- How to install Android SDK and setup AVD Emulator without Android Studio
- Understanding the Android SDK
- Installing the Android SDK
- Step 1 — Download the tools package
- Step 2— You need Java 8!
- Step 3 — Download the essential packages
- Step 4 — Set your environmental variables
- Step 5 — Download the platform specific packages you want
- Step 5 — Create a AVD device
- Step 6 — Run the Android Emulator
- steveclarke / Install Android SDK CLI Ubuntu 20.04 WSL2.md
- This comment has been minimized.
- PowerMogli commented Oct 12, 2020 •
- This comment has been minimized.
- steveclarke commented Oct 12, 2020
- This comment has been minimized.
- ReazerDev commented Nov 26, 2020
- This comment has been minimized.
- ReazerDev commented Nov 26, 2020
- This comment has been minimized.
- steviesteve commented Dec 7, 2020
- This comment has been minimized.
- ramitd1995 commented Jan 17, 2021
- This comment has been minimized.
- ariefitriadin commented Feb 11, 2021
- This comment has been minimized.
- mateusleon commented Apr 7, 2021
- This comment has been minimized.
- asafeca commented May 23, 2021
- This comment has been minimized.
- jason-s-yu commented Jun 5, 2021 •
- This comment has been minimized.
- mnirm commented Oct 24, 2021
- This comment has been minimized.
- joaop221 commented Nov 2, 2021
- Установка Android Studio в Ubuntu 20.04
- Системные требования Android Studio:
- Установка Android Studio в Ubuntu
- 1. Установка из snap-пакета
- 2. Установка из центра приложений
- 3. Установка с официального сайта
- 4. Установка в JetBrains Toolbox
- Как удалить Android Studio
- Выводы
How to install Android SDK and setup AVD Emulator without Android Studio
If you are trying to develop to Android, you probably will end up installing the Android Studio to get the Android SDK and the AVD Emulator working properly.
But if you are using another code editor, like Sublime Text or VSCode, installing the Android Studio will just mess up with your setup and consume your precious RAM for no good reason.
I had a hard time figuring out how to properly do this setup due the lack of documentation about it, so i hope this article helps you. 🙂
Recommended previous knowledge:
- SDK (Standard Development Kit); Read about on Wikipedia;
- AVD (Android Virtual Device); Read about on docs;
- CLI (Command Line Interface); Read about on Wikipedia;
- Android API levels; Read about on Vanderbilt University;
- How to open, navigate and execute files in your OS terminal;
- Know what are environmental variables;
Understanding the Android SDK
Basically, the Android SDK is a bunch of packages necessary to develop for Android.
These packages stays in subfolders of a folder called “sdk” (or “android-sdk” sometimes). You do not need to know how these packages really work, just what they do.
The picture below is my Android SDK folder, these are the basic packages you will need in order to get everything working properly.
Here is a brief explanation of each package:
- tools: This package is mainly used to manage the other packages and to create AVD’s;
- emulator: As the name suggest, this is the Android emulator;
- platform-tools: Some tools to communicate with Android devices when you plug then in your computer;
- patcher: This package is automatically downloaded by the SDK. I didn’t find what exactly this is for, so just leave it as it is;
The folders bellow contain sub-folders with the packages for each Android API level.
- platforms: The platform packages are required to compile your app for the specified API level.
- system-images: These are the android images used in the emulator.
- build-tools: These are necessary to build your Android apps
Installing the Android SDK
In order to install the SDK we will use the Command Line Tools. These are some quite simple CLI’s used to manage the Android SDK. You can read the documentation here for more details.
Step 1 — Download the tools package
First, you need to download the tools package. And with this package you can download the others.
- First, go to the Android Studio download page: https://developer.android.com/studio;
- Then click in “ Download Options”;
- There you will find a table named “ Command line tools only”;
- This table contain some zip files. Download the appropriate file for your system ( Windows, Mac or Linux);
- Extract this zip and you will get a folder called tools: This is the tools package i explained earlier;
Create a folder anywhere you prefer to place your SDK. I recommend you to stick with one of these commonly used places:
- Globally: C:\Android\sdk or C:\android-sdk (this is not default, but i usually set my SDK here on Windows)
- One user only: C:\Users\ \AppData\Local\Android\sdk
- Globally: /Library/Android/sdk
- One user only: /Users/ /Library/Android/sdk
And move the tools folder to this new sdk folder. Make sure you have admin access to this folder and any sub-folders inside it, or the tools package will fail to download new packages.
Note: You can also download a pre-build package for your SO (like the one available on Ubuntu repository). But i do not recommend you do to so, because they probably will not be updated and will be harder to manage, since it was automatically installed.
Step 2— You need Java 8!
The Android SDK packages require Java 8. If you do not have it, you need to download. If you are using a newer version, you have to downgrade to Java 8 or you will eventually get some errors, because it is not compatible.
If you do not have the Java 8 SDK, here is how you can install it:
On Ubuntu run these commands:
- # sudo apt-get update
- # sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk
Sorry for MacOS users, i don’t know how to install it on this OS.
Step 3 — Download the essential packages
Now, download the platform-tools and the emulator packages, because they contain some CLI binary files you will need later. I decided to download these packages first in order to set all the necessary environment variables at once and make the rest of the process easier.
Open a terminal window (you need to use a terminal, not the file explorer), go to your sdk folder and navigate to the /tools/bin directory.
This folder contain the SDKManager binary: this is a CLI used to list the available packages in the Google’s repository and download, update or remove them from your SDK folder.
The bellow command will list all packages installed (the first items on the list) and all packages available to download:
To download the packages, simply copy the package names and pass it as a parameter to the SDKManager CLI using the terminal:
# ./sdkmanager platform-tools emulator
If you open your sdk folder you should see these packages folders there.
Step 4 — Set your environmental variables
You need to set the below environmental variables containing the path to our SDK, so any running program can find it in your pc:
ANDROID_SDK_ROOT = Path to your SDK folder
ANDROID_HOME = The same as ANDROID_SDK_ROOT. This variable is now deprecated, but i recommend setting it because some programs still using it to locate your sdk.
And add these folders to the PATH variable, making their binary files accessible from everywhere:
To add the environment variables on WIndows, just follow these steps:
- Open the “Control Panel”;
- Go to “ System and Security” option in the side menu;
- In the window “ System Properties” open the tab “ Advanced”;
- Click in the button “ Environment Variables” in the bottom of the page;
- In the “ Environment Variables” window you will see two tables: “User Variables” and ” System Variables”.
- If you created your sdk folder for one user only, set the variables in the “ User Variables” table;
- But, if you create your sdk folder globally, set the variables in the “ System Variables” table instead;
On Linux, you can set your environment variables in many places. So i choose the ones I found the most appropriate:
- If you created your sdk folder for one user only, set your environment variables in the file
/.bashrc;
Here is how i set these variables in my Ubuntu, using the file /etc/environment:
And sorry again, no MacOS instructions for this task.
You can find more about these environmental variables in the oficial docs here.
Now your SDK is ready! If you do not need to run the emulator there’s no need to follow the next steps.
Step 5 — Download the platform specific packages you want
You need more three packages: The platform, the system-image and the build-tools. You can download these packages for any Android version you prefer. In this article, i will download the packages for the API Level 28.
Use the “ sdkmanager — list” command to find these packages and download them using the command “ sdkmanager
Here’s an example:
Step 5 — Create a AVD device
Creating a AVD device is a simple task: run the AVDManager command (this is a binary file located in the tools/bin folder of your sdk) with the create avd option, a name for the new AVD and the image you want to use.
Here is a example:
# avdmanager create avd — name android28 — package “system-images;android-28;default;x86”
You will be asked if you want to alter some configurations. You can also modify these configurations later in the file config.ini, located in the avd folder (this folder usually is created in your user folder, under the android directory). The currently active configurations can be find in the file hardware-qemu.ini (this file just will be created after the emulator runs for the first time).
Step 6 — Run the Android Emulator
Now you just need to run the emulator command (remember that we added this package to the environmental variables?):
The emulator take some time to init for the first time. But if you done everything correctly you should see this screen:
Источник
steveclarke / Install Android SDK CLI Ubuntu 20.04 WSL2.md
Install Android SDK CLI Ubuntu 20.04 WSL2 (Work in Progress)
Note: you can get an updated Android SDK link from https://developer.android.com/studio/#downloads
Background on the update to command line tools from android sdk https://stackoverflow.com/a/61176718
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
PowerMogli commented Oct 12, 2020 •
thank you so much! so much lost time before
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
steveclarke commented Oct 12, 2020
thank you so much! so much lost time before
Glad it helped. I haven’t figured out how to connect to emulator or physical device yet. Feel free to fork and share your config if you get that part working.
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
ReazerDev commented Nov 26, 2020
To connect to a physical device. Connect the device to a USB Port, in your windows cmd run adb tcpip 5555 . Then in your WSL cmd run adb connect IP_ADDRESS_OF_PHONE:5555 . You can find the IP_ADDRESS_OF_PHONE aprt, by going into your phone’s wifi settings, clicking on the wifi you are connected to click on Advanced and then you see an IP address field. That’s it
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
ReazerDev commented Nov 26, 2020
Oh and btw. really great tutorial. Saved me a ton of time
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
steviesteve commented Dec 7, 2020
Super helpful thanks!
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
ramitd1995 commented Jan 17, 2021
Great work Steve, this works like a charm and saved a lot of time.
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
ariefitriadin commented Feb 11, 2021
Great, super helpful, TQ
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
mateusleon commented Apr 7, 2021
I`ve struggled a little bit with the step after unzipping and placing the paths into $PATH variable. This thread helped me to figure out the issues: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/60440509/android-command-line-tools-sdkmanager-always-shows-warning-could-not-create-se
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
asafeca commented May 23, 2021
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
jason-s-yu commented Jun 5, 2021 •
The latest version of cmdline tools (7302050_latest) seems to have a different directory structure. The folder is now called cmdline-tools instead of tools so when you extract the folder it won’t work as expected. sdkmanager also seems to expect to want to be in $
So it looks like unzipping the newest version to $
Not sure how this whole forking gists thing is supposed to work but here are the changes I used: https://gist.github.com/jason-s-yu/30375db45c1f71c1259e042d216e4bd3
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
mnirm commented Oct 24, 2021
Thank you very much. Very easy to use ❤
This comment has been minimized.
Copy link Quote reply
joaop221 commented Nov 2, 2021
I recommend to add the update command and the unzip installation in this steps:
Источник
Установка Android Studio в Ubuntu 20.04
Android Studio — это официальная и самая популярная интегрированная среда разработки Android-приложений. Программа разрабатывается корпорацией Google и содержит все необходимые возможности. Среда основана на IntelliJ IDEA, которая написана на Java.
Среди возможностей Android Studio не только написание, сборка и тестирование программ, но и поддержка загрузки их на устройство, интеграция с облаком и многое другое. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как выполняется установка Android Studio в Ubuntu.
Системные требования Android Studio:
Рекомендованные системные требования:
- Дистрибутив — любой 64 битный дистрибутив с установленной glibc 2.31 или выше и окружением рабочего стола Gnome, KDE или Unity DE.
- Процессор — 64-битный, с поддержкой SSSE3 и Intel VT или AMD V;
- RAM — 8 Гб или больше;
- Свободное место на диске — 8 Гб;
- Разрешение экрана — 1280 x 800;
Установка Android Studio в Ubuntu
Вы можете установить Android Studio и Android SDK несколькими способами: c помощью snap-пакета, с официального сайта, из центра приложений, а также с использованием специального инструмента: JetBrains Toolbox. Каждый из способов имеет свои преимущества, и мы рассмотрим их все.
1. Установка из snap-пакета
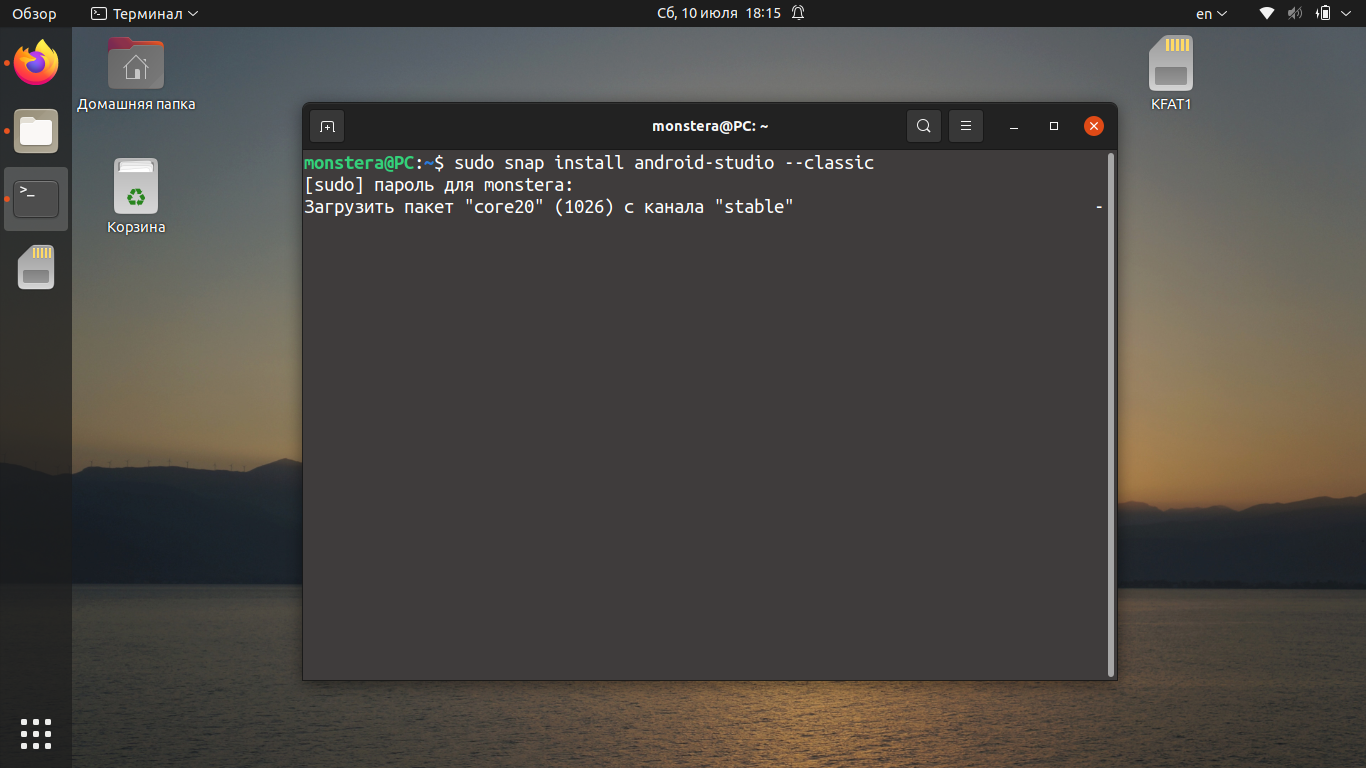
Для установки Android Studio с помощью snap-пакета откройте терминал и выполните команду:
sudo snap install android-studio —classic
После завершения загрузки пакета программа будет доступна в главном меню.
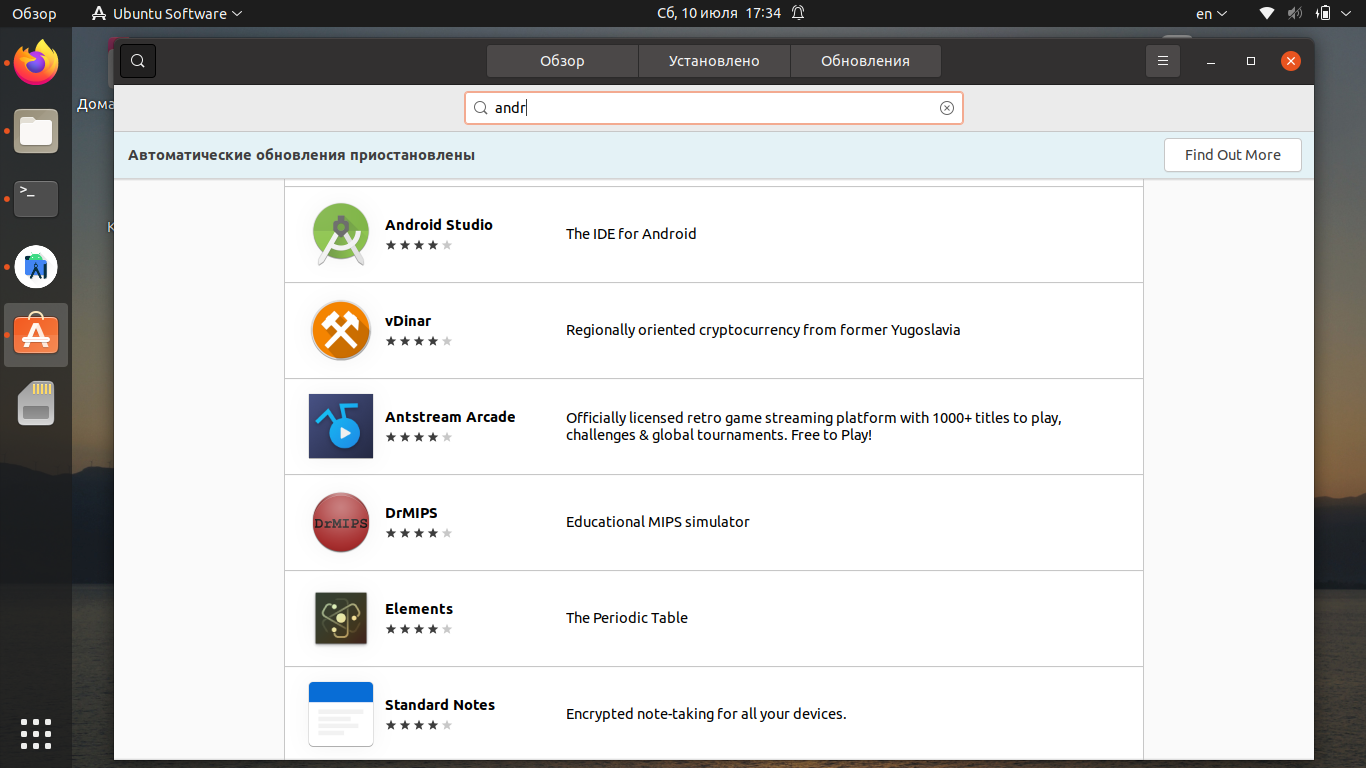
2. Установка из центра приложений
Запустите центр приложений Ubuntu и введите в поиске название программы:
В списке выберите Android Studio и нажмите на кнопку Установить.
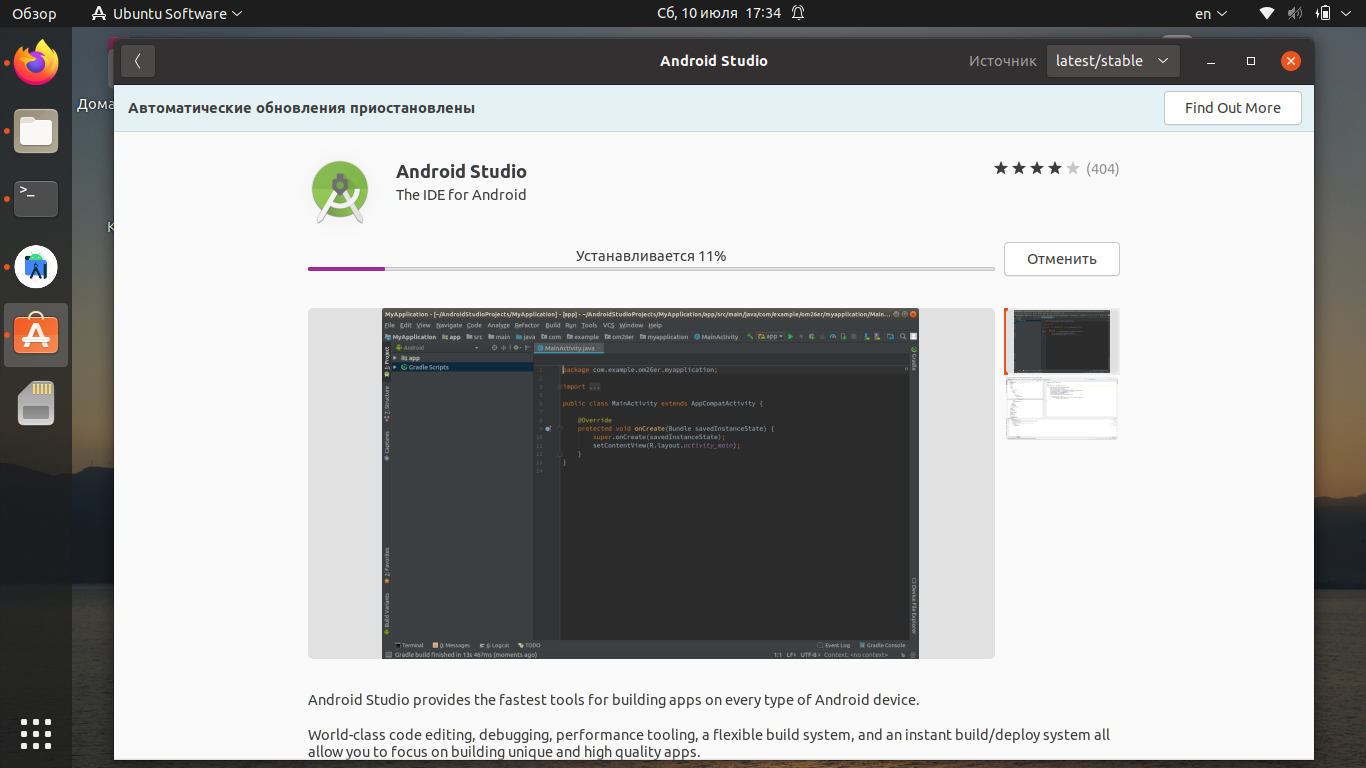
Дождитесь, пока инсталляция будет завершена.
Процесс установки может занять до 30 минут (зависит от скорости вашего интернет-соединения). По окончании загрузки вы сможете запустить приложение.
3. Установка с официального сайта
Прежде всего, вам необходимо загрузить установщик с официального сайта разработчиков. Перейдите на сайт и нажмите Download Android Studio.
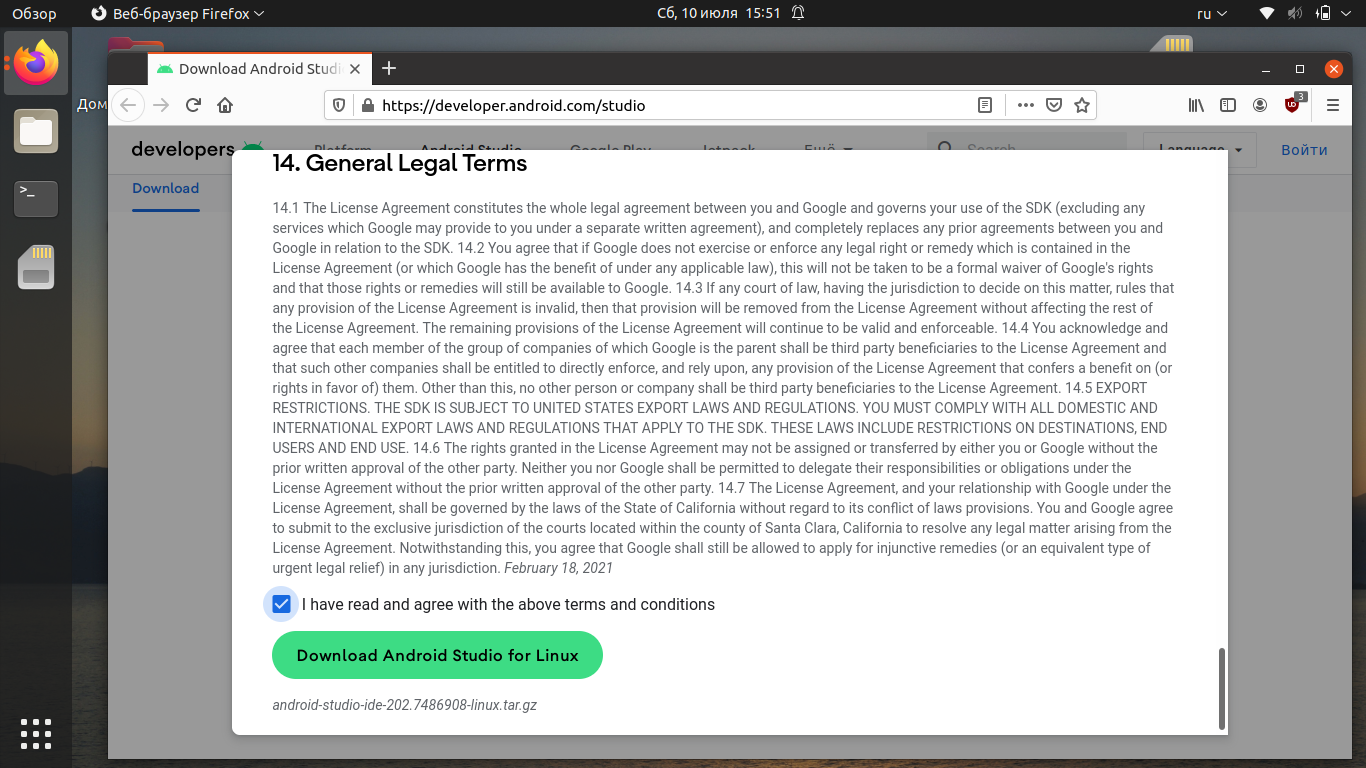
Ознакомьтесь с лицензионным соглашением, активируйте чекбокс и нажмите кнопку Download Android Studio for Linux.
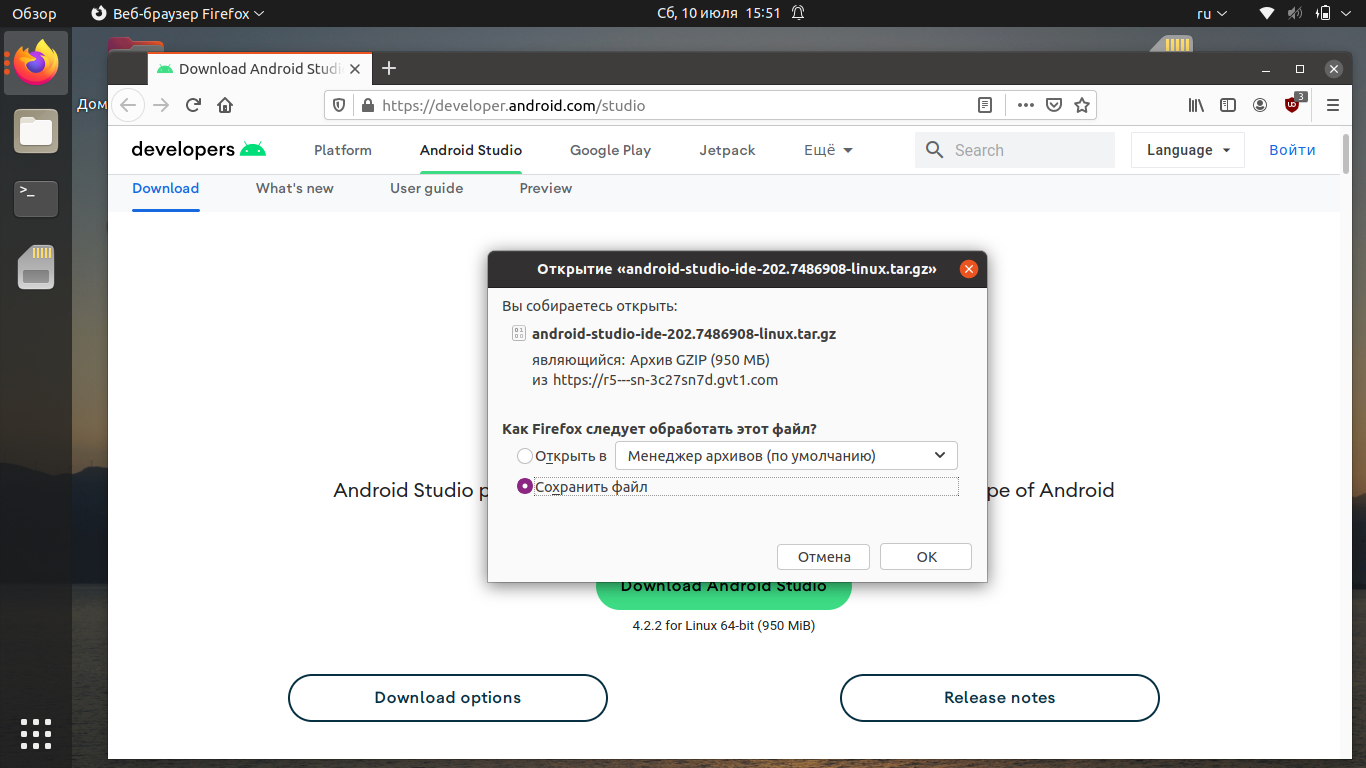
Выберите Сохранить файл и нажмите ОК.
Дождитесь завершения скачивания.
Когда файл будет загружен, перейдите в папку с загрузками и распакуйте содержимое архива в /opt. Для этого используйте команду вида (укажите скачанную вами версию приложения вместо 202.7486908):
/Загрузки/android-studio-ide-202.7486908-linux.tar.gz -C /opt
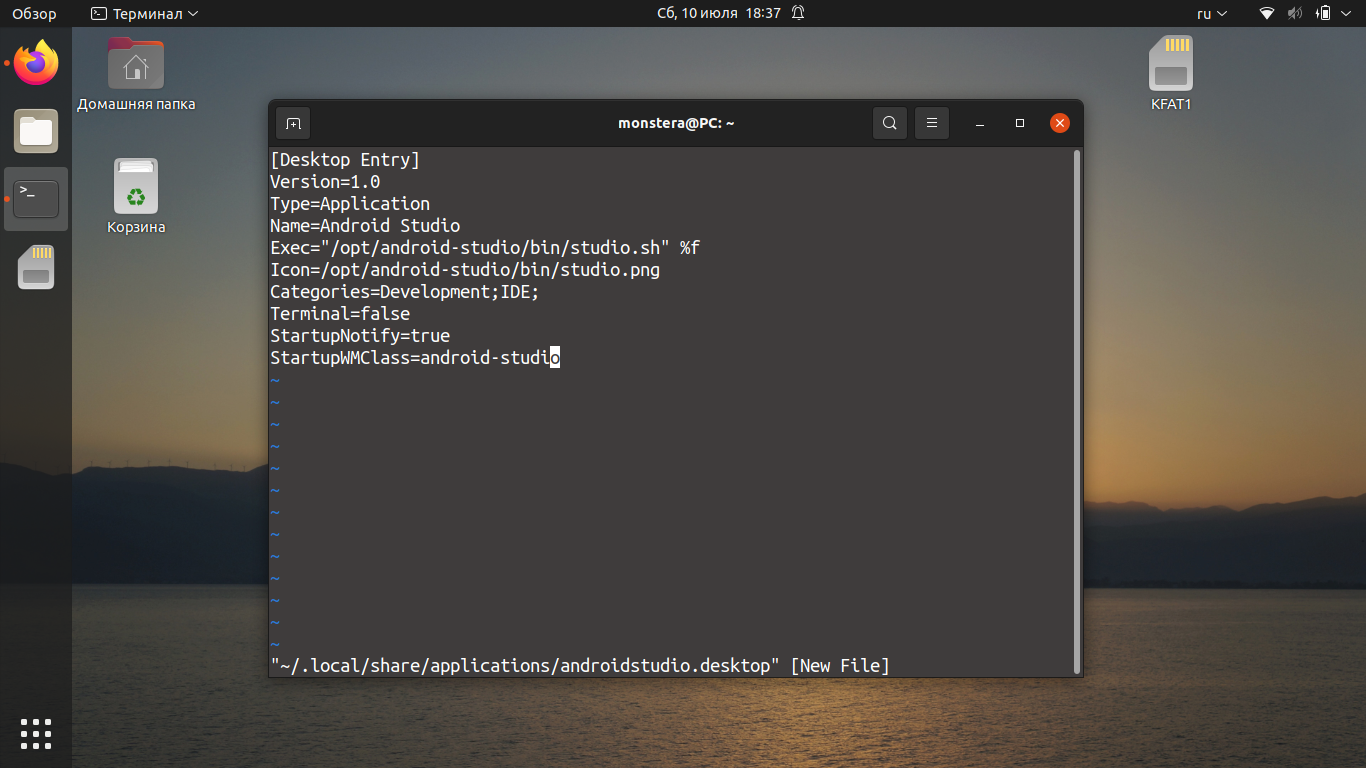
Чтобы добавить ярлык в меню приложений, создайте файл androidstudio.desktop командой:
Добавьте в файл следующий текст и сохраните его:
[Desktop Entry]
Version=1.0
Type=Application
Name=Android Studio
Exec=»/opt/android-studio/bin/studio.sh» %f
Icon=/opt/android-studio/bin/studio.png
Categories=Development;IDE;
Terminal=false
StartupNotify=true
StartupWMClass=android-studio
После этого установка будет завершена, и вы можете запустить среду разработки из главного меню:
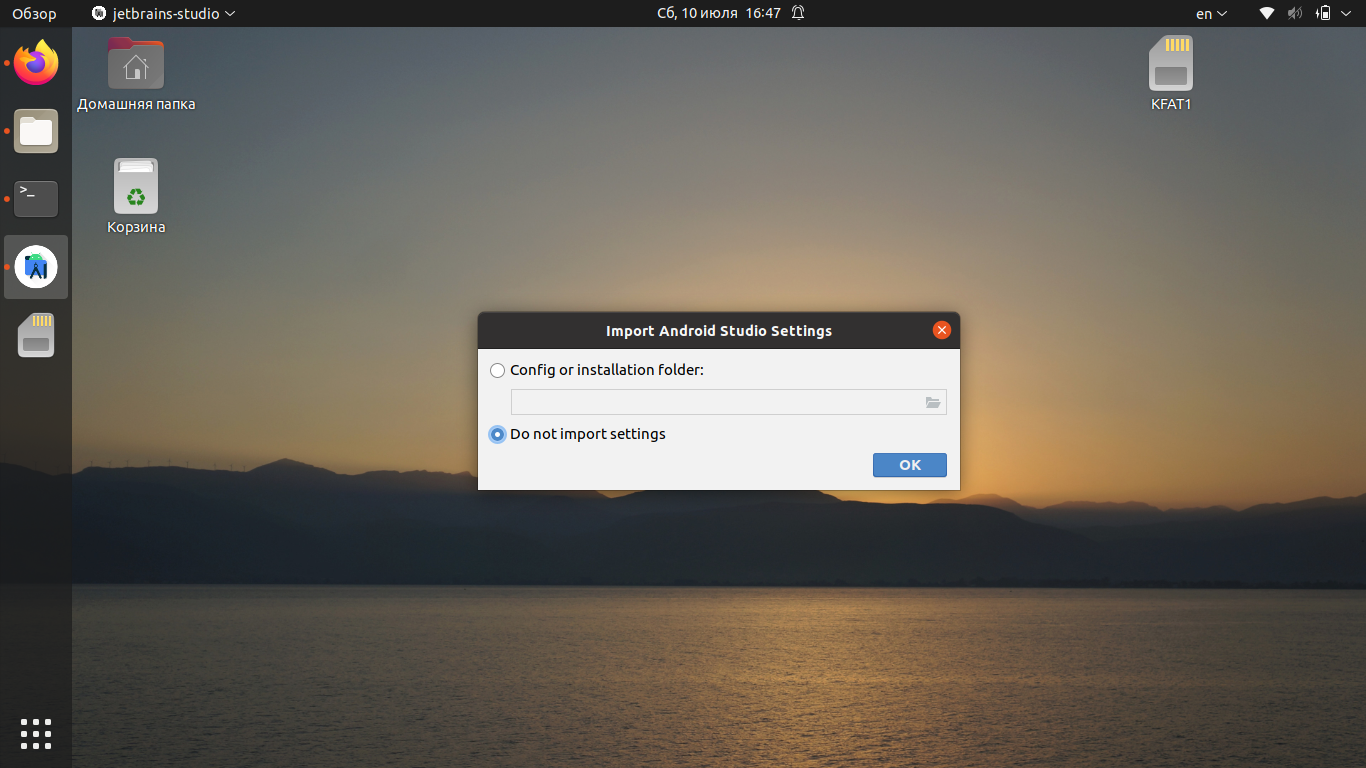
Но окончательная установка Android Studio ещё не завершена — программа должна скачать все необходимые компоненты и настройки. Если вы работали с Android Studio ранее, в следующем окне вы можете скопировать свои настройки. Если нет, — выберите Do not import settings и нажмите ОК.
Потребуется некоторое время, чтобы программа могла загрузить нужные компоненты и настроить систему.
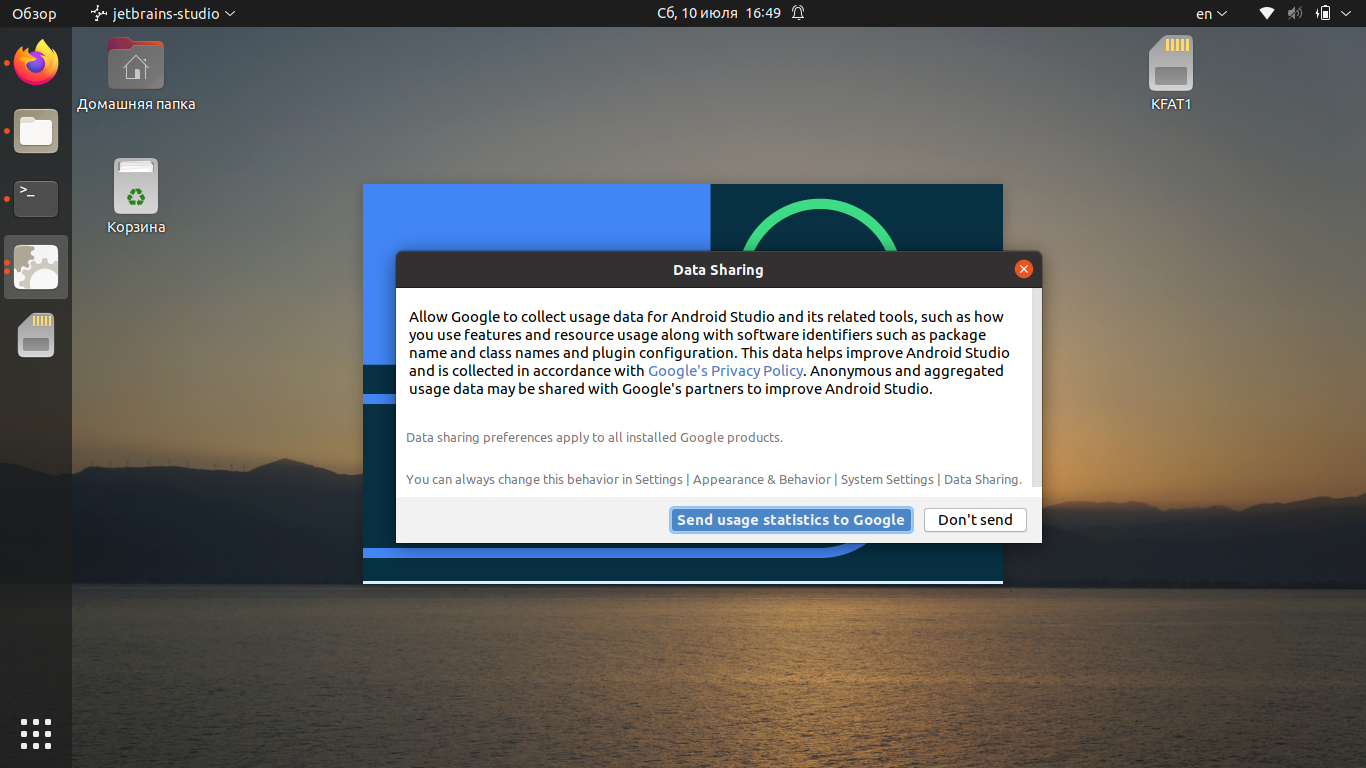
Приложение спросит, нужно ли отправлять статистику в Google. Эти данные могут использоваться для улучшения следующих версий Android Studio. Определитесь с выбором, чтобы продолжить установку.
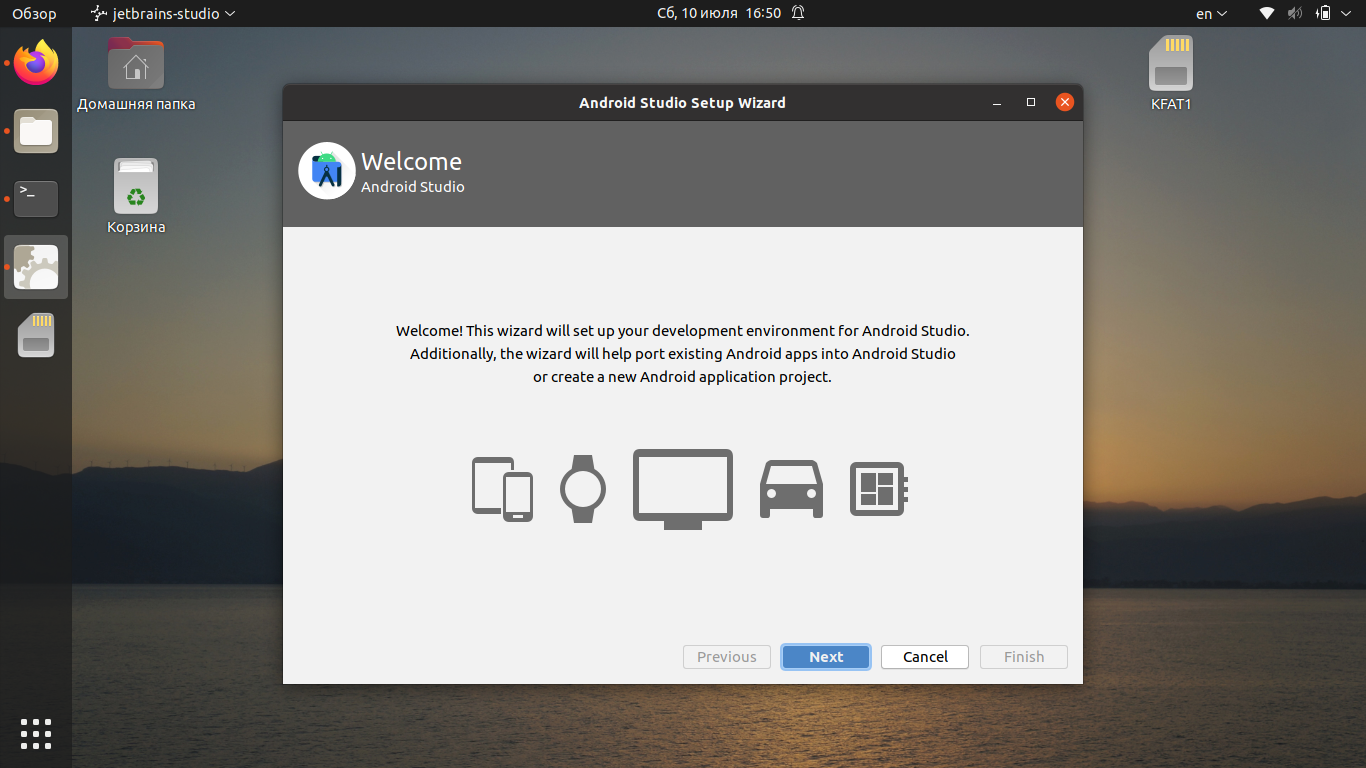
На следующем экране нажмите кнопку Next:
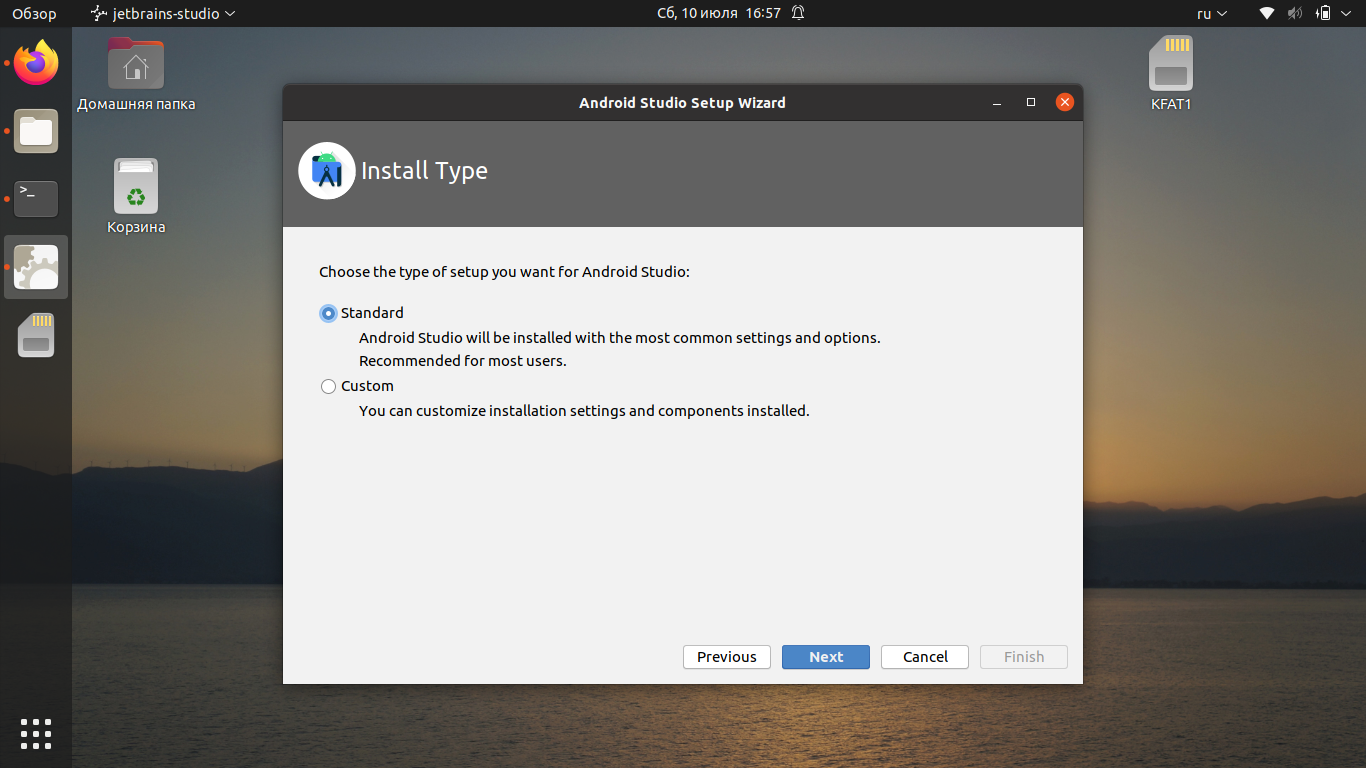
После этого вы сможете выбрать между стандартной автоматической инсталляцией и ручной. Второй способ позволяет выбрать для установки отдельные компоненты.
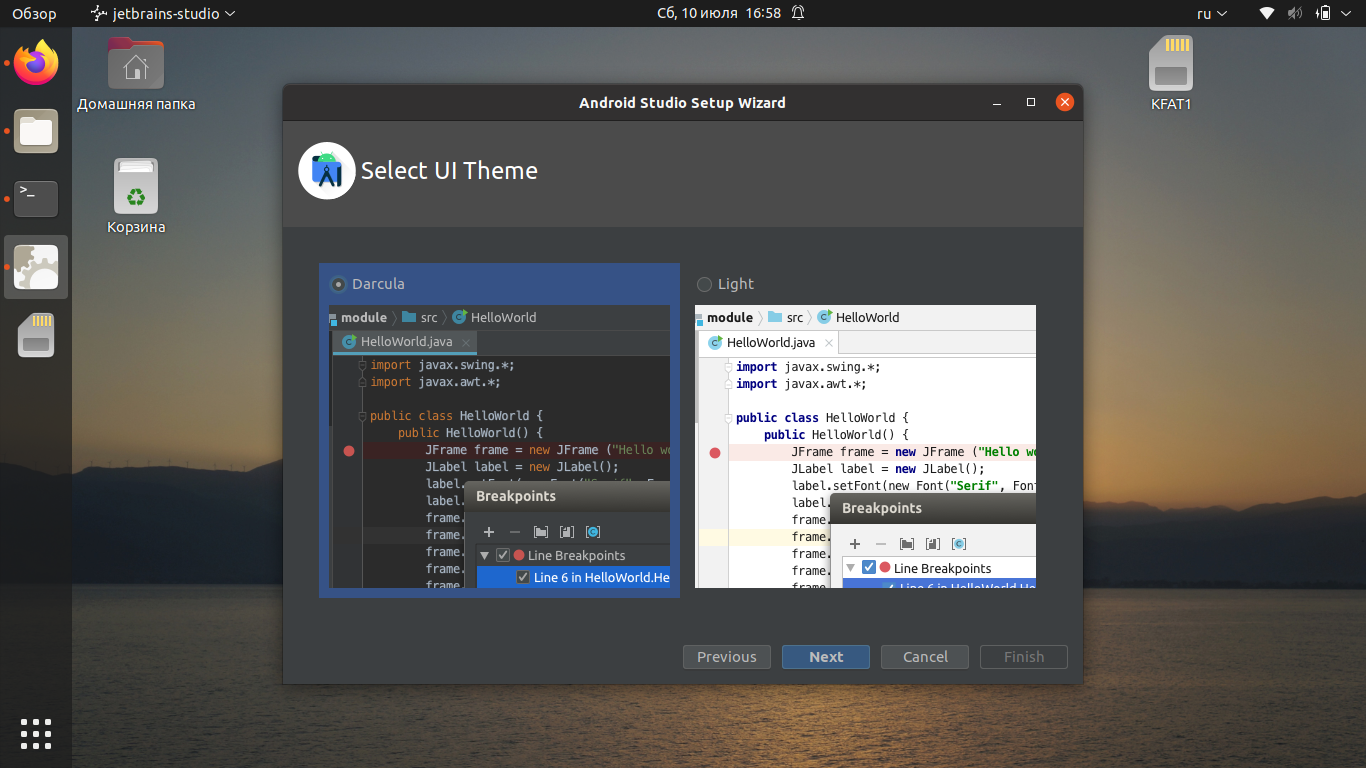
Выберите предпочитаемую тему оформления:
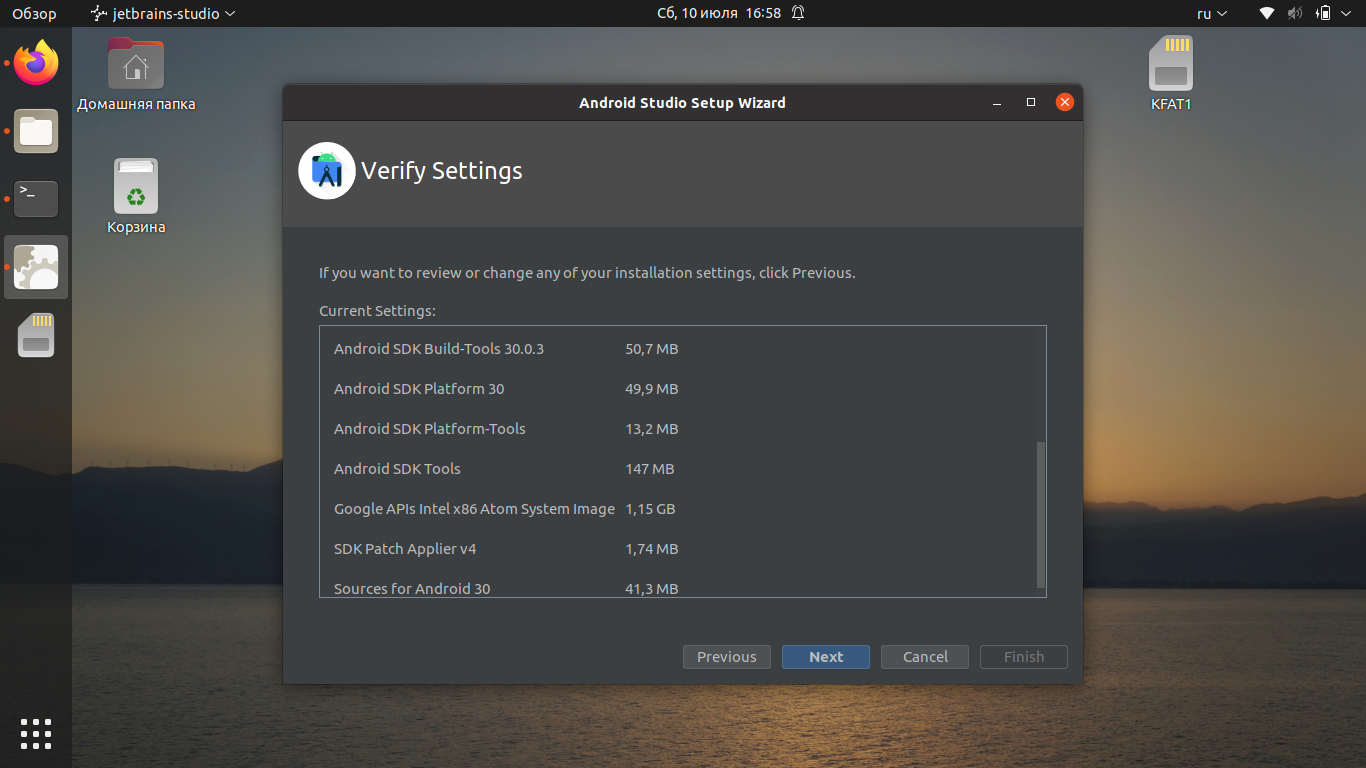
Ознакомьтесь со списком компонентов и их расположением:
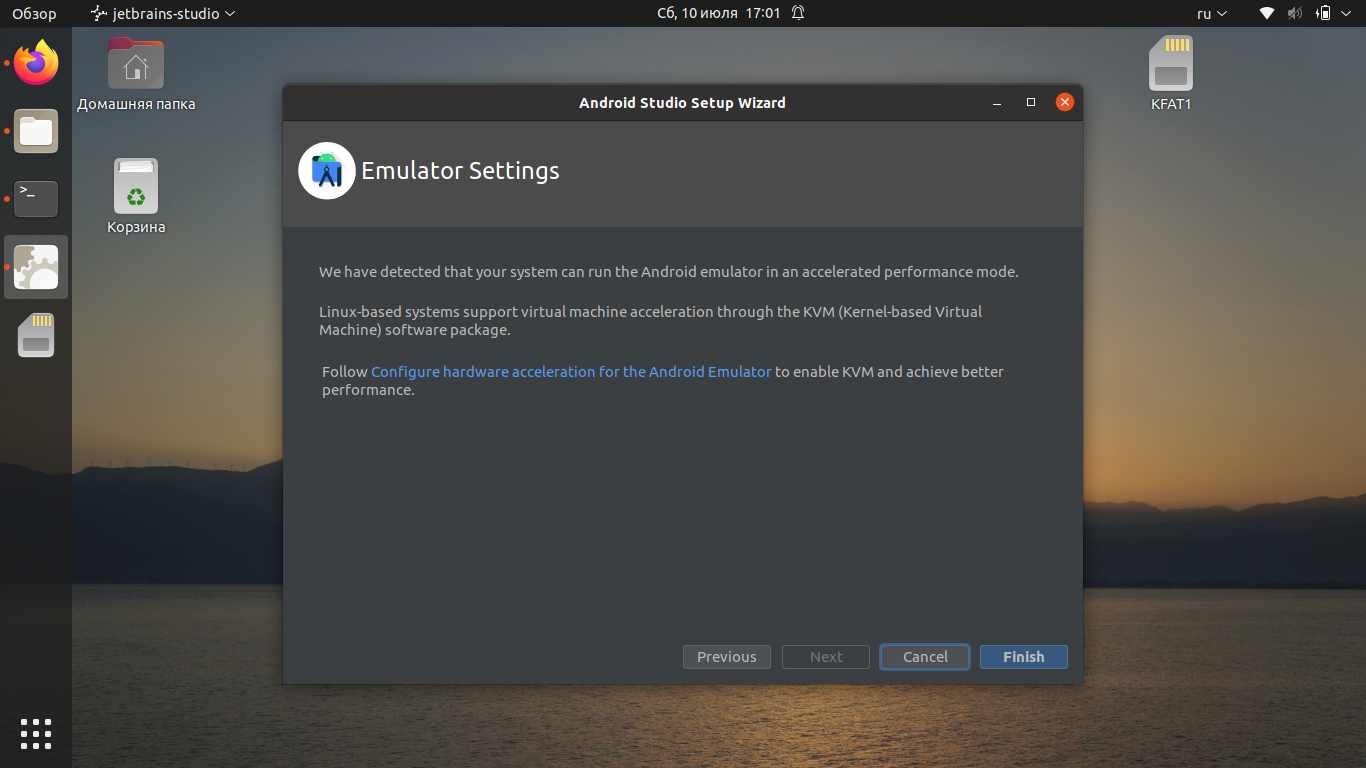
Приложение отобразит уведомление о том, можете ли вы использовать эмуляторы на своём компьютере (зависит от аппаратной составляющей).
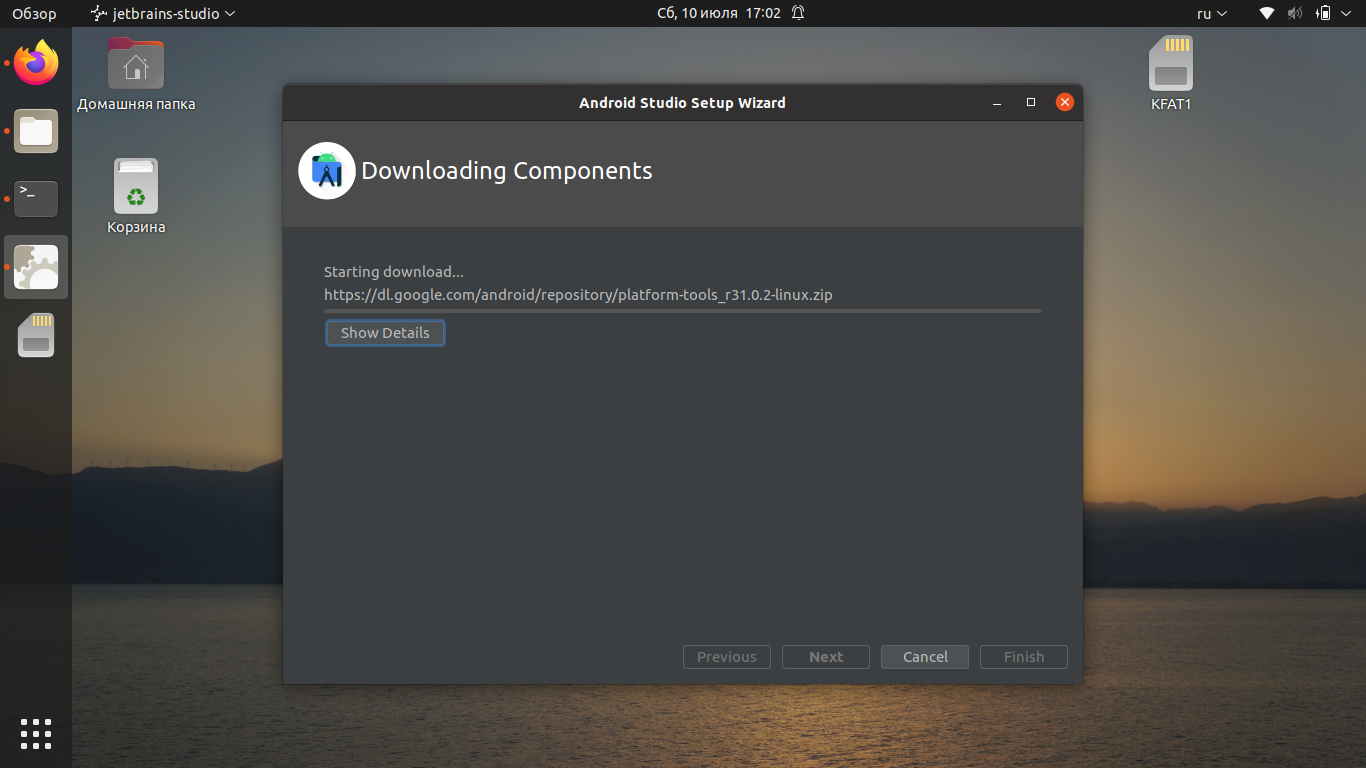
Далее начнётся загрузка, которая может занять довольно много времени, скорость зависит от вашего интернет соединения:
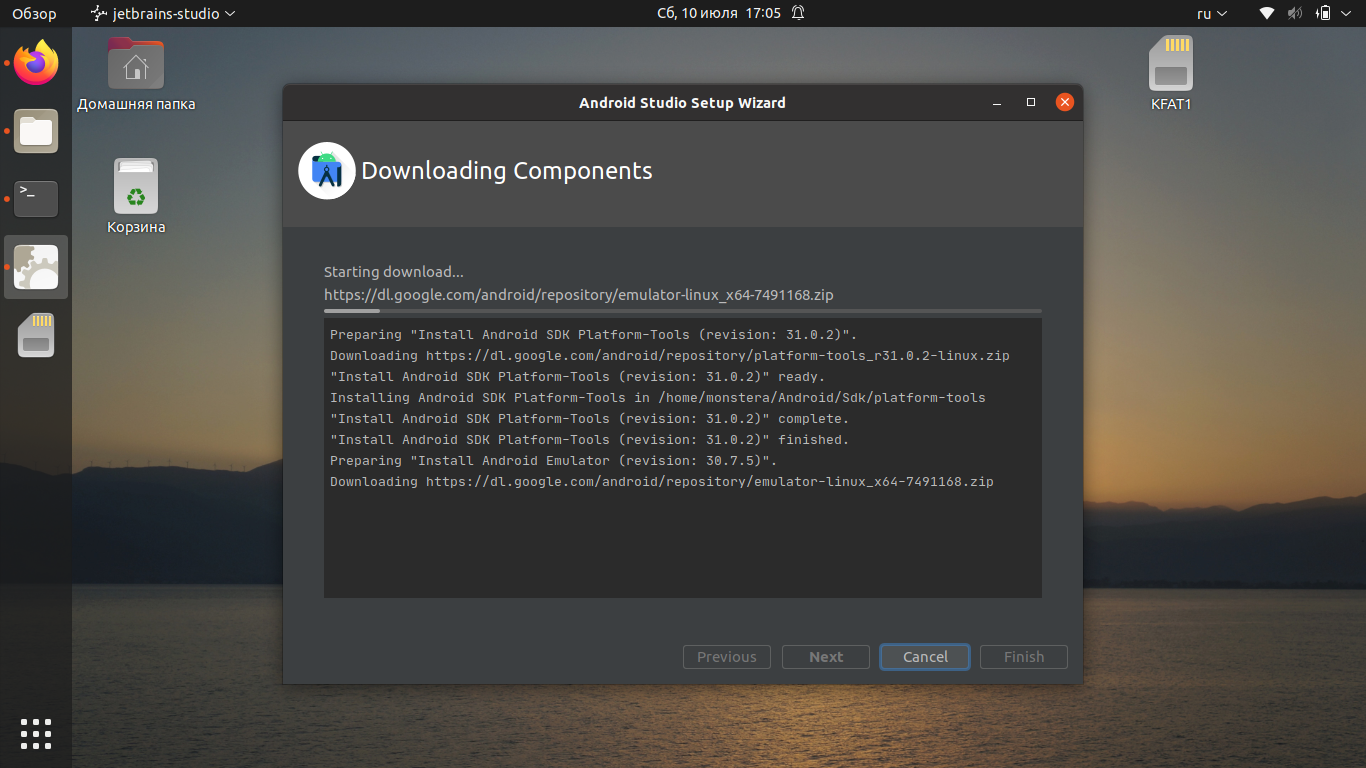
Можно нажать кнопку Show Details, чтобы наблюдать очерёдность установки компонентов:
Когда загрузка завершится, вы можете нажать Finish и перейти к созданию нового проекта.
4. Установка в JetBrains Toolbox
JetBrains Toolbox — это официальный инструмент для установки и пакетного обновления Android Studio и других продуктов JetBrains. Загрузить JetBrains Toolbox можно с официального сайта разработчиков.
После этого перейдите в директорию, куда был скачан архив. Например, если это папка Загрузки, выполните команду:
Распакуйте скачанный архив. Имя файла актуально на момент написания статьи, но в будущем версия может отличаться:
tar -xzvf jetbrains-toolbox-1.20.8804.tar.gz
Перейдите в созданную директорию:
Чтобы запустить менеджер пакетов, введите команду:
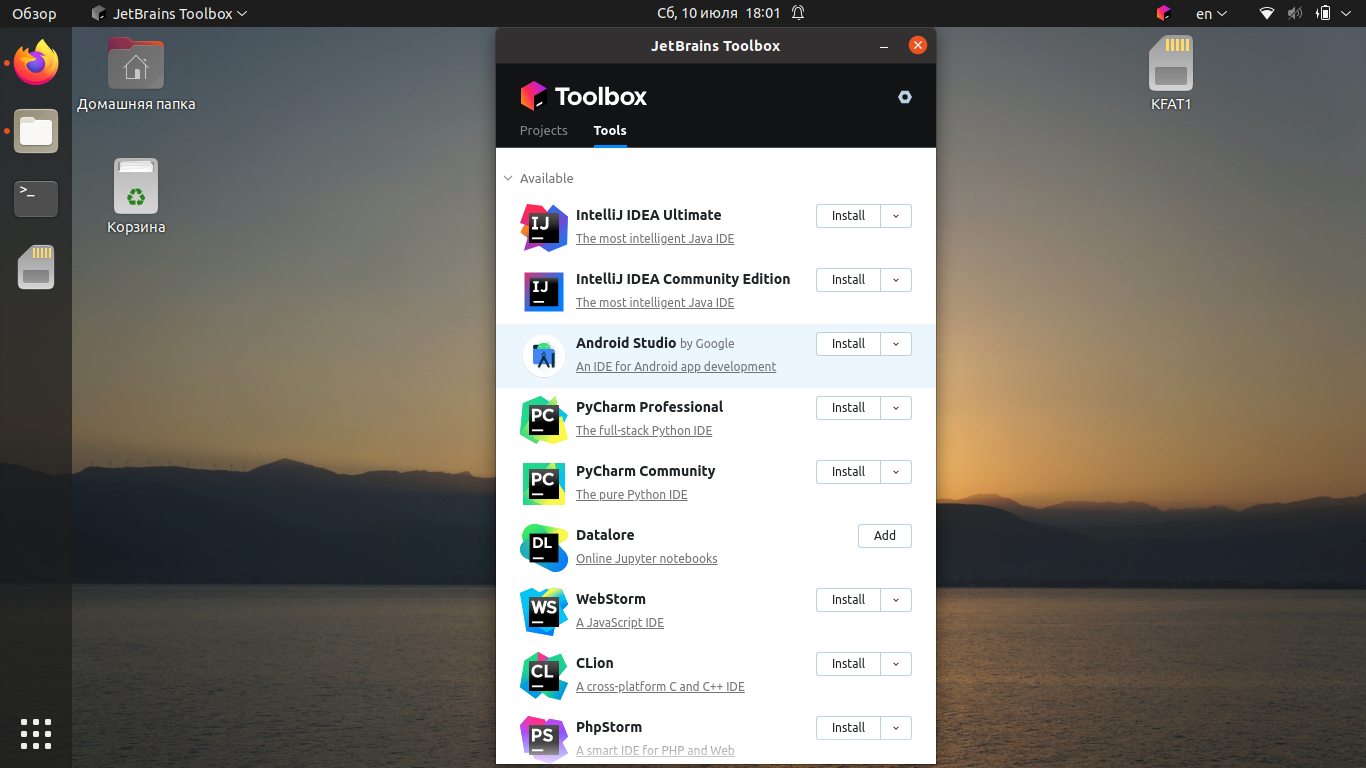
После запуска Toolbox найдите Android Studio в списке и нажмите кнопку Install:
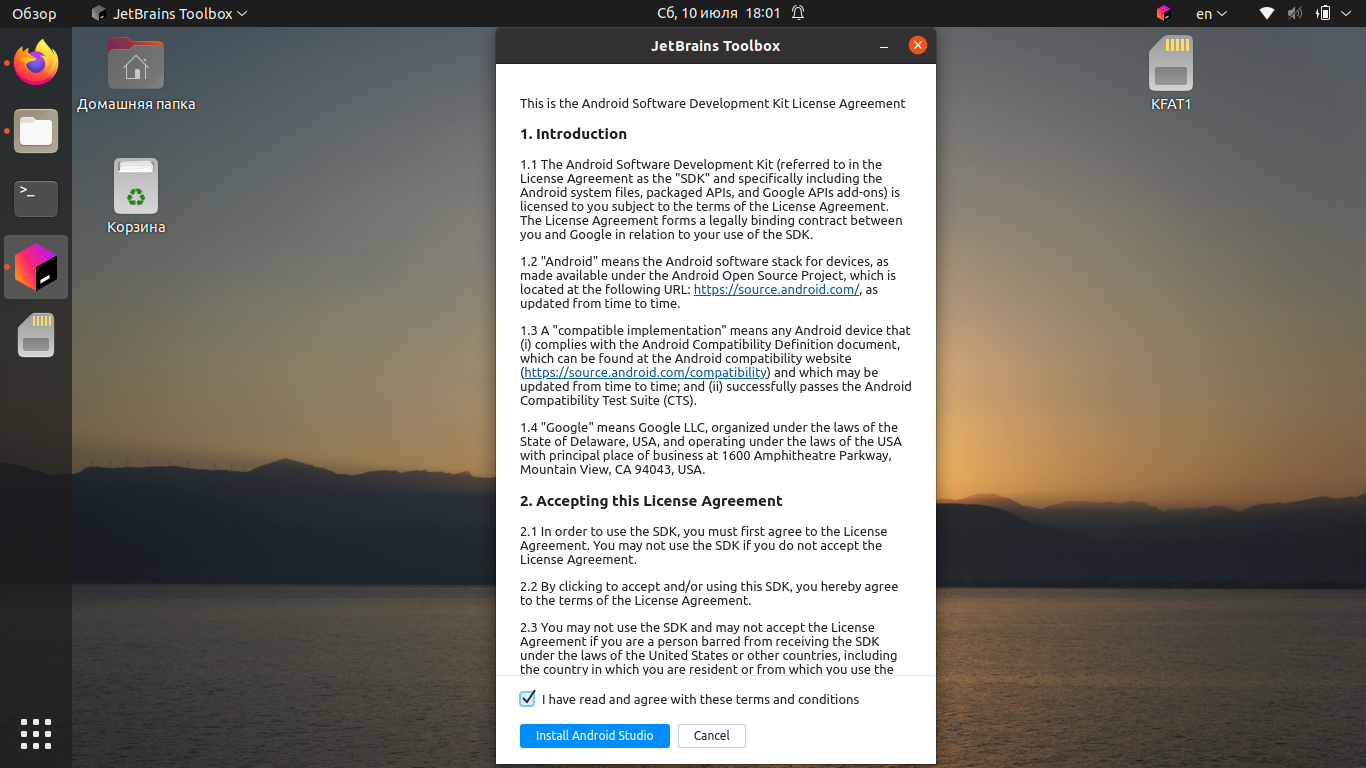
Подтвердите, что вы прочитали и принимаете лицензионное соглашение, после чего нажмите кнопку Install Android Studio.
Дождитесь, пока программа установится на ваш компьютер. После установки её можно будет запустить из главного меню Toolbox.
Как удалить Android Studio
Если вы устанавливали Android Studio с использованием snap-пакета или через центр приложений Ubuntu, её можно удалить командой:
sudo snap remove android-studio
Если же среда разработки была загружена с официального сайта, достаточно удалить распакованную папку вручную или с помощью команды в терминале:
sudo rm -Rf /opt/android-studio
Программа, установленная с помощью JetBrains Toolbox, удаляется с использованием этого инструмента. Перейдите в Toolbox, нажмите на значок шестерёнки рядом с Android Studio и выберите Delete.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели, как выполняется установка Android Studio в Ubuntu 20.04 различными способами. Можете выбрать тот способ установки, который лучше всего подходит именно для вас. Если остались вопросы, задавайте их в комментариях.
Источник