- Android Read Write Internal Storage File Example
- 1. Android Read Write Data To Internal File.
- 1.1 Where Your Android App Internal Data File Saved In?
- 1.2 Read Write Android File Code Snippets.
- 2. Android Internal File Operation Example.
- 2.1 Layout XML File.
- 2.2 Activity Java File.
- 3. Question & Answer.
- 3.1 Can not write text file to android internal storage.
- How to read text file in android – Read from any folder internal & external
- How to Read Text file in android
- Login & Download the Code
- Step by Step Process
- Add run time permission
- activity-main.xml
- MainActivity.java run time permission code
- Select file from gallery
- Get actual file path from URI
- Read text file in android
- Run the code
- Java – Read a file from resources folder
- 1. Files in resources folder
- 2. Get a file from the resources folder.
- 3. Get a file from the resources folder – Unit Test
- 4. Get all files from a resource folder. (NON-JAR environment)
- 5. Get all files from a resource folder. (JAR version)
- Download Source Code
- References
- Comments
Android Read Write Internal Storage File Example
Android data can be saved in internal storage ( ROM ), external storage(SD card), shared preferences, or SQLite database. This article will introduce how to read and write data in internal storage via a java file.
1. Android Read Write Data To Internal File.
- Android is based on Linux, the android file system is Linux-based also.
- Android studio provides the android device monitor tool for you to monitor and transfer files between Android devices and your PC. Please refer Android Device Monitor Cannot Open Data Folder Resolve Method.
1.1 Where Your Android App Internal Data File Saved In?
- All android app internal data files are saved in the /data/data/ folder.
- In this example, my app data internal file is saved in /data/data/com.dev2qa.example folder. You can watch the youtube video https://youtu.be/AJBgBBMKO5w to see the android app’s internal data files saved directory.
- From the youtube video, we can see that there are files and cache subfolders under the package name folder.
- files folder — android.content.Context’sgetFilesDir() method can return this folder. This folder is used to save general files.
- cache folder — android.content.Context’sgetCacheDir() method can return this folder. This folder is used to save cached files.
- When the device’s internal storage space is low, cache files will be removed by android os automatically to make internal storage space bigger. Generally, you need to delete the unused cache files in the source code timely, the total cache file size is better not more than 1 MB.
1.2 Read Write Android File Code Snippets.
- Android application is written in java, so the file operation uses java classes also.
- Below are the code snippets for read/write data from/to the file in android.
1.2.1 Read Android File In The Package files Folder.
- Call android.content.Context‘s openFileInput(userEmalFileName) method to get FileInputStream object.
- The input parameter is just the file name.
- This file should be saved in the files folder.
- Then use the FileInputStream object to read data.
1.2.2 Read Android File In The Package cache Folder.
- The below source code will read the android files in the package cache folder.
1.2.3 Write File To The Package files Folder.
- Method 1: Use Context’s getFilesDir() to get the package files folder, then write file into it.
- Method 2: Call Context’s openFileOutput(userEmalFileName, Context.MODE_APPEND) method to get FileOutputStream object.
- The first parameter is the file name, the second parameter’s value can be one of the below values.
- Context.MODE_PRIVATE: This means this file can only be read/write by this android app that creates it. This mode will overwrite an existing file, if not exist then create it.
- Context.MODE_APPEND: This mode will append data to an existing file. If not exist it will create a new one.
1.2.4 Write File To The Package cache Folder.
- Use Context’s getCacheDir() to get cache folder.
2. Android Internal File Operation Example.
- You can watch the example demo video on youtube https://youtu.be/HqbRR6TQVvY.
- There are one input text box and five buttons on the android example app main screen.
- The buttons’ function can be easily understood by the button’s label text.
- The button’s label text is WRITE TO FILE, READ FROM FILE, CREATE CACHED FILE, READ CACHED FILE, CREATE TEMP FILE from up to bottom.
- After you run the example, you can see the below files in the android device monitor. You can pull down the file to your local PC to see the file contents also.
- If you meet any problem in using the android device monitor, please refer to Android Device Monitor Cannot Open Data Folder Resolve Method. This article will tell you how to resolve those errors.
2.1 Layout XML File.
- activity_write_read_file.xml
2.2 Activity Java File.
- WriteReadFileActivity.java
- If you meet the error message Instant Run requires ‘Tools | Android | Enable ADB integration’ to be enabled when you run this example. You can click Tools —> Android menu, and check Enable ADB integration option in the popup menu to resolve it.
3. Question & Answer.
3.1 Can not write text file to android internal storage.
- My android app is very simple, I just want to write some text to a file and save the text file to the internal storage. I follow this article to write source code, but I can not find the text file in both the android physical device and the simulator. I can not read the file content out in java source code. Can you tell me why? Thanks a lot.
- Android 11 has announced a new policy when you want to manage storage. The internal storage root folder can not be used to store files unless you add the below permission in your AndroidManifest.xml file.
And when you run the application, you can request this permission to the user with the below code.
Then you can process user response in the onRequestPermissionsResult() method in the activity.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Thanks.Great Article Guys.
I am a beginner of android programming, and I want to write some data to a file saved in android internal storage device. I found this article and write the source code as below. But I found after I write the data to internal storage file with the method writeToFile, I can not read the written file content in android internal storage device in the readFileButton method. Can you tell me what wrong in my source code? Thanks a lot.
public void writeToFile(String fileName, String fileContent)<
try <
// Create a FileOutputStream object with the provided file name.
FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput(fileName , Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
// Write the file content to the file.
fos.write(fileContent.getBytes());
// Close the file output stream to flush the data to the file.
fos.close();
> catch (Exception e) <
e.printStackTrace();
>
>
public void readFileButton(View v) <
// Read the file text content.
try <
// Define the internal stored file name.
String fileName = “test.txt”;
// Create a FileInputStream object.
FileInputStream fis =openFileInput(fileName);
// Create a InputStreamReader object.
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
// Define the char array.
char[] ib= new char[1024];
// Store read out file data.
String fileData = “”;
// Read 1024 character data from file.
int charRead = isr.read(ib);
// While not end of the file.
while (charRead>0) <
// Convert the char array to a string object.
String readstring = String.copyValueOf(inputBuffer,0,charRead);
// Add the read out file data.
fileData +=readstring;
Источник
How to read text file in android – Read from any folder internal & external
Read text file . How to read text file in android app? Some time developer think that it is very difficult to read text file in android, but truth is – it is very easy. You can read any text file and excel sheet from android app whether file located in internal storage or external storage. If you want to know how to read excel file from asset folder, please read this tutorial.
To read any file from android app, you must take permission to read external storage. otherwise app will crash at run time. In this tutorial, I am going to show you, how to select text file from gallery OR internal storage OR external storage and read text file. I am using a simple textview to display the text written on selected text file.
So in this tutorial the process is as follow. First I am writing the code for run time permission, then code for select file from gallery then read the text written in text file. If you want work with PDF file than you can read this tutorial – How to create PDF file, write text and image
How to Read Text file in android
Login & Download the Code
Step by Step Process
- Add run time permission in Androidmanifest.xml
- MainActivity.java run time permission code
- Add select file from gallery or file manager
- Get actual file path from file URI
- Read file using bufferreader
- Run the code
Add run time permission
First, add run time permission in androidmanifest.xml file.
activity-main.xml
MainActivity.java run time permission code
Because we are trying to read text file from phone storage, so you must add the code for run time permission in android app. Android introduce run time permission in api 24 marshmallow. So first check user phone’s android version is greater than or equal to marshmallow.
If android version is greater than marshmallow than user will see a alert dialog to accept permission to read text file. Once user will click on allow/ denied button the response will be received in onRequestPermissionsResult() method. There if it is positive response (means allow) than you should start function to choose file from gallery, otherwise show error massage to user.
Select file from gallery
It is the best way to give complete control to user to select any file from the gallery. You have to use intent to open gallery option. The response of the intent will be receive in onActivityResult() method. The onActivityResult will return the intent data.
NOTE- you can only get the URI of the file using intent, not the actual file path. to get the actual file path, you have to write different functions. Actually the URI is a index of file not the exact path. The text file can be located into any folder, so we need to write multiple condition to get file path. below is the table of URI path according to folder location.
Get actual file path from URI
You must check auth of each file. auth is parent folder name, using this name you can identify which condition will be correct to get file path.
below is the code to get actual file path from gallery file. Please watch the above video to understand why you must check multiple condition to get file path.
Read text file in android
Now you have file path, use this file path to read file using buffer reader. below is the complete code of MainActivity.java
Run the code
Now every thing has setup. Please run the code, select file from gallery. You will see the text read from the text file will be display on screen.
If you have any question, please contact me or use chat box.
Please comment below, if this tutorial help you. Your feed back is more important for me to create new videos and tutorial.
Источник
Java – Read a file from resources folder
By mkyong | Last updated: September 4, 2020
Viewed: 1,546,378 (+4,744 pv/w)
In Java, we can use getResourceAsStream or getResource to read a file or multiple files from a resources folder or root of the classpath.
The getResourceAsStream method returns an InputStream .
The getResource method returns an URL and normally convert it to a File ; Not working in JAR file.
1. Files in resources folder
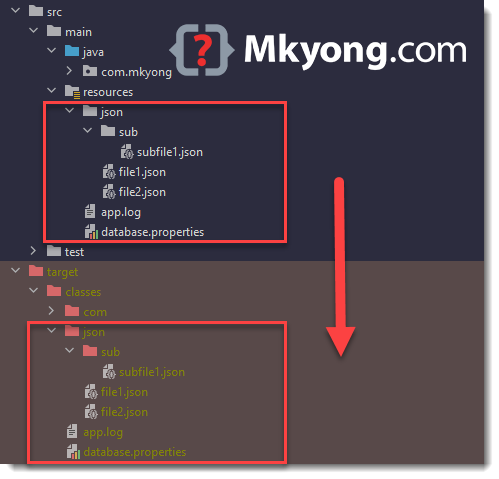
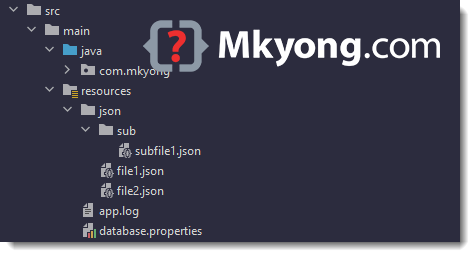
1.1 Review the files in the src/main/resources , later we will access the files and print out the file content.
1.2 By default, build tools like Maven, Gradle, or common Java practice will copy all files from src/main/resources to the root of target/classes or build/classes . So, when we try to read a file from src/main/resources , we read the file from the root of the project classpath.
1.3 Below is a JAR file structure. Usually, the files in the resources folder will copy to the root of the classpath.
2. Get a file from the resources folder.
2.1 The below example demonstrates the use of getResourceAsStream and getResource methods to read a file json/file1.json from the resources folder and print out the file content.
Note
- The getResource method is not working in the JAR file.
- The getResourceAsStream method works everywhere.
2.2 Now, we pack the project into a JAR file and run it; this time, the getResource will fail and returns either NoSuchFileException or InvalidPathException . We cannot read the files inside the JAR file via the resource URL.
Run the JAR file on Linux (Ubuntu), it throws NoSuchFileException .
Run the JAR file on Windows, it throws InvalidPathException .
P.S This example uses the Maven plugin maven-jar-plugin to create the JAR file.
3. Get a file from the resources folder – Unit Test
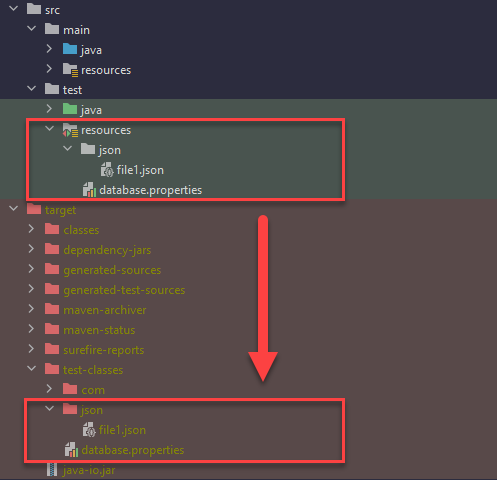
3.1 We put the test resources at folder src/test/resources for unit tests. Usually, the files in test resources will copy to the target/test-classes folder.
3.2 It works the same way we read the file from src/main/resources . We use the same getResourceAsStream and getResource methods to read the file from the src/test/resources .
4. Get all files from a resource folder. (NON-JAR environment)
If we don’t know the exact filename and want to read all files, including sub-folder files from a resources folder, we can use the NIO Files.walk to easily access and read the files.
4.1 The below example uses Files.walk to read all files from a folder src/main/resources/json :
4.2 However, the standard Files.walk in example 4.1 can’t access the files in the JAR file directly, try run the example 4.1 in a JAR environment, and it throws FileSystemNotFoundException .
5. Get all files from a resource folder. (JAR version)
5.1 This example shows how to Files.walk a folder inside a JAR file via FileSystems and URI jar:file:xxx.jar .
- File walks the folder inside a JAR file using FileSystems , and get all the filename, see getPathsFromResourceJAR()
- Loop all the filename, access and print each file like example 2.1, see getFileFromResourceAsStream() .
Download Source Code
References
mkyong
Founder of Mkyong.com, love Java and open source stuff. Follow him on Twitter. If you like my tutorials, consider make a donation to these charities.
Comments
How about reading al files under a resources directory like this?
src/main/resources
+ file1.txt
+ file2.txt
…
+ file9.txt
We updated the article, see example 4 and 5. Files.walk is your best friend.
And still, examples 4 and 5 shows how to access files in subfolder of resource folder, but not in resource folder itself.
Hi mkyong.This work fine ide but not work jar?
Can you help we ?
We updated the example to access the files inside the JAR file, the answer is getResourceAsStream .
The getResource is not working in JAR file.
The getResourceAsStream works everywhere.
ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
InputStream inputStream = classLoader.getResourceAsStream(“fileName”);
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
IOUtils.copy(inputStream, writer);
query = writer.toString();
i am added Apache commons in mvn pom.xml then what is the query means
^ Thanks a lot man!
new File(classLoader.getResource(fileName).getFile());This won’t work with files if they have whitespaces or special characters (e.g. #) in their paths. Rather use
Thanks, we updated the example with toURI()
toURI() does not work in jar and gives a error: URI is not hierarchical
Thanks to MyKong and you I got it working!
There is also one that I like the most:
File file = ResourceUtils.getFile(“classpath:file/test.txt”)
String txt= FileUtils.readFileToString(file);
ResourceUtils are in spring and FileUtils are in commons io.
OMG, many thanks for this ^^
Thanks for sharing this – ResourceUtils
I’m working on an app which uses a 3rd party library with an API expecting a java.io.File .
The data to be passed “as a file” I could create dynamically or get from a resource.
I could get the resource as a File with the class loader getResource method. But you already made the point: that will not work with a Jar.
The only solution so far (independently if I create the data on the fly or get it (as Stream) from a resource) is to store that data in a temporal file and give it to the API.
Is there a way to avoid the temporal file? Can we make a File object for something in memory?
Источник