- Adding an Android SDK
- Adding SDK Packages
- Get the latest SDK tools
- Get the support library for additional APIs
- Get Google Play services for even more APIs
- Install the packages
- Build something!
- Get started
- Build for wearables
- Use Google APIs
- Installing the Android SDK
- Installing the Android Development Tools
- Installing the JDK/SDK/NDK
- Handling an Android SDK Manager Issue on Windows 8
- Configuring RAD Studio to Work with Your Installed SDK
- Adding Java as a User Override to Your System Path
Adding an Android SDK
A software development kit (SDK) provides a set of files that are used to build applications for a target platform. When you develop applications for Android, the Android SDK and Android NDK are required on your development system, and they both need to be known to the SDK Manager.
When you install RAD Studio, the installer gives you the option of installing the recommended versions of the Android SDK and NDK. If you install these recommended versions during product installation , the SDK Manager detects their presence and sets the default paths and locations for you, as shown in this screenshot:
In this case, when the recommended versions of the Android SDK and NDK are installed by default, you do not need to add an Android SDK, because the default location is known to the SDK Manager, and so the libraries are automatically detected.
If you want to install the Android SDK and NDK yourself, even in alternate locations, or if you want to use an existing installation of the Android SDK and NDK, you must add your Android SDK to the RAD Studio SDK Manager. See Installing the Android Development Tools if you do not have the Android SDK or NDK installed yet and you want to install them yourself.
Caution: Versions of the Android SDK and NDK libraries that differ from those installed with RAD Studio might not work as expected.
To add an Android SDK to RAD Studio:
- Select Tools > Options > Environment Options >SDK Manager .
- Click the Add button.
- On the Add a New SDK dialog box, select Android from the Select a platform drop-down list. RAD Studio detects the Android SDKs installed in your system and populates the Select an SDK version drop-down list for you.
- Select an SDK from the Select an SDK version drop-down list. For details and troubleshooting, see SDK Manager.
- Check Make the selected SDK active if you want the new SDK to be the default SDK for Android.
- Click OK to continue. The Create a New Android SDK wizard opens.
- In the Android NDK Base path field on the first page of the wizard, enter the path to your installed NDK folder, and click Next.
- On the next page, wait for RAD Studio to automatically detect the paths of the required tools, and then click Finish.
Your Android SDK version is now listed in the SDK Manager:
The Android SDK version should now be included in your Android target platform in the Project Manager:
Источник
Adding SDK Packages
By default, the Android SDK does not include everything you need to start developing. The SDK separates tools, platforms, and other components into packages you can download as needed using the Android SDK Manager. So before you can start, there are a few packages you should add to your Android SDK.
To start adding packages, launch the Android SDK Manager in one of the following ways:
- In Eclipse or Android Studio, click SDK Manager
in the toolbar.
- If you’re not using Eclipse or Android Studio:
- Windows: Double-click the SDK Manager.exe file at the root of the Android SDK directory.
- Mac/Linux: Open a terminal and navigate to the tools/ directory in the location where the Android SDK was installed, then execute android sdk .
When you open the SDK Manager for the first time, several packages will be selected by default. Leave these selected, but be sure you have everything you need to get started by following these steps:
Get the latest SDK tools
As a minimum when setting up the Android SDK, you should download the latest tools and Android platform:
- Open the Tools directory and select:
- Android SDK Tools
- Android SDK Platform-tools
- Android SDK Build-tools (highest version)
- Open the first Android X.X folder (the latest version) and select:
- SDK Platform
- A system image for the emulator, such as
ARM EABI v7a System Image
Get the support library for additional APIs
The support library is required for:
It also provides these popular APIs:
The Android Support Library provides an extended set of APIs that are compatible with most versions of Android.
Open the Extras directory and select:
- Android Support Repository
- Android Support Library
Get Google Play services for even more APIs
The Google Play services APIs provide a variety of features and services for your Android apps, such as:
To develop with Google APIs, you need the Google Play services package:
Open the Extras directory and select:
- Google Repository
- Google Play services
Note: Google Play services APIs are not available on all Android-powered devices, but are available on all devices with Google Play Store. To use these APIs in the Android emulator, you must also install the the Google APIs system image from the latest Android X.X directory in the SDK Manager.
Install the packages
Once you’ve selected all the desired packages, continue to install:
- Click Install X packages.
- In the next window, double-click each package name on the left to accept the license agreement for each.
- Click Install.
The download progress is shown at the bottom of the SDK Manager window. Do not exit the SDK Manager or it will cancel the download.
Build something!
With the above packages now in your Android SDK, you’re ready to build apps for Android. As new tools and other APIs become available, simply launch the SDK Manager to download the new packages for your SDK.
Here are a few options for how you should proceed:
Get started
If you’re new to Android development, learn the basics of Android apps by following the guide to Building Your First App.
Build for wearables
If you’re ready to start building apps for Android wearables, see the guide to Building Apps for Android Wear.
Use Google APIs
To start using Google APIs, such as Maps or Play Game services, see the guide to Setting Up Google Play Services.
Источник
Installing the Android SDK
Android Studio provides everything you need to start developing apps for Android, including the Android Studio IDE and the Android SDK tools.
If you didn’t download Android Studio, go download Android Studio now, or switch to the stand-alone SDK Tools install instructions.
Before you set up Android Studio, be sure you have installed JDK 6 or higher (the JRE alone is not sufficient)—JDK 7 is required when developing for Android 5.0 and higher. To check if you have JDK installed (and which version), open a terminal and type javac -version . If the JDK is not available or the version is lower than 6, go download JDK.
To set up Android Studio on Windows:
- Launch the .exe file you just downloaded.
- Follow the setup wizard to install Android Studio and any necessary SDK tools.
On some Windows systems, the launcher script does not find where Java is installed. If you encounter this problem, you need to set an environment variable indicating the correct location.
Select Start menu > Computer > System Properties > Advanced System Properties. Then open Advanced tab > Environment Variables and add a new system variable JAVA_HOME that points to your JDK folder, for example C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_21 .
The individual tools and other SDK packages are saved outside the Android Studio application directory. If you need to access the tools directly, use a terminal to navigate to the location where they are installed. For example:
To set up Android Studio on Mac OSX:
- Unzip the downloaded zip file, android-studio-ide- -mac.zip .
- Drag and drop Android Studio into the Applications folder.
- Open Android Studio and follow the setup wizard to install any necessary SDK tools.
Depending on your security settings, when you attempt to open Android Studio, you might see a warning that says the package is damaged and should be moved to the trash. If this happens, go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy and under Allow applications downloaded from, select Anywhere. Then open Android Studio again.
The individual tools and other SDK packages are saved outside the Android Studio application directory. If you need access the tools directly, use a terminal to navigate into the location where they are installed. For example:
To set up Android Studio on Linux:
- Unpack the downloaded Tar file, android-studio-ide- -linux.zip , into an appropriate location for your applications.
- To launch Android Studio, navigate to the android-studio/bin/ directory in a terminal and execute studio.sh .
You may want to add android-studio/bin/ to your PATH environmental variable so that you can start Android Studio from any directory.
If the SDK is not already installed, follow the setup wizard to install the SDK and any necessary SDK tools.
Note: You may also need to install the ia32-libs, lib32ncurses5-dev, and lib32stdc++6 packages. These packages are required to support 32-bit apps on a 64-bit machine.
Android Studio is now ready and loaded with the Android developer tools, but there are still a couple packages you should add to make your Android SDK complete.
The stand-alone SDK Tools package does not include a complete Android development environment. It includes only the core SDK tools, which you can access from a command line or with a plugin for your favorite IDE (if available).
If you didn’t download the SDK tools, go download the SDK now, or switch to the Android Studio install instructions.
To get started on Windows:
Your download package is an executable file that starts an installer. The installer checks your machine for required tools, such as the proper Java SE Development Kit (JDK) and installs it if necessary. The installer then saves the Android SDK Tools to a specified the location outside of the Android Studio directories.
- Double-click the executable ( .exe file) to start the install.
- Make a note of the name and location where you save the SDK on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later when using the SDK tools from the command line.
- Once the installation completes, the installer starts the Android SDK Manager.
To get started on Mac OSX:
Unpack the ZIP file you’ve downloaded. By default, it’s unpacked into a directory named android-sdk-mac_x86 . Move it to an appropriate location on your machine, such as a «Development» directory in your home directory.
Make a note of the name and location of the SDK directory on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later when using the SDK tools from the command line.
To get started on Linux:
Unpack the .zip file you’ve downloaded. The SDK files are download separately to a user-specified directory.
Make a note of the name and location of the SDK directory on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later when using the SDK tools from the command line.
Troubleshooting Ubuntu
- If you need help installing and configuring Java on your development machine, you might find these resources helpful:
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Java
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/JavaInstallation
- Here are the steps to install Java:
-
If you are running a 64-bit distribution on your development machine, you need to install additional packages first. For Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) and above, install the libncurses5:i386 , libstdc++6:i386 , and zlib1g:i386 packages using apt-get :
For earlier versions of Ubuntu, install the ia32-libs package using apt-get :
The Android SDK tools are now ready to begin developing apps, but there are still a couple packages you should add to make your Android SDK complete.
Then, select which SDK bundle you want to install:
Источник
Installing the Android Development Tools
Important: You do not need to install the Android tools yourself.
- The installer for RAD Studio installs the current recommended and tested versions of the Android development tools during the RAD Studio product installation.
- The Android development tools are conveniently accessible using Start | All Programs | Embarcadero RAD Studio XE6 | Android SDKs , as shown here:
- The Android AVD Manager menu item opens a command window that invokes the Android SDK Manager, which in turn starts the Android Virtual Device Manager for you.
- The Android Tools menu item opens a command window that invokes the Android SDK Manager.
- The installer gives you the option to not install the Android SDK and NDK. If you opt out in the installer, you can either:
- Use a previously installed Android SDK and NDK.
- Install the Android development tools yourself, following the steps in this topic.
Be aware that you need to use the recommended versions of the Android development tools; alternate versions might introduce changes that cannot be supported by RAD Studio. Note: The JDK is installed if you do not have the recommended version of Java (1.6 or 1.7), regardless of whether the Android development tools are installed for you during product installation.
Having the Android development tools installed on your development system is required for developing Android apps using RAD Studio. To build mobile apps for the Android target platform, you also need to add an Android SDK to the RAD Studio SDK Manager.
Here are the default installed locations of the Android development tools as installed by the RAD Studio installer:
- Java Development Kit (JDK): C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_25
- Android Software Development Kit (SDK): C:\Users\Public\Documents\Embarcadero\Studio\14.0\PlatformSDKs\adt-bundle-windows-x86-20131030\sdk
- Android Native Development Kit (NDK): C:\Users\Public\Documents\Embarcadero\Studio\14.0\PlatformSDKs\android-ndk-r9c
Installing the JDK/SDK/NDK
- Install the JDK (Java development kit):
- On the PC, download and run the JDK installer, which is available here: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
- Install the Android SDK (software development kit):
- In your browser on the PC, open the Android SDK download page and click Download the SDK Tools ADT Bundle for Windows.
- On the Get the Android SDK page, you can select either 32-bit or 64-bit, according to your Windows platform.
- This download includes the SDK tools and the Eclipse IDE. After the download completes, you can safely delete the SDK\adt-bundle-windows-x86-20131030\eclipse folder, unless you want to use the Eclipse IDE.
- From your directory, run SDK Manager.exe. Tips: If the Android SDK Manager does not start, try these suggestions:
- Right-click SDK Manager.exe and choose Run As Administrator.
- Run android.bat from the \tools directory inside your directory.
- In the Android SDK Manager tree, check (enable) the following nodes:
- Tools node
- SDK Platform node within the Android (API ) node, where must be 9 or a higher value (for example, «18»). Note: RAD Studio supports Android 2.3 and later versions regardless of which SDK Platform you download. Android SDK platforms are backward compatible.
- Click Install packages, click Accept License to accept the required licenses, and click Install to install the required software.
- You can close the Android SDK Manager when the installation finishes.
- In your browser on the PC, open the Android SDK download page and click Download the SDK Tools ADT Bundle for Windows.
- Install the Android NDK (native development kit):
- On the PC, download and unzip the NDK for your Windows version (32-bit or 64-bit), available here: http://developer.android.com/tools/sdk/ndk/index.html.
After installing these tools, you need to add an Android SDK to RAD Studio, as described in the next section, and then you can start building mobile applications for the Android platform.
Handling an Android SDK Manager Issue on Windows 8
On Windows 8, you might see errors when you start the Android SDK Manager. If this happens, you might not be able to download any additional SDKs.
The solution is to edit the android.bat file and change the line that launches the Android SDK Manager. Add -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true to the call to Java, as follows:
call %java_exe% -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true %REMOTE_DEBUG% -Dcom.android.sdkmanager.toolsdir=»%tools_dir%» -Dcom.android.sdkmanager.workdir=%work_dir% -classpath «%jar_path%;%swt_path%\swt.jar» com.android.sdkmanager.Main %*
This issue seems to be related to Windows 8 wanting to use Internet Protocol V6.
Configuring RAD Studio to Work with Your Installed SDK
You can use specific versions of the Android SDK simply by pointing the RAD Studio SDK Manager to your installed location.
- Open the Create a New Android SDK wizard by using either Tools Options or Project Manager:
- Choose Tools > Options > Environment Options >SDK Manager | Add | Add new .
- In the Project Manager:
- Right-click the Android target platform and select Properties from the context menu.
- In the SDK field on the Platform Properties dialog box, click Add new in the dropdown list.
- On the Add a New SDK dialog, click Add new in the dropdown list.
- In the Android SDK Base Path and the Android NDK Base Path fields, browse to and select your installed and locations, respectively.
- The Create a new Android SDK wizard now populates the rest of the fields here and on the Android tools locations page. Allow a moment for this process to complete.
- For any fields that are not auto-populated or are marked with
, click the entry field and browse to the installed location of that library on your system.
Adding Java as a User Override to Your System Path
If you installed the JDK yourself, Java might not be in your system path. For example, if Java is not in your system path, you must use android.bat to start the Android SDK Manager (instead of SDK Manager.exe). If you want to optimize for Android development, you should add Java to your system path environment variable.
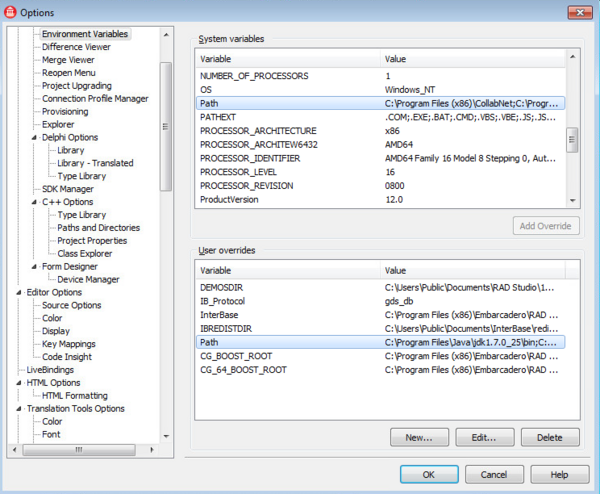
- Choose Tools > Options > Environment Options >Environment Variables .
- In the System variables pane, double-click the Path item.
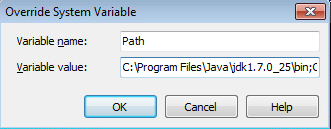
- In the Override System Variable dialog box, click the Home button on your keyboard to bring the focus to the beginning of the path.
- Add the path to Java at the beginning of your system path (it must precede all references to System32). For example, the default installed path to java.exe in RAD Studio is: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_25\bin Note that you should only need to add an override if your Java installation is different from this. End your path entry with a semicolon (;):
- Click OK on the Override dialog box, and click Yes on the Confirm dialog box that follows.
- Verify that you see the path to Java shown at the start of the Path field in the User overrides pane:
- Click OK to close the Tools Options Dialog Box.
Источник
-


 in the toolbar.
in the toolbar.

 , click the entry field and browse to the installed location of that library on your system.
, click the entry field and browse to the installed location of that library on your system.