Android studio modbus rtu
The aim of this library is to let users to leverage the power of modbus RTU protocol through RS485 on Android devices, specifically on the Ltouch multi-touch panels (picture on the right) and development boards.
Introduction
In order to communicate with your instruments and devices from Android through RS485 and modbus, you can link the modbus RTU library in your projects and call the methods, such as function code 3 Read Holding Registers or function 16 Preset Multiple Registers, the most widely used modbus functions.
This document helps you to understand how to design a project that uses the native modbus library for Android. Many approaches exist in the way a project could be structured; we suggest one of that is complete and efficient though.
Ltouch F touch panel
The Ltouch board is a high-performance system based on the Samsung ARM Cortex-A8 microcontroller specifically designed for industrial and home automation. Supports Android 2.3 and 4.0.4.
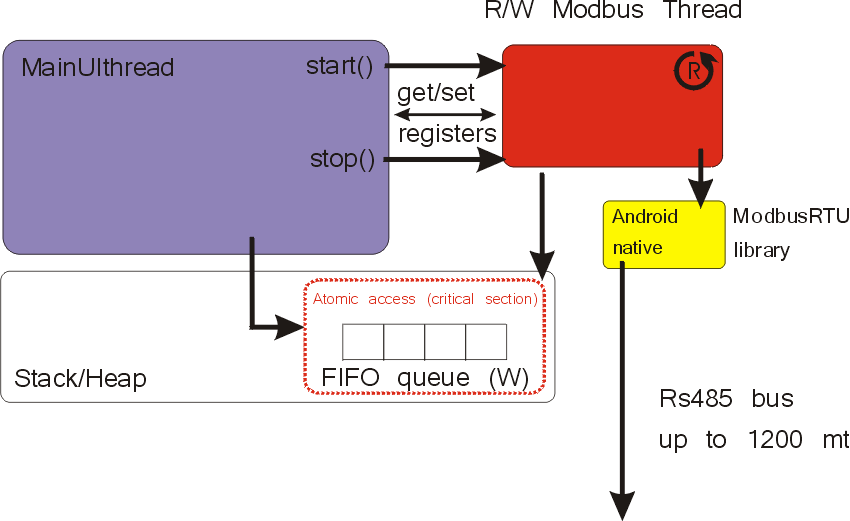
Architecture
The most frequent situation that is encountered in industrial and home automations applications is the following: one or more slave devices (such as PLCs, Power inverters, remote I/O modules) connected in a bus line and a touch panel that acts as a master displaying devices’ states accepting commands from users. Basically, this is at the heart of Human Machine Interface (HMI).
The HMI interface is designed using the Android framework. For those of you that are not familiar with creating Android projects, we suggest to take a look at this brief tutorial on how to create your first app with Android. Many other tutorials and books are available on the net.
The high-level architecture of a hypothetical Android project can be summarized in the picture below. The rounded boxes represent respectively:
- The main activity (that runs on the MainUIthread)
- The thread that manage all the modbus requests (red)
- The native modbus library (yellow)
- A FIFO queue data structure that is used for the modbus Writes.
The first question may arise is the following: why using a FIFO queue and critical sections? Because we supposed that the project has to manage regular graphical updates, therefore the stream of read requests has to be correctly overlapped with writes. Indeed, the FIFO queue garantees the requests will be processed with the same order as they arrive.
In this tutorial, modbus reads and writes are considered as synonyms of modbus function 3 and 16 respectively.
The mainUIthread represent the main thread Activity(«Window») that the users see. It contains all the code necessary to manage the UI, like buttons, progress bars, text boxes, etc. We used only one Activity, but obviously, real world applications use more than one activity for accomplish their jobs. Indeed, it starts and stops the thread that manages the modbus reads/writes. The java code might be:
The onResume method accounts for opening the serial port (in this case with baudrate set to 38400bps and timeouts 40000ns for both modbus reads and writes) and for starting the thread that manages the modbus requests. When creating the modbus thread, it needs four parameters:
- a blocking queue data structure,
- an handler for returning back the modbus replies to the UI thread,
- the file id that refers to the serial port you want to work with,
- the Reads Refresh Rate that is the ideal refresh rate with which the reads will be executed.
The queue_writes is a blocking queue with a maximum length of 2000. We used a BlockingQueue data structure because the elements must be added atomically, preserving also the order with which requests arrives. Because of that, the code that inserts the elements into the queue will be in a critical section.
The objects that are stored in the queue must be of type WriteRequest. The class WriteRequest simply defines the object «modbus function» and is coded as follow:
A modbus write request can be defined as
with hr as a valid reference to an integer array. As previously stated, the code that adds write requests has to be in a critical section to preserve the order. This is accomplished by using a Java synchronized statement specifying the name of the variable to be accessed atomically (i.e., the queue), namely:
The final statement wakes up the modbus thread in case it was sleeping, therefore it can process the new requests that are on the queue.
We are now ready to analyze how can be designed the main thread that manage the modbus requests. We called this class ReadsWrites and it extends Thread in order to be executed in parallel with the other threads in the Android OS. The class private variables wrqueue, hd, fid and reads_rr are the same as those passed to the object constructor together with some other variables referring to modbus reads.
The core of the class stands in the critical section. It works in a way that when the queue is not empty, it executes all the writing requests; otherwise it cyclically reads registers from the slave(s) and pause itself for a limited timespan. The thread wakes up when a new write request has to be executed.
Since in Android background threads can not access the graphical objects directly, it is mandatory to manage the UI updates with messages and in particular using the handle that were gathered at the time of thread creation. The messages are created and sent by calling the obtainMessage and sendMessage methods. The class’ code might be the following:
In this demo project, two values only are sent back to the main UI thread. If you need to exchange more than few values, please take a look at our blog post in which Android bundle is used to figure out this issue.
Final considerations
The design we presented in this overview helps you to lay out the architecture of your Android application. It is quite general so can be adopted in many situations and by many professional and home users of our Android touch panels and development boards. We strongly suggest to starting with it and extending as your needs.
© Biemme Automations 2015
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License.
Источник
Android studio modbus rtu
Modbus is an industrial communication system, connected to each other by a programmable controller and a computer with the intelligent terminal via the public line or dedicated line locally. Its system structure includes both hardware, including software. It can be applied to various data acquisitions and process monitoring.
As the open source android system, customizable, powerful, sophisticated network applications, many industrial equipment gradually began to use android devices to custom industrial equipment systems, then modbus android system came into being in the above application. During the work of the author, it led through the two large projects based on android modbus, the large-scale fire-fighting system of a large state-owned enterprises, a large state-owned electric company’s large charging plug system .
This is the Android version of the Modbus TCP examples, examples of which just write to holding register read and write capabilities, which should be noted that the initialization of the modbus, read, write, etc. operations should be carried out in a sub-thread inside, otherwise it will cause network Operation in the abnormality of the main thread.
Modbus of the coil, the discrete registers, input register and the like, the program basically the same idea, as an example without other; for modbus RTU / ASCII communication mode, without the above serial phone function, not take this feature, there is no upload.
Источник
Android и modbus
Откуда берутся атрибуты android:layout_width и android:layout_height в элементе LinearLayout?
Недавно начал изучать Android API, а сегодня более менее разобрал основы синтакиса XML. Затем стал.
Работа с файлами android которые находятся не в папке проекта Android Studio
Всех приветствую, начал разработку приложения под Android и не могу разобраться как работать с.
Не предлагается установка Android SDK при установке Android Studio
на сайте https://developer.android.com/studio/. скачал exeшник для установки Android Studio.
Android Studio не находит функцию TextView в пакете Android.Widget
Я создал новый проект в Android Studio. Android Studio не находит функцию TextView в пакете.
Я так понял это библиотека modbus. Все таки хочется увидеть как выглядит обработчик (код полной команды) задачи выше что бы понять суть
Добавлено через 2 часа 14 минут
Мне нужно разработать по для андроид для обмена данными с контроллера modbus. Примерно понятно как это делается детально нет времени и достаточных знаний этим заниматься. Может кто поможет написать программу за мат. Вознаграждение. Свои координаты оставляйте мне в личку. Спасибо!
Вы абсолютно неверно поняли. Библиотека ни причем, тем более что по представленным ссылкам примеры по сылок в явном виде (либы с открытым исходным кодом), даже протокол не нужен.
Если вы настолько ленивы, что не в состоянии найти Modbus TCP, вот вам прямая ссылка на протокол Modbus TCP http://raxp.radioliga.com/cnt/s.php?p=m5.zip, в котором расписан формат обмена.
Если вы не понимаете разницу между сериал-протоколами Modbus ASC, Modbus RTU и сетевым Modbus TCP — вот вам для изучения RS-485. Работа с Modbus протоколом. . Среди прочего нужно понимать, что Modbus реализуется каждым производителем на свой манер и наилучшим вариантом является описание протокола обмена от производителя вашего контроллера, который вы не указали, ни модели, ни названия.
Источник
Android studio modbus rtu
This is a Modbus library for Android.
1.Add the library to your project
Copy the jar to the lib directory of your project and add the config to build.gradle.
2.Create and init ModbusReq instance
Init ModbusReq instance through setting the modbus param.
6.Read InputRegisters(Child Thread)
10.Destroy Modbus Instance
if you use RTU Mode with SerialPort,you should do :
-
- Create a class to implement SerialPortWrapper interface.
-
- Create a ModbusMaster instance with createRtuMaster mothod of ModbusFactory class.
Источник
Android studio modbus rtu
Mobile Modbus is an Android Modbus polling client using modern android UI design guidelines and design patterns such as the Action bar for navigation, a slide-in menu for settings, and appropriately scaled data-display for the device you are working on (i.e. list views on a phone, and a grid on a tablet). And as I love all the new hottness, it also is built in Android Studio using the new gradle-based build system, so you will need to download that to work on this project.
More info to come as this project develops. Until then feel free to follow along with my blog for information, or follow me on twitter.
Contributing / Reporting Issues
Eventually I’ll put some basic stuff here to know how to contribute more easily — but basically for now, fork the project on github, and submit a pull request and I’ll evaluate it and add it if it is in line with the goals of the project.
If you see anything wrong with it in any way or just want to add something to the project, file a ticket or submit a pull request.
This project relies on two android support libraries, and one 3rd party library:
- Modbus4J — a Java Modbus library that is pretty extensible and full-featured with some nice batching functions that we (are going to) make use of. Just download and copy (or CVS-checkout) it into the top-level «Libraries/Modbus4J» folder (whole project). There should already be an appropriate build.gradle in that folder, all ready to build the library.
This project is Apache 2.0, which should be GPL 3.0 compatible, which I/you have to care about because Modbus4J is GPL3.
I’ll add the preamble here sometime soon, and get the class header comments all in line as well.
Last edited by Ben Catlin on July 29, 2013
Источник