- Download
- Terms and Conditions
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Accepting this License Agreement
- 3. SDK License from Google
- 4. Use of the SDK by You
- 5. Your Developer Credentials
- 6. Privacy and Information
- 7. Third Party Applications
- 8. Using Android APIs
- 9. Terminating this License Agreement
- 10. DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES
- 11. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
- 12. Indemnification
- 13. Changes to the License Agreement
- 14. General Legal Terms
- Android Studio
- Intelligent code editor
- Code templates and GitHub integration
- Multi-screen app development
- Virtual devices for all shapes and sizes
- Android builds evolved, with Gradle
- More about Android Studio
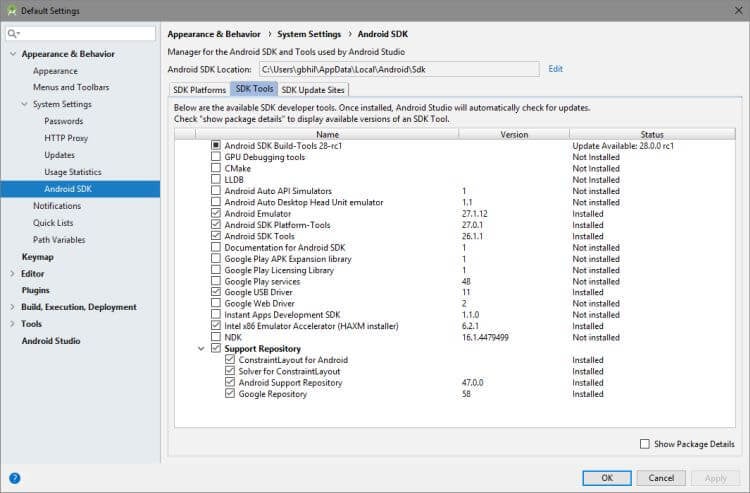
- System Requirements
- Windows
- Mac OS X
- Linux
- Как установить Android SDK на Windows, Mac и Linux
- Ручная установка
- Установка компонентов
- Ссылки
- Install Android Studio
- Windows
- Linux
- Required libraries for 64-bit machines
- Chrome OS
- How to install the Android SDK on Windows, Mac and Linux
- What to choose?
- Manually installing the Android SDK
- Prerequisites
- Installing the tools
- Setting your PATH
- On Windows
- On a Mac
- On Linux
- Wrapping it up
- Have you listened to this week’s Android Central Podcast?
- Samsung needs to bring back its iPod competitor
- VoLTE: How to use it and why you should care
- PlayStation reportedly planning service to compete with Xbox Game Pass
- These are the best USB-C cables you can find for Android Auto
Download
Before installing Android Studio or the standalone SDK tools, you must agree to the following terms and conditions.
Terms and Conditions
1. Introduction
2. Accepting this License Agreement
3. SDK License from Google
4. Use of the SDK by You
5. Your Developer Credentials
6. Privacy and Information
7. Third Party Applications
8. Using Android APIs
9. Terminating this License Agreement
10. DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES
11. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
12. Indemnification
13. Changes to the License Agreement
14. General Legal Terms
You’re just a few steps away from building apps for Android!
In a moment, you’ll be redirected to Installing the Android SDK.
I have read and agree with the above terms and conditions
Android Studio
The official Android IDE
- Android Studio IDE
- Android SDK tools
- Android 5.0 (Lollipop) Platform
- Android 5.0 emulator system image with Google APIs
Download Android Studio
To get Android Studio or stand-alone SDK tools, visit developer.android.com/sdk/
Intelligent code editor
At the core of Android Studio is an intelligent code editor capable of advanced code completion, refactoring, and code analysis.
The powerful code editor helps you be a more productive Android app developer.
Code templates and GitHub integration
New project wizards make it easier than ever to start a new project.
Start projects using template code for patterns such as navigation drawer and view pagers, and even import Google code samples from GitHub.
Multi-screen app development
Build apps for Android phones, tablets, Android Wear, Android TV, Android Auto and Google Glass.
With the new Android Project View and module support in Android Studio, it’s easier to manage app projects and resources.
Virtual devices for all shapes and sizes
Android Studio comes pre-configured with an optimized emulator image.
The updated and streamlined Virtual Device Manager provides pre-defined device profiles for common Android devices.
Android builds evolved, with Gradle
Create multiple APKs for your Android app with different features using the same project.
Manage app dependencies with Maven.
Build APKs from Android Studio or the command line.
More about Android Studio
For more details about features available in Android Studio, read the overview at Android Studio.
If you have been using Eclipse with ADT, be aware that Android Studio is now the official IDE for Android, so you should migrate to Android Studio to receive all the latest IDE updates. For help moving projects, see Migrating to Android Studio.
System Requirements
Windows
- Microsoft® Windows® 8/7/Vista/2003 (32 or 64-bit)
- 2 GB RAM minimum, 4 GB RAM recommended
- 400 MB hard disk space
- At least 1 GB for Android SDK, emulator system images, and caches
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 7
- Optional for accelerated emulator: Intel® processor with support for Intel® VT-x, Intel® EM64T (Intel® 64), and Execute Disable (XD) Bit functionality
Mac OS X
- Mac® OS X® 10.8.5 or higher, up to 10.9 (Mavericks)
- 2 GB RAM minimum, 4 GB RAM recommended
- 400 MB hard disk space
- At least 1 GB for Android SDK, emulator system images, and caches
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 6
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 7
- Optional for accelerated emulator: Intel® processor with support for Intel® VT-x, Intel® EM64T (Intel® 64), and Execute Disable (XD) Bit functionality
On Mac OS, run Android Studio with Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 6 for optimized font rendering. You can then configure your project to use Java Development Kit (JDK) 6 or JDK 7.
Linux
- GNOME or KDE desktop
- GNU C Library (glibc) 2.15 or later
- 2 GB RAM minimum, 4 GB RAM recommended
- 400 MB hard disk space
- At least 1 GB for Android SDK, emulator system images, and caches
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
- Oracle® Java Development Kit (JDK) 7
Tested on Ubuntu® 14.04, Trusty Tahr (64-bit distribution capable of running 32-bit applications).
Источник
Как установить Android SDK на Windows, Mac и Linux
22 октября 2008 года в Android появился магазин приложений Play Market. С тех пор прошло больше 10 лет и сегодня Google Play насчитывает почти 3 миллиона приложений в их числе Telegram с каналом AndroidInsider. Как же разработчикам со всего мира удается создавать качественные продукты? Они используют Android SDK. Чтобы получить все инструменты и средства разработки приложений, необходимо скачать среду разработки Android Studio. Но что, если вы хотите воспользоваться Android SDK с командной строкой без Android Studio и ненужных средств? В этом материале мы подскажем, как правильно установить и настроить Software Development Kit.
Ручная установка
Переходим по этой ссылке, находим раздел «Command line tools only» и скачиваем нужную версию в зависимости от вашей системы.
Создайте папку Android в корневой папке системы. В случае с Windows это локальный диск «С», а в OS X и Linux — домашняя папка пользователя. Распакуйте скачанный архив в папку Android. Для дальнейшей работы необходим установленный пакет Java на компьютере. OS X из коробки его поддерживает, чтобы проверить это, в терминале вбейте «which java», система должна выдать расположение пакета. На Windows и Linux устанавливаем JDK по этой ссылке.
Если вы используете Linux, вам понадобится установить еще несколько пакетов с помощью этой команды «sudo apt-get install lib32ncurses5 lib32stdc++6». Для других версий Linux необходимо найти подходящие пакеты ncurses5 и stdc++6.
Установка компонентов
Переходим в папку «Android/bin», находим исполняемый файл sdkmanager и запускаем, откроется следующее окно:
Выбираем «Android SDK Tools» и «Android SDK Platform-Tools», на Windows необходимо выбрать еще и «Google USB Driver». После этого подтвердите условия лицензионного соглашения, и начнется установка инструментов. В Windows они расположатся в папке «Windows\users\Имя пользователя\AppData\Local\Android», а на Linux и Mac в папке «.Android».
Ссылки
Теперь давайте создадим символическую ссылку на эти папки, чтобы можно было быстро запустить инструменты через командную строку.
В Windows переходим в «Этот компьютер → Свойства → Дополнительные параметры системы → Дополнительно → Переменные среды». В «Переменные среды для пользователя» находим строку «Path» и кликаем по ней 2 раза. Откроется окно, в нём нажимаем «Создать» и вставляем полный путь к инструментам через точку с запятой. Должно выглядеть примерно так «C:\Android\tools;C:\Android\platform-tools».
На Mac в домашней папке находим скрытый файл «.bash_profile» или просто «.profile». Открываем его командой «nano
/.profile» и добавляем путь до инструментов:
export PATH=»$HOME/Android/tools:$PATH»
export PATH=»$HOME/Android/platform-tools:$PATH»
Сохраняем файл комбинацией «CMD+X» и далее жмём «Y». На Linux процесс аналогичен, но нужно запускать файл .bashrc.
Вот и всё. Теперь команды Android SDK доступны через консоль. Вы сможете, например, устанавливать образы и вручную обновлять смартфон.
Источник
Install Android Studio
Setting up Android Studio takes just a few clicks.
Windows
To install Android Studio on Windows, proceed as follows:
- If you downloaded an .exe file (recommended), double-click to launch it.
If you downloaded a .zip file, unpack the ZIP, copy the android-studio folder into your Program Files folder, and then open the android-studio > bin folder and launch studio64.exe (for 64-bit machines) or studio.exe (for 32-bit machines).
That’s it. The following video shows each step of the setup procedure when using the recommended .exe download.
As new tools and other APIs become available, Android Studio tells you with a pop-up, or you can check for updates by clicking Help > Check for Update.
To install Android Studio on your Mac, proceed as follows:
- Launch the Android Studio DMG file.
- Drag and drop Android Studio into the Applications folder, then launch Android Studio.
- Select whether you want to import previous Android Studio settings, then click OK.
- The Android Studio Setup Wizard guides you through the rest of the setup, which includes downloading Android SDK components that are required for development.
That’s it. The following video shows each step of the recommended setup procedure.
As new tools and other APIs become available, Android Studio tells you with a pop-up, or you can check for updates by clicking Android Studio > Check for Updates.
Note: If you use Android Studio on macOS Mojave or later, you might see a prompt to allow the IDE to access your calendar, contacts, or photos. This prompt is caused by new privacy protection mechanisms for applications that access files under the home directory. So, if your project includes files and libraries in your home directory, and you see this prompt, you can select Don’t Allow.
Linux
To install Android Studio on Linux, proceed as follows:
- Unpack the .zip file you downloaded to an appropriate location for your applications, such as within /usr/local/ for your user profile, or /opt/ for shared users.
If you’re using a 64-bit version of Linux, make sure you first install the required libraries for 64-bit machines.
Tip: To make Android Studio available in your list of applications, select Tools > Create Desktop Entry from the Android Studio menu bar.
Required libraries for 64-bit machines
If you are running a 64-bit version of Ubuntu, you need to install some 32-bit libraries with the following command:
If you are running 64-bit Fedora, the command is:
That’s it. The following video shows each step of the recommended setup procedure.
As new tools and other APIs become available, Android Studio tells you with a pop-up, or you can check for updates by clicking Help > Check for Update.
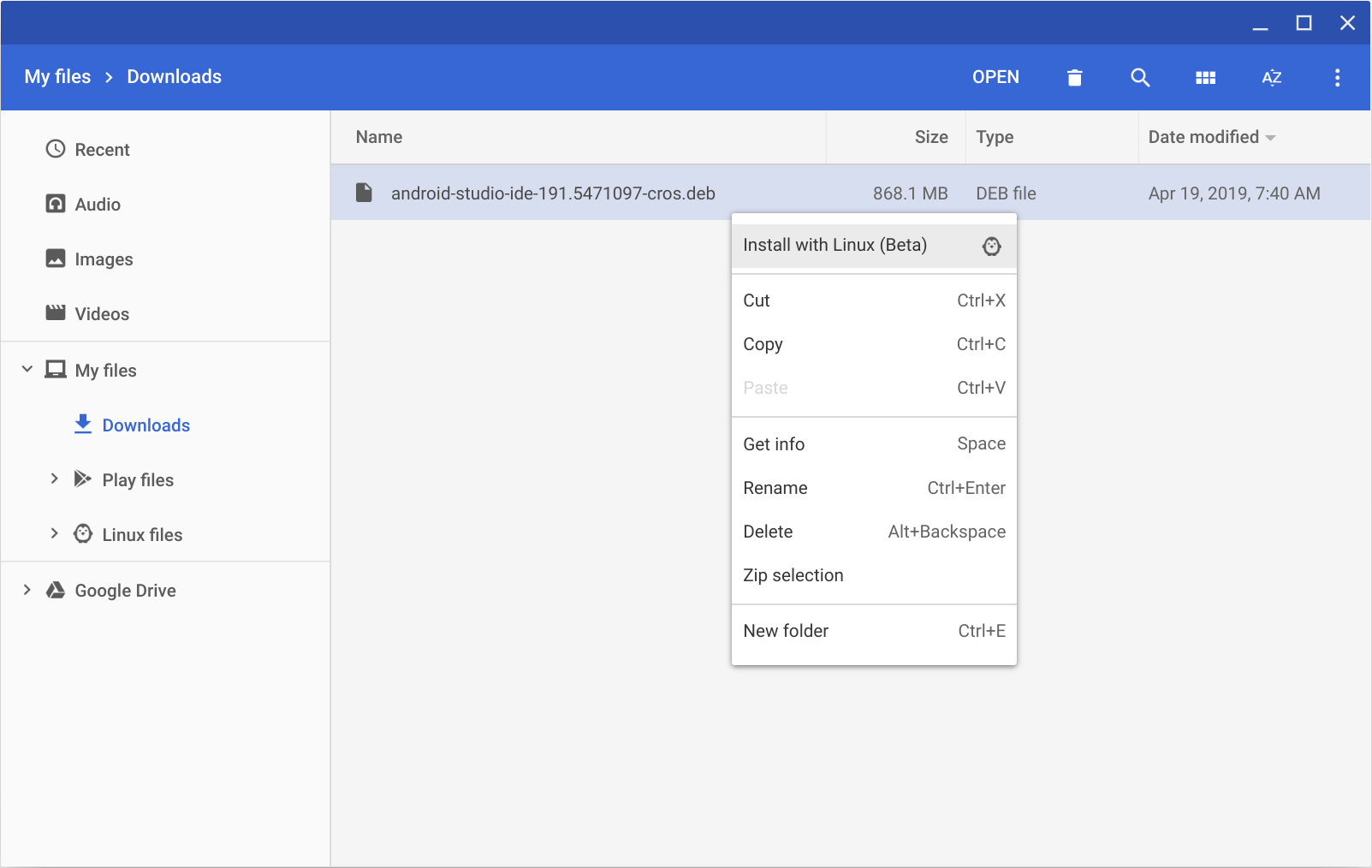
Chrome OS
Follow these steps to install Android Studio on Chrome OS:
- If you haven’t already done so, install Linux for Chrome OS.
- Open the Files app and locate the DEB package you downloaded in the Downloads folder under My files.
Right-click the DEB package and select Install with Linux (Beta).
- If you have installed Android Studio before, select whether you want to import previous Android Studio settings, then click OK.
The Android Studio Setup Wizard guides you through the rest of the setup, which includes downloading Android SDK components that are required for development.
After installation is complete, launch Android Studio either from the Launcher, or from the Chrome OS Linux terminal by running studio.sh in the default installation directory:
That’s it. As new tools and other APIs become available, Android Studio tells you with a pop-up, or you can check for updates by clicking Help > Check for Update.
Content and code samples on this page are subject to the licenses described in the Content License. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Источник
How to install the Android SDK on Windows, Mac and Linux
Most of us will never need to install the Android SDK. The reason why is right in the name — Software Development Kit. It’s built for people writing Android apps who need tools to work with Android from a computer.
But those tools can also be handy for folks wanting to do some more advanced stuff. Stuff like manually updating software or rooting their phone. Fastboot and ADB are vital if you’re into «hacking» at the Android software. And Google provides it free for everyone.
What to choose?
There are two ways to get a working set of Android tools on your computer. The easy way is just to install Android Studio. Everything needed to run and use the Android command line tools is part of Android Studio, as well as a way to keep the tools updated. While it’s designed for folks who want a complete development environment and includes a code editor, Android emulator, and compiler, you can use just the command line tools and never open the rest.
If you’re not afraid to get your feet wet, you can install just the SDK components outside of Android Studio. Installing them is easy (they’re inside a zip file), but setting up your computer to use them isn’t a straightforward process.
Manually installing the Android SDK

Download the SDK direct from Google by clicking here. Scroll down a bit and find the section marked «Get just the command line tools» and save it somewhere easy to get to, like your desktop. We’ll be extracting it to a better location in the next step.
The file you downloaded is compressed. You’ll need to be familiar with compressed files — and how to extract them — to go any further. If you’re not, stop here and spend the time to learn about them.
Extract your compressed file into the following location:
- Windows: The root of your C: drive
- OS X: Your home folder
- Linux: Your home folder
Rename the extracted folder to «Android». This will make the rest of this guide, and your time with the SDK, much easier.
Prerequisites

You’ll need a working version of Java to run the SDK components. For most things, you’ll be doing with the SDK, both Open Java and Sun Java from Oracle (yes, that Oracle) will work.
- On a Mac, it’s pretty easy because you’ll already have it installed unless you uninstalled it. If you did, install it again — you should know how to do that if you knew how to uninstall it.
- On Windows, head to the Oracle website and download the correct version (32- or 64-bit) for your computer. Again, if this gives you any trouble, stop what you’re doing and learn a bit more about your computer. If you can’t install Java, maybe you’re not yet ready to use the Android SDK.
- On a Linux computer, you’ll also need to install Java. You can find x86 and x64 binaries for Sun Java from Oracle at their website. OpenJDK also works for most things you’ll need to do with the SDK. (OpenJDK is now bundled with Android Studio which includes the SDK as well as a development environment) and you’ll find complete instructions to get it installed at the OpenJDK website. If you need more assistance or want to use a package manager to install Sun Java, you’ll need to refer to the documentation for your particular distro.
Linux users will also have to make sure they have some 32-bit libraries installed if they are running a 64-bit version of the operating system. If you’re using Ubuntu or another Debian variant, install ncurses5 and stdc++6 through your terminal:
sudo apt-get install lib32ncurses5 lib32stdc++6
If you’re using a different flavor of Linux, find the correct packages for ncurses5 and stdc++6 and install them.
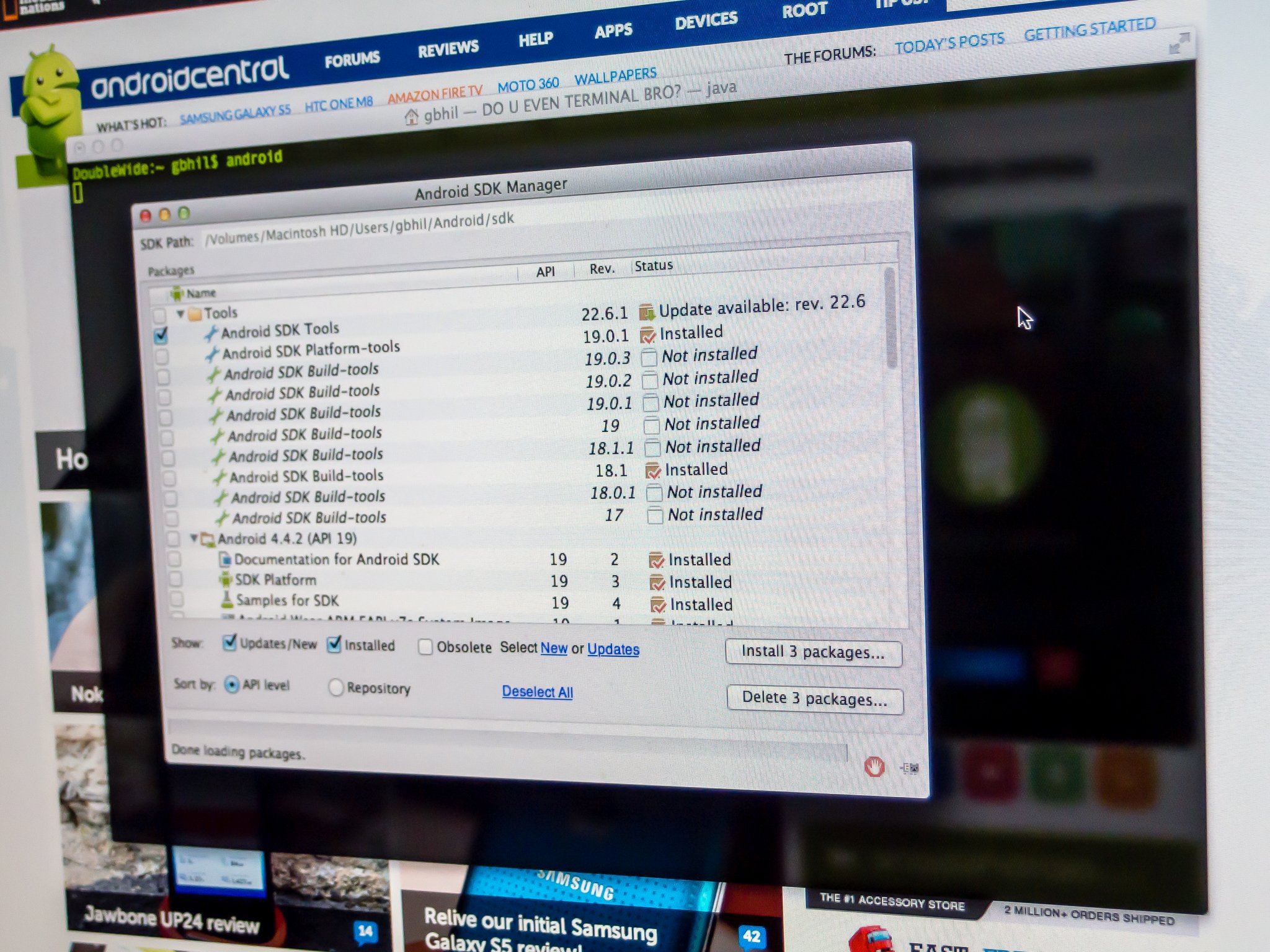
Installing the tools
Extract the file you downloaded above into a folder named Android on the root of your C drive (Windows) or into your Home folder (Mac, Linux). You might notice a few things are missing if you’ve ever downloaded the command line tools before as the tools and platform-tools folders are missing. That’s OK; we’re about to get them using the included SDK manager.
Open the bin folder in the extracted download and find the SDK manager executable file. It may look like a terminal or shell command, but it will open a GUI as long as you have Java installed correctly.

In the SDK manager, you’ll choose to install Android SDK Tools and Android SDK Platform-Tools. If you’re using Windows, you’ll also want to install the Google USB Driver, and if you plan on building AOSP from the source, you may want to install the Android SDK Build-Tools.
Choose the correct files and proceed through the process (it will show you a license agreement you should read), and both tools folders will be installed. But you’re not quite finished!
The tools will be installed into the application data folder. On Windows, it’s in Windows\users\YourUserName\AppData\Local\Android, and on a Mac or Linux, it’s in .Android (notice the dot!) in your home folder. Create a symbolic link (information for Windows users here) for both tools folders in the Android folder you created earlier. This will help get them into your PATH and make life a lot easier.
Setting your PATH

The PATH variable in your computer’s operating system tells it where to look when you want to run a command from a terminal or the command line. For example, to run the ADB command, you either need to type and provide the complete path — ie, the folder ADB is actually in, inside the SDK folder — or have the location set in the PATH variable itself. It’s a bit confusing, but the good news is that doing it is easier than explaining it.
For these directions to work as written, you will have to have extracted and renamed the SDK download folder as mentioned above, and to the correct location for this tutorial.
On Windows
Unless you’re still using an older version of Windows, you no longer can set the PATH in the autoexec.bat file or autoexec.nt file. You’ll need to update the system Environment Variable settings instead. Here’s how it’s done on a Windows 10 machine:
- Hit the Start key on your Keyboard.
- Start typing the words Environment Variables.
- As you type, you’ll see the choice to Edit the system environment variables. Choose it.
- In the Environment Variables window, select the PATH line item in the User variables for (your user name) section, then click the Edit button.
Add the full path to the Android SDK tools and Android SDK platform-tools folders in the edit box, separated by a semi-colon. It should look something like this:
For older versions of Windows, refer to the documentation that came with your computer for assistance on setting the PATH. And, again: If you’ve installed your SDK somewhere other than \Android, you’ll need to adjust accordingly.
On a Mac

You can set your PATH variable on a machine running OS X in your bash profile. Doing so is easy, and is all done in one file.
In your Home folder is a file named .bash_profile. Open it with any text editor. Never touch the .bashrc or .bash_profile files you might find in the /etc. directory!
You may see a blank file, or it may be full of other information. All we need to do is add a couple of lines to the top of the file:
(Did we mention that if your SDK is in another location, you’ll need to adjust things accordingly? Good.)
Save the file and reboot your computer so that the new PATH is sourced properly.
On Linux
Setting the PATH on a Linux computer is almost the same as on a Mac, you just edit a different file.
Using your favorite text editor, open the
/.bashrc file. It will probably exist and have multiple entries. If you get an error that the file does not exist, simply create a new file and save it as
/.bashrc when finished.
You’ll want to add the following two lines to the END of the .bashrc file:
Save the file and close the terminal window. Open a new instance of the terminal and type this command:
Your session will reference the changes you made, and the SDK will be in your PATH.
Wrapping it up

You should now have a working set of Android command-line tools and be able to do things like flash the latest factory images or manually update your phone with a zip file. And because you did it yourself, you have what you need to fix it when things go wrong.
Good luck, and have fun!
Have you listened to this week’s Android Central Podcast?
Every week, the Android Central Podcast brings you the latest tech news, analysis and hot takes, with familiar co-hosts and special guests.
- Subscribe in Pocket Casts: Audio
- Subscribe in Spotify: Audio
- Subscribe in iTunes: Audio
We may earn a commission for purchases using our links. Learn more.
Samsung needs to bring back its iPod competitor
I don’t want to buy an iPod Touch. Since I want a reasonably priced PMP with acceptable audio hardware that can install a few crucial apps, I might have to.
VoLTE: How to use it and why you should care
VoLTE — or Voice over LTE — is the new standard for calling throughout the U.S., Canada, and parts of Europe. Not only does it facilitate much higher call quality between cell phones, but it allows devices to stay connected to LTE while on a call, improving data speeds for everyone.
PlayStation reportedly planning service to compete with Xbox Game Pass
Sony is planning to create a service similar to Xbox Game Pass, according to a new report. The service could launch as early as sometime in the spring of 2022, with multiple tiers.
These are the best USB-C cables you can find for Android Auto
Android Auto is an absolute necessity when driving, regardless of whether you’re headed out to the grocery store or for a long road trip. These cables will ensure your phone stays protected and charged, no matter what.
Источник