- Android sdk x86 linux
- System Requirements for Android SDK Installation
- Eclipse IDE
- How To Install Android SDK Tools On Ubuntu 20.04
- Download SDK Tools
- Install SDK Tools
- Download and Install Platform Tools
- Configure Environment Variable
- Using the SDK Manager
- Using the Emulator and AVD Manager
- Summary
- Android
- Contents
- Transferring files
- App development
- Android Studio
- SDK packages
- Android Emulator
- Other SDK packages in the AUR
- Making /opt/android-sdk group-writeable
- Other IDEs
- Netbeans
- Vim / Neovim
- Emacs
- Other Tools
- Marvin
- Building
- Required packages
- Java Development Kit
- Setting up the build environment
- Downloading the source code
- Building the code
- Testing the build
- Creating a flashable Image
- Flashing
- Fastboot
- Samsung devices
- samloader
- Heimdall
- Odin (Virtualbox)
- Use Android on GNU/Linux
- Troubleshooting
- Android Studio: Android Virtual Devices show ‘failed to load’.
- Android Studio: ‘failed to create the SD card’
- Eclipse: During Debugging «Source not found»
- ValueError: unsupported pickle protocol
- libGL error: failed to load driver: swrast OR AVD does not load and no error message displayed
- sh: glxinfo: command not found
- Android Emulator: no keyboard input in xfwm4
- Android Emulator: Window is shaking and blinking when used in WM tiled mode
- Android Emulator: Segmentation fault (core dumped)
- adb: sideload connection failed: insufficient permissions for device
Android sdk x86 linux
Android SDK is a software development kit, that enables apps developers to create applications/games for the Android platform. Sample projects are included in Android Software Development Kit with source code. The SDK also includes, development tools, an emulator, and required libraries to build Android applications. Applications can be written by using the Java programming language and run on Dalvik, a custom virtual machine designed for embedded use which runs on top of a Linux kernel.
System Requirements for Android SDK Installation
1- Supported Operating Systems for Android SDK
- Windows XP (32-bit), Vista (32- or 64-bit), or Windows 7 (32- or 64-bit)
- Mac OS X 10.5.8 or later (x86 only)
- Linux (tested on Ubuntu Linux, Lucid Lynx)
- GNU C Library (glibc) 2.7 or later is required.
- On Ubuntu Linux, version 8.04 or later is required.
- 64-bit distributions must be capable of running 32-bit applications.
2- Supported Development Environment for Android SDK
Eclipse IDE
- Eclipse 3.6 (Helios) or greater
Note: Eclipse 3.5 (Galileo) is no longer supported with the latest version of ADT. - Eclipse JDT plugin (included in most Eclipse IDE packages)
- Several types of Eclipse packages are available for each platform. For developing Android applications, we recommend that you install one of these packages:
- Eclipse IDE for Java Developers
- Eclipse Classic
- Eclipse IDE for Java EE Developers
- JDK 5 or JDK 6 (JRE alone is not sufficient)
- Android Development Tools plugin (recommended)
Note: If JDK is already installed on your development computer, please take a moment to make sure that it meets the version requirements listed above. In particular, note that some Linux distributions may include JDK 1.4 or Gnu Compiler for Java, both of which are not supported for Android development.
2- Recommended Hardware Requirements for Android SDK
— Minimum 2 GBs of RAM
— Intel Core2Due or equel Processor for x86 Architechure
— 4 GB Hard Disk Space
Источник
How To Install Android SDK Tools On Ubuntu 20.04
It provides all the steps required to install Android SDK Tools on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
In this tutorial, we will discuss all the steps required to install Android SDK Tools, SDK Manager, and AVD Manager on the popular Linux distribution i.e. Ubuntu 20.04 with Java 16. This tutorial provides the steps to install Android SDK Tools on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, though the steps should be the same for other versions of Ubuntu and Linux systems.
This post is useful for the developers using Android SDK Tools with other IDEs without installing Android Studio for the use cases including hybrid app development using Ionic. It also assumes that a valid JAVA_HOME environment variable exists pointing to the installation directory of Java. You may follow the Java installation tutorials written by us including How To Install Java 8 On Ubuntu, How To Install Java 16 On Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, and How To Install OpenJDK 16 On Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
In case you are interested in developing Android applications using Android Studio, you can also follow the other tutorials written by us including How To Install Android SDK Tools On Windows, How To Install Android Studio On Windows, and How To Install Android Studio On Ubuntu 20.04.
You may also be required to execute the below-mentioned command in case you have set the options previously for Java 9 or Java 10.
Notes: The Ubuntu 18.04 LTS version of this tutorial is available at — How To Install Android SDK Tools On Ubuntu 18.04. You can continue this tutorial for Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
Download SDK Tools
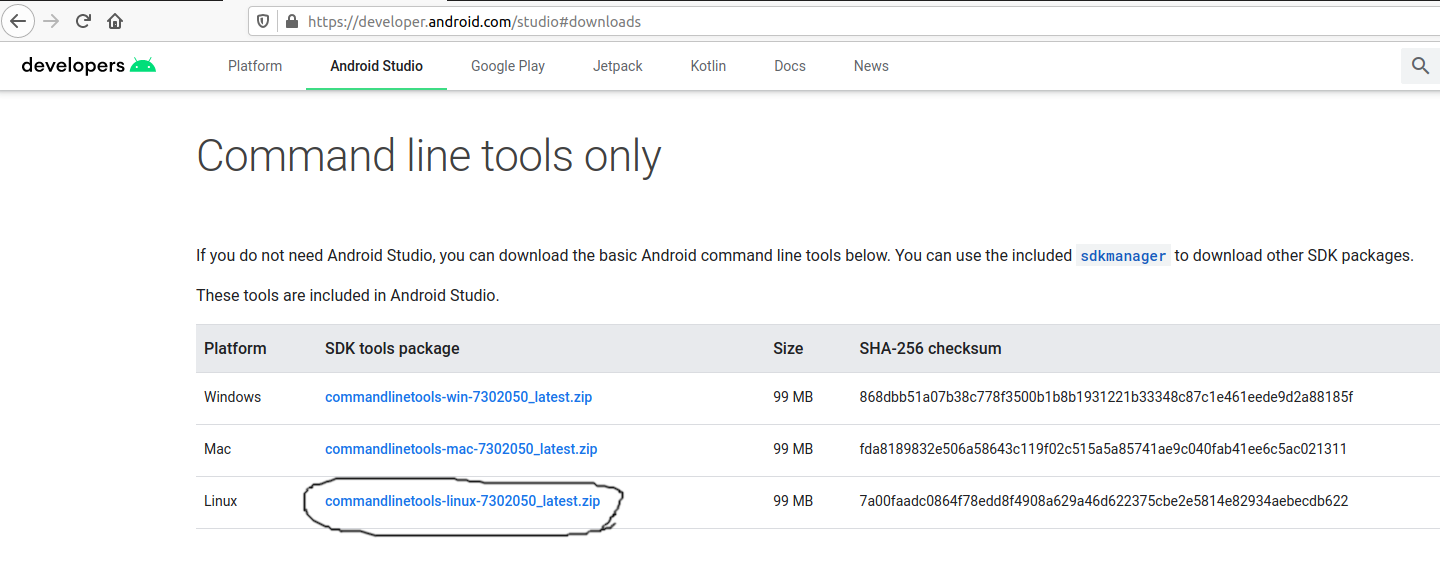
Open the download tab of Android Studio and scroll down to the Command line tools only section. This section shows various options to download the SDK tools as shown in Fig 1.
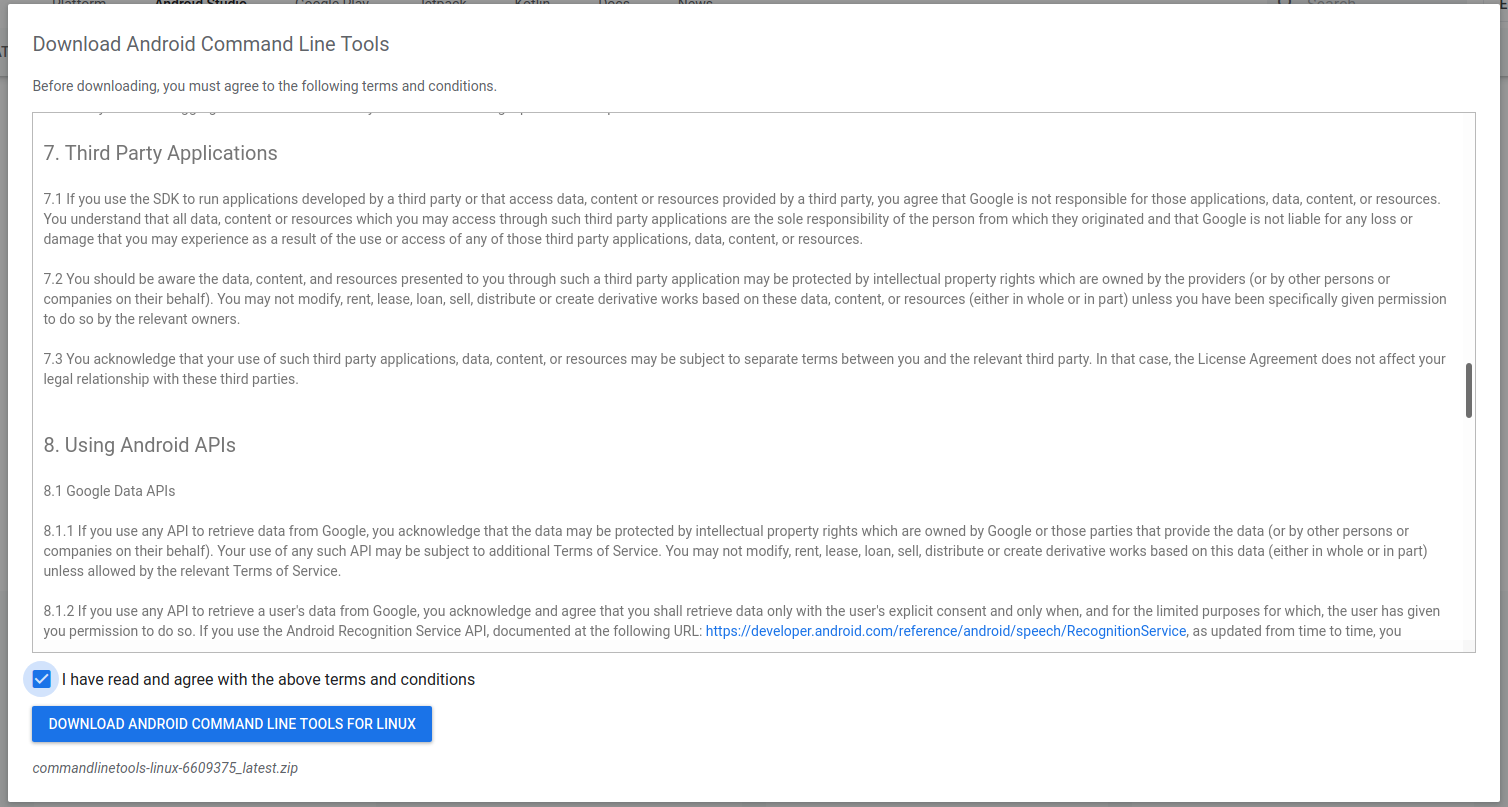
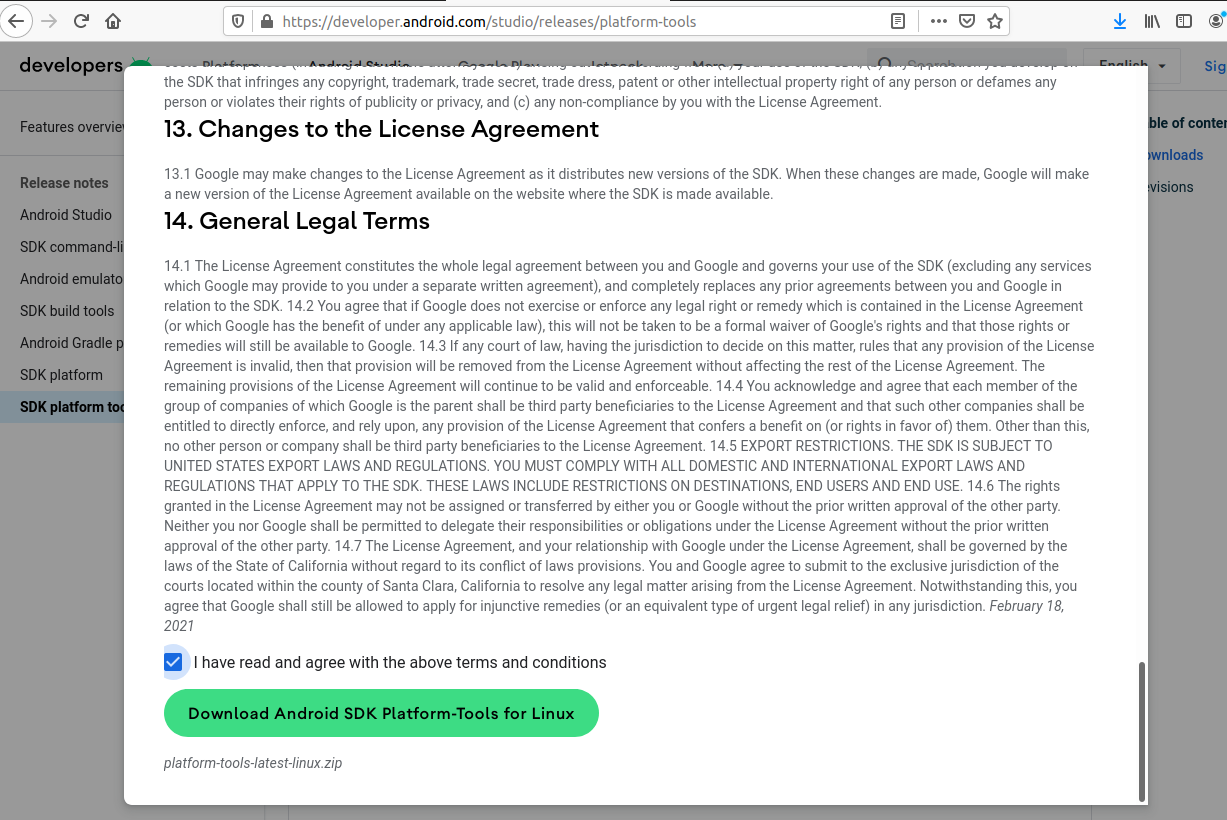
Click on the Download Link as highlighted in Fig 1. It will ask to accept the Terms and Conditions as shown in Fig 2.
Go through the details, agree to the terms and conditions, and click the Download Button to start the download.
Install SDK Tools
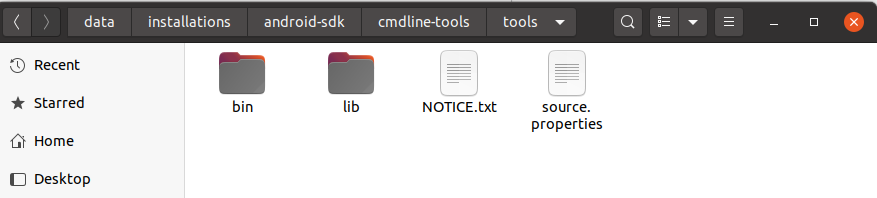
In this step, we will install the Android SDK Tools on Ubuntu. Create a directory having the name set to android-sdk and extract the content of the downloaded SDK Tools zip to this directory. Create another directory android-sdk/cmdline-tools to store the sdk-tools. Make sure that the tools directory is available directly within the android-sdk/cmdline-tools directory created by us.
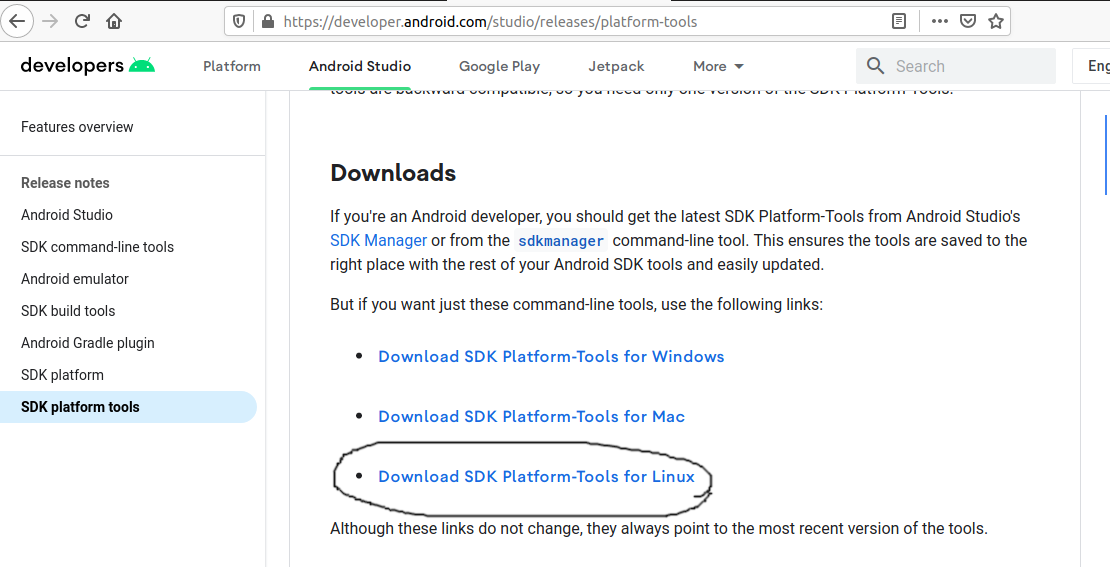
Download and Install Platform Tools
In this step, we will install the Android Platform Tools on Ubuntu. Follow the same steps similar to Android SDK Tools as shown in Fig 4, Fig 5, and Fig 6 to install Android Platform Tools using the download link.
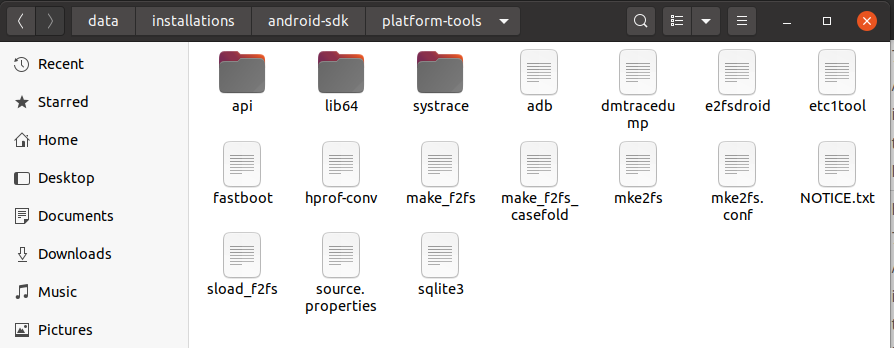
Make sure that the platform-tools content is available within the directory platform-tools. The directory structure should be similar to:
Configure Environment Variable
In this step, we will configure the environment variable to use the SDK tools installed by us. There are two ways to do it. In the first approach, we can update the .bashrc file of the user account. Another approach is to update /etc/profile file which works for all the accounts.
Approach A
Update .bashrc file of the user account.
Notes: Replace the android sdk path based on your installation directory.
Approach B
Update /etc/profile file.
Scroll down by pressing the Page Down button and add at the end of this file:
Make sure that you provide the correct path to the android-sdk directory.
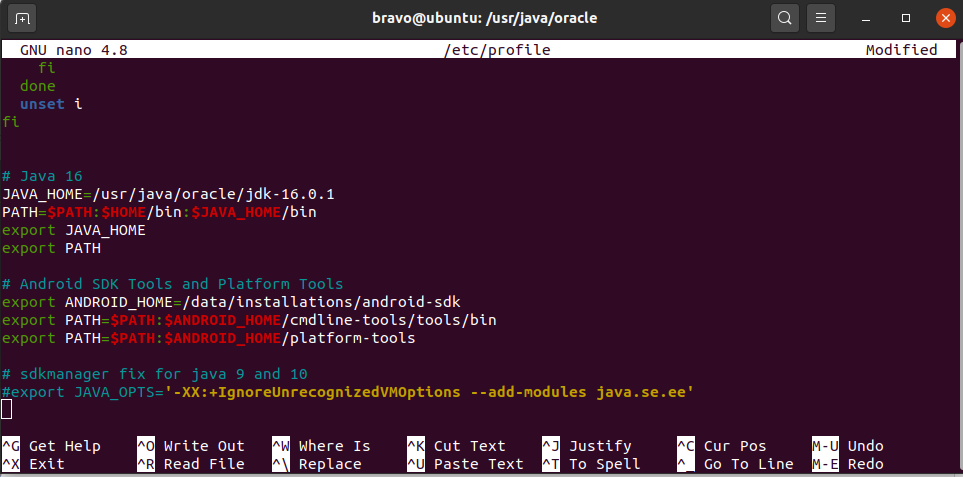
Now press Ctrl + O and press Enter to write our change. Press Ctrl + X to exit the nano editor. The nano editor should look like Fig 7.
Notes: Approach B didn’t work for me.
Now test the Android SDK installed by us using the environment variables configured by us.
Using the SDK Manager
Update SDK Manager — Update the SDK manager using the below-mentioned command.
List — We can list the installed and available packages and images using the list command as shown below.
Install Platform — Use the below-mentioned command to install the Android 10 (API level 29) using the SDK manager.
It will ask to accept the terms and conditions. Enter y and hit Enter Key to accept the terms and conditions. This command creates the directories licenses and platforms within android-sdk and installs the package android-30 within the platforms directory having all the required files to run the emulator for Android 11.
If we again check the installed packages, the list command shows the installed options as shown below.
After installing the platforms, the directory structure should be:
Add System Image — We can add system image from available images shown by the list command using the SDK manager as shown below. We are adding the most recent default 64-bit system image.
Accept the License Agreement to complete the download. There are several projects which need Google Play Services. We need system images specific to Google Play Services as shown below.
Now again use the command list as shown below.
After installing the default system image, the directory structure should be:
Install Emulator — You might be required to install the emulator before creating the AVD using SDK Manager. The emulator gets installed while adding the system images in the previous steps.
Install Build Tools — Install the most recent build tool listed by the list command.
After installing the build tools, the directory structure should be:
Now again use the command list as shown below.
Using the Emulator and AVD Manager
Create AVD — Create the AVD using the system image downloaded in the previous step as shown below. Replace with actual name.
The above commands ask a bunch of questions to configure the AVD if we choose the custom hardware profile option. We have excluded the details of these options from this tutorial since these configuration details depend on the actual needs. After completing all the configurations, it creates the AVD using the name provided by us while configuring it.
List AVDs — Now go to the tools directory(only required in case you have omitted to add tools path to PATH while configuring environment variables) on the command line and check the installed platform as shown below.
It will list all the AVDs installed by us.
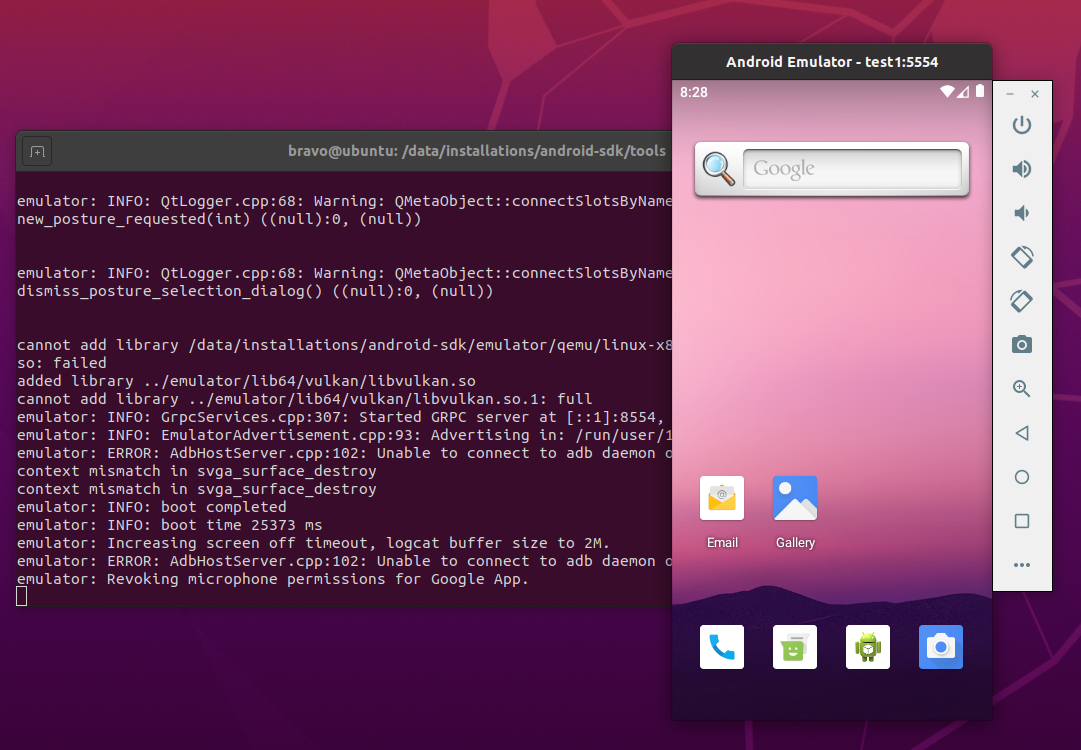
Launch AVD — We can launch the AVD using the emulator as shown below.
The emulator will take some time to completely launch the AVD. The final results should look similar to Fig 8.
Notes: I have used Ubuntu 20.04 LTS installed as VM using VMware Workstation Player, hence I have enabled the Virtualization for my Virtual Machine.
Delete Emulator — We can also delete an existing emulator as shown below.
Summary
This tutorial provided all the steps required to install Android SDK Tools and Android Platform Tools on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. It also provided the steps required to launch the AVD using the Android Emulator.
Источник
Android
Contents
Transferring files
There are various ways to transfer files between a computer and an Android device:
- USB cable
- Media Transfer Protocol for modern Android devices
- USB mass storage for older devices
- Android Debug Bridge
- special USB sticks / regular USB stick with adapter
- Bluetooth
- Arch Linux software with Android counterparts
- client or server for protocols that can be used to transfer files (eg. SSH, FTP, Samba or HTTP)
- KDE Connect ( kdeconnect ) – integrates your Android device with the KDE or Gnome desktop (featuring synced notifications & clipboard, multimedia control, and file/URL sharing).
- cloud synchronization clients
- Syncthing
- sendanywhereAUR – cross-platform file sharing
- qrcpAUR – transfer files over wifi from your computer to your mobile device by scanning a QR code
App development
The officially supported way to build Android apps is to use #Android Studio.[1]
Android Studio
Android Studio is the official Android development environment based on IntelliJ IDEA. It provides integrated Android developer tools for development and debugging.
Android Studio creates a .android directory in home directory. To reset Android Studio, this directory can be removed.
The Android Studio Setup Wizard installs the required #SDK packages and places the SDK by default in
To build apps from the command-line (using e.g. ./gradlew assembleDebug ) set the ANDROID_SDK_ROOT environment variable to your SDK location.
SDK packages
Android SDK packages can be installed directly from upstream using #Android Studio’s SDK Manager or the sdkmanager command line tool (part of the Android SDK Tools). Some Android SDK packages are also available as AUR packages, they generally install to /opt/android-sdk/ .
| Android SDK Package | SDK-style path | AUR package | AUR dummy | CLI tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Command-Line Tools | tools | android-sdk-cmdline-tools-latest AUR | android-sdk-cmdline-tools-latest-dummy AUR | apkanalyzer, avdmanager, lint, retrace, screenshot2, sdkmanager |
| SDK Build-Tools | build-tools;version | android-sdk-build-tools AUR | android-sdk-build-tools-dummy AUR | aapt, aapt2, aidl, apksigner, bcc_compat, d8, dexdump, dx, lld, llvm-rs-cc, mainDexClases, split-select, zipalign |
| SDK Platform-Tools | platform-tools | android-sdk-platform-tools AUR | android-sdk-platform-tools-dummy AUR | adb, dmtracedump, e2fsdroid, etc1tool, #fastboot, hprof-conv, make_f2fs, make_f2fs_casefold, mke2fs, sload_f2fs, sqlite3, systrace |
| SDK Platform | platforms;android-level | android-platform AUR , older versions | android-platform-dummy AUR (unnecessary) |
The android-tools package provides adb, #fastboot, e2fsdroid and mke2fs.android from the SDK Platform-Tools along with mkbootimg and ext2simg .
Android Emulator
The Android Emulator is available as the emulator SDK package, the android-emulator AUR package, and there is also a dummy package for it: android-emulator-dummy AUR .
To run the Android Emulator you need an Intel or ARM System Image. You can install them through the AUR[2], with the sdkmanager or using Android Studio’s AVD Manager.
Other SDK packages in the AUR
The Android Support Library is now available online from Google’s Maven repository. You can also install it offline through the extras;android;m2repository SDK package (also available as android-support-repository AUR ).
Making /opt/android-sdk group-writeable

The AUR packages install the SDK in /opt/android-sdk/ . This directory has root permissions, so keep in mind to run sdk manager as root. If you intend to use it as a regular user, create the android-sdk users group, add your user.
Set an access control list to let members of the newly created group write into the android-sdk folder. As running sdkmanager can also create new files, set the ACL as default ACL. the X in the default group entry means «allow execution if executable by the owner (or anyone else)»
Re-login or as log your terminal in to the newly created group:
Other IDEs
Android Studio is the official Android development environment based on IntelliJ IDEA. Alternatively, you can use Netbeans with the NBAndroid-V2. All are described below.
Netbeans
If you prefer using Netbeans as your IDE and want to develop Android applications, use NBAndroid-V2 .
Install android-sdk AUR package and follow the instructions from the NBANDROID README.
Vim / Neovim
It is possible to write flutter applications for Android and iOS using (Neo)vim like an IDE. Install coc using a Vim plugin manager. Also install the coc-flutter extension for autocompletion (like in Android Studio) and to load the code into an Android emulator.
Emacs
To develop a mobile flutter application using Emacs, as the the official instruction at flutter.dev suggests, install lsp-dart.
Other Tools
Marvin
Marvin is a tool which helps beginners set up an Android development environment. Installing marvin_dsc AUR helps you set up the following things: JDK, Android SDK, IDE(s), and AVD.
Building
Please note that these instructions are based on the official AOSP build instructions. Other Android-derived systems such as LineageOS will often require extra steps.
Required packages
As of 2020/April, to build either AOSP 10 or LineageOS 17.1 you need (possibly a subset of) base-devel , multilib-devel , gcc , repo , git , gnupg , gperf , sdl , wxgtk2 , squashfs-tools , curl , ncurses , zlib , schedtool , perl-switch , zip , unzip , libxslt , bc , rsync , ccache , lib32-zlib , lib32-ncurses , lib32-readline , ncurses5-compat-libs AUR , lib32-ncurses5-compat-libs AUR , and a TTF font installed (e.g. ttf-dejavu ). In particular, no Python2 or Java are required, as they are provided by AOSP/Lineage. The aosp-devel AUR metapackage provides them all for simple installation.
Additionally, LineageOS requires the following packages: xml2 AUR , lzop , pngcrush , imagemagick . They can be installed with the lineageos-devel AUR metapackage.

Java Development Kit
The required JDK version depends on the Android version you are building:
- For Android 9 (Pie) and up, Java is included with the Android source and no separate installation is needed.
- For Android 7 and 8 (Nougat and Oreo), OpenJDK 8 is required, which is available with the jdk8-openjdk package.
- For Android 5 and 6 (Lollipop and Marshmallow), OpenJDK 7 is required, which is available with the jdk7-openjdk package.
Set JAVA_HOME to avoid this requirement and match the Arch Linux installation path. Example:
This change will be valid only for the current terminal session.
Setting up the build environment
Create a directory to build.
The Android build process expects python to be python2. Prepend it to the PATH :
Alternatively, create a python2 virtual environment and activate it:
/android to reflect your build directory if different than above).
or (assuming build directory Data/Android_Build):
Downloading the source code
This will clone the repositories. You only need to do this the first time you build Android, or if you want to switch branches.
- The repo has a -j switch that operates similarly to the one used with make . Since it controls the number of simultaneous downloads, you should adjust the value depending on downstream network bandwidth.
- You will need to specify a branch (list of branches) to check out with the -b switch. If you leave the switch out, you will get the so-called master branch.
The -c switch will only sync the branch which is specified in the manifest, which in turn is determined by the branch specified with the -b switch, or the default branch set by the repository maintainer.
Wait a long time. Just the uncompiled source code, along with the .repo and .git directories that are used to keep track of it, are very large. As of Android 10, at least 250 GB of free disk space is required.
Building the code
This should do what you need for AOSP:
If you run lunch without arguments, it will ask what build you want to create. Use -j with a number between one and two times number of cores/threads.
The build takes a very long time.
Testing the build
When finished, run/test the final image(s).
Creating a flashable Image
To create an image that can be flashed it is necessary to:
This will create a zip image under out/target/product/hammerhead (hammerhead being the device name) that can be flashed.
Flashing
In some cases, you want to return to the stock Android after flashing custom ROMs to your Android mobile device. For flashing instructions of your device, please use XDA forums.
Fastboot
Fastboot (as well as ADB) is included in the android-tools package.
Samsung devices
Samsung devices cannot be flashed using Fastboot tool. Alternatives are Heimdall and Odin (by using Windows and VirtualBox).
samloader
To download original Samsung firmware, a platform independent script, samloader can be used.
Heimdall
Heimdall is a cross-platform open-source tool suite used to flash firmware (also known as ROMs) onto Samsung mobile devices and is also known as an alternative to Odin. It can be installed as heimdall .
The flashing instructions can be found on Heimdall’s GitHub repository or on XDA forums.
Odin (Virtualbox)
It is also possible to restore firmware (Android) on the Samsung devices using Odin, but inside the VirtualBox.
Arch Linux (host) preparation:
- Install VirtualBox together with its extension pack and guest additions.
- Install your preferred, but compatible with Odin, Windows operating system (with VirtualBox guest additions) into a virtual hard drive using VirtualBox.
- Open VirtualBox settings of your Windows operating system, navigate to USB, then tick (or make sure it is ticked) Enable USB 2.0 (EHCI) Controller.
- At VirtualBox running Windows operating system, click in the menu bar Devices > USB Devices, then click on your Samsung mobile device from the list, which is connected to your computer via USB.
Windows (guest) preparation:
Check if configuration is working:
- Turn your device into Download mode and connect to your Linux machine.
- In virtual machine toolbar, select Devices > USB > . Samsung. device.
- Open Odin. The white box (a big one at the bottom-left side) named Message, should print a line similar to this:
which means that your device is visible to Odin & Windows operating system and is ready to be flashed.
Use Android on GNU/Linux
There are several projects and methods which support running Android on GNU/Linux:
- Anbox: container-based software to run Android on Linux kernels
- Android-x86: a direct port of Android for the x86 architecture
Troubleshooting
Android Studio: Android Virtual Devices show ‘failed to load’.
Make sure you have exported the variable ANDROID_HOME as explained in #Android Studio.
Android Studio: ‘failed to create the SD card’
If you try to run an AVD (Android Virtual Device) under x86_64 Arch and get the error above, install the lib32-gcc-libs package from the multilib repository.
Eclipse: During Debugging «Source not found»
Most probably the debugger wants to step into the Java code. As the source code of Android does not come with the Android SDK, this leads to an error. The best solution is to use step filters to not jump into the Java source code. Step filters are not activated by default. To activate them: Window > Preferences > Java > Debug > Step Filtering. Consider to select them all. If appropriate you can add the android.* package. See the forum post for more information: http://www.eclipsezone.com/eclipse/forums/t83338.rhtml
ValueError: unsupported pickle protocol
One fix is to issue:
If that does not work, then try this:
libGL error: failed to load driver: swrast OR AVD does not load and no error message displayed
Sometimes, beginning to load an AVD will cause an error message similar to this to be displayed, or the loading process will appear to finish but no AVD will load and no error message will be displayed.
The AVD loads an incorrect version of libstdc++, you can remove the folder libstdc++ from
/.android-sdk/emulator/lib64 (for 64-bit) or
/.android-sdk/emulator/lib (for 32-bit) , e.g.:
Note that in versions before Android Studio 3.0, this directory was in a different location:
Alternatively you can set and export ANDROID_EMULATOR_USE_SYSTEM_LIBS in
Fix for the .desktop file might be achieved by using env command, prefixing the Exec line Desktop entries#Modify environment variables
sh: glxinfo: command not found
Here is the full error:
You can try to install glxinfo ( mesa-utils ) but if your computer has enough power you could simply use software to render graphics. To do so, go to Tools > Android > AVD Manager, edit the AVD (click the pencil icon), then select Software — GLES 2.0 for Emulated Performance > Graphics.
Android Emulator: no keyboard input in xfwm4
In xfwm4, the vertical toolbar buttons window that is on the right of the emulator takes focus from the emulator and consumes keyboard events. (bug report)
You can use the workaround described in [3]:
- Open the xfwm4 settings.
- Switch to the Focus tab.
- Change the Focus Model to «Focus follow mouse».
- Disable Automatically raise windows when they receive focus option below.\
Android Emulator: Window is shaking and blinking when used in WM tiled mode
When using Tiled Window Manager like dwm, Android Emulator will shake and blink. You can use the workaround described in krohnkite issue 72 (window floating is induced by Alt+f in dwm).
Android Emulator: Segmentation fault (core dumped)
When using Nouveau drivers try to disable gpu hardware acceleration.
In some devices it can only be done by editing $HOME/.avd/device_name.avd/config.ini .[4]
- Set hw.gpu.enabled=no
- Set hw.gpu.mode=off
adb: sideload connection failed: insufficient permissions for device
If you get the error:
you might solve it by restarting the adb server:
Источник