- SeekBar (Слайдер)
- Меняем задний фон экрана
- Дополнительное чтение
- Android studio seekbar get value
- How To Add Listener To Notify The Changes In SeekBar:
- Attributes of SeekBar In Android:
- SeekBar Example In Android Studio:
- Custom vertical SeekBar Example In Android Studio:
- Android SeekBar with Examples
- Create Android SeekBar in XML Layout File
- Android SeekBar with Determinate Mode
- Android SeekBar with Indeterminate Mode
- Android SeekBar Control Attributes
- Android SeekBar Control Example
- activity_main.xml
- MainActivity.java
- Output of Android SeekBar Example
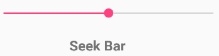
SeekBar (Слайдер)
SeekBar — это обычный слайдер, когда пользователь может передвигать ползунок пальцем на экране. Ползунок также можно двигать при помощи клавиш-стрелок.
Компонент SeekBar находится в разделе Widgets и наследуется от класса ProgressBar. В Android Studio 3.0 представлен в двух вариантах: SeekBar и SeekBar (Discrete).
Для отслеживания перемещения ползунка SeekBar необходимо реализовать интерфейс-слушатель SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener с методами-заглушками:
- onProgressChanged() — уведомляет об изменении положения ползунка;
- onStartTrackingTouch() — уведомляет о том, что пользователь начал перемещать ползунок;
- onStopTrackingTouch() — уведомляет о том, что пользователь закончил перемещать ползунок
Заготовка для Kotlin (на Java будет ниже в статье).
Создадим новый проект и добавим компоненты SeekBar и TextView:
Напишем код, чтобы в текстовом поле отображалось текущее значение ползунка после того, как пользователь отпустит его.
Ниже представлены вариант на Android 5.0 и старый вариант на Android 2.3 до появления Material Design, чтобы вы видели, как менялся интерфейс.
Меняем задний фон экрана
Усложним пример и будем менять цвет у фона экрана. Добавим на форму три компонента SeekBar:
Напишем код, меняющий значение цвета через значения ползунка:
Кот Рыжик попросил выставить цвет, наиболее подходящий цвету его шкурки. Я решил ему немного польстить:
Дополнительное чтение
patryk1007/ShootingSlider — прикольный слайдер, напоминающий стрельбу из пушки в играх
Источник
Android studio seekbar get value
In Android, SeekBar is an extension of ProgressBar that adds a draggable thumb, a user can touch the thumb and drag left or right to set the value for current progress.
SeekBar is one of the very useful user interface element in Android that allows the selection of integer values using a natural user interface. An example of SeekBar is your device’s brightness control and volume control.
Important Note: Attribute of a SeekBar are same as ProgressBar and the only difference is user determine the progress by moving a slider (thumb) in SeekBar. To add a SeekBar to a layout (XML) file, you can use the element.
SeekBar code in XML:
Table Of Contents
How To Add Listener To Notify The Changes In SeekBar:
SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener is a listener used as a callback that notifies client when the progress level of seekbar has been changed. This listener can be used for both user initiated changes (in xml file or java class) as well as for programmatic changes.
seekBarInstanceVariable.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(new OnSeekBarChangeListener() – This method is used to notify the user changes/actions in the SeekBar.
Methods Needs To Be Implemented:
In Seek bar for getting changes in progress we need to implement three abstract methods. Below is detail description of these three methods:
1. public void onProgressChanged (SeekBar seekBar, int progresValue, boolean fromUser) –
This listener method will be invoked if any change is made in the SeekBar.
2. public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) –
This listener method will be invoked at the start of user’s touch event. Whenever a user touch the thumb for dragging this method will automatically called.
3. public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) –
This listener method will be invoked at the end of user touch event. Whenever a user stop dragging the thump this method will be automatically called.
getMax():
We can get the maximum value of the SeekBar programmatically means in java class. This method returns an integer value. Below code will get the maximum value from a Seekbar.
getProgress():
We can get the current progress value from a Seekbar in java class using getProgress() method. This method returns an integer value. Below code is used to get the current progress value from a Seek bar.
Attributes of SeekBar In Android:
Now let’s we discuss important attributes that helps us to configure a SeekBar in xml file (layout).
1. id: id attribute uniquely identify SeekBar.
2. max: max attribute in SeekBar define the maximum it can take. It must be an integer value like 10, 20, 100, 200 etc. We can set the max value in XML file as well as in java class. By default, a SeekBar takes maximum value of 100.
Below we set 150 maximum value for a Seek bar.
Setting max value of SeekBar Progress In Java Class :
3. progress: progress is an attribute of SeekBar used to define the default progress value, between 0 and max. It must be an integer value.
Below we set the 200 max value and then set 50 default progress value.
Setting progress In Java Class :
4. progressDrawable: progress drawable attribute is used in Android to set the custom drawable xml for the progress mode of a seekbar. Progress drawable is used when we need to use a custom progress of a seekbar.
Below we set the custom gradient drawable for the progress mode of a Seekbar.
Step 1: Add this code in activity_main.xml or main.xml
Step 2: Create a new drawable resource xml in drawable folder and name it custom_progress. Here add the below code which creates gradient effect in seekbar.
5. indeterminate: indeterminate is an attribute used in android to enable the indeterminate mode of a seekbar. In this mode a seekbar shows a cyclic animation without an indication of progress. This mode is used in application when we don’t know the amount of work has been done. Here actual progress will be hidden from user.
Below we set the indeterminate to true.
6. background: background attribute of seekbar is used to set the background. We can set a color or a drawable in the background of a Seekbar. We can also set the background color in JAVA class.
Below we set the green color for the background of a Seek bar.
Setting Background of SeekBar In Java class:
7. padding: padding attribute of seekbar is used to set the padding from left, right, top or bottom.
- paddingRight: padding right attribute is used to set the padding from the right side of the Seekbar.
- paddingLeft: padding left attribute is used to set set the padding from the left side of the Seekbar.
- paddingTop: padding top attribute is used to set the padding from the top side of the Seekbar.
- paddingBottom: padding bottom attribute is used to set the padding from the bottom side of the Seek bar.
- Padding: padding attribute is used to set the padding from the all side’s of the Seekbar.
Below we set the 20dp padding from the top of the Seek bar.
8. thumb: thumb attribute is used in seekbar to draw a thumb on a seekbar. We can use an image or a drawable for the thumb.
Below is an example code in which we set a drawable icon for the thumb of the seekbar.
First download the thumb icon from here and save in drawable folder of your project. You can also click on below icon and then download it:
SeekBar Example In Android Studio:
Example 1: In the below example of seekbar in Android we display a simple seekbar by using its different attributes as discussed earlier in this post. We also perform seekbar changed listener event which is used to get the changes in the progress of a seek bar. After getting changes, the changed value of progress is displayed by using a Toast. Below is the download code, final output and step by step tutorial:
Important Note: Don’t miss the 2nd example of Custom SeekBar in Android which is discussed right after this example.
Step 1: Create a new project and name it SeekBarExample
Step 2: Open res -> layout -> activity_main.xml (or) main.xml and add following code:
In this step we open an xml file and add the code for displaying a seekbar by using its different attributes like max, default progress and few more.
Step 3: Open src -> package -> MainActivity.java
In this step we open MainActivity and add the code to initiate the seekbar and then perform seekbar changed listener event for getting the changes in the progress of the seekbar. By using this event listener we set get the current value of a seekbar and when a user stop the tracking touch, the value of progress is displayed by using a Toast.
Custom vertical SeekBar Example In Android Studio:
In the 2nd example of seekbar we displayed a custom vertical seekbar by using its different attributes. Similar to first example we perform seekbar changed listener event which is used in getting the changes done in the progress and then those changed value of progress is displayed by using a Toast.
Step 1: Create a new project and name it SeekBarExample
Step 2: Open res -> layout -> activity_main.xml (or) main.xml and add following code:
In this step we open xml file and add the code for displaying a vertical seekbar by using its different attributes like max, default progress etc. In this xml for displaying a vertical seekbar we used a rotational attribute and set 270 value for that.
Step 3: Create an xml file in drawable -> custom_progress.xml
In this step we create a custom drawable xml for the seek bar. In this xml we create a layer list in which we create an item and then set the gradient colors for our custom seek bar.
Step 4: Open src -> package -> MainActivity.java
In this step we open MainActivity and here we add the code to initiate the vertical seekbar and then perform seek bar changed listener event for getting the changes in the progress of the seek bar. By using this event listener we get the current progress value of a seek bar and when a user stop the tracking touch, that value of progress is displayed by using a Toast.
Источник
Android SeekBar with Examples
In android, SeekBar is an extension of ProgressBar control with a draggable thumb. The SeekBar allows users to touch the thumb and drag left or right to set the current progress levels.
The android SeekBar is one of the useful UI element and it provides a user interface to select the integer values within the defined range.
Following is the pictorial representation of using a SeekBar in android applications.
By using the draggable thumb in SeekBar we can slide left or right to choose a value between 0 and maximum integer value which we defined using android:max attribute. An example of SeekBar is our device Brightness control or volume control.
In android, by using SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener listener, we can notify the client when the progress level of seekbar has been changed.
Create Android SeekBar in XML Layout File
In android, we can create SeekBar in XML layout file using element with different attributes like as shown below.
SeekBar android :id= «@+id/seekBar1»
android :layout_width= » wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :max= «100»
android :indeterminate= «false»
android :progress= «50»/>
If you observe above code snippet, we defined a seekbar ( ) with different attributes, those are
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| android:id | It is used to uniquely identify the control |
| android:indeterminate | It is used to show the cyclic animation in seekbar without an indication of progress. |
| android:max | It is used to set the maximum value of seekbar. |
| android:progress | It is used to set the default progress value between 0 and max. It must be an integer value. |
In android, the SeekBar supports two types of modes to show the progress, those are Determinate and Indeterminate.
Android SeekBar with Determinate Mode
Generally, we use the Determinate progress mode in seekbar when we want to show the quantity of progress has occurred. For example, the percentage of a file downloaded, number of records inserted into a database, etc.
Following is the example which shows a Determinate seekbar that is 50% complete.
SeekBar
android :id= «@+id/seekBar1»
android :layout_width= «300dp»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :max= «100»
android :progress= «50»/>
The above code snippet will show the SeekBar like as shown below
Generally, when the progress value reaches 100 then the progress bar is full. By using android:max attribute we can adjust this value.
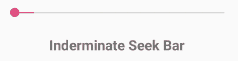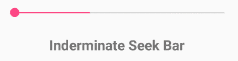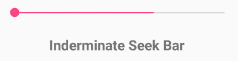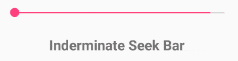
Android SeekBar with Indeterminate Mode
Generally, we use the Indeterminate progress mode in seekbar when we don’t know how long an operation will take or how much work has done.
In indeterminate mode the actual progress will not be shown, only the cyclic animation will be shown to indicate that some progress is happing.
Following is the example to set Indeterminate progress mode in an XML layout file.
SeekBar android :id= «@+id/seekBar1»
android :layout_width= «300dp»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :max= «100»
android :indeterminate= «true»
android :progress= «0»/>
The above code snippet will show the SeekBar like as shown below.
This is how we can define the Progress modes in SeekBar based on our requirements in android applications.
Android SeekBar Control Attributes
The following are some of the commonly used attributes related to SeekBar control in android applications.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| android:id | It is used to uniquely identify the control |
| android:max | It is used to specify the maximum value of the progress can take |
| android:progress | It is used to specify default progress value. |
| android:background | It is used to set the background color for a progress bar. |
| android:indeterminate | It is used to enable the indeterminate progress mode. |
| android:padding | It is used to set the padding for left, right, top or bottom of a progress bar. |
| android:progressDrawable | It is used to set the custom drawable XML for the progress mode of a seekbar. |
| android:thumb | It is used to set the thumb icon on seekbar to drag left or right. |
Android SeekBar Control Example
Following is the example of defining a SeekBar control and TextView control in RelativeLayout to get the progress changes in seekbar using SeekBar changed listener event.
Create a new android application using android studio and give names as SeekBarExample. In case if you are not aware of creating an app in android studio check this article Android Hello World App.
Now open an activity_main.xml file from \res\layout path and write the code like as shown below
activity_main.xml
xml version= «1.0» encoding= «utf-8» ?>
RelativeLayout xmlns: android = «http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
android :layout_width= «match_parent» android :layout_height= «match_parent» >
SeekBar
android :id= «@+id/seekBar1»
android :layout_width= «300dp»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «40dp»
android :layout_marginTop= «200dp»
android :max= «100»
android :indeterminate= «false»
android :progress= «0»/>
TextView
android :id= «@+id/textview1»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_alignLeft= «@+id/seekBar1»
android :layout_below= «@+id/seekBar1»
android :layout_marginTop= «40dp»
android :layout_marginLeft= «130dp»
android :textSize= «20dp»
android :textStyle= «bold»/>
RelativeLayout >
If you observe above code we created a one SeekBar control and one TextView control in XML Layout file.
Once we are done with the creation of layout with required controls, we need to load the XML layout resource from our activity onCreate() callback method, for that open main activity file MainActivity.java from \java\com.tutlane.seekbarexample path and write the code like as shown below.
MainActivity.java
package com.tutlane.seekbarexample;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.SeekBar;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity <
private SeekBar sBar ;
private TextView tView ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) <
super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout. activity_main );
sBar = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id. seekBar1 );
tView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id. textview1 );
tView .setText( sBar .getProgress() + «/» + sBar .getMax());
sBar .setOnSeekBarChangeListener( new SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener() <
int pval = 0 ;
@Override
public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar, int progress, boolean fromUser) <
pval = progress;
>
@Override
public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) <
//write custom code to on start progress
>
@Override
public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) <
tView .setText( pval + «/» + seekBar.getMax());
>
>);
>
>
If you observe above code we are calling our layout using setContentView method in the form of R.layout.layout_file_name in our activity file. Here our xml file name is activity_main.xml so we used file name activity_main and we are trying to show the progress of task in seek bar on progress change event.
Generally, during the launch of our activity, the onCreate() callback method will be called by the android framework to get the required layout for an activity.
Output of Android SeekBar Example
When we run the above example using an android virtual device (AVD) we will get a result like as shown below.
If you observe the above result, we are able to start showing the progress of the task in the seekbar when we click on it in the android application.
This is how we can use SeekBar control in android applications to show the progress of tasks or work based on our requirements.
Источник