- Install and configure the NDK and CMake
- Install NDK and CMake automatically
- Install the NDK and CMake
- Configure a specific version of CMake
- Groovy
- Kotlin
- Install a specific version of the NDK
- Configure specific versions of the NDK in your project
- Groovy
- Kotlin
- Default NDK version per AGP version
- agrcrobles / android_instructions_29.md
- Android NDK
- Terms and Conditions
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Accepting this License Agreement
- 3. SDK License from Google
- 4. Use of the SDK by You
- 5. Your Developer Credentials
- 6. Privacy and Information
- 7. Third Party Applications
- 8. Using Android APIs
- 9. Terminating this License Agreement
- 10. DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES
- 11. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
- 12. Indemnification
- 13. Changes to the License Agreement
- 14. General Legal Terms
- In this document
- Downloads
- Revisions
- System and Software Requirements
- The Android SDK
- Supported operating systems
- Required development tools
- Android platform compatibility
- Installing the NDK
- Getting Started with the NDK
- Using the NDK
- Contents of the NDK
- Development tools
- Documentation
- Sample apps
- Exploring the hello-jni Sample
- Exploring the native-activity Sample Application
Install and configure the NDK and CMake
To compile and debug native code for your app, you need the following components:
- The Android Native Development Kit (NDK): a set of tools that allows you to use C and C++ code with Android.
- CMake: an external build tool that works alongside Gradle to build your native library. You do not need this component if you only plan to use ndk-build.
- LLDB: the debugger Android Studio uses to debug native code. By default, LLDB will be installed alongside Android Studio.
This page describes how to install these components automatically, or by using Android Studio or the sdkmanager tool to download and install them manually.
Install NDK and CMake automatically
Android Gradle Plugin 4.2.0+ can automatically install the required NDK and CMake the first time you build your project if their licenses have been accepted in advance. If you’ve already read and agree to the license terms, then you can pre-accept the licenses in scripts with the following command:
Install the NDK and CMake
When you install the NDK, Android Studio selects the latest available NDK. For most projects, installing this default version of the NDK is sufficient. If your project needs one or more specific versions of the NDK, though, you can download and configure specific versions. Doing so helps you ensure reproducible builds across projects that each depend on a specific version of the NDK. Android Studio installs all versions of the NDK in the android-sdk /ndk/ directory.
To install CMake and the default NDK in Android Studio, do the following:
With a project open, click Tools > SDK Manager.
Click the SDK Tools tab.
Select the NDK (Side by side) and CMake checkboxes.
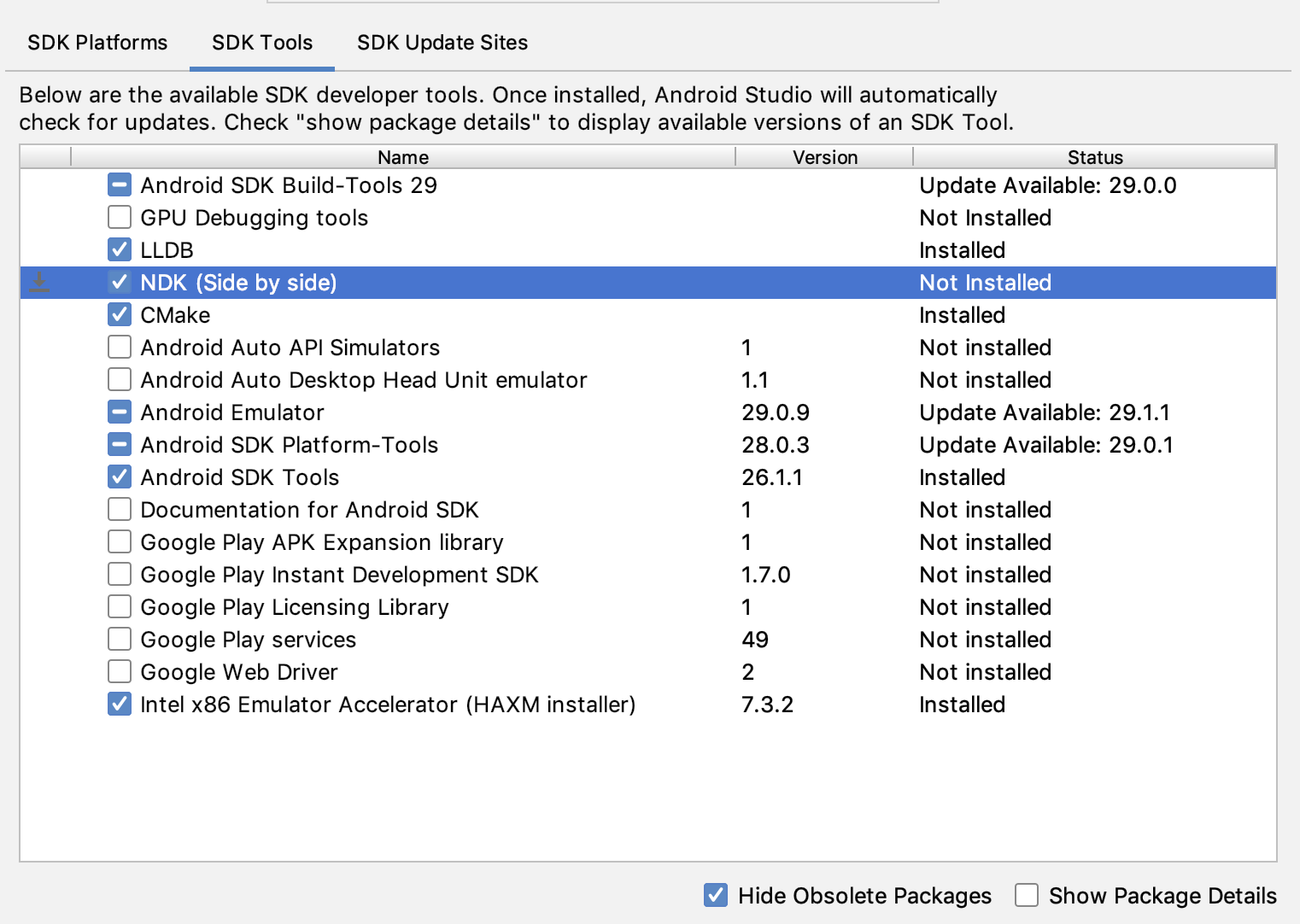
Click OK.
A dialog box tells you how much space the NDK package consumes on disk.
Click OK.
When the installation is complete, click Finish.
Your project automatically syncs the build file and performs a build. Resolve any errors that occur.
Configure a specific version of CMake
The SDK Manager includes the 3.6.0 forked version of CMake and version 3.10.2. Projects that don’t set a specific CMake version are built with CMake 3.10.2. To set the CMake version, add the following to your module’s build.gradle file:
Groovy
Kotlin
If you want to use a CMake version that is not included by the SDK Manager, follow these steps:
- Download and install CMake from the official CMake website.
- Specify the CMake version you want Gradle to use in your module’s build.gradle file.
Either add the path to the CMake installation to your PATH environment variable or include it in your project’s local.properties file, as shown. If Gradle is unable to find the version of CMake you specified in your build.gradle file, you get a build error.
If you don’t already have the Ninja build system installed on your workstation, go to the official Ninja website, and download and install the latest version of Ninja available for your OS. Make sure to also add the path to the Ninja installation to your PATH environment variable.
Install a specific version of the NDK
To install a specific version of the NDK, do the following:
With a project open, click Tools > SDK Manager.
Click the SDK Tools tab.
Select the Show Package Details checkbox.
Select the NDK (Side by side) checkbox and the checkboxes below it that correspond to the NDK versions you want to install. Android Studio installs all versions of the NDK in the android-sdk /ndk/ directory.
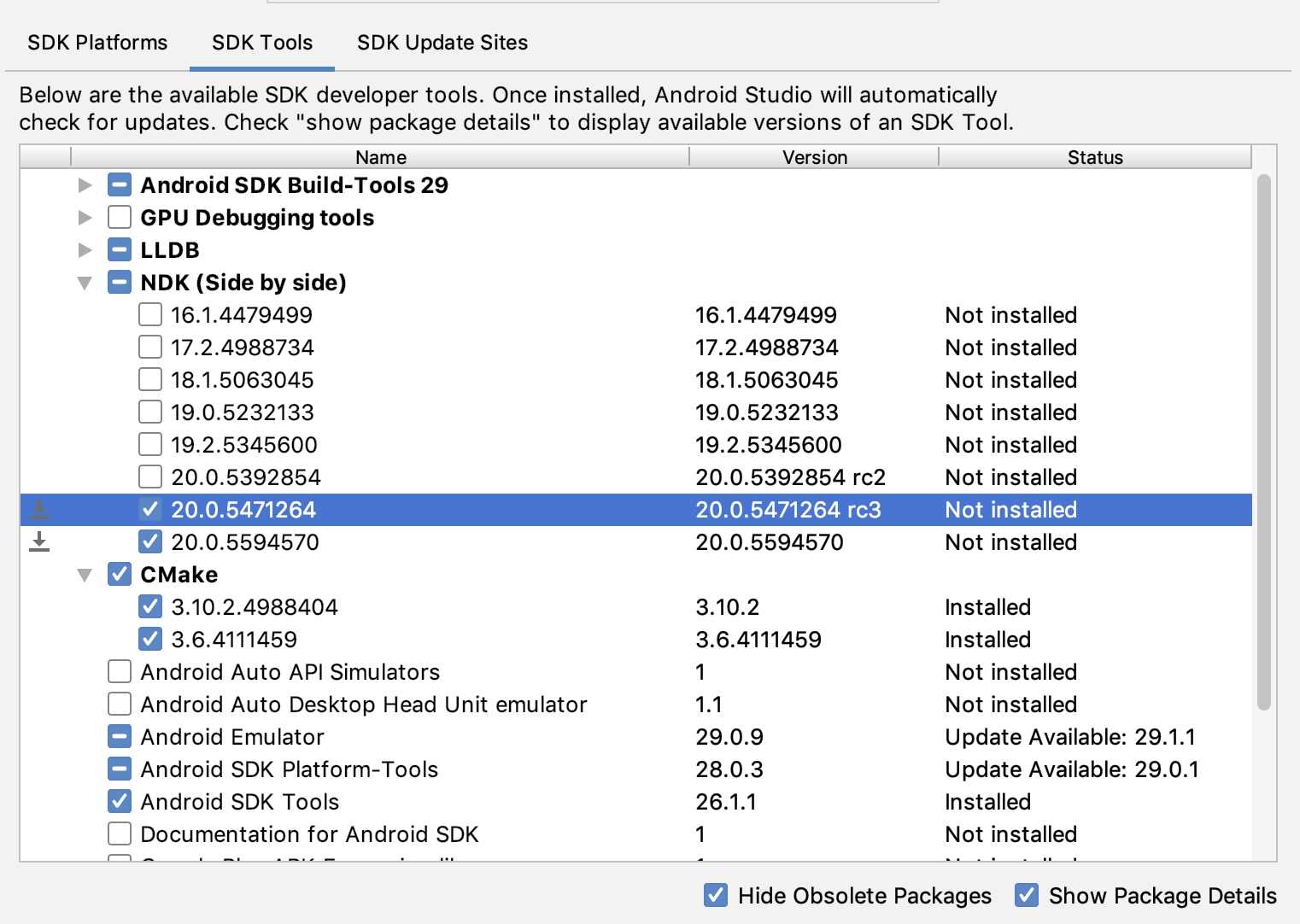
Click OK.
A dialog box tells you how much space the NDK package(s) consumes.
Click OK.
When the installation is complete, click Finish.
Your project automatically syncs the build file and performs a build. Resolve any errors that occur.
Configure each module with the version of the NDK you want it to use. When using Android Studio 3.6 or higher, if you do not specify the version, the Android Gradle plugin chooses a version that it is known to be compatible with.
Configure specific versions of the NDK in your project
You may need to configure the version of the NDK in your project if one of the following is true:
- Your project is inherited and you need to use specific versions of the NDK and the Android Gradle plugin (AGP). For more information, see Configure the NDK for the Android Gradle plugin.
You have multiple versions of the NDK installed and you want to use a specific one. In this case, specify the version using the android.ndkVersion property in the module’s build.gradle file, as shown in the following code sample.
Groovy
Kotlin
Default NDK version per AGP version
Before release, each AGP version is thoroughly tested with the latest stable NDK release at that time. For AGP version 3.6 and above, that NDK version will be used to build your projects if you do NOT specify an NDK version in the build.gradle file. The default NDK version is documented inside the AGP release notes. The current default NDK versions are listed in the following table:
| Android Studio/Gradle Plugin Version | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.0 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 4.0 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.4 | |
| Default NDK version specified for the version of AGP | 21.4.7075529 | 21.4.7075529 | 21.1.6352462 | 21.0.6113669 | 20.0.5594570 | No default specified | |
Content and code samples on this page are subject to the licenses described in the Content License. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Источник
agrcrobles / android_instructions_29.md
A high level overview for what I need to do to get most of an Android environment setup and maintained on OSX higher Catalina and Big Sur with and without Android Studio been installed.
Considering the SDK is installed under /Users/ /Library/Android/sdk folder which is the Android Studio preferred SDK location, but it works fine under /usr/local/share/android-sdk as well, which is a location pretty much used on CI mostly.
Open JDK 14 works fine with gradle 6.x
Preferred: To install the JDKs 8 ( LTS ) AdoptOpenJDK:
Alternative: Do not follow this step if followed the step before
Be sure JAVA_HOME is exported on your bash profile or zshrc depending the shell in usage.
Without Android Studio
Or try Command line tools | Android
Use Command line tools or SDK Manager
Quick reminder: Have as many build tools as you want, have a single one platform tool with backwards compatibility :=)
Download and Install Command line tools for mac ( not the android studio unless I need it )
Use Homebrew to install Android dev tools: Note that Java8 is tricky since licence changed: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/24342886/how-to-install-java-8-on-mac
Install all of the Android SDK components (you will be prompted to agree to license info and then this will take a while to run):
If you need to have openjdk first in your PATH run: echo ‘export PATH=»/usr/local/opt/openjdk/bin:$PATH»‘ >>
For compilers to find openjdk you may need to set: export CPPFLAGS=»-I/usr/local/opt/openjdk/include»
Be sure Intel Hardware Accelerated Execution Manager (HAXM) is properly installed.
HAXM is a cross-platform hardware-assisted virtualization engine (hypervisor), be sure HAXM is properly installed.
SDK preferred location
sdk can be installed on /Library/Android/sdk or /usr/local/ to be sure check it by
All locations are valid ones from what I am aware of 🙂
Suggested: You will have to add the ANDROID_HOME to the profile configuration settings either on .zshrc, .bashrc or .bash_profile
If emulator doesn’t run, i am here to remind you to provide access into System Preferences — Security & Privacy
Источник
Android NDK
| Platform | Package | Size (Bytes) | MD5 Checksum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 32-bit | android-ndk-r10d-windows-x86.exe | 455427281 | c0930abfae0c990c4d191cc4ebd46b68 |
| Windows 64-bit | android-ndk-r10d-windows-x86_64.exe | 472613732 | 9a33f96da58a7e0b70e47d27b4a880b4 |
| Mac OS X 32-bit | android-ndk-r10d-darwin-x86.bin | 441545213 | 0aeb3dc062dc457a4cd01e72eadb2379 | Mac OS X 64-bit | android-ndk-r10d-darwin-x86_64.bin | 442691567 | cb101e1e62d56ea75b215f6bc6c27fae |
| Linux 32-bit (x86) | android-ndk-r10d-linux-x86.bin | 449997190 | 70ed6d8c34e7e620c145b791e8eeef89 |
| Linux 64-bit (x86) | android-ndk-r10d-linux-x86_64.bin | 459151600 | 263b83071e6bca15f67898548d8d236e |
Before installing the Android NDK, you must agree to the following terms and conditions.
Terms and Conditions
1. Introduction
2. Accepting this License Agreement
3. SDK License from Google
4. Use of the SDK by You
5. Your Developer Credentials
6. Privacy and Information
7. Third Party Applications
8. Using Android APIs
9. Terminating this License Agreement
10. DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES
11. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
12. Indemnification
13. Changes to the License Agreement
14. General Legal Terms
I have read and agree with the above terms and conditions
In this document
The NDK is a toolset that allows you to implement parts of your app using native-code languages such as C and C++. For certain types of apps, this can be helpful so you can reuse existing code libraries written in these languages, but most apps do not need the Android NDK.
Before downloading the NDK, you should understand that the NDK will not benefit most apps. As a developer, you need to balance its benefits against its drawbacks. Notably, using native code on Android generally does not result in a noticable performance improvement, but it always increases your app complexity. In general, you should only use the NDK if it is essential to your app—never because you simply prefer to program in C/C++.
Typical good candidates for the NDK are CPU-intensive workloads such as game engines, signal processing, physics simulation, and so on. When examining whether or not you should develop in native code, think about your requirements and see if the Android framework APIs provide the functionality that you need.
Downloads
Revisions
The following sections provide information about releases of the NDK.


For more detailed information, see Important bug fixes below.
- ARM and x86 default to using the integrated assembler. If this causes issues, use -fno-integrated-as as a workaround.
- Clang 3.5 issues more warnings for unused flags, such as the -finline-functions option that GCC supports.
When migrating from projects using GCC, you can use -Wno-invalid-command-line-argument and -Wno-unused-command-line-argument to ignore the unused flags until you’re able decide on what to do with them longer-term.
93% of NEON intrinsics. For more information about NEON support:
- Navigate to the NDK Programmer’s Guide ( docs/Programmers_Guide/html/ ), and see Architectures and CPUs > Neon.
- Examine the updated hello-neon sample in samples/ .
- See Intel’s guide to porting from ARM NEON to Intel SSE.
Important bug fixes:
- Fixed an internal compiler error with GCC4.9/aarch64 that was causing the following error message (Issue 77564):
- Fixed incorrect code generation from GCC4.9/arm. (Issue 77567)
- Fixed an internal compiler error with GCC4.9/mips involving inline-assembly. (Issue 77568)
- Fixed incorrect code that GCC4.9/arm was generating for x = (cond) ? y : x . (Issue 77569)
- Fixed GCC4.9/aarch64 and Clang3.5/aarch64 to work around the Cortex-A53 erratum (835769) by default. Disable the workaround by specifying -mno-fix-cortex-a53-835769 .
Other bug fixes:
- Made the following header and library fixes to android-21 :
- Added more TV keycodes: android/keycodes.h
- Added more constants and six new sensor functions to android/sensor.h : ASensorManager_getDefaultSensorEx , ASensor_getFifoMaxEventCount , ASensor_getFifoReservedEventCount , ASensor_getStringType , ASensor_getReportingMode , and ASensor_isWakeUpSensor .
- Fixed stdatomic.h to improve compatibility with GCC 4.6, and provide support for the header.
- Added sys/ucontext.h and sys/user.h to all API levels. The signal.h header now includes . You may remove any existing definition of struct ucontext .
- Added posix_memalign to API levels 17, 18, and 19.
- Added the following functions to all architectures: android_set_abort_message , posix_fadvise , posix_fadvise64 , pthread_gettid_np .
- Added the required permissions to the native-media/AndroidManifest.xml sample. (Issue 106640)
- Added clock_nanosleep and clock_settime to API level 21. (Issue 77372)
- Removed the following symbols from all architectures: get_malloc_leak_info , free_malloc_leak_info , __srget , __swbuf , __srefill , __swsetup , __sdidinit , __sflags , __sfp , __sinit , __smakebuf , __sflush , __sread , __swrite , __sseek , __sclose , _fwalk , __sglue , __get_thread , __wait4 , __futex_wake , __open , __get_tls , __getdents64 , and dlmalloc .
- Removed the following functions from the 64-bit architectures: basename_r , dirname_r , __isthreaded , _flush_cache (mips64).
- Removed the following function from the 32-bit architectures: __signalfd4 .
- Changed the type of the third argument from size_t to int in the following functions: strtoll_l , strtoull_l , wcstoll_l , and wcstoull_l .
- Restored the following functions to the 64-bit architecture: arc4random , arc4random_buf , and arc4random_uniform .
- Moved cxa_* and the new and delete operators back to libstdc++.so . This change restores r9d behavior; previous versions of r10 contained dummy files.
- Restored MXU support in GCC 4.8 and 4.9 for mips. This support had been absent from r10 and r10b because those versions of GCC had been compiled with binutils-2.24, which did not support MXU. It now does.
- Fixed —toolchain= in make-standalone-toolchain.sh so that it now properly supports use of a suffix specifying a version of Clang.
- Fixed the libc++/armeabi strtod() functions.
- Made fixes to NDK documentation in docs/ .
Other changes:
- Enhanced cpu-features to detect ARMv8 support for the following instruction sets: AES, CRC32, SHA2, SHA1, and 64-bit PMULL/PMULL2. (Issue 106360)
- Modified ndk-build to use *-gcc-ar , which is available in GCC 4.8, GCC 4.9, and Clang. Clang specifies it, instead of *-ar . This setting brings improved LTO support.
- Removed the include-fixed/linux/a.out.h and include-fixed/linux/compiler.h headers from the GCC compiler. (Issue 73728)
- Fixed an issue related to -flto with GCC 4.8 on Mac OS X. The error message read:
- Fixed a typo in build-binary.mk. (Issue 76992)
Important known issues:
- Specifying -Os ( -fauto-profile ) in GCC4.9 may cause crashing. (Issue 77571)


47% of Neon. There is currently no support for 64-bit types. For more information, see the section on ARM Neon intrinsics support in the x86 documentation.


This is a bug-fix-only release.
Important bug fixes:
- Fixed a problem with GCC 4.8 ARM, in which the stack pointer is restored too early. This problem prevented the frame pointer from reliably accessing a variable in the stack frame. (GCC Issue 58854)
- Fixed a problem with GCC 4.8 libstdc++, in which a bug in std::nth_element was causing generation of code that produced a random segfault. (Issue 62910)
- Fixed GCC 4.8 ICE in cc1/cc1plus with -fuse-ld=mcld , so that the following error no longer occurs:
- Fixed -mhard-float support for __builtin math functions. For ongoing information on fixes for -mhard-float with STL, please follow Issue 61784.
Other bug fixes:
- Header fixes:
- Changed prototype of poll to poll(struct pollfd *, nfds_t, int); in poll.h .
- Added utimensat to libc.so for Android API levels 12 and 19. These libraries are now included for all Android API levels 12 through 19.
- Introduced futimens into libc.so , for Android API level 19.
- Added missing clock_settime() and clock_nanosleep() to time.h for Android API level 8 and higher.
- Added CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW, CLOCK_REALTIME_COARSE, CLOCK_MONOTONIC_COARSE, CLOCK_BOOTTIME, CLOCK_REALTIME_ALARM, and CLOCK_BOOTTIME_ALARM in time.h.
- Removed obsolete CLOCK_REALTIME_HR and CLOCK_MONOTONIC_HR.
- In samples Teapot, MoreTeapots, and source/android/ndk_helper :
- Changed them so that they now use a hard-float abi for armeabi-v7a.
- Updated them to use immersive mode on Android API level 19 and higher.
- Fixed a problem with Check_ReleaseStringUTFChars in /system/lib/libdvm.so that was causing crashes on x86 devices.
- Fixed ndk-build fails that happen in cygwin when the NDK package is referenced via symlink.
- Fixed ndk-build.cmd fails that happen in windows cmd.exe when LOCAL_SRC_FILES contains absolute paths. (Issue 69992)
- Fixed the ndk-stack script to proceed even when it can’t parse a frame due to inability to find a routine, filename, or line number. In any of these cases, it prints ?? .
- Fixed the ndk-stack stack for windows-x64_64 targets so that it no longer erroneously matches a frame line with a line in the stack: section that doesn’t contain pc , eip , or ip . For example:
- Fixed gabi++ so that it:
- Does not use malloc() to allocate C++ thread-local objects.
- Avoids deadlocks in gabi++ in cases where libc.debug.malloc is non-zero in userdebug/eng Android platform builds.
Other changes:
- Added LOCAL_EXPORT_LDFLAGS .
- Introduced the NDK_PROJECT_PATH=null setting for use in an integrated build system where options are explicitly passed to ndk-build . With this setting, ndk-build makes no attempt to look for NDK_PROJECT_PATH. This setting also prevents variables from deriving default settings from NDK_PROJECT_PATH. As a result, the following variables must now be explicitly specified (with their default values if such exist): NDK_OUT, NDK_LIBS_OUT, APP_BUILD_SCRIPT, NDK_DEBUG (optional, default to 0), and other APP_* ‘s contained in Application.mk .
- APP_ABI can now be enumerated in a comma-delimited list. For example:
- Provided the ability to rebuild all of STL with debugging info in an optional, separate package called android-ndk-r9c-cxx-stl-libs-with-debugging-info.zip , using the -g option. This option helps the ndk-stack script provide better a stack dump across STL. This change should not affect the code/size of the final, stripped file.
- Enhanced hello-jni samples to report APP_ABI at compilation.
- Used the ar tool in Deterministic mode (option -D ) to build static libraries. (Issue 60705)


Note: The -Wunused-local-typedefs option is enabled by -Wall . Be sure to add __attribute__((unused)) if you use compile-time asserts like sources/cxx-stl/stlport/stlport/stl/config/features.h , line #311. For more information, see Change 55460
Note: In the GCC 4.7 release and later, ARM compilers generate unaligned access code by default for ARMv6 and higher build targets. You may need to add the -mno-unaligned-access build option when building for kernels that do not support this feature.
Added Clang 3.3 support. The NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=clang build option now picks Clang 3.3 by default.
Note: Both GCC 4.4.3 and Clang 3.1 are deprecated, and will be removed from the next NDK release.
Important bug fixes:
- Fixed potential event handling issue in android_native_app_glue . (Issue 41755)
- Fixed ARM/GCC-4.7 build to generate sufficient alignment for NEON load and store instructions VST and VLD. (GCC Issue 57271)
- Fixed a GCC 4.4.3/4.6/4.7 internal compiler error (ICE) for a constant negative index value on a string literal. (Issue 54623)
- Fixed GCC 4.7 segmentation fault for constant initialization with an object address. (Issue 56508)
- Fixed GCC 4.6 ARM segmentation fault for -O values when using Boost 1.52.0. (Issue 42891)
- Fixed libc.so and libc.a to support the wait4() function. (Issue 19854)
- Updated the x86 libc.so and libc.a files to include the clone() function.
- Fixed LOCAL_SHORT_COMMANDS bug where the linker.list file is empty or not used.
- Fixed GCC MIPS build on Mac OS to use CFI directives, without which ld.mcld —eh-frame-hdr fails frequently.
- Fixed Clang 3.2 X86/MIPS internal compiler error in llvm/lib/VMCore/Value.cpp . (Change 59021)
- Fixed GCC 4.7 64-bit Windows assembler crash. (Error: out of memory allocating 4294967280 bytes ).
- Updated ndk-gdb script so that the —start or —launch actions now wait for the GNU Debug Server, so that it can more reliably hit breakpoints set early in the execution path (such as breakpoints in JNI code). (Issue 41278)
Note: This feature requires jdb and produces warning about pending breakpoints. Specify the —nowait option to restore previous behavior.
- Fixed GDB crash when library list is empty.
- Fixed GDB crash when using a stepi command past a bx pc or blx pc Thumb instruction. (Issue 56962, Issue 36149)
- Fixed MIPS gdbserver to look for DT_MIPS_RLD_MAP instead of DT_DEBUG . (Issue 56586)
- Fixed a circular dependency in the ndk-build script, for example: If A->B and B->B, then B was dropped from build. (Issue 56690)
Other bug fixes:
- Fixed the ndk-build script to enable you to specify a version of Clang as a command line option (e.g., NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=clang3.2 ). Previously, only specifying the version as an environment variable worked.
- Fixed gabi++ size of _Unwind_Exception to be 24 for MIPS build targets when using the Clang compiler. (Change 54141)
- Fixed the ndk-build script to ensure that built libraries are actually removed from projects that include prebuilt static libraries when using the ndk-build clean command. (Change 54461, Change 54480)
- Modified the NDK_ANALYZE=1 option to be less verbose.
- Fixed gnu-libstdc++/Android.mk to include a backward/ path for builds that use backward compability. (Issue 53404)
- Fixed a problem where stlport new sometimes returned random values.
- Fixed ndk-gdb to match the order of CPU_ABIS , not APP_ABIS . (Issue 54033)
- Fixed a problem where the NDK 64-bit build on MacOSX choses the wrong path for compiler. (Issue 53769)
- Fixed build scripts to detect 64-bit Windows Vista. (Issue 54485)
- Fixed x86 ntonl/swap32 error: invalid ‘asm’: operand number out of range . (Issue 54465, Change 57242)
- Fixed ld.gold to merge string literals.
- Fixed ld.gold to handle large symbol alignment.
- Updated ld.gold to enable the —sort-section=name option.
- Fixed GCC 4.4.3/4.6/4.7 to suppress the -export-dynamic option for statically linked programs. GCC no longer adds an .interp section for statically linked programs.
- Fixed GCC 4.4.3 stlport compilation error about inconsistent typedef of _Unwind_Control_Block . (Issue 54426)
- Fixed awk scripts to handle AndroidManifest.xml files created on Windows which may contain trailing \r characters and cause build errors. (Issue 42548)
- Fixed make-standalone-toolchain.sh to probe the prebuilts/ directory to detect if the host is 32 bit or 64 bit.
- Fixed the Clang 3.2 -integrated-as option.
- Fixed the Clang 3.2 ARM EHABI compact model pr1 and pr2 handler data.
- Added Clang -mllvm -arm-enable-ehabi option to fix the following Clang error:
- Fixed build failure when there is no uses-sdk element in application manifest. (Issue 57015)
Other changes:
- Header Fixes
- Modified headers to make __set_errno an inlined function, since __set_errno in errno.h is deprecated, and libc.so no longer exports it.
- Modified elf.h to include stdint.h . (Issue 55443)
- Fixed sys/un.h to be included independently of other headers. (Issue 53646)
- Fixed all of the MotionEvent_getHistorical API family to take the const AInputEvent* motion_event . (Issue 55873)
- Fixed malloc_usable_size to take const void* . (Issue 55725)
- Fixed stdint.h to be more compatible with C99. (Change 46821)
- Modified wchar.h to not redefine WCHAR_MAX and WCHAR_MIN
- Fixed declaration for pointer-related PRI and SCN macros. (Issue 57218)
- Changed the sys/cdefs.h header so that __WCHAR_TYPE__ is 32-bit for API levels less than 9, which means that wchat_t is 32-bit for all API levels. To restore the previous behavior, define the _WCHAR_IS_8BIT boolean variable. (Issue 57267)
- Added more formatting in NDK docs/ and miscellaneous documentation fixes.
- Added support for a thin archive technique when building static libraries. (Issue 40303)
- Updated script make-standalone-toolchain.sh to support the stlport library in addition to gnustl , when you specify the option —stl=stlport . For more information, see STANDALONE-TOOLCHAIN.html .
- Updated the make-standalone-toolchain.sh script so that the —llvm-version= option creates the $TOOLCHAIN_PREFIX-clang and $TOOLCHAIN_PREFIX-clang++ scripts in addition to clang and clang++ , to avoid using the host’s clang and clang++ definitions by accident.
- Added two flags to re-enable two optimizations in upstream Clang but disabled in NDK for better compatibility with code compiled by GCC:
- Added a -fcxx-missing-return-semantics flag to re-enable missing return semantics in Clang 3.2+. Normally, all paths should terminate with a return statement for a value-returning function. If this is not the case, clang inserts an undefined instruction (or trap in debug mode) at the path without a return statement. If you are sure your code is correct, use this flag to allow the optimizer to take advantage of the undefined behavior. If you are not sure, do not use this flag. The caller may still receive a random incorrect value, but the optimizer will not exploit it and make your code harder to debug.
- Added a -fglobal-ctor-const-promotion flag to re-enable promoting global variables with static constructor to be constants. With this flag, the global variable optimization pass of LLVM tries to evaluate the global variables with static constructors and promote them to global constants. Although this optimization is correct, it may cause some incompatability with code compiled by GCC. For example, code may do const_cast to cast the constant to mutable and modify it. In GCC, the variable is in read-write and the code is run by accident. In Clang, the const variable is in read-only memory and may cause your application to crash.
- Added -mldc1-sdc1 to the MIPS GCC and Clang compilers. By default, compilers align 8-byte objects properly and emit the ldc1 and sdc1 instructions to move them around. If your app uses a custom allocator that does not always align with a new object’s 8-byte boundary in the same way as the default allocator, your app may crash due to ldc1 and sdc1 operations on unaligned memory. In this case, use the -mno-ldc1-sdc1 flag to workaround the problem.
- Downgraded the event severity from warning to info if APP_PLATFORM_LEVEL is larger than APP_MIN_PLATFORM_LEVEL . The APP_PLATFORM_LEVEL may be lower than APP_PLATFORM in jni/Application.mk because the NDK does not have headers for all levels. In this case, the actual level is shifted downwards. The APP_MIN_PLATFORM_LEVEL is specified by the android:minSdkVersion in your application’s manifest. (Issue 39752)
- Added the android_getCpuIdArm() and android_setCpuArm() methods to cpu-features.c . This addition enables easier retrieval of the ARM CPUID information. (Issue 53689)
- Modified ndk-build to use GCC 4.7’s as/ld for Clang compiling.
Note: In GCC 4.7, monotonic_clock and is_monotonic have been renamed to steady_clock and is_steady , respectively.
- Added the following new warnings to the ndk-build script:
- Added warnings if LOCAL_LDLIBS/LDFLAGS are used in static library modules.
- Added a warning if a configuration has no module to build.
- Added a warning for non-system libraries being used in LOCAL_LDLIBS/LDFLAGS of a shared library or executable modules.
- Updated build scripts, so that if APP_MODULES is not defined and only static libraries are listed in Android.mk , the script force-builds all of them. (Issue 53502)
- Updated ndk-build to support absolute paths in LOCAL_SRC_FILES .
- Removed the *-gdbtui executables, which are duplicates of the *-gdb executables with the -tui option enabled.
- Updated the build scripts to warn you when the Edison Design Group (EDG) compiler front-end turns _STLP_HAS_INCLUDE_NEXT back on. (Issue 53646)
- Added the environment variable NDK_LIBS_OUT to allow overriding of the path for libraries/gdbserver from the default $PROJECT/libs . For more information, see OVERVIEW.html .
- Changed ndk-build script defaults to compile code with format string protection -Wformat -Werror=format-security . You may set LOCAL_DISABLE_FORMAT_STRING_CHECKS=true to disable it. For more information, see ANDROID-MK.html
- Added STL pretty-print support in ndk-gdb-py . For more information, see NDK-GDB.html .
- Added tests based on the googletest frameworks.
- Added a notification to the toolchain build script that warns you if the current shell is not bash .


Note: This feature is experimental. Please try it and report any issues.
- You can no longer build a static executable using the -static option or include libstlport_static.a using APP_STL := stlport_static . (You can still use the -static option with a standalone toolchain.) Compiling a dynamic executable using include $(BUILD_EXECUTABLE) continues to work because the compiler automatically adds the -ldl option.
- If your project links using -nostdlib and <-Wl,--no-undefined>, you must manually include the -ldl option.
For more information, see CPLUSPLUS-SUPPORT.html .
Note: This feature is experimental and works better with the GCC 4.6/4.7 compilers than with GCC 4.4.3 or Clang 3.1. Please try it and report any issues.
Added a -mstack-protector-guard= option for x86 to choose between a global default path which is compatible with older Android C library (bionic) and a new tls path (%gs:20) for -fstack-protector , -fstack-protector-all and -fstack-protector-strong using the GCC 4.6 and higher compilers.
Note: The -mstack-protector-guard setting itself does not enable any -fstack-protector* options.
Important bug fixes:
- Fixed unnecessary rebuild of object files when using the ndk-build script. (Issue 39810)
- Fixed a linker failure with the NDK 8c release for Mac OS X 10.6.x that produced the following error: This problem was caused by building on Mac OS X 10.7, which produced binaries that were not compatible with Mac OS 10.6.x and the NDK.
- Removed the -x c++ options from the Clang++ standalone build script. (Issue 39089)
- Fixed issues using the NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=clang3.1 option in Cygwin. (Issue 39585)
- Fixed the make-standalone-toolchain.sh script to allow generation of a standalone toolchain using the Cygwin or MinGW environments. The resulting toolchain can be used in Cygwin, MingGW or CMD.exe environments. (Issue 39915, Issue 39585)
- Added missing SL_IID_ANDROIDBUFFERQUEUESOURCE option in android-14 builds for ARM and X86. (Issue 40625)
- Fixed x86 CPU detection for the ANDROID_CPU_X86_FEATURE_MOVBE feature. (Issue 39317)
- Fixed an issue preventing the Standard Template Library (STL) from using C++ sources that do not have a .cpp file extension.
- Fixed GCC 4.6 ARM internal compiler error at reload1.c:1061. (Issue 20862)
- Fixed GCC 4.4.3 ARM internal compiler error at emit-rtl.c:1954. (Issue 22336)
- Fixed GCC 4.4.3 ARM internal compiler error at postreload.c:396. (Issue 22345)
- Fixed problem with GCC 4.6/4.7 skipping lambda functions. (Issue 35933)
Other bug fixes:
- NDK header file fixes:
- Fixed __WINT_TYPE__ and wint_t to be the same type.
- Corrected typo in android/bitmap.h . (Issue 15134)
- Corrected typo in errno.h .
- Added check for the presence of __STDC_VERSION__ in sys/cdefs.h . (Issue 14627)
- Reorganized headers in byteswap.h and dirent.h .
- Fixed limits.h to include page.h which provides PAGE_SIZE settings. (Issue 39983)
- Fixed return type of glGetAttribLocation() and glGetUniformLocation() from int to GLint .
- Fixed __BYTE_ORDER constant for x86 builds. (Issue 39824)
- Fixed ndk-build script to not overwrite -Os with -O2 for ARM builds.
- Fixed build scripts to allow overwriting of HOST_AWK , HOST_SED , and HOST_MAKE settings.
- Fixed issue for ld.gold on fsck_msdos builds linking objects built by the Intel C/C++ compiler (ICC).
- Fixed ARM EHABI support in Clang to conform to specifications.
- Fixed GNU Debugger (GDB) to shorten the time spent on walking the target’s link map during solib events. (Issue 38402)
- Fixed missing libgcc.a file when linking shared libraries.
Other changes:
- Backported 64-bit built-in atomic functions for ARM to GCC 4.6.
- Added documentation for audio output latency, along with other documentation and fixes.
- Fixed debug builds with Clang so that non-void functions now raise a SIGILL signal for paths without a return statement.
- Updated make-standalone-toolchain.sh to accept the suffix -clang3.1 which is equivalent to adding —llvm-version=3.1 to the GCC 4.6 toolchain.
- Updated GCC and Clang bug report URL to: http://source.android.com/source/report-bug s.html
- Added ARM ELF support to llvm-objdump .
- Suppressed treating c input as c++ warning for Clang builds.
- Updated build so that only the 32-bit version of libiberty.a is built and placed in lib32/ .

Note: This feature is experimental. Please try it and report any issues.
- Modified build logic so that projects that specify android-10 through android-13 in APP_PLATFORM , project.properties or default.properties link against android-9 instead of android-14 .
- Updated build so that executables using android-16 (Jelly Bean) or higher are compiled with the -fPIE option for position-independent executables (PIE). A new APP_PIE option allows you to control this behavior. See APPLICATION-MK.html for details.
Note: All API levels above 14 still link against platforms/android-14 and no new platforms/android-N have been added.
- Modified this build type to pass the -march=armv7-a parameter to the linker. This change ensures that v7-specific libraries and crt*.o are linked correctly.
- Added -mfpu=vfpv3-d16 to ndk-build instead of the -mfpu=vfp option used in previous releases.
Important bug fixes:
- Fixed an issue where running make-standalone-toolchain.sh with root privileges resulted in the stand alone tool chain being inaccessible to some users. (Issue 35279)
- All files and executables in the NDK release package are set to have read and execute permissions for all.
- The ownership/group of libstdc++.a is now preserved when copied.
- Removed redundant \r from Windows prebuilt echo.exe . The redundant \r caused gdb.setup to fail in the GNU Debugger (GDB) because it incorrectly became part of the path. (Issue 36054)
- Fixed Windows parallel builds that sometimes failed due to timing issues in the host-mkdir implementation. (Issue 25875)
- Fixed GCC 4.4.3 GNU libstdc++ to not merge typeinfo names by default. For more details, see toolchain repo gcc/gcc-4.4.3/libstdc++-v3/libsupc++/typeinfo . (Issue 22165)
- Fixed problem on null context in GCC 4.6 cp/mangle.c::write_unscoped_name , where GCC may crash when the context is null and dereferenced in TREE_CODE .
- Fixed GCC 4.4.3 crashes on ARM NEON-specific type definitions for floats. (Issue 34613)
- Fixed the STLport internal _IteWrapper::operator*() implementation where a stale stack location holding the dereferenced value was returned and caused runtime crashes. (Issue 38630)
- ARM-specific fixes:
- Fixed ARM GCC 4.4.3/4.6 g++ to not warn that the mangling of was changed in GCC 4.4. The workaround using the -Wno-psabi switch to avoid this warning is no longer required.
- Fixed an issue when a project with .arm or .neon suffixes in LOCAL_SRC_FILES also used APP_STL . With APP_STL , the ndk-build script searches for C++ files in LOCAL_SRC_FILES before adding STL header/lib paths to compilation. Modified ndk-build to filter out .arm and .neon suffixes before the search, otherwise items in LOCAL_SRC_FILES like myfile.cpp.arm.neon won’t be compiled as C++ code.
- Fixed binutils-2.21/ld.bfd to be capable of linking object from older binutils without tag_FP_arch , which was producing assertion fail error messages in GNU Binutils. (Issue 35209)
- Removed Unknown EABI object attribute 44 warning when binutils-2.19/ld links prebuilt object by newer binutils-2.21
- Fixed an issue in GNU stdc++ compilation with both -mthumb and -march=armv7-a , by modifying make-standalone-toolchain.sh to populate headers/libs in sub-directory armv7-a/thumb . (Issue 35616)
- Fixed unresolvable R_ARM_THM_CALL relocation error. (Issue 35342)
- Fixed internal compiler error at reload1.c:3633 , caused by the ARM back-end expecting the wrong operand type when sign-extend from char . (GCC Issue 50099)
- Fixed internal compiler error with negative shift amount. (GCC Issue)
- Fixed -fstack-protector for X86, which is also the default for the ndk-build x86 ABI target.
- MIPS-specific fixes:
- Fixed STLport endian-ness by setting _STLP_LITTLE_ENDIAN to 1 when compiling MIPS libstlport_* .
- Fixed GCC __builtin_unreachable issue when compiling LLVM. (GCC Issue 54369)
- Backported fix for cc1 compile process consuming 100% CPU. (GCC Issue 50380)
- GNU Debugger-specific fixes:
- Disabled Python support in gdb-7.x at build, otherwise the gdb-7.x configure function may pick up whatever Python version is available on the host and build gdb with a hard-wired dependency on a specific version of Python. (Issue 36120)
- Fixed ndk-gdb when APP_ABI contains all and matchs none of the known architectures. (Issue 35392)
- Fixed Windows pathname support, by keeping the : character if it looks like it could be part of a Windows path starting with a drive letter. (GDB Issue 12843)
- Fixed adding of hardware breakpoint support for ARM in gdbserver . (GDB Issue)
- Added fix to only read the current solibs when the linker is consistent. This change speeds up solib event handling. (Issue 37677)
- Added fix to make repeated attempts to find solib breakpoints. GDB now retries enable_break() during every call to svr4_current_sos() until it succeeds. (Change 43563)
- Fixed an issue where gdb would not stop on breakpoints placed in dlopen-ed libraries. (Issue 34856)
- Fixed SIGILL in dynamic linker when calling dlopen() , on system where /system/bin/linker is stripped of symbols and rtld_db_dlactivity() is implemented as Thumb , due to not preserving LSB of sym_addr . (Issue 37147)
Other bug fixes:
- Fixed NDK headers:
- Fixed arch-mips/include/asm/* code that was incorrectly removed from original kernel. (Change 43335)
- Replaced struct member data __unused with __linux_unused in linux/sysctl.h and linux/icmp.h to avoid conflict with #define __unused in sys/cdefs.h .
- Fixed fenv.h for enclosed C functions with __BEGIN_DECLS and __END_DECLS .
- Removed unimplemented functions in malloc.h .
- Fixed stdint.h defintion of uint64_t for ANSI compilers. (Issue 1952)
- Fixed preprocessor macros in /include/machine/* .
- Replaced link.h for MIPS with new version supporting all platforms.
- Removed linux-unistd.h
- Move GLibc-specific macros LONG_LONG_MIN , LONG_LONG_MAX and ULONG_LONG_MAX from
to
- .
- Fixed a buffer overflow in ndk-stack-parser .
- Fixed _STLP_USE_EXCEPTIONS , when not defined, to omit all declarations and uses of __Named_exception . Compiling and use of __Named_exception settings only occurs when STLport is allowed to use exceptions.
- Fixed building of Linux-only NDK packages without also building Windows code. Use the following settings to perform this type of build:
- Fixed libc.so so it does not export atexit() and __do_handler . These symbols are exported for ARM builds by the system version of the C library to support legacy native libraries. NDK-generated should never reference them directly. Instead, each shared library or executable should embed its own version of these symbols, provided by crtbegin_*.o .
If your project is linked with the -nostdlib -Wl,—no-undefined options, you must provide your own __dso_handle because crtbegin_so.o is not linked in this case. The content of __dso_handle does not matter, as shown in the following example code:
- Fixed symbol decoder for ARM used in objdump for plt entries to generate a more readable form function@plt .
- Removed the following symbols, introduced in GCC 4.6 libgcc.a , from the X86 platform libc.so library: __aeabi_idiv0 , __aeabi_ldiv0 , __aeabi_unwind_cpp_pr1 , and __aeabi_unwind_cpp_pr2 .
- Removed unused .ctors , .dtors , and .eh_frame in MIPS crt*_so.S .
- Updated ndk-gdb so that it only takes the last line of output for ndk-build DUMP_XXXX . This change ensures that if Application.mk or Android.mk print something with $(info . ) syntax, it does not get injected into the result of DUMP_XXXX . (More info)
Other changes:
- Removed arch-x86 and arch-mips headers from platforms/android-[3,4,5,8] . Those headers were incomplete, since both X86 and MIPS ABIs are only supported at API 9 or higher.
- Simplified c++ include path in standalone packages, as shown below. (Issue 35279)
- Fixed ndk-build to recognize more C++ file extensions by default: .cc .cp .cxx .cpp .CPP .c++ .C . You may still use LOCAL_CPP_EXTENSION to overwrite these extension settings.
- Fixed an issue in samples/san-angeles that caused a black screen or freeze frame on re-launch.
- Replaced deprecated APIs in NDK samples. (Issue 20017)
- hello-gl2 from android-5 to android-7
- native-activity from android-9 to android-10
- native-audio from android-9 to android-10
- native-plasma from android-9 to android-10
- Added new branding for Android executables with a simpler scheme in section .note.android.ident (defined in crtbegin_static/dynamic.o ) so that debugging tools can act accordingly. The structure member and values are defined as follows:
The previous branding options in section .note.ABI-tag are deprecated.
- Added a new script run-tests-all.sh which calls run-tests.sh and standalone/run.sh with various conditions. The script run-tests.sh runs without the —abi option, and is enhanced to compile most of the tests for all supported ABIs and run on all attached devices

The main features of this release are a new GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) 4.6 toolchain and GNU Debugger (GDB) 7.3.x which adds debugging support for the Android 4.1 (API Level 16) system image.
Important bug fixes:
- Fixed LOCAL_SHORT_COMMANDS issues on Mac OS, Windows Cygwin environments for static libraries. List file generation is faster, and it is not regenerated to avoid repeated project rebuilds.
- Fixed several issues in ndk-gdb :
- Updated tool to pass flags -e , -d and -s to adb more consistently.
- Updated tool to accept device serial names containing spaces.
- Updated tool to retrieve /system/bin/link information, so gdb on the host can set a breakpoint in __dl_rtld_db_dlactivity and be aware of linker activity (e.g., rescan solib symbols when dlopen() is called).
- Fixed ndk-build clean on Windows, which was failing to remove ./libs/*/lib*.so .
- Fixed ndk-build.cmd to return a non-zero ERRORLEVEL when make fails.
- Fixed libc.so to stop incorrectly exporting the __exidx_start and __exidx_end symbols.
- Fixed SEGV when unwinding the stack past __libc_init for ARM and MIPS.
Important changes:
- Added GCC 4.6 toolchain ( binutils 2.21 with gold and GDB 7.3.x) to co-exist with the original GCC 4.4.3 toolchain ( binutils 2.19 and GDB 6.6).
- GCC 4.6 is now the default toolchain. You may set NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=4.4.3 in Application.mk to select the original one.
- Support for the gold linker is only available for ARM and x86 architectures on Linux and Mac OS hosts. This support is disabled by default. Add LOCAL_LDLIBS += -fuse-ld=gold in Android.mk to enable it.
- Programs compiled with -fPIE require the new GDB for debugging, including binaries in Android 4.1 (API Level 16) system images.
- The binutils 2.21 ld tool contains back-ported fixes from version 2.22:
- Fixed ld —gc-sections , which incorrectly retains zombie references to external libraries. (more info).
- Fixed ARM strip command to preserve the original p_align and p_flags in GNU_RELRO section if they are valid. Without this fix, programs built with -fPIE could not be debugged. (mor e info)
- Disabled sincos() optimization for compatibility with older platforms.
- Updated build options to enable the Never eXecute (NX) bit and relro / bind_now protections by default:
- Added —noexecstack to assembler and -z noexecstack to linker that provides NX protection against buffer overflow attacks by enabling NX bit on stack and heap.
- Added -z relro and -z now to linker for hardening of internal data sections after linking to guard against security vulnerabilities caused by memory corruption. (more info: 1, 2)
- These features can be disabled using the following options:
- Disable NX protection by setting the —execstack option for the assembler and -z execstack for the linker.
- Disable hardening of internal data by setting the -z norelro and -z lazy options for the linker.
- Disable these protections in the NDK jni/Android.mk by setting the following options:
See docs/ANDROID-MK.html for more details.
Android NDK, Revision 8 (May 2012)
This release of the NDK includes support for MIPS ABI and a few additional fixes.
New features:
- Added support for the MIPS ABI, which allows you to generate machine code that runs on compatible MIPS-based Android devices. Major features for MIPS include MIPS-specific toolchains, system headers, libraries and debugging support. For more details regarding MIPS support, see docs/CPU-MIPS.html in the NDK package.
By default, code is generated for ARM-based devices. You can add mips to your APP_ABI definition in your Application.mk file to build for MIPS platforms. For example, the following line instructs ndk-build to build your code for three distinct ABIs:
Unless you rely on architecture-specific assembly sources, such as ARM assembly code, you should not need to touch your Android.mk files to build MIPS machine code.
- You can build a standalone MIPS toolchain using the —arch=mips option when calling make-standalone-toolchain.sh . See docs/STANDALONE-TOOLCHAIN.html for more details.
Note: To ensure that your applications are available to users only if their devices are capable of running them, Google Play filters applications based on the instruction set information included in your application ? no action is needed on your part to enable the filtering. Additionally, the Android system itself also checks your application at install time and allows the installation to continue only if the application provides a library that is compiled for the device’s CPU architecture.
Important bug fixes:
- Fixed a typo in GAbi++ implementation where the result of dynamic_cast (b) of base class object b to derived class D is incorrectly adjusted in the opposite direction from the base class. (Issue 28721)
- Fixed an issue in which make-standalone-toolchain.sh fails to copy libsupc++.* .
Other bug fixes:
- Fixed ndk-build.cmd to ensure that ndk-build.cmd works correctly even if the user has redefined the SHELL environment variable, which may be changed when installing a variety of development tools in Windows environments.
Android NDK, Revision 7c (April 2012)
This release of the NDK includes an important fix for Tegra2-based devices, and a few additional fixes and improvements:
Important bug fixes:
- Fixed GNU STL armeabi-v7a binaries to not crash on non-NEON devices. The files provided with NDK r7b were not configured properly, resulting in crashes on Tegra2-based devices and others when trying to use certain floating-point functions (e.g., cosf , sinf , expf ).
Important changes:
- Added support for custom output directories through the NDK_OUT environment variable. When defined, this variable is used to store all intermediate generated files, instead of $PROJECT_PATH/obj . The variable is also recognized by ndk-gdb .
- Added support for building modules with hundreds or even thousands of source files by defining LOCAL_SHORT_COMMANDS to true in your Android.mk .
This change forces the NDK build system to put most linker or archiver options into list files, as a work-around for command-line length limitations. See docs/ANDROID-MK.html for details.
Other bug fixes:
- Fixed android_getCpuCount() implementation in the cpufeatures helper library. On certain devices, where cores are enabled dynamically by the system, the previous implementation would report the total number of active cores the first time the function was called, rather than the total number of physically available cores.
Android NDK, Revision 7b (February 2012)
This release of the NDK includes fixes for native Windows builds, Cygwin and many other improvements:
Important bug fixes:
- Updated sys/atomics.h to avoid correctness issues on some multi-core ARM-based devices. Rebuild your unmodified sources with this version of the NDK and this problem should be completely eliminated. For more details, read docs/ANDROID-ATOMICS.html .
- Reverted to binutils 2.19 to fix debugging issues that appeared in NDK r7 (which switched to binutils 2.20.1).
- Fixed ndk-build on 32-bit Linux. A packaging error put a 64-bit version of the awk executable under prebuilt/linux-x86/bin in NDK r7.
- Fixed native Windows build ( ndk-build.cmd ). Other build modes were not affected. The fixes include:
- Removed an infinite loop / stack overflow bug that happened when trying to call ndk-build.cmd from a directory that was not the top of your project path (e.g., in any sub-directory of it).
- Fixed a problem where the auto-generated dependency files were ignored. This meant that updating a header didn’t trigger recompilation of sources that included it.
- Fixed a problem where special characters in files or paths, other than spaces and quotes, were not correctly handled.
- Fixed the standalone toolchain to generate proper binaries when using -lstdc++ (i.e., linking against the GNU libstdc++ C++ runtime). You should use -lgnustl_shared if you want to link against the shared library version or -lstdc++ for the static version.
See docs/STANDALONE-TOOLCHAIN.html for more details about this fix.
- Fixed gnustl_shared on Cygwin. The linker complained that it couldn’t find libsupc++.a even though the file was at the right location.
- Fixed Cygwin C++ link when not using any specific C++ runtime through APP_STL .
Other changes:
- When your application uses the GNU libstdc++ runtime, the compiler will no longer forcibly enable exceptions and RTTI. This change results in smaller code.
If you need these features, you must do one of the following:
- Enable exceptions and/or RTTI explicitly in your modules or Application.mk . (recommended)
- Define APP_GNUSTL_FORCE_CPP_FEATURES to ‘exceptions’ , ‘rtti’ or both in your Application.mk . See docs/APPLICATION-MK.html for more details.
- ndk-gdb now works properly when your application has private services running in independent processes. It debugs the main application process, instead of the first process listed by ps , which is usually a service process.
- Fixed a rare bug where NDK r7 would fail to honor the LOCAL_ARM_MODE value and always compile certain source files (but not all) to 32-bit instructions.
- STLport : Refresh the sources to match the Android platform version. This update fixes a few minor bugs:
- Fixed instantiation of an incomplete type
- Fixed minor «==» versus «=» typo
- Used memmove instead of memcpy in string::assign
- Added better handling of IsNANorINF , IsINF , IsNegNAN , etc.
For complete details, see the commit log.
- STLport : Removed 5 unnecessary static initializers from the library.
- The GNU libstdc++ libraries for armeabi-v7a were mistakenly compiled for armeabi instead. This change had no impact on correctness, but using the right ABI should provide slightly better performance.
- The cpu-features helper library was updated to report three optional x86 CPU features ( SSSE3 , MOVBE and POPCNT ). See docs/CPU-FEATURES.html for more details.
- docs/NDK-BUILD.html was updated to mention NDK_APPLICATION_MK instead of NDK_APP_APPLICATION_MK to select a custom Application.mk file.
- Cygwin: ndk-build no longer creates an empty «NUL» file in the current directory when invoked.
- Cygwin: Added better automatic dependency detection. In the previous version, it didn’t work properly in the following cases:
- When the Cygwin drive prefix was not /cygdrive .
- When using drive-less mounts, for example, when Cygwin would translate /home to \\server\subdir instead of C:\Some\Dir .
- Cygwin: ndk-build does not try to use the native Windows tools under $NDK/prebuilt/windows/bin with certain versions of Cygwin and/or GNU Make.
Android NDK, Revision 7 (November 2011)
This release of the NDK includes new features to support the Android 4.0 platform as well as many other additions and improvements:
New features
- Added official NDK APIs for Android 4.0 (API level 14), which adds the following native features to the platform:
- Added native multimedia API based on the Khronos Group OpenMAX AL? 1.0.1 standard. The new and headers allow applications targeting API level 14 to perform multimedia output directly from native code by using a new Android-specific buffer queue interface. For more details, see docs/openmaxal/index.html and http://www.khronos.org/openmax/.
- Updated the native audio API based on the Khronos Group OpenSL ES 1.0.1? standard. With API Level 14, you can now decode compressed audio (e.g. MP3, AAC, Vorbis) to PCM. For more details, see docs/opensles/index.html and http://www.khronos.org/opensles/.
- Added CCache support. To speed up large rebuilds, define the NDK_CCACHE environment variable to ccache (or the path to your ccache binary). When declared, the NDK build system automatically uses CCache when compiling any source file. For example:
Note: CCache is not included in the NDK release so you must have it installed prior to using it. For more information about CCache, see http://ccache.samba.org.
Added support for setting APP_ABI to all to indicate that you want to build your NDK modules for all the ABIs supported by your given NDK release. This means that either one of the following two lines in your Application.mk are equivalent with this release:
This also works if you define APP_ABI when calling ndk-build from the command-line, which is a quick way to check that your project builds for all supported ABIs without changing the project’s Application.mk file . For example:
- Added a LOCAL_CPP_FEATURES variable in Android.mk that allows you to declare which C++ features (RTTI or Exceptions) your module uses. This ensures that the final linking works correctly if you have prebuilt modules that depend on these features. See docs/ANDROID-MK.html and docs/CPLUSPLUS-SUPPORT.html for more details.
- Shortened paths to source and object files that are used in build commands. When invoking $NDK/ndk-build from your project path, the paths to the source, object, and binary files that are passed to the build commands are significantly shorter now, because they are passed relative to the current directory. This is useful when building projects with a lot of source files, to avoid limits on the maximum command line length supported by your host operating system. The behavior is unchanged if you invoke ndk-build from a sub-directory of your project tree, or if you define NDK_PROJECT_PATH to point to a specific directory.
Experimental features You can now build your NDK source files on Windows without Cygwin by calling the ndk-build.cmd script from the command line from your project path. The script takes exactly the same arguments as the original ndk-build script. The Windows NDK package comes with its own prebuilt binaries for GNU Make, Awk and other tools required by the build. You should not need to install anything else to get a working build system.
Important: ndk-gdb does not work on Windows, so you still need Cygwin to debug.
This feature is still experimental, so feel free to try it and report issues on the public bug database or public forum. All samples and unit tests shipped with the NDK succesfully compile with this feature.
Important bug fixes
- Imported shared libraries are now installed by default to the target installation location ( libs/ ) if APP_MODULES is not defined in your Application.mk . For example, if a top-level module foo imports a module bar , then both libfoo.so and libbar.so are copied to the install location. Previously, only libfoo.so was copied, unless you listed bar in your APP_MODULES too. If you define APP_MODULES explicitly, the behavior is unchanged.
- ndk-gdb now works correctly for activities with multiple categories in their MAIN intent filters.
- Static library imports are now properly transitive. For example, if a top-level module foo imports static library bar that imports static library zoo , the libfoo.so will now be linked against both libbar.a and libzoo.a .
Other changes
- docs/NATIVE-ACTIVITY.HTML : Fixed typo. The minimum API level should be 9, not 8 for native activities.
- docs/STABLE-APIS.html : Added missing documentation listing EGL as a supported stable API, starting from API level 9.
- download-toolchain-sources.sh : Updated to download the toolchain sources from android.googlesource.com, which is the new location for the AOSP servers.
- Added a new C++ support runtime named gabi++ . More details about it are available in the updated docs/CPLUSPLUS-SUPPORT.html .
- Added a new C++ support runtime named gnustl_shared that corresponds to the shared library version of GNU libstdc++ v3 (GPLv3 license). See more info at docs/CPLUSPLUS-SUPPORT.html
- Added support for RTTI in the STLport C++ runtimes (no support for exceptions).
- Added support for multiple file extensions in LOCAL_CPP_EXTENSION . For example, to compile both foo.cpp and bar.cxx as C++ sources, declare the following:
- Removed many unwanted exported symbols from the link-time shared system libraries provided by the NDK. This ensures that code generated with the standalone toolchain doesn’t risk to accidentally depend on a non-stable ABI symbol (e.g. any libgcc.a symbol that changes each time the toolchain used to build the platform is changed)
- Refreshed the EGL and OpenGLES Khronos headers to support more extensions. Note that this does not change the NDK ABIs for the corresponding libraries, because each extension must be probed at runtime by the client application.
The extensions that are available depend on your actual device and GPU drivers, not the platform version the device runs on. The header changes simply add new constants and types to make it easier to use the extensions when they have been probed with eglGetProcAddress() or glGetProcAddress() . The following list describes the newly supported extensions:
GLES 1.x
- GL_OES_vertex_array_object
- GL_OES_EGL_image_external
- GL_APPLE_texture_2D_limited_npot
- GL_EXT_blend_minmax
- GL_EXT_discard_framebuffer
- GL_EXT_multi_draw_arrays
- GL_EXT_read_format_bgra
- GL_EXT_texture_filter_anisotropic
- GL_EXT_texture_format_BGRA8888
- GL_EXT_texture_lod_bias
- GL_IMG_read_format
- GL_IMG_texture_compression_pvrtc
- GL_IMG_texture_env_enhanced_fixed_function
- GL_IMG_user_clip_plane
- GL_IMG_multisampled_render_to_texture
- GL_NV_fence
- GL_QCOM_driver_control
- GL_QCOM_extended_get
- GL_QCOM_extended_get2
- GL_QCOM_perfmon_global_mode
- GL_QCOM_writeonly_rendering
- GL_QCOM_tiled_rendering
GLES 2.0
- GL_OES_element_index_uint
- GL_OES_get_program_binary
- GL_OES_mapbuffer
- GL_OES_packed_depth_stencil
- GL_OES_texture_3D
- GL_OES_texture_float
- GL_OES_texture_float_linear
- GL_OES_texture_half_float_linear
- GL_OES_texture_npot
- GL_OES_vertex_array_object
- GL_OES_EGL_image_external
- GL_AMD_program_binary_Z400
- GL_EXT_blend_minmax
- GL_EXT_discard_framebuffer
- GL_EXT_multi_draw_arrays
- GL_EXT_read_format_bgra
- GL_EXT_texture_format_BGRA8888
- GL_EXT_texture_compression_dxt1
- GL_IMG_program_binary
- GL_IMG_read_format
- GL_IMG_shader_binary
- GL_IMG_texture_compression_pvrtc
- GL_IMG_multisampled_render_to_texture
- GL_NV_coverage_sample
- GL_NV_depth_nonlinear
- GL_QCOM_extended_get
- GL_QCOM_extended_get2
- GL_QCOM_writeonly_rendering
- GL_QCOM_tiled_rendering
EGL
- EGL_ANDROID_recordable
- EGL_NV_system_time
Android NDK, Revision 6b (August 2011)
This release of the NDK does not include any new features compared to r6. The r6b release addresses the following issues in the r6 release:
Important bug fixes
- Fixed the build when APP_ABI=»armeabi x86″ is used for multi-architecture builds.
- Fixed the location of prebuilt STLport binaries in the NDK release package. A bug in the packaging script placed them in the wrong location.
- Fixed atexit() usage in shared libraries with the x86standalone toolchain.
- Fixed make-standalone-toolchain.sh —arch=x86 . It used to fail to copy the proper GNU libstdc++ binaries to the right location.
- Fixed the standalone toolchain linker warnings about missing the definition and size for the __dso_handle symbol (ARM only).
- Fixed the inclusion order of $(SYSROOT)/usr/include for x86 builds. See the bug for more information.
- Fixed the definitions of ptrdiff_t and size_t in x86-specific systems when they are used with the x86 standalone toolchain.
Android NDK, Revision 6 (July 2011)
This release of the NDK includes support for the x86 ABI and other minor changes. For detailed information describing the changes in this release, read the CHANGES.HTML document included in the NDK package.
General notes:
- Adds support for the x86 ABI, which allows you to generate machine code that runs on compatible x86-based Android devices. Major features for x86 include x86-specific toolchains, system headers, libraries and debugging support. For all of the details regarding x86 support, see docs/CPU-X86.html in the NDK package.
By default, code is generated for ARM-based devices, but you can add x86 to your APP_ABI definition in your Application.mk file to build for x86 platforms. For example, the following line instructs ndk-build to build your code for three distinct ABIs:
Unless you rely on ARM-based assembly sources, you shouldn’t need to touch your Android.mk files to build x86 machine code.
- You can build a standalone x86 toolchain using the —toolchain=x86-4.4.3 option when calling make-standalone-toolchain.sh . See docs/STANDALONE-TOOLCHAIN.html for more details.
- The new ndk-stack tool lets you translate stack traces in logcat that are generated by native code. The tool translates instruction addresses into a readable format that contains things such as the function, source file, and line number corresponding to each stack frame. For more information and a usage example, see docs/NDK-STACK.html .
Other changes: arm-eabi-4.4.0 , which had been deprecated since NDK r5, has been removed from the NDK distribution.

This release of the NDK does not include any new features compared to r5b. The r5c release addresses the following problems in the r5b release:
: Fixed the definition of PTHREAD_RWLOCK_INITIALIZER for API level 9 (Android 2.3) and higher.

This release of the NDK does not include any new features compared to r5. The r5b release addresses the following problems in the r5 release:
- The r5 binaries required glibc 2.11, but the r5b binaries are generated with a special toolchain that targets glibc 2.7 or higher instead. The Linux toolchain binaries now run on Ubuntu 8.04 or higher.
- Fixes a compiler bug in the arm-linux-androideabi-4.4.3 toolchain. The previous binary generated invalid thumb instruction sequences when dealing with signed chars.
- Adds missing documentation for the «gnustl_static» value for APP_STL, that allows you to link against a static library version of GNU libstdc++. the
- Fixed the following ndk-build issues:
- A bug that created inconsistent dependency files when a compilation error occured on Windows. This prevented a proper build after the error was fixed in the source code.
- A Cygwin-specific bug where using very short paths for the Android NDK installation or the project path led to the generation of invalid dependency files. This made incremental builds impossible.
- A typo that prevented the cpufeatures library from working correctly with the new NDK toolchain.
- Builds in Cygwin are faster by avoiding calls to cygpath -m from GNU Make for every source or object file, which caused problems with very large source trees. In case this doesn’t work properly, define NDK_USE_CYGPATH=1 in your environment to use cygpath -m again.
- The Cygwin installation now notifies the user of invalid installation paths that contain spaces. Previously, an invalid path would output an error that complained about an incorrect version of GNU Make, even if the right one was installed.
- Fixed a typo that prevented the NDK_MODULE_PATH environment variable from working properly when it contained multiple directories separated with a colon.
- The prebuilt-common.sh script contains fixes to check the compiler for 64-bit generated machine code, instead of relying on the host tag, which allows the 32-bit toolchain to rebuild properly on Snow Leopard. The toolchain rebuild scripts now also support using a 32-bit host toolchain.
- A missing declaration for INET_ADDRSTRLEN was added to .
- Missing declarations for IN6_IS_ADDR_MC_NODELOCAL and IN6_IS_ADDR_MC_GLOBAL were added to .
- ‘asm’ was replaced with ‘__asm__’ in to allow compilation with -std=c99 .

This release of the NDK includes many new APIs, most of which are introduced to support the development of games and similar applications that make extensive use of native code. Using the APIs, developers have direct native access to events, audio, graphics and window management, assets, and storage. Developers can also implement the Android application lifecycle in native code with help from the new NativeActivity class. For detailed information describing the changes in this release, read the CHANGES.HTML document included in the downloaded NDK package.

Includes fixes for several issues in the NDK build and debugging scripts — if you are using NDK r4, we recommend downloading the NDK r4b build. For detailed information describing the changes in this release, read the CHANGES.TXT document included in the downloaded NDK package.
General notes:
- Provides a simplified build system through the new ndk-build build command.
- Adds support for easy native debugging of generated machine code on production devices through the new ndk-gdb command.
- Adds a new Android-specific ABI for ARM-based CPU architectures, armeabi-v7a . The new ABI extends the existing armeabi ABI to include these CPU instruction set extensions:
- Thumb-2 instructions
- VFP hardware FPU instructions (VFPv3-D16)
- Optional support for ARM Advanced SIMD (NEON) GCC intrinsics and VFPv3-D32. Supported by devices such as Verizon Droid by Motorola, Google Nexus One, and others.
- Adds a new cpufeatures static library (with sources) that lets your app detect the host device’s CPU features at runtime. Specifically, applications can check for ARMv7-A support, as well as VFPv3-D32 and NEON support, then provide separate code paths as needed.
- Adds a sample application, hello-neon , that illustrates how to use the cpufeatures library to check CPU features and then provide an optimized code path using NEON instrinsics, if supported by the CPU.
- Lets you generate machine code for either or both of the instruction sets supported by the NDK. For example, you can build for both ARMv5 and ARMv7-A architectures at the same time and have everything stored to your application’s final .apk .
- To ensure that your applications are available to users only if their devices are capable of running them, Google Play now filters applications based on the instruction set information included in your application — no action is needed on your part to enable the filtering. Additionally, the Android system itself also checks your application at install time and allows the installation to continue only if the application provides a library that is compiled for the device’s CPU architecture.
- Adds support for Android 2.2, including a new stable API for accessing the pixel buffers of Bitmap objects from native code.


Originally released as «Android 1.6 NDK, Release 1».
General notes:
- Adds OpenGL ES 1.1 native library support.
- Adds a sample application, san-angeles , that renders 3D graphics through the native OpenGL ES APIs, while managing activity lifecycle with a GLSurfaceView object.

Originally released as «Android 1.5 NDK, Release 1».
General notes:
- Includes compiler support (GCC) for ARMv5TE instructions, including Thumb-1 instructions.
- Includes system headers for stable native APIs, documentation, and sample applications.
System and Software Requirements
The sections below describe the system and software requirements for using the Android NDK, as well as platform compatibility considerations that affect appplications using libraries produced with the NDK.
The Android SDK
- A complete Android SDK installation (including all dependencies) is required.
- Android 1.5 SDK or later version is required.
Supported operating systems
- Windows XP (32-bit) or Vista (32- or 64-bit)
- Mac OS X 10.4.8 or later (x86 only)
- Linux (32 or 64-bit; Ubuntu 8.04, or other Linux distributions using GLibc 2.7 or later)
Required development tools
- For all development platforms, GNU Make 3.81 or later is required. Earlier versions of GNU Make might work but have not been tested.
- A recent version of awk (either GNU Awk or Nawk) is also required.
- For Windows, Cygwin 1.7 or higher is required. The NDK will not work with Cygwin 1.5 installations.
Android platform compatibility
- The native libraries created by the Android NDK can only be used on devices running specific minimum Android platform versions. The minimum required platform version depends on the CPU architecture of the devices you are targeting. The following table details which Android platform versions are compatible with native code developed for specific CPU architectures.
Native Code CPU Architecture Used Compatible Android Platform(s) ARM, ARM-NEON Android 1.5 (API Level 3) and higher x86 Android 2.3 (API Level 9) and higher MIPS Android 2.3 (API Level 9) and higher
These requirements mean you can use native libraries produced with the NDK in applications that are deployable to ARM-based devices running Android 1.5 or later. If you are deploying native libraries to x86 and MIPS-based devices, your application must target Android 2.3 or later.
| OpenGL ES Version Used | Compatible Android Platform(s) | Required uses-sdk Attribute |
|---|---|---|
| OpenGL ES 1.1 | Android 1.6 (API Level 4) and higher | android:minSdkVersion=»4″ |
| OpenGL ES 2.0 | Android 2.0 (API Level 5) and higher | android:minSdkVersion=»5″ |
For more information about API Level and its relationship to Android platform versions, see Android API Levels.
Additionally, an application using the OpenGL ES APIs should declare a element in its manifest, with an android:glEsVersion attribute that specifies the minimum OpenGl ES version required by the application. This ensures that Google Play will show your application only to users whose devices are capable of supporting your application. For example:
For more information, see the documentation.
Installing the NDK
Installing the NDK on your development computer is straightforward and involves extracting the NDK from its download package.
Before you get started make sure that you have downloaded the latest Android SDK and upgraded your applications and environment as needed. The NDK is compatible with older platform versions but not older versions of the SDK tools. Also, take a moment to review the System and Software Requirements for the NDK, if you haven’t already.
To install the NDK, first download the appropriate package from the table at the top of this page. Then, follow the procedure for your development platform:
- On Linux and Mac OS X (Darwin):
- Download the appropriate package from this page.
- Open a terminal window.
- Go to the directory to which you downloaded the package.
- Run chmod a+x on the downloaded package.
- Execute the package. For example:
The folder containing the NDK extracts itself.
Note that you can also use a program like 7z to extract the package.
- Download the appropriate package from this page.
- Navigate to the folder to which you downloaded the package.
- Double-click the downloaded file. The folder containing the NDK extracts itself.
When uncompressed, the NDK files are contained in a directory called android-ndk- . You can rename the NDK directory if necessary and you can move it to any location on your computer. This documentation refers to the NDK directory as .
You are now ready to start working with the NDK.
Getting Started with the NDK
Once you’ve installed the NDK successfully, take a few minutes to read the documentation included in the NDK. You can find the documentation in the /docs/ directory. In particular, please read the OVERVIEW.HTML document completely, so that you understand the intent of the NDK and how to use it.
If you used a previous version of the NDK, take a moment to review the list of NDK changes in the CHANGES.HTML document.
Here’s the general outline of how you work with the NDK tools:
- Place your native sources under
/jni/Android.mk to describe your native sources to the NDK build system
Optional: Create
/jni/Application.mk .
Build your native code by running the ‘ndk-build’ script from your project’s directory. It is located in the top-level NDK directory:
The build tools copy the stripped, shared libraries needed by your application to the proper location in the application’s project directory.
For complete information on all of the steps listed above, please see the documentation included with the NDK package.
Using the NDK
The Android framework provides two ways to use native code:
- Write your application using the Android framework and use JNI to access the APIs provided by the Android NDK. This technique allows you to take advantage of the convenience of the Android framework, but still allows you to write native code when necessary. If you use this approach, your application must target specific, minimum Android platform levels, see Android platform compatibility for more information.
Write a native activity, which allows you to implement the lifecycle callbacks in native code. The Android SDK provides the NativeActivity class, which is a convenience class that notifies your native code of any activity lifecycle callbacks ( onCreate() , onPause() , onResume() , etc). You can implement the callbacks in your native code to handle these events when they occur. Applications that use native activities must be run on Android 2.3 (API Level 9) or later.
You cannot access features such as Services and Content Providers natively, so if you want to use them or any other framework API, you can still write JNI code to do so.
Contents of the NDK
The NDK contains the APIs, documentation, and sample applications that help you write your native code. Specifically:
- A set of tools and build files used to generate native code libraries from C and C++ sources
- A way to embed the corresponding native libraries into an application package file ( .apk ) that can be deployed on Android devices
- A set of native system headers and libraries that will be supported in all future versions of the Android platform, starting from Android 1.5. Applications that use native activities must be run on Android 2.3 or later.
- Documentation, samples, and tutorials
The latest release of the NDK supports the following instruction sets:
- ARMv5TE, including Thumb-1 instructions (see docs/CPU-ARCH-ABIS.html for more information)
- ARMv7-A, including Thumb-2 and VFPv3-D16 instructions, with optional support for NEON/VFPv3-D32 instructions (see docs/CPU-ARM-NEON.html for more information)
- x86 instructions (see docs/CPU-X86.html for more information)
- MIPS instructions (see docs/CPU-MIPS.html for more information)
ARMv5TE machine code will run on all ARM-based Android devices. ARMv7-A will run only on devices such as the Verizon Droid or Google Nexus One that have a compatible CPU. The main difference between the two instruction sets is that ARMv7-A supports hardware FPU, Thumb-2, and NEON instructions. You can target either or both of the instruction sets — ARMv5TE is the default, but switching to ARMv7-A is as easy as adding a single line to the application’s Application.mk file, without needing to change anything else in the file. You can also build for both architectures at the same time and have everything stored in the final .apk . Complete information is provided in the CPU-ARCH-ABIS.HTML in the NDK package.
The NDK provides stable headers for libc (the C library), libm (the Math library), OpenGL ES (3D graphics library), the JNI interface, and other libraries, as listed in the Development tools section.
Development tools
The NDK includes a set of cross-toolchains (compilers, linkers, etc.) that can generate native ARM binaries on Linux, OS X, and Windows (with Cygwin) platforms.
It provides a set of system headers for stable native APIs that are guaranteed to be supported in all later releases of the platform:
- libc (C library) headers
- libm (math library) headers
- JNI interface headers
- libz (Zlib compression) headers
- liblog (Android logging) header
- OpenGL ES 1.1 and OpenGL ES 2.0 (3D graphics libraries) headers
- libjnigraphics (Pixel buffer access) header (for Android 2.2 and above).
- A Minimal set of headers for C++ support
- OpenSL ES native audio libraries
- Android native application APIS
The NDK also provides a build system that lets you work efficiently with your sources, without having to handle the toolchain/platform/CPU/ABI details. You create very short build files to describe which sources to compile and which Android application will use them — the build system compiles the sources and places the shared libraries directly in your application project.
Important: With the exception of the libraries listed above, native system libraries in the Android platform are not stable and may change in future platform versions. Your applications should only make use of the stable native system libraries provided in this NDK.
Documentation
The NDK package includes a set of documentation that describes the capabilities of the NDK and how to use it to create shared libraries for your Android applications. In this release, the documentation is provided only in the downloadable NDK package. You can find the documentation in the /docs/ directory. Included are these files (partial listing):
- INSTALL.HTML — describes how to install the NDK and configure it for your host system
- OVERVIEW.HTML — provides an overview of the NDK capabilities and usage
- ANDROID-MK.HTML — describes the use of the Android.mk file, which defines the native sources you want to compile
- APPLICATION-MK.HTML — describes the use of the Application.mk file, which describes the native sources required by your Android application
- CPLUSPLUS-SUPPORT.HTML — describes the C++ support provided in the Android NDK
- CPU-ARCH-ABIS.HTML — a description of supported CPU architectures and how to target them.
- CPU-FEATURES.HTML — a description of the cpufeatures static library that lets your application code detect the target device’s CPU family and the optional features at runtime.
- CHANGES.HTML — a complete list of changes to the NDK across all releases.
- DEVELOPMENT.HTML — describes how to modify the NDK and generate release packages for it
- HOWTO.HTML — information about common tasks associated with NDK development
- IMPORT-MODULE.HTML — describes how to share and reuse modules
- LICENSES.HTML — information about the various open source licenses that govern the Android NDK
- NATIVE-ACTIVITY.HTML — describes how to implement native activities
- NDK-BUILD.HTML — describes the usage of the ndk-build script
- NDK-GDB.HTML — describes how to use the native code debugger
- PREBUILTS.HTML — information about how shared and static prebuilt libraries work
- STANDALONE-TOOLCHAIN.HTML — describes how to use Android NDK toolchain as a standalone compiler (still in beta).
- SYSTEM-ISSUES.HTML — known issues in the Android system images that you should be aware of, if you are developing using the NDK.
- STABLE-APIS.HTML — a complete list of the stable APIs exposed by headers in the NDK.
Additionally, the package includes detailed information about the «bionic» C library provided with the Android platform that you should be aware of, if you are developing using the NDK. You can find the documentation in the /docs/system/libc/ directory:
- OVERVIEW.HTML — provides an overview of the «bionic» C library and the features it offers.
Sample apps
The NDK includes sample applications that illustrate how to use native code in your Android applications:
- hello-jni — a simple application that loads a string from a native method implemented in a shared library and then displays it in the application UI.
- two-libs — a simple application that loads a shared library dynamically and calls a native method provided by the library. In this case, the method is implemented in a static library imported by the shared library.
- san-angeles — a simple application that renders 3D graphics through the native OpenGL ES APIs, while managing activity lifecycle with a GLSurfaceView object.
- hello-gl2 — a simple application that renders a triangle using OpenGL ES 2.0 vertex and fragment shaders.
- hello-neon — a simple application that shows how to use the cpufeatures library to check CPU capabilities at runtime, then use NEON intrinsics if supported by the CPU. Specifically, the application implements two versions of a tiny benchmark for a FIR filter loop, a C version and a NEON-optimized version for devices that support it.
- bitmap-plasma — a simple application that demonstrates how to access the pixel buffers of Android Bitmap objects from native code, and uses this to generate an old-school «plasma» effect.
- native-activity — a simple application that demonstrates how to use the native-app-glue static library to create a native activity
- native-plasma — a version of bitmap-plasma implemented with a native activity.
For each sample, the NDK includes the corresponding C source code and the necessary Android.mk and Application.mk files. There are located under /samples/ / and their source code can be found under /samples/ /jni/ .
You can build the shared libraries for the sample apps by going into /samples/ / then calling the ndk-build command. The generated shared libraries will be located under /samples/ /libs/armeabi/ for (ARMv5TE machine code) and/or /samples/ /libs/armeabi-v7a/ for (ARMv7 machine code).
Next, build the sample Android applications that use the shared libraries:
- If you are developing in Eclipse with ADT, use the New Project Wizard to create a new Android project for each sample, using the «Import from Existing Source» option and importing the source from /samples/ / . Then, set up an AVD, if necessary, and build/run the application in the emulator.
- If you are developing with Ant, use the android tool to create the build file for each of the sample projects at /samples/ / . Then set up an AVD, if necessary, build your project in the usual way, and run it in the emulator.
For more information about developing with the Android SDK tools and what you need to do to create, build, and run your applications, see the Overview section for developing on Android.
Exploring the hello-jni Sample
The hello-jni sample is a simple demonstration on how to use JNI from an Android application. The HelloJni activity receives a string from a simple C function and displays it in a TextView.
The main components of the sample include:
- The familiar basic structure of an Android application (an AndroidManifest.xml file, a src/ and res directories, and a main activity)
- A jni/ directory that includes the implemented source file for the native code as well as the Android.mk file
- A tests/ directory that contains unit test code.
- Create a new project in Eclipse from the existing sample source or use the android tool to update the project so it generates a build.xml file that you can use to build the sample.
- In Eclipse:
- Click File > New Android Project.
- Select the Create project from existing source radio button.
- Select any API level above Android 1.5.
- In the Location field, click Browse. and select the /samples/hello-jni directory.
- Click Finish.
- On the command line:
- Change to the /samples/hello-jni directory.
- Run the following command to generate a build.xml file:
- In Eclipse:
- Compile the native code using the ndk-build command.
- Build and install the application as you would a normal Android application. If you are using Eclipse, run the application to build and install it on a device. If you are using Ant, run the following commands from the project directory:
When you run the application on the device, the string Hello JNI should appear on your device. You can explore the rest of the samples that are located in the /samples directory for more examples on how to use the JNI.
Exploring the native-activity Sample Application
The native-activity sample provided with the Android NDK demonstrates how to use the android_native_app_glue static library. This static library makes creating a native activity easier by providing you with an implementation that handles your callbacks in another thread, so you do not have to worry about them blocking your main UI thread. The main parts of the sample are described below:
Источник



