP support (VoIP calls), and added support for Near Field Communication. [ 43 ]
- 3.0 Honeycomb was a tablet-oriented [ 44 ][ 45 ][ 46 ] release which supports larger screen devices and introduces many new user interface features, and supports multi-core processors and hardware acceleration for graphics. [ 47 ] The first device featuring this version, the Motorola Xoom tablet, went on sale in February 2011. [ 48 ][ 49 ]
- 3.1 Honeycomb, released in May 2011, added support for extra input devices, USB host mode for transferring information directly from cameras and other devices, and the Google Movies and Books apps. [ 50 ]
- 3.2 Honeycomb, released in July 2011, added optimization for a broader range of screen sizes, new «zoom-to-fill» screen compatibility mode, loading media files directly from SD card, and an extended screen support API. [ 51 ]Huawei MediaPad is the first 7 inch tablet to use this version [ 52 ]
- 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich, announced on October 19, 2011, brought Honeycomb features to smartphones and added new features including facial recognition unlock, network data usage monitoring and control, unified social networking contacts, photography enhancements, offline email searching, and information sharing using NFC. Android 4.0.1 Ice Cream Sandwich is the latest Android version that is available to phones. The source code of Android 4.0.1 was released on November 14, 2011 [ 53 ]
Licensing
With the exception of brief update periods, Android has been available under free and open source software licenses from October 21, 2008 until March 2011. [ 54 ] Google published the source code for their Linux kernel changes under the GNU General Public License version 2, and the rest of the code (including network and telephony stacks) [ 55 ] under the Apache License version 2.0. [ 56 ] [ 57 ] [ 58 ] Google also keeps the reviewed issues list publicly open for anyone to see and comment. [ 59 ]
The Open Handset Alliance develops the GPL-licensed part of Android, that is their changes to the Linux kernel, in public, with source code publicly available at all times. The rest of Android is developed in private, with source code released publicly when a major new version is released. Typically Google collaborates with a hardware manufacturer to produce a flagship device featuring the new version of Android, then makes the source code available after that device has been released. [ 60 ]
In early 2011, Google chose to temporarily withhold the Android source code to the tablet-only Honeycomb release, creating doubts over Google’s commitment to open source with Android. [ 54 ] The reason, according to Andy Rubin in an official Android blog post, was because Honeycomb was rushed for production of the Motorola Xoom, [ 61 ] and they did not want third parties creating a «really bad user experience» by attempting to put onto smartphones a version of Android intended for tablets. [ 62 ] Google later confirmed that the Honeycomb source code would not be released until after it was merged with the Gingerbread release in Ice Cream Sandwich. [ 63 ]
Even though the software is open source, device manufacturers cannot use Google’s Android trademark unless Google certifies that the device complies with their Compatibility Definition Document (CDD). Devices must also meet this definition to be eligible to license Google’s closed-source applications, including the Android Market. [ 64 ]
In September 2010, Skyhook Wireless filed a lawsuit against Google in which they alleged that Google had used the compatibility document to block Skyhook’s mobile positioning service (XPS) from Motorola’s Android mobile devices. [ 65 ] In December 2010 a judge denied Skyhook’s motion for preliminary injunction, saying that Google had not closed off the possibility of accepting a revised version of Skyhook’s XPS service, and that Motorola had terminated their contract with Skyhook because Skyhook wanted to disable Google’s location data collection functions on Motorola’s devices, which would have violated Motorola’s obligations to Google and its carriers. [ 66 ]
Design
Linux
Android’s kernel is a fork of the Linux kernel and has further architecture changes by Google outside the typical Linux kernel development cycle. [ 67 ] Android does not have a native X Window System nor does it support the full set of standard GNU libraries, and this makes it difficult to port existing Linux applications or libraries to Android. [ 68 ]
Certain features that Google contributed back to the kernel, notably a power management feature called wakelocks, were rejected by mainline kernel developers, partly because kernel maintainers felt that Google did not show any intent to maintain their own code. [ 69 ] [ 70 ] [ 71 ] Even though Google announced in April 2010 that they would hire two employees to work with the Linux kernel community, [ 72 ] Greg Kroah-Hartman, the current Linux kernel maintainer for the -stable branch, said in December 2010 that he was concerned that Google was no longer trying to get their code changes included in mainstream Linux. [ 70 ] Some Google Android developers hinted that «the Android team was getting fed up with the process», because they were a small team and had more urgent work to do on Android. [ 73 ]
However, in September 2010 Linux kernel developer Rafael J. Wysocki added a patch that improved the mainline Linux wakeup events framework. He said that Android device drivers that use wakelocks can now be easily merged into mainline Linux, but that Android’s opportunistic suspend features should not be included in the mainline kernel. [ 74 ] [ 75 ] In 2011 Linus Torvalds said that «eventually Android and Linux would come back to a common kernel, but it will probably not be for four to five years.» [ 76 ]
Features
Current features and specifications: [ 77 ] [ 78 ] [ 79 ]
Handset layouts The platform is adaptable to larger, VGA, 2D graphics library, 3D graphics library based on OpenGL ES 2.0 specifications, and traditional smartphone layouts. Storage SQLite, a lightweight relational database, is used for data storage purposes. Connectivity Android supports connectivity technologies including GSM/EDGE, IDEN, CDMA, EV-DO, UMTS, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, LTE, NFC and WiMAX. Messaging SMS and MMS are available forms of messaging, including threaded text messaging and now Android Cloud To Device Messaging Framework (C2DM) is also a part of Android Push Messaging service. Multiple language support Android supports multiple human languages. [ 43 ] Web browser The web browser available in Android is based on the open-source WebKit layout engine, coupled with Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine. The browser scores a 95/100 on the Acid3 Test. Java support While most Android applications are written in Java, there is no Java Virtual Machine in the platform and Java byte code is not executed. Java classes are compiled into Dalvik executables and run on Dalvik, a specialized virtual machine designed specifically for Android and optimized for battery-powered mobile devices with limited memory and CPU. J2ME support can be provided via third-party applications. Media support Android supports the following audio/video/still media formats: WebM, H.263, H.264 (in 3GP or MP4 container), MPEG-4 SP, AMR, AMR-WB (in 3GP container), AAC, HE-AAC (in MP4 or 3GP container), MP3, MIDI, Ogg Vorbis, FLAC, WAV, JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP. [ 79 ] Streaming media support RTP/RTSP streaming (3GPP PSS, ISMA), HTML progressive download (HTML5 tag). Adobe Flash Streaming (RTMP) and HTTP Dynamic Streaming are supported by the Flash plugin. [ 80 ] Apple HTTP Live Streaming is supported by RealPlayer for Mobile, [ 81 ] and by the operating system in Android 3.0 (Honeycomb). [ 47 ] Additional hardware support Android can use video/still cameras, touchscreens, GPS, accelerometers, gyroscopes, barometers, magnetometers, dedicated gaming controls, proximity and pressure sensors, thermometers, accelerated 2D bit blits (with hardware orientation, scaling, pixel format conversion) and accelerated 3D graphics. Multi-touch Android has native support for multi-touch which was initially made available in handsets such as the HTC Hero. The feature was originally disabled at the kernel level (possibly to avoid infringing Apple’s patents on touch-screen technology at the time). [ 82 ] Google has since released an update for the Nexus One and the Motorola Droid which enables multi-touch natively. [ 83 ] Bluetooth Supports A2DP, AVRCP, sending files (OPP), accessing the phone book (PBAP), voice dialing and sending contacts between phones. Keyboard, mouse and joystick (HID) support is available in Android 3.1+, and in earlier versions through manufacturer customizations and third-party applications. [ 84 ] Video calling Android does not support native video calling, but some handsets have a customized version of the operating system that supports it, either via the UMTS network (like the Samsung Galaxy S) or over IP. Video calling through Google Talk is available in Android 2.3.4 and later. Gingerbread allows Nexus S to place Internet calls with a SIP account. This allows for enhanced VoIP dialing to other SIP accounts and even phone numbers. Skype 2.1 offers video calling in Android 2.3, including front camera support. Multitasking Multitasking of applications is available. [ 85 ] Voice based features Google search through voice has been available since initial release. [ 86 ] Voice actions for calling, texting, navigation, etc. are supported on Android 2.2 onwards. [ 87 ] Tethering Android supports tethering, which allows a phone to be used as a wireless/wired Wi-Fi hotspot. Before Android 2.2 this was supported by third-party applications or manufacturer customizations. [ 88 ] Screen capture Android has native support for screenshot capture ability by pressing the power and volume buttons at the same time on an Android device. This native support came about with the release of Android’s 4.0 (Ice Cream Sandwich) update which is first seen on the Galaxy Nexus smartphone. [ 89 ] Previously Android did not feature native support for screen capturing which would have likely been due to security concerns. Furthermore previously, manufacturer and third-party customizations as well as using a PC connection (DDMS developer’s tool) were the only known methods of capturing a screenshot on Android. [ 90 ]
The open and customizable nature of the Android operating system allows it to be used in pretty much any electronics, including but not limited to: smartphones, laptops, netbooks, tablet computers, Google TV, wristwatches, [ 91 ] headphones, [ 92 ] Car CD and DVD players [ 93 ] and other devices. [ 94 ] [ 95 ] [ 96 ]
The main hardware platform for Android is the ARM architecture. There is support for x86 from the Android-x86 project, [ 97 ] and Google TV uses a special x86 version of Android.
The first commercially available phone to run Android was the HTC Dream, released on 22 October 2008. [ 98 ] In early 2010 Google collaborated with HTC to launch its flagship [ 99 ] Android device, the Nexus One. This was followed later in 2010 with the Samsung-made Nexus S and in 2011 with the Galaxy Nexus.
iOS and Android 2.3.3 ‘Gingerbread’ may be set up to dual boot on a jailbroken iPhone or iPod Touch with the help of OpeniBoot and iDroid. [ 100 ] [ 101 ]
Applications
Applications are usually developed in the Java language using the Android Software Development Kit, but other development tools are available, including a Native Development Kit for applications or extensions in C or C++, Google App Inventor, a visual environment for novice programmers and various cross platform mobile web applications frameworks .
Android Market
Android Market is the online software store developed by Google for Android devices. An application program («app») called «Market» is preinstalled on most Android devices and allows users to browse and download apps published by third-party developers, hosted on Android Market. As of December 2010 [update] there were about 200,000 games, applications and widgets available on the Android Market. [ 102 ] In April 2011 Google said there had been more than 3 billion Android apps installed [ 103 ] and at end of June 2011 there are 6 billion apps installs from the Android market. The operating system itself is installed on 130 million total devices. [ 104 ]
Only devices that comply with Google’s compatibility requirements are allowed to preinstall Google’s closed-source Android Market app and access the Market. [ 105 ] The Market filters the list of applications presented by the Market app to those that are compatible with the user’s device, and developers may restrict their applications to particular carriers or countries for business reasons. [ 106 ]
Google has participated in the Android Market by offering several applications themselves, including Google Voice (for the Google Voice service), Sky Map (for watching stars), Finance (for their finance service), Maps Editor (for their MyMaps service), Places Directory (for their Local Search), Google Goggles that searches by image, Gesture Search (for using finger-written letters and numbers to search the contents of the phone), Google Translate, Google Shopper, Listen for podcasts and My Tracks, a jogging application. In August 2010, Google launched «Voice Actions for Android», [ 107 ] which allows users to search, write messages, and initiate calls by voice.
Alternatively, users can install apps from third party app stores such as the Amazon Appstore, [ 108 ] or directly onto the device if they have the application’s APK file.
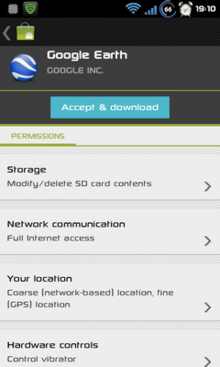
Application security
Android applications run in a sandbox, an isolated area of the operating system that does not have access to the rest of the system’s resources, unless access permissions are granted by the user when the application is installed. Before installing an application, Android Market displays all required permissions. A game may need to enable vibration, for example, but should not need to read messages or access the phonebook. After reviewing these permissions, the user can decide whether to install the application. [ 109 ]
Some Android malware incidents have been reported involving rogue applications on Android Market. In August 2010, Kaspersky Lab reported detection of the first malicious program for Android, named Trojan-SMS.AndroidOS.FakePlayer.a, an SMS trojan which had already infected a number of devices. [ 110 ] In some cases applications which contained trojans were hidden in pirated versions of legitimate apps. [ 111 ] [ 112 ] Google has responded by removing malicious apps from the Android Market, and remotely disabling them on infected devices. [ 113 ] Security firms such as AVG Technologies and Symantec have released antivirus software for Android devices.
Privacy
Android smartphones have the ability to report the location of Wi-Fi access points, encountered as phone users move around, to build vast databases containing the physical locations of hundreds of millions of such access points. These databases form electronic maps to locate smartphones, allowing them to run apps like Foursquare, Latitude, Places, and to deliver location-based ads. [ 114 ]
One design issue is that average users cannot monitor how applications access and use private and sensitive data (e.g. location and hardware ID numbers). Even during installation, permission checks do not often indicate to the user how critical services and data will be used or misused. Third party monitoring software such as TaintDroid, [ 115 ] an academic research-funded project, can identify personal information sent from applications to remote servers. [ 116 ]
Marketing
The Android logo was designed along with the Droid font family made by Ascender Corporation. [ 117 ]
Android Green is the color of the Android Robot that represents the Android operating system. The print color is PMS 376C and the RGB color value in hexadecimal is #A4C639, as specified by the Android Brand Guidelines. [ 118 ] The custom typeface of Android is called Norad (cf. NORAD). It is only used in the text logo. [ 119 ]
Market share
Research company Canalys estimated in Q2 2009 that Android had a 2.8% share of worldwide smartphone shipments. [ 120 ] By Q4 2010 this had grown to 33% of the market, becoming the top-selling smartphone platform. This estimate includes the Tapas and OMS variants of Android. [ 24 ] By Q3 2011 Gartner estimates more than half (52.5%) of the smartphone market belongs to Android. [ 121 ]
In February 2010 ComScore said the Android platform had 9.0% of the U.S. smartphone market, as measured by current mobile subscribers. This figure was up from an earlier estimate of 5.2% in November 2009. [ 122 ] By the end of Q3 2010 Android’s U.S. market share had grown to 21.4%. [ 123 ]
In May 2010, Android’s first quarter U.S. sales surpassed that of the rival iPhone platform. According to a report by the NPD group, Android achieved 25% smartphone sales in the US market, up 8% from the December quarter. In the second quarter, Apple’s iOS was up by 11%, indicating that Android is taking market share mainly from RIM, and still has to compete with heavy consumer demand for new competitor offerings. [ 124 ] Furthermore, analysts pointed to advantages that Android has as a multi-channel, multi-carrier OS, which allowed it to duplicate the quick success of Microsoft’s Windows Mobile. [ 125 ] In Q4 2010 Android had 59% of the total installed user base of Apple’s iOS in the U.S. and 46% of the total installed user base of iOS in Europe. [ 126 ] [ 127 ]
As of June 2011 [update] Google said that 550,000 new Android devices were being activated every day [ 128 ] —up from 400,000 per day a month earlier in May 2011, and more than 100 million devices have been activated. [ 22 ] Android hit 300,000 activations per day back in December 2010. On July 14, 2011 550,000 Android devices are now activated by Google each day with growth 4.4% per week. [ 129 ] On the 1st of August 2011 Canalys estimates Android has about 48% of the smartphone market share. [ 130 ] On October 13, 2011, Google announced that there are 190 million Android devices in the market. [ 131 ]
Usage share
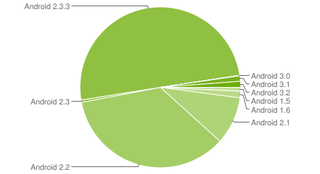
Usage share of the different versions, by November 3, 2011. [ 132 ]
Version
| Distribution | API level | % |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich | 14-15 | 0% |
| 3.x.x Honeycomb | 11-13 | 1.9% |
| 2.3.x Gingerbread | 9-10 | 44.4% |
| 2.2 Froyo | 8 | 40.7% |
| 2.1 Eclair | 7 | 10.7% |
| 1.6 Donut | 4 | 1.4% |
| 1.5 Cupcake | 3 | 0.9% |
According to Google’s Chet Hasse and Roman Guy, at AnDevCon II, San Francisco, 2011, there were two more internal releases called «Astro» and «Bender». The code names are in alphabetic order, and were allegedly changed from robots to desserts to avoid copyright issues.
Intellectual property infringement claims
Both Android and Android phone manufacturers have been the target of numerous patent lawsuits. On 12 August 2010, Oracle sued Google over claimed infringement of copyrights and patents related to the Java programming language. [ 133 ] Specifically, the patent infringement claim references seven United States patents including US 5966702 «Method and apparatus for pre-processing and packaging class files», and US 6910205 «Interpreting functions utilizing a hybrid of virtual and native machine instructions». [ 134 ] In response, Google submitted multiple lines of defense, counterclaiming that Android did not infringe on Oracle’s patents or copyright, that Oracle’s patents were invalid, and several other defenses. They said that Android is based on Apache Harmony, a clean room implementation of the Java class libraries, and an independently developed virtual machine called Dalvik. [ 135 ] [ 136 ] [ 137 ]
Microsoft has also sued several manufacturers of Android devices for patent infringement, and collects patent licensing fees from others. In October 2011 Microsoft said they had signed license agreements with ten Android device manufacturers, accounting for 55% of worldwide revenue for Android devices. [ 138 ] These include Samsung and HTC. [ 139 ]
Google has publicly expressed its dislike for the current patent landscape in the United States, accusing Apple, Oracle and Microsoft of trying to take down Android through patent litigation, rather than innovating and competing with better products and services. [ 140 ] In August 2011, Google purchased Motorola Mobility for US$12.5 billion, which was viewed in part as a defensive measure to protect Android, since Motorola Mobility had a 17,000-strong patent pool. [ 141 ]
Источник
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/photo__james_chen-5bfc26144cedfd0026c00af8.jpeg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/P2-ThomasCatalano-d5607267f385443798ae950ece178afd.jpg)