Полный список
В этом уроке мы:
— создадим и вызовем второе Activity в приложении
Урок был обновлен 12.06.2017
Мы подобрались к очень интересной теме. На всех предыдущих уроках мы создавали приложения, которые содержали только один экран (Activity). Но если вы пользуетесь смартфоном с Android, то вы замечали, что экранов в приложении обычно больше. Если рассмотреть, например, почтовое приложение, то в нем есть следующие экраны: список аккаунтов, список писем, просмотр письма, создание письма, настройки и т.д. Пришла и нам пора научиться создавать многоэкранные приложения.
Application/Library name: TwoActivity
Module name: p0211twoactivity
Package name: ru.startandroid.p0211twoactivity
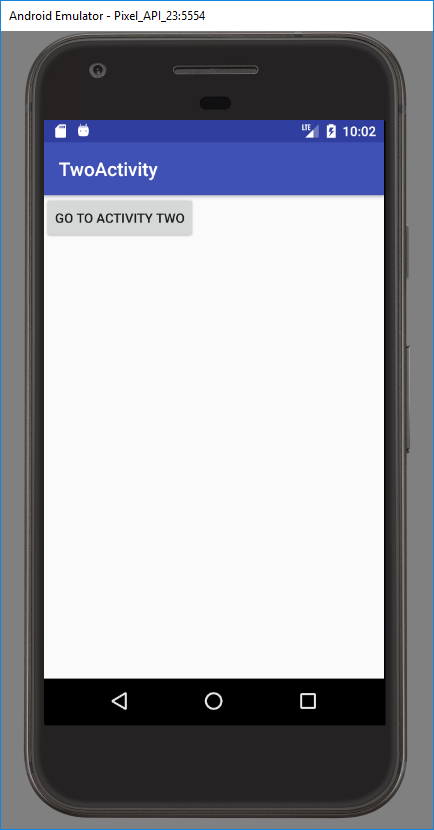
Откроем activity_main.xml и создадим такой экран:
На экране одна кнопка, по нажатию которой будем вызывать второй экран.
Открываем MainActivity.java и пишем код:
Мы определили кнопку btnActTwo и присвоили ей Activity в качестве обработчика. Реализация метода onClick для кнопки пока заполнена частично — определяем, какая кнопка была нажата. Чуть позже здесь мы будем вызывать второй экран. Но сначала этот второй экран надо создать.
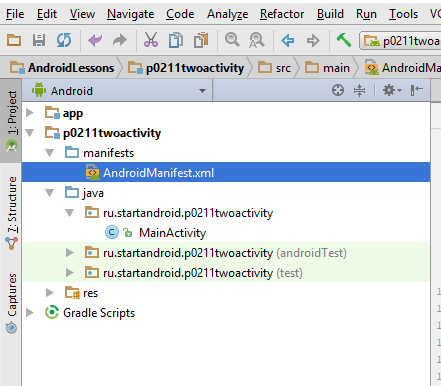
Если помните, при создании проекта у нас по умолчанию создается Activity.
От нас требуется только указать имя этого Activity – обычно мы пишем здесь MainActivity. Давайте разбираться, что при этом происходит.
Мы уже знаем, что создается одноименный класс MainActivity.java – который отвечает за поведение Activity. Но, кроме этого, Activity «регистрируется» в системе с помощью манифест-файла — AndroidManifest.xml.
Давайте откроем этот файл:
Нас интересует тег application. В нем мы видим тег activity с атрибутом name = MainActivity. В activity находится тег intent-filter с определенными параметрами. Пока мы не знаем что это и зачем, сейчас нам это не нужно. Забегая вперед, скажу, что android.intent.action.MAIN показывает системе, что Activity является основной и будет первой отображаться при запуске приложения. А android.intent.category.LAUNCHER означает, что приложение будет отображено в общем списке приложений Android.
Т.е. этот манифест-файл — это что-то типа конфигурации. В нем мы можем указать различные параметры отображения и запуска Activity или целого приложения. Если в этом файле не будет информации об Activity, которое вы хотите запустить в приложении, то вы получите ошибку.
Android Studio при создании модуля создала MainActivity и поместила в манифест данные о нем. Если мы надумаем сами создать новое Activity, то студия также предоставит нам визард, который автоматически добавит создаваемое Activity в манифест.
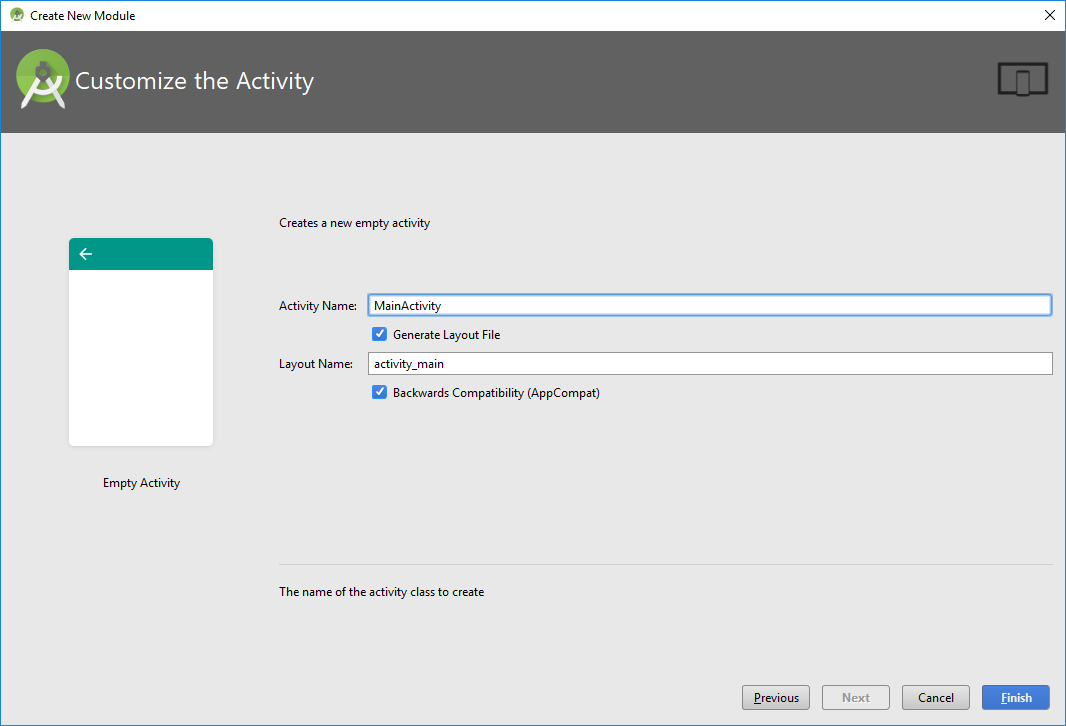
Давайте создадим новое Activity
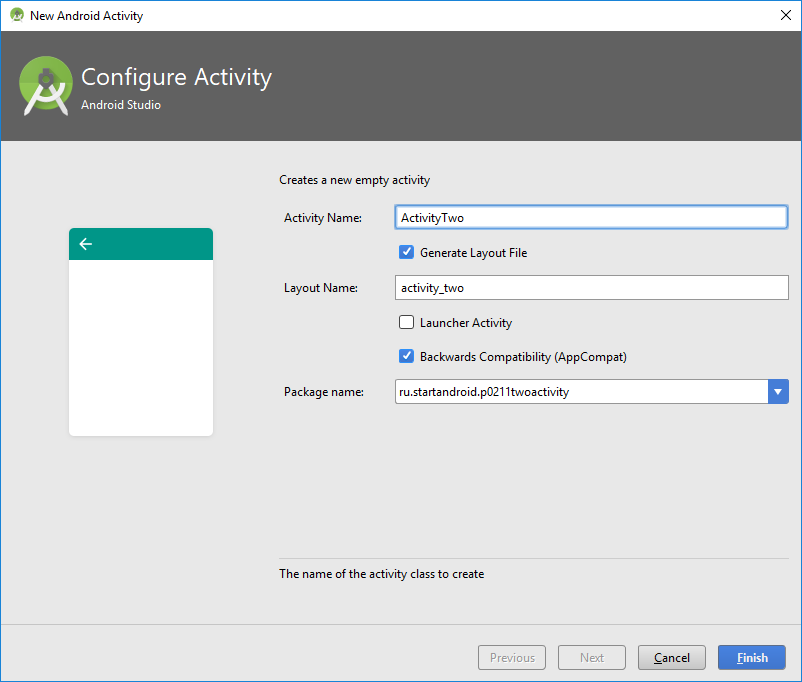
Жмем правой кнопкой на package ru.startandroid.p0211twoactivity в папке проекта и выбираем New -> Activity -> Empty Activity
В появившемся окне вводим имя класса – ActivityTwo, и layout – activity_two.
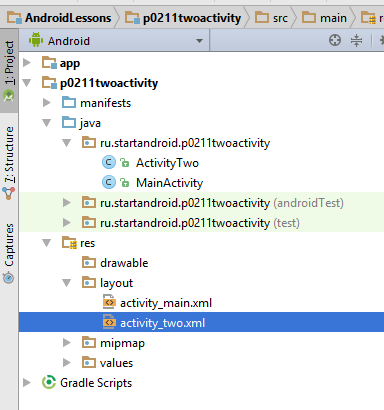
Класс ActivityTwo создан.
В setContentView сразу указан layout-файл activty_two.
Он был создан визардом
Откройте activty_two.xml и заполните следующим кодом:
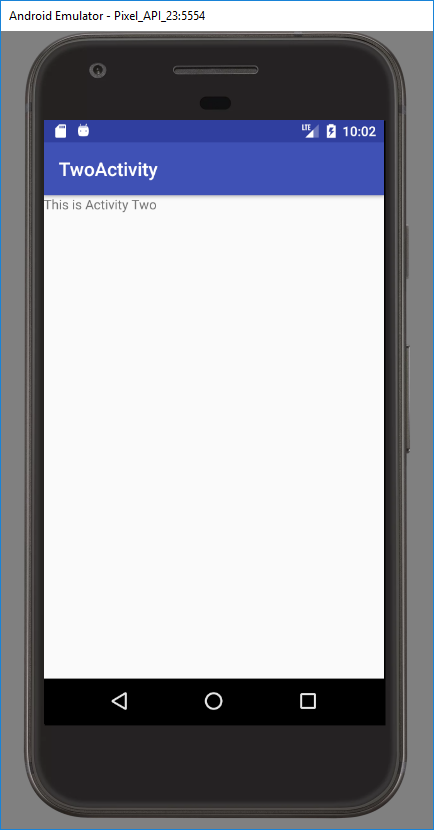
Экран будет отображать TextView с текстом «This is Activity Two».
Сохраните все. Класс ActivityTwo готов, при отображении он выведет на экран то, что мы настроили в layout-файле two.xml.
Давайте снова заглянем в файл манифеста
Появился тег activity с атрибутом name = .ActivityTwo. Этот тег совершенно пустой, без каких либо параметров и настроек. Но даже пустой, он необходим здесь.
Нам осталось вернуться в MainActivity.java и довершить реализацию метода onClick (нажатие кнопки), а именно — прописать вызов ActivityTwo. Открываем MainActivity.java и добавляем строки:
(добавляете только строки 2 и 3)
Обновите импорт, сохраните все и можем всю эту конструкцию запускать. При запуске появляется MainActivity
Нажимаем на кнопку и переходим на ActivityTwo
Код вызова Activity пока не объясняю и теорией не гружу, урок и так получился сложным. Получилось много текста и скриншотов, но на самом деле процедура минутная. Поначалу, возможно, будет непонятно, но постепенно втянемся. Создадим штук 5-6 новых Activity в разных проектах и тема уляжется в голове.
Пока попробуйте несколько раз пройти мысленно эту цепочку действий и усвоить, что для создания Activity необходимо создать класс (который наследует android.app.Activity) и создать соответствующую запись в манифест-файле.
На следующем уроке:
— разбираемся в коде урока 21
— теория по Intent и Intent Filter (не пропустите, тема очень важная)
— немного о Context
Присоединяйтесь к нам в Telegram:
— в канале StartAndroid публикуются ссылки на новые статьи с сайта startandroid.ru и интересные материалы с хабра, medium.com и т.п.
— в чатах решаем возникающие вопросы и проблемы по различным темам: Android, Kotlin, RxJava, Dagger, Тестирование
— ну и если просто хочется поговорить с коллегами по разработке, то есть чат Флудильня
— новый чат Performance для обсуждения проблем производительности и для ваших пожеланий по содержанию курса по этой теме
Источник
Starting Another Activity
This lesson teaches you to
You should also read
After completing the previous lesson, you have an app that shows an activity (a single screen) with a text field and a button. In this lesson, you’ll add some code to MainActivity that starts a new activity when the user clicks the Send button.
Respond to the Send Button
To respond to the button’s on-click event, open the activity_main.xml layout file and add the android:onClick attribute to the element:
The android:onClick attribute’s value, «sendMessage» , is the name of a method in your activity that the system calls when the user clicks the button.
Open the MainActivity class (located in the project’s src/ directory) and add the corresponding method:
This requires that you import the View class:
Tip: In Eclipse, press Ctrl + Shift + O to import missing classes (Cmd + Shift + O on Mac).
In order for the system to match this method to the method name given to android:onClick , the signature must be exactly as shown. Specifically, the method must:
- Be public
- Have a void return value
- Have a View as the only parameter (this will be the View that was clicked)
Next, you’ll fill in this method to read the contents of the text field and deliver that text to another activity.
Build an Intent
An Intent is an object that provides runtime binding between separate components (such as two activities). The Intent represents an app’s «intent to do something.» You can use intents for a wide variety of tasks, but most often they’re used to start another activity.
Inside the sendMessage() method, create an Intent to start an activity called DisplayMessageActivity :
The constructor used here takes two parameters:
- A Context as its first parameter ( this is used because the Activity class is a subclass of Context )
- The Class of the app component to which the system should deliver the Intent (in this case, the activity that should be started)
Sending an intent to other apps
The intent created in this lesson is what’s considered an explicit intent, because the Intent specifies the exact app component to which the intent should be given. However, intents can also be implicit, in which case the Intent does not specify the desired component, but allows any app installed on the device to respond to the intent as long as it satisfies the meta-data specifications for the action that’s specified in various Intent parameters. For more information, see the class about Interacting with Other Apps.
Note: The reference to DisplayMessageActivity will raise an error if you’re using an IDE such as Eclipse because the class doesn’t exist yet. Ignore the error for now; you’ll create the class soon.
An intent not only allows you to start another activity, but it can carry a bundle of data to the activity as well. Inside the sendMessage() method, use findViewById() to get the EditText element and add its text value to the intent:
Note: You now need import statements for android.content.Intent and android.widget.EditText . You’ll define the EXTRA_MESSAGE constant in a moment.
An Intent can carry a collection of various data types as key-value pairs called extras. The putExtra() method takes the key name in the first parameter and the value in the second parameter.
In order for the next activity to query the extra data, you should define the key for your intent’s extra using a public constant. So add the EXTRA_MESSAGE definition to the top of the MainActivity class:
It’s generally a good practice to define keys for intent extras using your app’s package name as a prefix. This ensures they are unique, in case your app interacts with other apps.
Start the Second Activity
To start an activity, call startActivity() and pass it your Intent . The system receives this call and starts an instance of the Activity specified by the Intent .
With this new code, the complete sendMessage() method that’s invoked by the Send button now looks like this:
Now you need to create the DisplayMessageActivity class in order for this to work.
Create the Second Activity
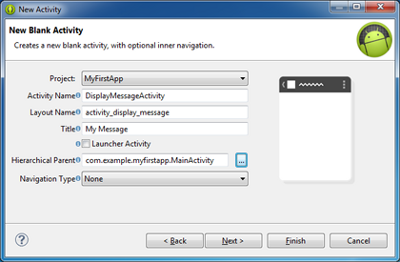
Figure 1. The new activity wizard in Eclipse.
To create a new activity using Eclipse:
- Click New
in the toolbar.
- In the window that appears, open the Android folder and select Android Activity. Click Next.
- Select BlankActivity and click Next.
- Fill in the activity details:
- Project: MyFirstApp
- Activity Name: DisplayMessageActivity
- Layout Name: activity_display_message
- Title: My Message
- Hierarchial Parent: com.example.myfirstapp.MainActivity
- Navigation Type: None
Click Finish.
If you’re using a different IDE or the command line tools, create a new file named DisplayMessageActivity.java in the project’s src/ directory, next to the original MainActivity.java file.
Open the DisplayMessageActivity.java file. If you used Eclipse to create this activity:
- The class already includes an implementation of the required onCreate() method.
- There’s also an implementation of the onCreateOptionsMenu() method, but you won’t need it for this app so you can remove it.
- There’s also an implementation of onOptionsItemSelected() which handles the behavior for the action bar’s Up behavior. Keep this one the way it is.
Because the ActionBar APIs are available only on HONEYCOMB (API level 11) and higher, you must add a condition around the getActionBar() method to check the current platform version. Additionally, you must add the @SuppressLint(«NewApi») tag to the onCreate() method to avoid lint errors.
The DisplayMessageActivity class should now look like this:
If you used an IDE other than Eclipse, update your DisplayMessageActivity class with the above code.
All subclasses of Activity must implement the onCreate() method. The system calls this when creating a new instance of the activity. This method is where you must define the activity layout with the setContentView() method and is where you should perform initial setup for the activity components.
Note: If you are using an IDE other than Eclipse, your project does not contain the activity_display_message layout that’s requested by setContentView() . That’s OK because you will update this method later and won’t be using that layout.
Add the title string
If you used Eclipse, you can skip to the next section, because the template provides the title string for the new activity.
If you’re using an IDE other than Eclipse, add the new activity’s title to the strings.xml file:
Add it to the manifest
All activities must be declared in your manifest file, AndroidManifest.xml , using an element.
When you use the Eclipse tools to create the activity, it creates a default entry. If you’re using a different IDE, you need to add the manifest entry yourself. It should look like this:
The android:parentActivityName attribute declares the name of this activity’s parent activity within the app’s logical hierarchy. The system uses this value to implement default navigation behaviors, such as Up navigation on Android 4.1 (API level 16) and higher. You can provide the same navigation behaviors for older versions of Android by using the Support Library and adding the element as shown here.
Note: Your Android SDK should already include the latest Android Support Library. It’s included with the ADT Bundle but if you’re using a different IDE, you should have installed it during the Adding Platforms and Packages step. When using the templates in Eclipse, the Support Library is automatically added to your app project (you can see the library’s JAR file listed under Android Dependencies). If you’re not using Eclipse, you need to manually add the library to your project—follow the guide for setting up the Support Library then return here.
If you’re developing with Eclipse, you can run the app now, but not much happens. Clicking the Send button starts the second activity but it uses a default «Hello world» layout provided by the template. You’ll soon update the activity to instead display a custom text view, so if you’re using a different IDE, don’t worry that the app won’t yet compile.
Receive the Intent
Every Activity is invoked by an Intent , regardless of how the user navigated there. You can get the Intent that started your activity by calling getIntent() and retrieve the data contained within it.
In the DisplayMessageActivity class’s onCreate() method, get the intent and extract the message delivered by MainActivity :
Display the Message
To show the message on the screen, create a TextView widget and set the text using setText() . Then add the TextView as the root view of the activity’s layout by passing it to setContentView() .
The complete onCreate() method for DisplayMessageActivity now looks like this:
You can now run the app. When it opens, type a message in the text field, click Send, and the message appears on the second activity.
Figure 2. Both activities in the final app, running on Android 4.0.
That’s it, you’ve built your first Android app!
To learn more about building Android apps, continue to follow the basic training classes. The next class is Managing the Activity Lifecycle.
Источник

 in the toolbar.
in the toolbar.



