- Tek Eye
- Android Versions by Name, Number, Availability and API Level
- List of Android Versions and Their Names, API Level and Dates
- Do you have a question or comment about this article?
- Android Version History – Names and Features from Cupcake to Android 11
- Android Version Names and Features
- Android Operating System List
- 1. Android 1.1
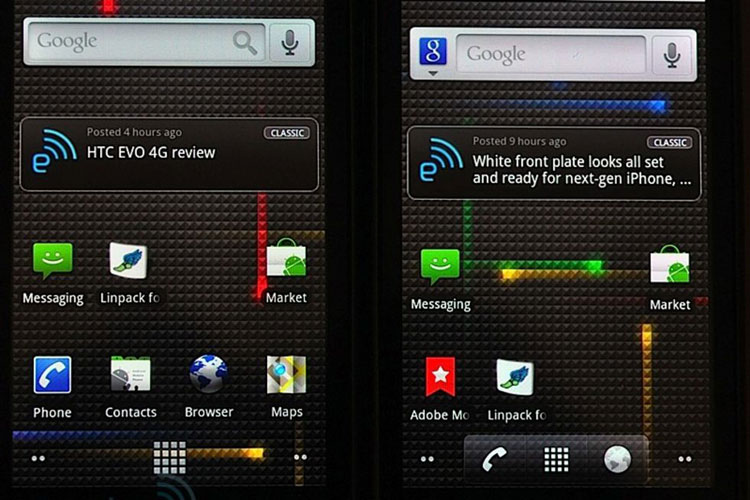
- 2. Android 1.5 Cupcake
- 3. Android 1.6 Donut
- 4. Android 2.0 and 2.1 Eclair
- 5. Android 2.2 Froyo
- 6 Android 2.3 Gingerbread
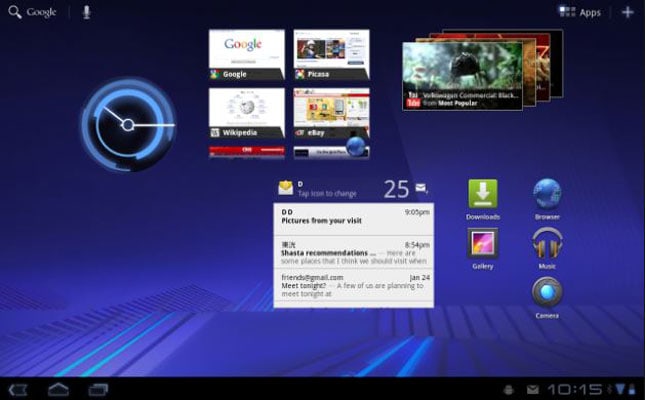
- 7. Android 3.0 and 3.1 Honeycomb
- 8. Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich
- 9. Android 4.1, 4.2 and 4.3 Jellybean
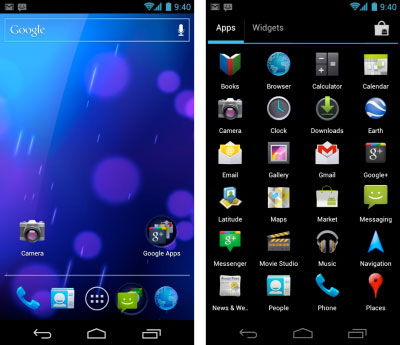
- 10. Android 4.4 KitKat
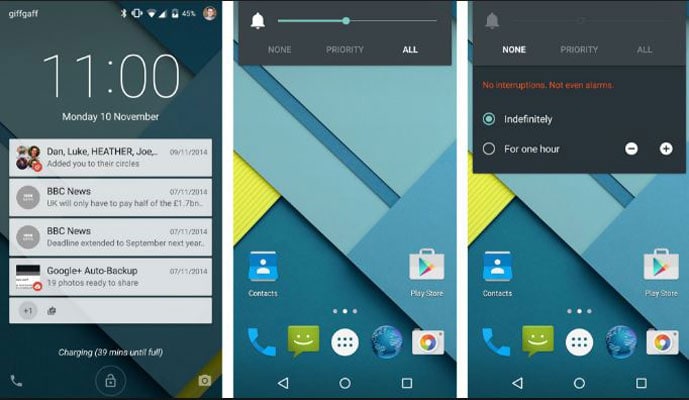
- 11. Android 5.0 Lollipop
- 12. Android 6.0 Marshmallow
- 13. Android 7.0 Nougat
- 14. Android 8.0 Oreo
- 15. Android 9.0 Pie
- 16. Android 10
- 17. Android 11
- Conclusion – Android Version Names and Features
Tek Eye
The table in this article lists all the different versions of Android, starting with the earliest Application Programming Interface (API) level to the latest API level. Thus the list is from the oldest Android versions to the latest.
Android Versions by Name, Number, Availability and API Level
Each version of Android is given a code name. The code name is traditionally the name of a dessert, cake or sweet, e.g, Gingerbread, Froyo, Jelly Bean, etc. — as the sugar laden picture below shows. The table that follows lists the code names, version numbers, first release date and Application Programming Interface (API) versions, along with the equivalent Software Development Kit (SDK) constants (Build.VERSION_CODES). The Android version number on a device is normally found in the settings. Select Settings, then About Phone or About Device and look at the Firmware Version or Android Version entry.
List of Android Versions and Their Names, API Level and Dates
| Name | Version | Available | API | VERSION_CODES |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | 1.0 | October 2008 | 1 | BASE |
| N/A | 1.1 | February 2009 | 2 | BASE_1_1 |
| Cupcake | 1.5 | May 2009 | 3 | CUPCAKE |
| Donut | 1.6 | September 2009 | 4 | DONUT |
| Eclair | 2.0 | November 2009 | 5 | ECLAIR |
| Eclair | 2.0.1 | December 2009 | 6 | ECLAIR_0_1 |
| Eclair | 2.1 | January 2010 | 7 | ECLAIR_MR1 |
| Froyo | 2.2 to 2.2.3 | June 2010 | 8 | FROYO |
| Gingerbread | 2.3 to 2.3.2 | November 2010 | 9 | GINGERBREAD |
| Gingerbread | 2.3.3 to 2.3.7 | February 2011 | 10 | GINGERBREAD_MR1 |
| Honeycomb | 3.0 | February 2011 | 11 | HONEYCOMB |
| Honeycomb | 3.1 | May 2011 | 12 | HONEYCOMB_MR1 |
| Honeycomb | 3.2 to 3.2.6 | June 2011 | 13 | HONEYCOMB_MR2 |
| Ice Cream Sandwich | 4.0.1 to 4.0.2 | October 2011 | 14 | ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH |
| Ice Cream Sandwich | 4.0.3 to 4.0.4 | December 2011 | 15 | ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH_MR1 |
| Jelly Bean | 4.1 to 4.1.1 | July 2012 | 16 | JELLY_BEAN |
| Jelly Bean | 4.2 to 4.2.2 | November 2012 | 17 | JELLY_BEAN_MR1 |
| Jelly Bean | 4.3 | July 2013 | 18 | JELLY_BEAN_MR2 |
| Kit Kat | 4.4 to 4.4.4 | October 2013 | 19 | KITKAT |
| Kit Kat | 4.4W to 4.4W.2 | June 2014 | 20 | KITKAT_WATCH |
| Lollipop | 5.0 to 5.0.2 | November 2014 | 21 | LOLLIPOP |
| Lollipop | 5.1 to 5.1.1 | March 2015 | 22 | LOLLIPOP_MR1 |
| Marshmallow | 6.0 to 6.0.1 | October 2015 | 23 | M |
| Nougat | 7.0 | August 2016 | 24 | N |
| Nougat | 7.1 to 7.1.2 | October 2016 | 25 | N_MR1 |
| Oreo | 8.0.0 | August 2017 | 26 | O |
| Oreo | 8.1.0 | December 2017 | 27 | O_MR1 |
The above table was derived from the following sources (note that some release dates are derived from the Android developers documentation, the actual SDK availability may have been a little earlier, see the Wikipedia article):
When programming an App the API level is used to determine whether specific Android features are present or not. The API level can be read in versions prior to Donut (Cupcake, 1.1 and 1.0) using:
int APILevel = Integer.parseInt(Build.VERSION.SDK);
And from Donut onwards using:
int APILevel = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
(Build.VERSION.SDK is deprecated, i.e. it will be removed from the API at some future release).
When using functionality from a later API, but the App needs to support earlier Android versions, wrap the newer functionality in a separate class. Then check the API level before instantiating the class to prevent a VerifyError exception from occurring. See the article Support Multiple API Versions in Android.
Author: Daniel S. Fowler Published: 2012-05-25 Updated: 2017-01-08
Do you have a question or comment about this article?
(Alternatively, use the email address at the bottom of the web page.)
↓markdown↓ CMS is fast and simple. Build websites quickly and publish easily. For beginner to expert.
Free Android Projects and Samples:
Источник
Android Version History – Names and Features from Cupcake to Android 11
Android is the most popular mobile operating system no doubt. Most of the credit for the popularity and adoption of Android goes to the fact that it’s open by nature. Since the early days when the T-Mobile G1 was the only Android powered handset, you could possibly get, the source code for the operating system has been available for everyone to download and play with. This article is geared towards going down the memory lane of Android version names with features, basically Android versions list, and taking a look at what new features they brought in with them.
Before that let’s look at the back story which I’m sure most of you aren’t aware of. Before Android or any other fork of Android existed, there was a small mobile software company named Danger which was founded by a former Apple engineer Andy Rubin. What made Danger popular was Hiptop, a smartphone with a landscape keyboard and an interface which prioritized web browsing and messaging. Danger entered into a unique business model with Hiptop (later renamed to Sidekick) which facilitated a revenue sharing mechanism.
Android Version Names and Features
Note: A Android KitKat version was released exclusively for Android wear devices with an API level of 20 on Jun 25, 2014.
In a way, it was Danger’s services that were being sold rather than the hardware. Rubin was removed from the company Danger, but soon enough he founded Android Inc. When it was founded it was a purely software based company with no products to sell for 2 years. They planned on focusing on creating the best possible web-connected experience and they believed that investors would come along if their product was great. Google at the time was looking for a mobile OS of its own, trying to compete with Microsoft and Blackberry (Oh! how have times changed). Google wanted more phones with Google as the default search engine and Android helped it achieve exactly that.
While all of this was happening, Apple was busy minting dollars via the newly announced iPhone, RIM (the Blackberry manufacturer) was still very popular and Nokia was still a respected brand. In 2008 Google finally released the first Android powered handset with the G1. A smartphone buyer today won’t be impressed with the specs of the G1 which had a 528MHz, single-core CPU with 192MB of RAM and a 3.2-inch 320 x 480 display.
Android Operating System List
Table of Contents
1. Android 1.1
Android as the OS was born on the T-Mobile G1 which was extremely powerful for its time. This version of Android showcased its potential but it was best suited for early adopters and gadget freaks.
While the G1 couldn’t beat the iPhone sales in numbers and revenue, it offered some of the features key features of Android which we still find on our phones. Following are the features that came with it.
- The Android Market was used as a single source of delivery for Android apps and contrary to Apple’s tight restrictions on the App Store, the Android Market served apps without any restrictions.
- It came with the Android browser which made surfing the web fun.
- It was the first version of Android to offer data syncing with Google.
- It came with Google maps which used GPS to point hot location on a map. This was the beginning of never getting lost again.
2. Android 1.5 Cupcake
In the list of Android versions list comes Cupcake. The cupcake was the Android version which started the tasty treat naming tradition for Android releases.
This was the very first major Android update and was released in May 2009. The most noticeable feature with Cupcake was the virtual keyboard support which paced the way for buttonless smartphones of the future. Following are the features that came with it.
- It came with shortcuts and widgets on the home screen which allowed infinite ways to customize the home screen.
- Video recording was added to the camera along with the ability to directly upload videos to YouTube.
- The browser got a speed improvement along with copy-paste support.
3. Android 1.6 Donut
Android 1.6 Donut was released in October of 2009. It offered a few major improvements. The biggest feature addition was the added support for CDMA which brought a whole new crowd to Android.
CDMA was the technology used by American mobile networks at the time. Following are the features that came with it.
- It came with support for multiple screen resolutions and paved the way for Android devices of different screen sizes.
- Google Maps Navigation was added with turn by turn satellite navigation support.
- Donut included universal search feature which allowed us to pinpoint apps on the phone or searching the web.
4. Android 2.0 and 2.1 Eclair
There wasn’t a long wait after the release of Donut, for Eclair to be released. In fact, it was launched just a month after Donut in November of 2009.
Eclair 2.1 however, arrived in January 2010 with bug fixes and new APIs to play with. There weren’t any significant new additions in terms of features for users. Following are the features that came with it.
- Multi-touch support was added to Android.
- Web browser received a visual overhaul with a new address bar and thumbnails for a sneak peek.
- Eclair brought a unified inbox to Android. Support for multiple Google accounts was added.
- Support for searching within text messages.
5. Android 2.2 Froyo
Android Froyo was released in May 2010.
The major update that came with Froyo was the addition of Flash. Following are the features that came with it.
- Phone flash could be used in videos too.
- Settings joined contacts and email in backing up to Google’s servers allowing you to automatically restore everything on a new device.
- Enhanced Bluetooth compatibility with docks and car speakers.
- Portable WiFi hotspot to share the device’s 3G connection with other gadgets.
6 Android 2.3 Gingerbread
Gingerbread was released in 2010 but it wasn’t a release which made a lot of noise.
Main features included NFC support, SIP for Internet calling. Following are the features that came with it.
- UI overhaul to avoid screen burn-in and improve battery life.
- Front facing camera support for video calling.
- Download manager for keeping an eye on your downloads.
- Improved on-screen keyboard with shortcuts and a cursor to help with copy paste.
7. Android 3.0 and 3.1 Honeycomb
This version of Android is the most disregarded of all. It was released specifically for tablets and never came to the phones.
Honeycomb was launched in May 2011 and it basically expanded Android to support big screens of tablets. Following are the features that came with it.
- Several UI improvements to make use of the large screen.
- Hardware buttons are dropped in favor of on-screen buttons.
- Web browser introduced tabbed browsing.
- Bigger and bolder widgets.
- Apps like Gmail and YouTube were redesigned to make use of the large screen.
8. Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich
Ice Cream Sandwich (ICS) was the first Android version to be announced at the Google I/O conference in May 2011.
Although there was a long delay of around 7 months till anyone could use it because the Samsung Galaxy Nexus started shipping only in December. Following are the features that came with it.
- The biggest redesign to Android with the Holo theme.
- Faster smoother browsing experience.
- Multi storage space for apps.
- Face recognition for unlocking the phone.
9. Android 4.1, 4.2 and 4.3 Jellybean
Jellybean was released in June 2012 and while the version number wasn’t a huge one, it added a lot of new features.
Following are the features that came with it.
- Google Now, an assistant tool that displays relevant information based on your search history.
- Project Butter to support higher frame rates while swiping through menus and home screens.
- Ability to quickly view photos by swiping from the camera to go to the filmstrip.
- Widgets realign themselves on adding new ones.
- Richer notifications.
- New gestures and accessibility features.
10. Android 4.4 KitKat
Android 4.4 KitKat was the last 4.x release and brought some major improvements both internally and visually to Android.
It was released in November of 2013. Following are the features that came with it.
- Immersive mode for better content consumption.
- Better navigation bar for getting in and out of Immersive mode.
- Lock screen widgets support.
- New dialer with Caller ID feature.
- Full-screen wallpapers.
- Emoji keyboard for emoticons.
- Unified Hangouts and messaging app.
- Better cloud print support.
- Smarter, hands-free Google Now Integration.
11. Android 5.0 Lollipop
Android 5.0 Lollipop was announced at Google I/O in May 2014, and so far it’s been the biggest redesign for Android.
The biggest improvement that Lollipop brought was the introduction of Material Design which quickly became the unified design language implemented across Google products. Following are the features that came with it.
- Better quick settings support.
- Enhanced battery life with new Battery Saver mode.
- New lock screen.
- Smart Lock features via Google Play Services.
- Guest mode for device sharing.
- App pinning.
12. Android 6.0 Marshmallow
While Lollipop was a big feature release, Marshmallow served the purpose of polishing out the rough corners and making the experience of Lollipop even better.
It was showcased at Google I/O in 2015. Following are the features that came with it.
- Marshmallow came with Doze for better standby time.
- Official fingerprint support for devices.
- Support for mobile payments via Android Pay.
- Better permissions model for apps.
- Google Now on Tap.
- Deep linking of Apps.
13. Android 7.0 Nougat
This brings us to the last and most recent version of Android, and that is Android 7.0 Nougat.
Unlike others, Nougat was released way before Google I/O in the month of March 2016. It brought with it some significant improvements and features. Following are the features that came with it.
- Doze on the Go for even better standby time.
- Multi Window for using two apps at the same time.
- Better Settings app.
- Clear all in the recent apps screen.
- Direct Reply to notifications.
- Bundled notifications.
- Quick Settings toggles customization.
14. Android 8.0 Oreo
This brings us to the last and most fresh version of Android and that is Android 8.0 Oreo. Just like Nougat, Oreo was released as a preview version before I/O and over the months it was iterated over to stabilize the release. Now that the version is out here’s all that’s new about it.
- Newly redesigned notification shade.
- New Easter Egg.
- Strict rules for background processes Picture in Picture for using one app (video player for example) on top of another.
- Notification dots to quickly view an app’s activity by long pressing on it Adaptive icons for dynamic adaptation to launcher styles.
- Notification channels for better priority and categorization of notifications.
- Better overall color management for a more richer viewing experience.
- New emojis (I hate them) the Android O emoji collection has been redesigned and you’ll most likely hate it.
- Faster boot time: On Pixel devices, you can now experience up to twice as fast boot times compared to Nougat.
- AutoFill for filling and remembering passwords within apps.
15. Android 9.0 Pie
Resembling the other versions of Android, Android v9.0 Pie was also available in Developer Beta. After a lot of waiting, Android Pie was publicly released on 6, August 2018. It’s the ninth major release of Android and the update packs a lot of changes. Android Pie is also one of the biggest visual overhauls the Android ecosystem has seen in recent times — due to the shift to gesture navigation and more. Some of the notable features of Android v9.0 Pie are as follows.
- Adaptive Battery: This optimizes battery performance and backup time by analyzing your patterns of smartphone usage, including the specific apps.
- Adaptive Display: Taking inspiration from Auto Brightness and machine learning, Adaptive Display is taking care of your display brightness.
- App Actions are shortcuts that involve multiple actions. You can set up these actions for occasions like Work, Home etc.
- Slices are a great way to go into the apps. Along with app icons, Search will also show you the specific tasks you can do inside the app. For instance, get a cab to go home using Lyft.
- Gesture-based Navigation is the big thing. You can now swipe your fingers to navigate within the Android system. This includes shifting between apps, going to the home screen and more.
- Digital Wellbeing features to make sure that you’re not spending too much time with your phone. It notifies you.
- Better performance when compared to Oreo.
16. Android 10
Android 10 is different from the previous versions of Android in that it does not have a name. Deviating from the food-based names that were being followed, Google decided to go for a numerical way to indicate the versions of Android. And, Android 10 marks the beginning and would be followed by Android 11. This version of Android was launched on September 3, 2019. While Pixel devices got the update instantly, some devices are still on the waiting line to get the update. However, Google had this time worked with manufacturers like OnePlus to make Android 10 available quickly. While Android 10 was not of a visual change per se, there were some revolutionary improvements. Some of them are:
- Gesture Navigation: With Android 10, Google has gone for an advanced gesture navigation, which is familiar for those who have used iOS. You can swipe from the left side of the screen to go back and pull up to go to the Home screen. You can swipe from the corner to launch Google Assistant as well.
- Better Privacy Controls: In the wake of security issues, Google also included some privacy features in the new release. Users now have better control over aspects like Location Access, Data Storage and Ad Targeting. All these are available under a unified Privacy tab in the System Settings.
- Dark Theme: One of the most awaited features, Android 10 brings a system-wide Dark Mode. When enabled, this mode will make your Android experience easier on your eyes. Of course, users can choose an automatic mode as well.
- Improved Security: Google has also managed to change the way important security updates are reaching smartphones. With Android 10, these updates are distributed through Google Play Store — and they can be updated just like apps are updated.
- Smart Reply: This is a great way to reply to messages you receive via Messenger, WhatsApp or some other IM applications. The system can now suggest some potential replies according to the message you have received. This is a great time-saver.
- Digital Wellbeing: Although it started with Android Pie, Digital Wellbeing has become way better in the latest release. In addition to letting you know how much time you spend; you can now enable a Focus Mode that blocks certain apps. There are also family-centric controls in the end.
- Sound Amplifier and Live Captions: While the Sound Amplifier feature allows you to control how the sound experience works in your device, Live Captions are made for video content. In a single click, it allows you to display live captions of the video you are playing.
In addition, there are features that add value to each of these sections. For instance, with Privacy Controls, you get better control of how you share Location Data. Similarly, with Sound, you get built-in support for hearing aids as well.
17. Android 11
Google made the initial release of Android 11 on the 8 th of September 2020. Even during the peak times of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Open Handset Alliance led by Google did an impressive task. Like the previous version, Android 11 is not a visual overhaul. The design stays true to the philosophy that Google had started a couple of iterations back. On the other hand, Android 11 attempted to optimize the user experience by keeping Google services close to the smartphone experience. Thanks to Google’s efforts to speed up the rolling-out procedure, Android 11 runs on a considerable number of devices from different manufacturers. Most devices launched after September 2020 are shipping with Android 11 or offer an easy-upgrade option. The top features of Android 11 are:
- Conversations: Android 11 makes it easy to manage conversations from multiple messaging apps. It uses a couple of features on the lock-screen and the notifications panel. You can also use Bubbles, which take inspiration from Messenger chat-heads. However, Bubbles are available for apps other than Facebook Messenger.
- Content Capture: The new version of Android comes with a built-in screen recording function. More importantly, you can customize how the recording works. For instance, you can select the source for audio, or mix audio streams from multiple sources. There are better options to share the recorded content on Pixel devices.
- Predictive Tech: Google has implemented predictive tools and machine learning in different parts of Android 11 OS. For instance, the OS can offer Smart-Reply suggestions and App Suggestions. It even creates smart folders on your home screen. Android 11 makes this possible by learning about your usage patterns.
- Smart Device Controls: With 11, Android has become closer to the Smart Home network that Google has been building over years. Now, users can press and hold the power button to access all connected devices with ease. You can also use the space to access your virtual Credit Cards and NFC-based data with no hassle.
- Better Security: Users have been asking for enhanced security, and Android 11 has delivered. On top of the regular security updates, Android 11 has brought a better permissions manager. Users can now provide one-time permissions for apps. There are also better options for Permissions auto-reset that can stop unused apps from accessing camera, microphone, or location.
In addition to these major features, Google has introduced better security updates and increased speed. We must add, however, that many Android 11 features work the best when you have a Pixel device with you. In the end, Android 11 does improve the overall smartphone experience by a long shot.
Conclusion – Android Version Names and Features
Android as a platform has evolved significantly since its inception in 2008. The platform now powers more than 2.8 Billion users who use the platform daily. It has also become one of the biggest sources of revenue and has essentially driven the smartphone era forward with its forward-thinking features which have become so popular that recent versions of iOS have started implementing it.
Источник