- How To Set Android SDK Path In Windows And Mac
- 1. Configure Android SDK Variable In Windows.
- 1.1 Get Android SDK Install Directory Path.
- 1.2 Set %ANDROID_HOME% and %Path% System Environment Variable.
- 2. Configure Android SDK Variable In macOS.
- How to Set Java SDK Path in Android Studio?
- How to Fix the Java SDK Path?
- Method #1: For Android Studio Version 4.2 and Above
- Method #2: For Android Studio Version Below 4.2
- Method #3: Adding a new SDK to Your Android Studio
- Method #4: For the Command Line Enthusiasts
- Method #5: Using the Embedded SDK
- Method #6: Setting and Viewing SDK using the Studio Project Structure
- How to Fix “SDK location not found” in Android Studio?
- When switching from one IDE to another (Like from Eclipse to Android Studio)
- Android Studio для NDK под Windows
- Установка и настройка Android Studio
- Using local.properties file to avoid API Keys check-in into Version Control System
How To Set Android SDK Path In Windows And Mac
After you installed android studio, you still need to configure some android SDK environment variables then you can use it easily. This article will tell you how to correctly configure Android SDK environment variables such as ANDROID_HOME, PATH on Windows and macOS.
1. Configure Android SDK Variable In Windows.
1.1 Get Android SDK Install Directory Path.
Before you can configure it, you should first get the android SDK install directory follow below steps.
- Open android studio, click File —> Settings menu item in the top men bar.
- Expand Appearance & Behavior —>System Settings —>Android SDK menu item on the left side of the popup window. Then you can find the Android SDK Location directory path on the right side ( in this example, the Android SDK location path is C:\Users\Jerry\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk ), remember it.
1.2 Set %ANDROID_HOME% and %Path% System Environment Variable.
- Right-click the computer icon in Windows file explorer left side, click Properties menu item in the popup menu list. This will open the windows system configuration window.
- Click the Advanced system settings link on left panel, it will popup the System Properties window, click the Environment Variables button to open Environment Variables window.
- Click the New… button to add a new system variable, input ANDROID_HOME as the variable name, and input the Android SDK location directory path ( such as C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk ) as the variable value.
- Select variable Path and click Edit button and add ;%ANDROID_HOME%\tools;%ANDROID_HOME%\tools\bin;%ANDROID_HOME%\platform-tools at the end of its value. Please note the ; must be English character otherwise it will not take effect .
- Click OK to close the system environment variables settings window, open a dos window, type command adb in it. If you see output like below that means the android SDK path variable has been configured successfully.
2. Configure Android SDK Variable In macOS.
- Open Android Studio on macOS, then click Android Studio —> Preferences menu item at the left top toolbar.
- Input search keyword sdk in the search box of the popup Preferences dialog window left side.
- It will focus on the Android SDK menu item on the left side, and you can get the Android SDK Location directory path value on the right side Android SDK Location text box.
- Generally, the Android SDK is installed in the /Users/user-name/Library/Android/sdk folder on macOS.
- If you can not find the above folder in macOS finder or terminal, this is because the Library folder is a hidden folder by default, you should make the hidden folder visible by executing the command $ defaults write com. apple . finder AppleShowAllFiles TRUE in a macOS terminal window ( please read article How To Show Hidden Files In Mac OS Finder And Select Hidden Files In Html Upload File Form ).
- You can also see the hidden Library folder by opening a macOS Finder window, then click Go —> Go to Folder… menu item, and input
/Library in the popup dialog input text box, then click Go button.
Источник
How to Set Java SDK Path in Android Studio?
The Java SDK for Android is a sophisticated suite of tools for managing, monitoring, profiling, and debugging Java code written in Android Studio. But sometimes as software is unpredictable you might be caught in an error that Android Studio stopped compiling projects and says that it can’t locate the 1.7.0_21 folder. Well, this is exactly what is referred to as a missing Java SDK Path.
How to Fix the Java SDK Path?
There are several methods that can help you resolve this issue, the ones which have the highest score in fixing this problem are mentioned below:
Method #1: For Android Studio Version 4.2 and Above
Navigate to File > Project Structure > SDK Location. Upon navigating there you will find that a tab named “JDK Location”, select that and then you can set the JDK path for the current project on which you’re working.
Image I. Setting Project SDK location in 4.2 & +
Method #2: For Android Studio Version Below 4.2
Chances are that you might be rocking an older version of Android Studio, if yes then
Navigate to File > Project Structure > [Platform Settings] > SDKs
You’ll then need to either update your current SDK setup to make use of the new directory or create a new directory and then adjust the settings in your project to make use of the new directory. This will make it applicable to the present project.
Method #3: Adding a new SDK to Your Android Studio
Sometimes only updating your SDKs won’t allow you to compile projects just because the SDK has lived its life and requires an update to itself. In that scenario, you’ll need to recreate the configurations from 0.
- Navigate to Project Structure > Platform Settings > SDKs and click the “+” button.
- Go to your Android SDK folder and select “Choose” on the pop-up.
- A new pop-up window will open, asking which SDK and JDK you’d want to use. Select any Android SDK and the JDK 1.7.
Note: Change your Project SDK to the one you just established under Project Structure > Project Settings > Project. The name of the SDK should now include the new Java version that you installed.
Method #4: For the Command Line Enthusiasts
If you want to be a Geek and the above methods are just too much GUI for you, you might want to handle the SDK path using the terminal. In order to achieve that using the command line, follow the below commands in the Android Studio’s Terminal
and just like that, you’ve achieved the desired result
Note: the ‘oldjre‘ here refers to your old JRE path
Method #5: Using the Embedded SDK
If you are on Android Version 3.2 or older then you’ll be having the option of using the embedded JDK & SDK for your project and that is one of the optimal ways you can fix this issue as Android Studio will handle the management of the services in the Backend!
Navigate to File > Project Structure > JDK Location and Checkmark the box saying “Use embedded JDK (recommended)”.
Image II. Checking the Recommended JDK Location
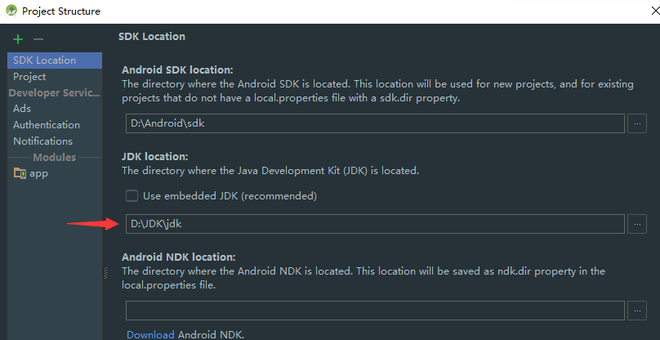
Method #6: Setting and Viewing SDK using the Studio Project Structure
If all the above-mentioned ways didn’t work out for you, the best you can do is to get the SDK path of another Android Studio Project and then providing that path to your particular project (as in Method #1)
Press Ctrl (Command on Mac) + Alt + Shift + S
Then in the SDK Location tab, you will find your SDK Location, just copy it and paste it in the SDK Location as mentioned in Method #1.
Источник
How to Fix “SDK location not found” in Android Studio?
Google developed Android SDK which is a Software Development Kit developed by Google for the Android platform. You can create Android apps using Android SDK, and you don’t need to be an expert to use it. Android SDK and Android Studio come bundled together, with Google’s official integrated development environment (IDE) for the Android operating system.
In this article, we see how to fix an error that is related to the main Android building component of Android Studio that is the Android SDK. The most common error related to Android SDK is “SDK location not found“. This message pops up stating that the location of Android SDK was not detected when the path of SDK is assigned incorrectly. There can also be other reasons for this error message as well and we will see ways to get rid of this error.
When switching from one IDE to another (Like from Eclipse to Android Studio)
Method 1
In this case, follow the below steps:
Method 2
In case the above procedure doesn’t work then add the ANDROID_HOME variable in “Environment Variables” as C:\Users\Username\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk.
Method 3
In case it does not work even then, then you need to change the directory path on Project Structure as well.
- Close the current project and you’ll see a pop-up with a dialog which will then proceed to Configure option.
- Configure -> Project Defaults -> Project Structure -> SDKs on left column -> Android SDK Home Path -> give the exact path as you did on local.properties and select Valid Target.
Method 4
A settings.gradle file might be missing from the project. Make sure that the file exists from the project you are importing. If not add the settings.gradle file with the following:
Save the file and put it in the top-level folder in your project.
Источник
Android Studio для NDK под Windows
На днях я обнаружил, что версия Android Studio неуклонно стремится к единице, в связи с чем задумался об изучении этого инструмента. Чтобы не было скучно, я решил поделиться своим опытом и собранными граблями в виде статьи-туториала.
Сразу хочу оговориться, что я не являюсь гуру Android-разработки, поэтому каких-либо откровений в тексте вы не найдете. Зато тут есть пошаговая инструкция по установке и настройке Android Studio под Windows и созданию простейшего проекта с использованием Android NDK.
Также заранее предупреждаю: статья получилась большой и очень подробной (честно, сам не ожидал), даже несмотря на то, что я почти все скриншоты и некоторые листинги кода спрятал под спойлеры.
На момент написания последней версией Android Studio была 0.8.1, для последующих версий необходимые действия могут отличаться от нижеописанных (очень надеюсь, что в лучшую сторону).
Установка и настройка Android Studio
1. Необходимо установить JDK (Java Development Kit) и JRE (Java Runtime Environment).
Раньше Android SDK поддерживал только JDK версии 6, но теперь это в прошлом. Поддерживается 7 и даже 8 (по крайней мере, именно 8-ю версию я указал в качестве JAVA_HOME и в настройках Android Studio, и никаких проблем не испытал).
JRE же нужен для запуска самой студии. У меня она использует версию 7.
Скачать JDK и JRE версий больше 6 можно с сайта Oracle.
Переменную JAVA_HOME теперь, вроде бы, можно не устанавливать, так как в Android Studio мы будем в настройках прописывать путь к JDK. Но я ее установил. Для этого нужно:
- Зайти в Панель управления\Система и безопасность\Система, выбрать слева Дополнительные параметры системы, в открывшемся диалоге найти кнопку Переменные среды.
- Создать системную или пользовательскую переменную JAVA_HOME и указать для нее путь к JDK. У меня указан вот такой путь: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_05.
2. Если у вас установлен Android SDK.
В комплекте с Android Studio идет свой Android SDK. И, если вы хотите использовать именно его, то в некоторых случаях может случиться странное. Например, у меня при обновлении SDK через SDK Manager часть файлов записывалась в старую папку, и возникли проблемы, когда я эту папку удалил. Скорее всего это произошло из-за того, что в реестре хранился ключ с путем к старой папке. Поэтому имеет смысл почистить реестр. Для этого нужно запустить regedit.exe и найти HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Android SDK Tools для 32-битных машин либо HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\Android SDK Tools для 64-битных машин и удалить Android SDK Tools. Если в реестре вашей системы таких ключей нет, то все в порядке.
Если у вас установлена переменная среды ANDROID_SDK_HOME и вы хотите, чтобы она указывала на старую установку, то, по идее, это не должно стать проблемой, так как при настройке Android Studio мы укажем ей путь к SDK. Проблемы могут возникнуть, если эту переменную использует какое-либо из приложений, входящих в состав Android SDK.
3. Теперь переходим к установке Android Studio.
Нужно скачать Android Studio для вашей системы с официальной страницы и установить ее. По умолчанию, если выбрать «Установить только для меня» ставится в \Users\ \AppData\Local\Android\android-studio\, иначе ставится в \Program FIles (x86)\Android\android-studio\. Можно выбрать и другую папку.
После установки запускаем Android Studio.
Источник
Using local.properties file to avoid API Keys check-in into Version Control System
One of the best benefits of being an Android Developer is that we can create and contribute to open source projects! We can share our code with millions of developers around the globe. Thanks to code hosting platforms like GitHub!
Now, when we make our code available as public repositories, we should ensure we take care of some things such as the sharing of private API keys, restricted URLs, etc., How can we achieve this by using the “local.properties” file in our root project? Let’s find out in this article.
Welcome to our MindOrks blog on Using local.properties file to avoid API Keys check-in into Version Control System.
Every time, we create a new project in Android Studio, we see a file created with the name “local.properties” containing the following content:
So local.properties is a file that is generated by Android Studio and it is recommended not to include this in the version control system.
So, if we take a look at our gitignore files in general, we have:
We can see that local.properties file is excluded in the version control system.
Tip: Updating the gitignore files with the relevant extensions and file folders is really important for creating an open-source project. Since the “local.properties” file is not shared in the version control system, we can use this for declaring our local user-specific variables or private variables such as API keys or restricted base URLs, etc.,
Let’s take a use case. Let’s consider our recently released open-source project on GitHub:
This project helps to build a ride-sharing Android Taxi Clone App like Uber, Lyft. You can fork it and learn many awesome functionalities. Please go through the Readme file for details of the project.
Now, since our use case is a ride-sharing application, we will be using google maps in it. To use Google Maps, the developer should have an associated API Key. Let’s see how we can achieve this by using “local.properties” file.
First of all, let’s append a parameter in the local.properties file:
Now, let’s extract this value and use it in our app-level Gradle file through a variable.
In order to access our API key, we can use:
There are some files that get generated during build time such as gradleResValues.xml, BuildConfig.java, etc. Let’s make the use of these files to store the value of our API key. How can we add values to files that are generated during the build process? We shall use our buildTypes section in our app-level build.gradle file
Now once we add this in our build.gradle file, we rebuild our project and we can see a file named gradleResValues.xml is generated in the res(generated) folder.
In order to use this value inside the application, we can try extracting the values like follows:
If we wish to store the value in the BuildConfig.java file, we can replace the resValue with buildConfigField in the app-level build.gradle file as follows:
After changing the build.gradle file, let’s rebuild the project and take a look at our BuildConfig.java file:
Now, we can access this parameter anywhere in the code like
Источник