- Android Studio lock unlock file make read only or writable
- Další témata . (Topics)
- R.string to string R.array to array Android | r-string-to-string-r-array-to-array-android
- Draw Rect Android basic example | draw-rect-android-basic-example
- Draw color line set stroke width Android basic example | draw-line-android-basic-example
- Change TableRow background color if on row click Android example | change-tablerow-background-color-if-on-row-click-android-example
- Samsung Galaxy Mini (S5570) | samsung-galaxy-mini-s5570
- android studio put itself into read only mode for all files #2994
- Comments
- james-lawrence commented Dec 23, 2018
- Steps to Reproduce
- Version info
- pq commented Dec 25, 2018 •
- james-lawrence commented Dec 25, 2018
- pq commented Dec 26, 2018
- alexander-doroshko commented Dec 26, 2018
- james-lawrence commented Dec 26, 2018
- alexander-doroshko commented Dec 26, 2018
- EHBradford commented Mar 28, 2019
- EHBradford commented Apr 8, 2019
- How to Generate APK and Signed APK Files in Android Studio
- Creating an APK file
- Creating a Signed APK File
- Creating a New Key Store
- Finishing Up
- Summary
- Create an APK File
- Create a Signed APK File
- Create a New Key Store and Key
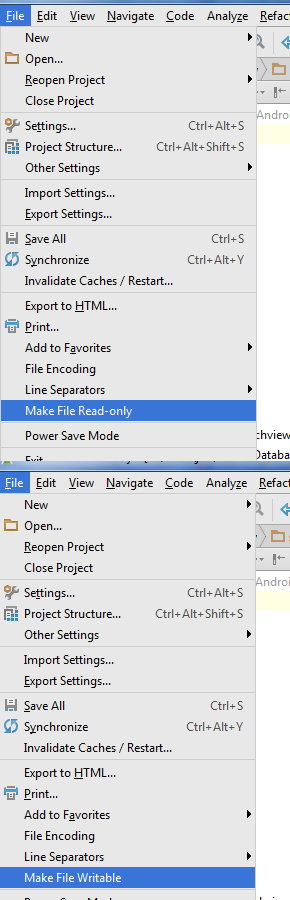
Android Studio lock unlock file make read only or writable
Select file in project explorer
Menu:
File — Make File Read-only — to lock
File — Make File Writable — to unlock
397LW NO topic_id
Další témata . (Topics)
R.string to string R.array to array Android | r-string-to-string-r-array-to-array-android
R.string to string Android source code
R.array to string [] Android source code
Draw Rect Android basic example | draw-rect-android-basic-example
Draw color line set stroke width Android basic example | draw-line-android-basic-example
Change TableRow background color if on row click Android example | change-tablerow-background-color-if-on-row-click-android-example
Change table row background color if user click on row Android example code.
MainActivity.java
main.xml
strings.xml
Samsung Galaxy Mini (S5570) | samsung-galaxy-mini-s5570
| Brand | Samsung |
| Model (codename) | Galaxy Mini (S5570) |
| Price (cena, včetně DPH) | 3500 / 06.2012 |
| Display size in Inch (v palcích) | 3.14 |
| Display-resolution | 240×320 |
| Dotek-typ | kapacitní |
| CPU typ | MSM7227 |
| CPU MHz | 600 |
| CPU core | |
| L2 cache | yes |
| RAM | 256 |
| ROM | 512 |
| GPU | Adreno 200 |
| NenaMark2 Benchmark | |
| GPU-GLBenchmark | |
| Baterie mAh | 1200 |
| Foto MPx | 3 |
| Autofocus | no |
| Video | QVGA (320 x 240) při 15 frames/s |
| Official Android ICS | Android Froyo 2.2 |
| CyanogenMod support | yes |
| Dotek-prstů-max | Dual-touch (two fingers) |
| Display-ppi | 127 |
| Display-retina | 39% |
| Networks | GSM&EDGE (850 / 900 / 1.800 / 1.900 MHz) 3G (900 / 2.100 MHz) |
| Connectivity | Bluetooth V2.1 , USB V2.0 , USB mass storage , SyncML(DM) , WIFI , AGPS, 3.5 mm jack |
| Note |
Samsung S5570 Galaxy Mini — image
Editace: 2015-12-04 19:50:55
Počet článků v kategorii: 397
Url:android-studio-lock-unlock-file-make-read-only-or-writable
Источник
android studio put itself into read only mode for all files #2994
Comments
james-lawrence commented Dec 23, 2018
Steps to Reproduce
standard development for flutter, somehow android studio decided every file was read only (which was not the case). seems clearing .idea directories fixed the issue. but this sort of behavior isn’t acceptable.
begging that flutter move away from android studio as the defacto development environment. its extremely fragile and brittle. to the point where everytime I’ve tried to use android studio I spend more time debugging the IDE than actually writing code.
Version info
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
pq commented Dec 25, 2018 •
Sorry you had this experience. It would be great for us to track down what happened so please do share whatever context you can. Certainly if this recurs.
begging that flutter move away from android studio as the defacto development environment. its extremely fragile and brittle. to the point where everytime I’ve tried to use android studio I spend more time debugging the IDE than actually writing code.
Again, this is really unfortunate. If you have any actionable feedback we can pass on to the Android Studio team we’d be happy to.
Thanks again for the report and do check back if you hit any other issues.
PS: we’ve had a few quick releases of the flutter plugin since 31.3.1 to address a number of issues. Worth an update for sure.
EDIT: Sorry, misread. You’re up to date.
james-lawrence commented Dec 25, 2018
problem is I’m not even sure how to debug these issues. android studio is extremely opaque regarding errors.
pq commented Dec 26, 2018
android studio is extremely opaque regarding errors.
@alexander-doroshko : any suggestions that may help debug AS in general?
alexander-doroshko commented Dec 26, 2018
To narrow down the «read-only mode» problem I’d first ask what the problem looks like.
Was it a dialog saying ‘You are trying to edit non-project file. Are you sure?’? If so then it means that the project structure somehow got messed up and the files appeared to be outside of the configured content roots.
The root cause might be the same as in #2993. My guess is that it could be related to Gradle. I’m not an expert in Gradle, neither in its support in the IDE. Just a guess: on Gradle project reimport all the current IDE project configuration is wiped out and reconfigured from scratch based on gradle config file. So content roots might be changed as well as module dependencies, which means that knowledge that that was a Flutter project gets lost.
The cause might be different.
james-lawrence commented Dec 26, 2018
@alexander-doroshko the read only mode presented itself when editing the files themselves. AS would just ignore my input and display a little note saying read only. i ‘fixed’ the issue by deleting gradle and .idea caches. havent been able to reproduce it. #2993 still happens all the time though.
alexander-doroshko commented Dec 26, 2018
the read only mode presented itself when editing the files themselves. AS would just ignore my input and display a little note saying read only.
Not sure I understand. Should you see it again please paste a screenshot. Thanks!
Speaking of #2993, Gradle reimport is probably deleting knowledge about Flutter from the IDE project files. Gradle doesn’t know anything about Dart/Flutter, so maybe Flutter projects shouldn’t be backed by Gradle config. Sorry, not my area of expertise. Not sure I can help much with it. I think responsible developers might be interested in a sample project they could use to reproduce the issue.
EHBradford commented Mar 28, 2019
Since no one ever provided you with a screen shot here it is. Every file in Android Studio is locked, I cannot edit anything. BTW I know that the res definitions as shown in this example are wrong, I was working on fixing the issue when I suddenly am no longer able to edit any file.
The little popup message happens on any edit action, such as hitting enter or any other character.
EHBradford commented Apr 8, 2019
I continue to have this issue. Have tracked it down in Android Studio 3.3.2 to when I go to Open Module Settings (F4) and I create the APK module, press Apply, and then Ok all of my files are now locked with Android Studio.
To restore my ability to edit the project I have to Re-import Gradle Project. But as soon as I do that I loose all of my «Modules» that I created using the Open Module Settings (F4) window.
Источник
How to Generate APK and Signed APK Files in Android Studio
Android Studio allows you to create two kinds of APK files.
First are the debug APK files that are generated solely for testing purposes. They will run on your Android mobile. However, they cannot be uploaded to the Play Store or made available to the public.
Secondly, you can generate signed APK files. Signed APK files come in handy when you’ve tested your application and it is ready to be uploaded on the Play Store and released to the general public.
This tutorial will show you how to create an Android app by generating APK files using Android Studio.
First things first: open up a project file in Android Studio. If you don’t have a project file yet, simply create a New Project.



Creating an APK file
Generating a debug APK file is easy and is a matter of just a few clicks.
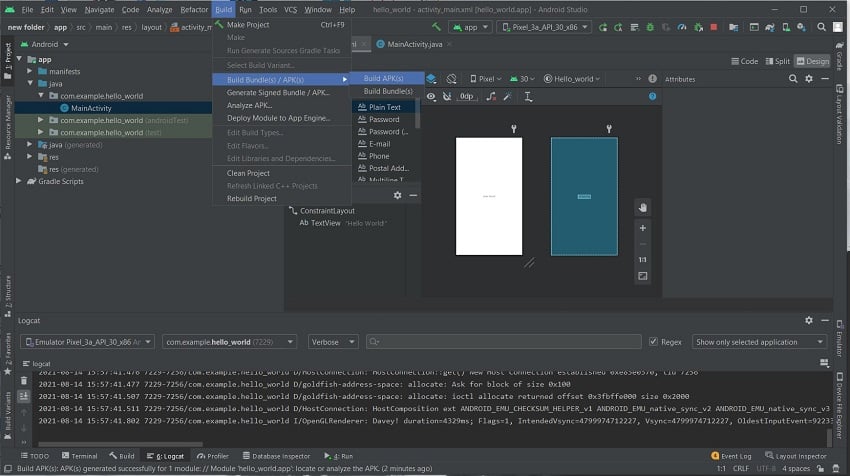
First, open up your project or application that you want to import into an APK file. Then, select Build > Build Bundle(s)/APK(s) > Build APK(s) from the toolbar menu.
Android Studio will take a few moments to generate an APK file.
Once the APK build is complete, you’ll receive a notification on the bottom right corner of your screen. From that notification, select Locate and you will be led to the APK file location.

If you miss the notification, you can still locate the APK file in the following path within your project folder: app/build/outputs/apk/debug. The file is named app-debug.apk by default.
Creating a Signed APK File
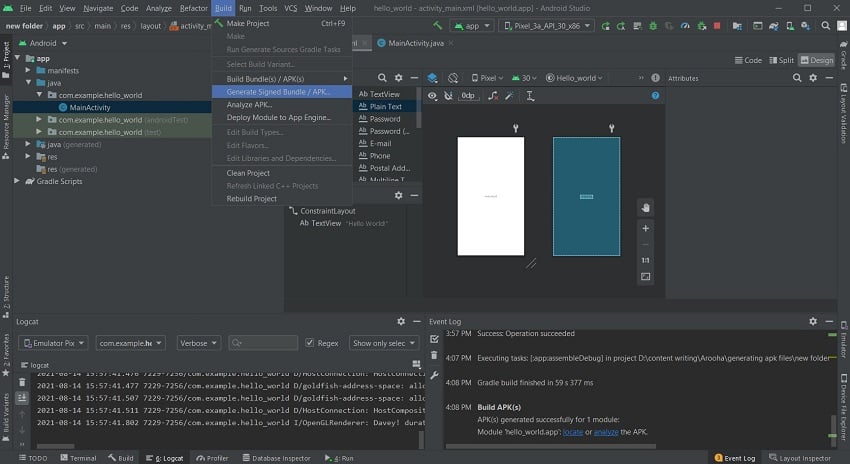
To generate a signed APK file, open the Build menu from the toolbar and select Generate Signed Bundle/APK.

This opens up a screen where you have to select between creating an Android App Bundle and creating an APK file. Check the APK radio button and proceed to the next window.

In the next window, you will be shown the module (your application) for which the APK file is being generated. You’ll be asked about your Key store path, Key store password, Key alias, and the Key password.

Creating a New Key Store
Assuming that this is the first time you’re creating a Signed APK file, you will have to create a new key store.
Keys are used by the developer to access their application once it has been uploaded to the Play Store. The need for the keys usually arises when you have to update your application. All of the keys are stored in the key store.
Both the key store and the keys are protected by passwords of their own. The passwords should be at least six characters in length. Also, it is a good practice to keep multiple copies of your keys since they are your only gateway to your application. If the key is lost, you will not be able to access your application or update it.
Creating your own app requires you to create a new key store. To do so, select Create new. You will find it underneath the input field where you enter the key store path.

You will then be redirected to a new window.

In the new window, enter the path for your new key store, and then enter a password to protect it.
In the same window, you will also be setting a new key for your application. Enter an identity for your key in the key alias field and then enter a password for it.
You can keep the same password as that of your key store, but it’s a good practice to give a new password to each of your keys. The same goes for the key alias.
The next field defines the validity of your application. This is the duration after which the key to your application will expire, leaving your application inaccessible. The default validity for a key is 25 years.
For each key that you generate, you’re given a certificate that contains all the information about you and your company. You don’t necessarily have to fill in all the details—just choose the ones you think should go on your certificate. A key will still be generated, even without filling in each field of the certificate.
Finishing Up
Once you have filled in the details for the certificate, select OK. You will then be directed back to the Generate Signed Bundle or APK screen.
Here, all of the fields will now be pre-filled for you. Go through all the details to stay on the safe side. Then, select Next.

On the last screen, you will now be able to see the destination of your Signed APK file. Below that, you will see two more options: Debug and Release.
Debugging is used when the application is still in the testing phase. Since your application has passed the testing phase and is ready for deployment, select Release.
There are two more checkboxes towards the bottom of the screen. Select V2 (Full APK Signature) and click Finish.

You will be notified by Android Studio once the APK build is finished. Now, you can click on Locate from the notification to open up the file location.
The Signed APK file is named app-release.apk by default. You will find it in your project folder in the app/release directory.
Summary
These are the steps you need to follow to generate APK and Signed APK files for the purposes of testing your app and making it downloadable via Google Play respectively:
Create an APK File
- Create the project in Android Studio.
- Select Build >Build Bundle(s)/APK(s) >Build APK(s) from the toolbar menu.
You can now transfer your debug APK file to your Android mobile phone and test it for bugs. You can also test it out on your PC using the Android emulator.
Create a Signed APK File
- Create the project in Android Studio.
- Select Build >Signed Bundle/APK from the toolbar menu.
- Configure the settings for your APK file and possibly create a new key store and key.
Create a New Key Store and Key
- Select a key store path.
- Enter a password for your key store.
- Give your key an identity, validity period, and password.
- Enter any personal or organizational details you want included in the key certificate.
You can now release this signed APK file to the public by publishing it on Google Play Store.
Easy but tricky, right? Hopefully, this tutorial helped to clear up any confusion you had about generating APK and signed APK files and bettered your understanding of both file types.
Источник