- Работа с файловой системой
- Чтение и сохранение файлов
- Полный список
- Внутренняя память
- SD карта
- Android Read Write Internal Storage File Example
- 1. Android Read Write Data To Internal File.
- 1.1 Where Your Android App Internal Data File Saved In?
- 1.2 Read Write Android File Code Snippets.
- 2. Android Internal File Operation Example.
- 2.1 Layout XML File.
- 2.2 Activity Java File.
- 3. Question & Answer.
- 3.1 Can not write text file to android internal storage.
Работа с файловой системой
Чтение и сохранение файлов
Работа с настройками уровня activity и приложения позволяет сохранить небольшие данные отдельных типов (string, int), но для работы с большими массивами данных, такими как графически файлы, файлы мультимедиа и т.д., нам придется обращаться к файловой системе.
ОС Android построена на основе Linux. Этот факт находит свое отражение в работе с файлами. Так, в путях к файлам в качестве разграничителя в Linux использует слеш «/», а не обратный слеш «\» (как в Windows). А все названия файлов и каталогов являются регистрозависимыми, то есть «data» это не то же самое, что и «Data».
Приложение Android сохраняет свои данные в каталоге /data/data/ / и, как правило, относительно этого каталога будет идти работа.
Для работы с файлами абстрактный класс android.content.Context определяет ряд методов:
boolean deleteFile (String name) : удаляет определенный файл
String[] fileList () : получает все файлы, которые содержатся в подкаталоге /files в каталоге приложения
File getCacheDir() : получает ссылку на подкаталог cache в каталоге приложения
File getDir(String dirName, int mode) : получает ссылку на подкаталог в каталоге приложения, если такого подкаталога нет, то он создается
File getExternalCacheDir() : получает ссылку на папку /cache внешней файловой системы устройства
File getExternalFilesDir(String type) : получает ссылку на каталог /files внешней файловой системы устройства
File getFileStreamPath(String filename) : возвращает абсолютный путь к файлу в файловой системе
FileInputStream openFileInput(String filename) : открывает файл для чтения
FileOutputStream openFileOutput (String name, int mode) : открывает файл для записи
Все файлы, которые создаются и редактируются в приложении, как правило, хранятся в подкаталоге /files в каталоге приложения.
Для непосредственного чтения и записи файлов применяются также стандартные классы Java из пакета java.io.
Итак, применим функционал чтения-записи файлов в приложении. Пусть у нас будет следующая примитивная разметка layout:
Поле EditText предназначено для ввода текста, а TextView — для вывода ранее сохраненного текста. Для сохранения и восстановления текста добавлены две кнопки.
Теперь в коде Activity пропишем обработчики кнопок с сохранением и чтением файла:
При нажатии на кнопку сохранения будет создаваться поток вывода FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput(FILE_NAME, MODE_PRIVATE)
В данном случае введенный текст будет сохраняться в файл «content.txt». При этом будет использоваться режим MODE_PRIVATE
Система позволяет создавать файлы с двумя разными режимами:
MODE_PRIVATE : файлы могут быть доступны только владельцу приложения (режим по умолчанию)
MODE_APPEND : данные могут быть добавлены в конец файла
Поэтому в данном случае если файл «content.txt» уже существует, то он будет перезаписан. Если же нам надо было дописать файл, тогда надо было бы использовать режим MODE_APPEND:
Для чтения файла применяется поток ввода FileInputStream :
Подробнее про использование потоков ввода-вывода можно прочитать в руководстве по Java: https://metanit.com/java/tutorial/6.3.php
В итоге после нажатия кнопки сохранения весь текст будет сохранен в файле /data/data/название_пакета/files/content.txt
Где физически находится созданный файл? Чтобы увидеть его на подключенном устройстве перейдем в Android Stud в меню к пункту View -> Tool Windows -> Device File Explorer
После этого откроектся окно Device File Explorer для просмотра файловой системы устройства. И в папке data/data/[название_пакета_приложения]/files мы сможем найти сохраненный файл.
Источник
Полный список
— работаем с файлами
Работа с файлами в Android не сильно отличается от таковой в Java. В этом уроке рассмотрим, как записать/прочесть файл во внутреннюю память и на SD-карту.
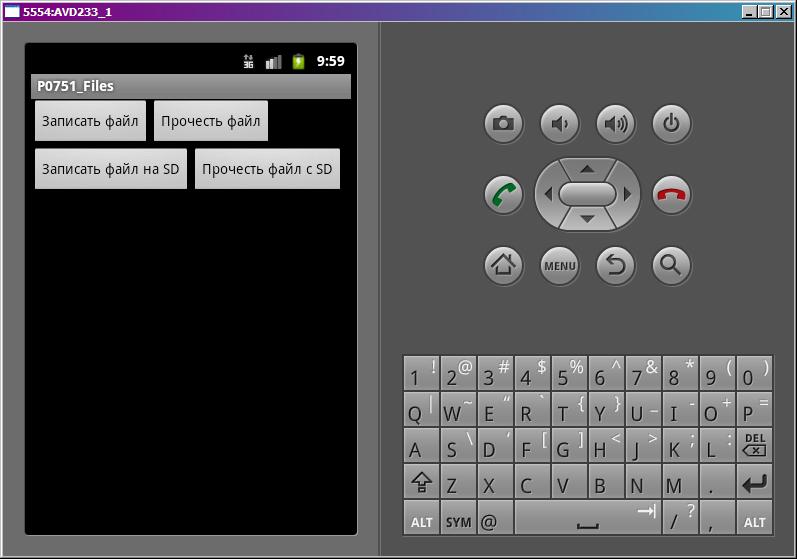
Project name: P0751_Files
Build Target: Android 2.3.3
Application name: Files
Package name: ru.startandroid.develop.p0751files
Create Activity: MainActivity
Рисуем экран main.xml:
4 кнопки, смысл которых понятен по тексту на них.
В onclick обрабатываем нажатия 4-х кнопок и вызываем соответствующие методы.
writeFile – запись файла во внутреннюю память. Используется метод openFileOutput, который на вход берет имя файла и режим записи: MODE_PRIVATE – файл доступен только этому приложению, MODE_WORLD_READABLE – файл доступен для чтения всем, MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE — файл доступен для записи всем, MODE_APPEND – файл будет дописан, а не начат заново.
readFile – чтение файла из внутренней памяти. Используем метод openFileInput, принимающий на вход имя файла. Здесь и в методе записи внутреннего файла вы можете задать только имя файла, а каталог для ваших файлов вам уже выделен.
writeFileSD – запись файла на SD. Используем метод getExternalStorageState для получения состояния SD-карты. Здесь можно посмотреть какие бывают состояния. Нам нужно MEDIA_MOUNTED – когда SD-карта вставлена и готова к работе. Далее мы получаем путь к SD-карте (метод getExternalStorageDirectory), добавляем свой каталог и имя файла, создаем каталог и пишем данные в файл.
readFileSD – чтение файла с SD. Все аналогично предыдущему методу, только файл не пишем, а читаем.
Осталось в манифест добавить разрешение на работу с файлами на SD — android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE.
Все сохраним и запустим. Видим экран с 4-мя кнопками:
Внутренняя память
Жмем кнопку Записать файл. Видим в логе:
Проверим. Идем в File Explorer (Window > Show View > Other > Android > File Explorer) и открываем там папку data/data/ru.startandroid.develop.p0751files/files и видим там наш файл file.
Возвращаемся в эмулятор. Жмем Прочесть файл и в логе видим:
Это тот текст, который мы записывали в файл.
SD карта
Теперь жмем Записать файл на SD.
Файл записан на SD: /mnt/sdcard/MyFiles/fileSD
Проверяем. Идем в FileExplorer и открываем там папку mnt/sdcard/MyFiles/ а в ней файл fileSD.
Возвращаемся в эмулятор и жмем кнопку Прочесть файл с SD. В логе видим:
Содержимое файла на SD
Этот текст мы и записывали.
mnt/sdcard — обычно этот путь ведет к содержимому SD-карты. Возможно у вас он будет другой.
В общем, при работе с файлами на SD вы используете стандартные java механизмы. А при работе с внутренним хранилищем для удобства можно использовать методы-оболочки от Activity:
openFileOutput – открыть файл на запись
openFileInput – открыть файл на чтение
И есть метод getFilesDir – возвращает объект File, соответствующий каталогу для файлов вашей программы. Используйте его, чтобы работать напрямую, без методов-оболочек.
Подробности работы в java с файловой системой я здесь описывать не буду. На нашем форуме пользователь SKR сделал отличную памятку по работе с файлами. Скорее всего, вы найдете там все что нужно.
Если у вас проверка SD-карты показывает, что карта недоступна (см. лог), то убедитесь в свойствах AVD, что у вас для SDCard указан Size или File. Если указаны, то попробуйте перезапустить AVD.
На следующем уроке:
— создаем экран с вкладками
— используем иконку в названии вкладки
— используем обработчик перехода между вкладками
Присоединяйтесь к нам в Telegram:
— в канале StartAndroid публикуются ссылки на новые статьи с сайта startandroid.ru и интересные материалы с хабра, medium.com и т.п.
— в чатах решаем возникающие вопросы и проблемы по различным темам: Android, Kotlin, RxJava, Dagger, Тестирование
— ну и если просто хочется поговорить с коллегами по разработке, то есть чат Флудильня
— новый чат Performance для обсуждения проблем производительности и для ваших пожеланий по содержанию курса по этой теме
Источник
Android Read Write Internal Storage File Example
Android data can be saved in internal storage ( ROM ), external storage(SD card), shared preferences, or SQLite database. This article will introduce how to read and write data in internal storage via a java file.
1. Android Read Write Data To Internal File.
- Android is based on Linux, the android file system is Linux-based also.
- Android studio provides the android device monitor tool for you to monitor and transfer files between Android devices and your PC. Please refer Android Device Monitor Cannot Open Data Folder Resolve Method.
1.1 Where Your Android App Internal Data File Saved In?
- All android app internal data files are saved in the /data/data/ folder.
- In this example, my app data internal file is saved in /data/data/com.dev2qa.example folder. You can watch the youtube video https://youtu.be/AJBgBBMKO5w to see the android app’s internal data files saved directory.
- From the youtube video, we can see that there are files and cache subfolders under the package name folder.
- files folder — android.content.Context’sgetFilesDir() method can return this folder. This folder is used to save general files.
- cache folder — android.content.Context’sgetCacheDir() method can return this folder. This folder is used to save cached files.
- When the device’s internal storage space is low, cache files will be removed by android os automatically to make internal storage space bigger. Generally, you need to delete the unused cache files in the source code timely, the total cache file size is better not more than 1 MB.
1.2 Read Write Android File Code Snippets.
- Android application is written in java, so the file operation uses java classes also.
- Below are the code snippets for read/write data from/to the file in android.
1.2.1 Read Android File In The Package files Folder.
- Call android.content.Context‘s openFileInput(userEmalFileName) method to get FileInputStream object.
- The input parameter is just the file name.
- This file should be saved in the files folder.
- Then use the FileInputStream object to read data.
1.2.2 Read Android File In The Package cache Folder.
- The below source code will read the android files in the package cache folder.
1.2.3 Write File To The Package files Folder.
- Method 1: Use Context’s getFilesDir() to get the package files folder, then write file into it.
- Method 2: Call Context’s openFileOutput(userEmalFileName, Context.MODE_APPEND) method to get FileOutputStream object.
- The first parameter is the file name, the second parameter’s value can be one of the below values.
- Context.MODE_PRIVATE: This means this file can only be read/write by this android app that creates it. This mode will overwrite an existing file, if not exist then create it.
- Context.MODE_APPEND: This mode will append data to an existing file. If not exist it will create a new one.
1.2.4 Write File To The Package cache Folder.
- Use Context’s getCacheDir() to get cache folder.
2. Android Internal File Operation Example.
- You can watch the example demo video on youtube https://youtu.be/HqbRR6TQVvY.
- There are one input text box and five buttons on the android example app main screen.
- The buttons’ function can be easily understood by the button’s label text.
- The button’s label text is WRITE TO FILE, READ FROM FILE, CREATE CACHED FILE, READ CACHED FILE, CREATE TEMP FILE from up to bottom.
- After you run the example, you can see the below files in the android device monitor. You can pull down the file to your local PC to see the file contents also.
- If you meet any problem in using the android device monitor, please refer to Android Device Monitor Cannot Open Data Folder Resolve Method. This article will tell you how to resolve those errors.
2.1 Layout XML File.
- activity_write_read_file.xml
2.2 Activity Java File.
- WriteReadFileActivity.java
- If you meet the error message Instant Run requires ‘Tools | Android | Enable ADB integration’ to be enabled when you run this example. You can click Tools —> Android menu, and check Enable ADB integration option in the popup menu to resolve it.
3. Question & Answer.
3.1 Can not write text file to android internal storage.
- My android app is very simple, I just want to write some text to a file and save the text file to the internal storage. I follow this article to write source code, but I can not find the text file in both the android physical device and the simulator. I can not read the file content out in java source code. Can you tell me why? Thanks a lot.
- Android 11 has announced a new policy when you want to manage storage. The internal storage root folder can not be used to store files unless you add the below permission in your AndroidManifest.xml file.
And when you run the application, you can request this permission to the user with the below code.
Then you can process user response in the onRequestPermissionsResult() method in the activity.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Thanks.Great Article Guys.
I am a beginner of android programming, and I want to write some data to a file saved in android internal storage device. I found this article and write the source code as below. But I found after I write the data to internal storage file with the method writeToFile, I can not read the written file content in android internal storage device in the readFileButton method. Can you tell me what wrong in my source code? Thanks a lot.
public void writeToFile(String fileName, String fileContent)<
try <
// Create a FileOutputStream object with the provided file name.
FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput(fileName , Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
// Write the file content to the file.
fos.write(fileContent.getBytes());
// Close the file output stream to flush the data to the file.
fos.close();
> catch (Exception e) <
e.printStackTrace();
>
>
public void readFileButton(View v) <
// Read the file text content.
try <
// Define the internal stored file name.
String fileName = “test.txt”;
// Create a FileInputStream object.
FileInputStream fis =openFileInput(fileName);
// Create a InputStreamReader object.
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
// Define the char array.
char[] ib= new char[1024];
// Store read out file data.
String fileData = “”;
// Read 1024 character data from file.
int charRead = isr.read(ib);
// While not end of the file.
while (charRead>0) <
// Convert the char array to a string object.
String readstring = String.copyValueOf(inputBuffer,0,charRead);
// Add the read out file data.
fileData +=readstring;
Источник