- Android и кастомные шрифты или «Да здравствует API 26»
- Как было раньше. Краткий обзор
- view.xml
- CustomFontTextView.class
- Но все изменилось в API 26
- Using Custom and Downloadable Fonts in Android
- The Older way of using Fonts
- Using Custom Font in Android
- Downloadable Fonts
- Fonts in XML
- Creating a font family
- Using fonts in XML layouts
- Adding fonts to a TextView
- Adding fonts to style
- Using fonts programmatically
- Kotlin
- Using the support library
- Kotlin
- Совет: Работаем со своими шрифтами в Android O
- Добавление ваших шрифтов в проект
- Использование своих шрифтов
- Создание семейства шрифта
- Не забудьте протестировать!
- Заключение
Android и кастомные шрифты или «Да здравствует API 26»
Как было раньше. Краткий обзор
Если было много view где требовались нестандартные шрифты, то мы использовали что-то вроде такого:
view.xml
CustomFontTextView.class
И это я пропустил огромный кусок который отвечает за то, чтобы не писать каждый раз путь к шрифту, а указывать
Ну, или шли на гитхаб и в результате находили Calligraphy (7000 звезд!)
Ни для кого не секрет что этот подход содержал много минусов как в огромном количестве boilerplate кода, так и в том, чтобы сделать это эффективно и где-нибудь не утечь по памяти запрашивая каждый раз Typeface.
Но все изменилось в API 26
Похоже, гугл наконец-то сдался и решил отказаться от навязывания Roboto и сделал удобное подключение сторонних шрифтов, за что ему огромное спасибо.
Линк для тех, кто любит читать в оригинале.
Теперь подключение состоит всего из нескольких несложных шагов:
1. Создаем папку font в res
Resource type выбираем font
2. Перетаскиваем в новую папку все нужные нам в проекте шрифты
3. Создаем файл для семейства шрифтов.
Обратите внимание: я сразу добавил в пример то как должен выглядеть файл, если вы хотите поддерживать и более старые версии Андроида. (Начиная с 14). Если вам повезло и у вас таргет только на супер-новые девайсы, то ваш файл сократится в 2 раза
Ну а дальше остается только наслаждаться сборкой
Использование в TextView
Используем в стилях
И у вас больше не болит голова об эффективности 🙂
Источник
Using Custom and Downloadable Fonts in Android
At the Google I/O 2017, Android O or simple Android Oreo was launched and it came with a lot of cool features. One of the really interesting features for developers was the new way to apply fonts right in your XML files. Yeah, you heard it right. Now there is no need of writing some piece of code for using the fonts. Also, you can choose from any of the thousands of fonts on Google Fonts and use them in your app.
So, in this blog, you will understand how to use Custom and Downloadable Fonts in Android?
The Older way of using Fonts
Before we move forward to look for the new or the latest way of using the font, let’s revise the older way of using fonts. Before the release of Android O, fonts can be used in the following 2 ways :
- Using Typeface: One would typically need a custom view that extends the equivalent view were trying to apply a font to. In the custom view, one would create a Typeface and then call setTypeface (or a similar method, that, sets the typeface). One would also need to have the font file placed in the assets folder. The code in the custom view typically looks like:
- Calligraphy Library : You can use some existing libraries for various fonts used in Android. One of them is Calligraphy Library.
Using Custom Font in Android
To work with Custom Font, you need to install the latest version of Android Studio 3.x. This is important as some of the features are not supported on Android Studio 2.x — for example, the font resource directory. Once you are done with the installation of the latest version of Android Studio, create a project and add a text view in any of the activity(This is the text view on which we are going to apply custom font). Then follow the below steps :
- Add a font directory to your project: In the Android View, right click on the resfolder and go to New -> Android Resource Directory. Type fontas the name of the font and select fontas the resource type. Then click on Ok.
- Add the downloaded font to the font directory: Copy and Paste your font into res/font.I am using Pacifico font. You can get this font from FontSqirrel.
- Create a font-family XML file: You can create font families which contain a set of font files with their style and weight details. To create a new font family you need to create a new XML font resource. The benefit is that you can access it as a single unit instead of referencing individual font files for each style and weight. To create a font-family, right click on res/fontand choose New -> Font Resource File and give any name. In my case, I am using my_custom_font.xml.
Note: A really important thing to note is that we had to define attributes using both android and app namespaces. The app namespace is what ensures that the feature is backward compatible.
- Set the font in the XML: Now you can use the font-familyattribute to set the font in XML.
Below is the preview of the above code :
Downloadable Fonts
Now that we have seen how custom fonts work, let’s jump onto another novality — downloadable font . Android 8.0 (API level 26) and Android Support Library 26 introduce support for APIs to request fonts from a provider application instead of bundling files into APK or letting the APK download fonts. A font provider application retrieves fonts and caches them locally so that other apps can request and share fonts. How cool is that!
The feature is available on devices running Android API version 14 and higher through the Support Library 26.
Picture courtesy : Android Developer website
As you can see in the image above, apps using Downloadable Fonts make a FontRequest using the FontsContract API which retrieves the Typeface from the Font Provider. The Font Provider does not need to download fonts if it already exists in the Font Cache.
Benefits of downloadable fonts :
- Reduces the APK size
- Increase the app installation success rate
- Improves the overall system health as multiple APKs can share the same font through a provider. This saves users cellular data, phone memory, and disk space. In this model, the font is fetched over the network when needed.
In order to use the downloadable font in android studio, follow the below steps :
- If you want to use Android Studio to generate the required files, then you’ll need version 3.0+. Add the following (version 26+) to your module’s build.gradle:
- Select a text view in your app that you want to apply the font to and click on the fontFamily attribute under Attributes in the graphical layout
Select the “More Fonts…” at the bottom, which will open the dialog below.
- Make sure to have “ Create downloadable font” selected. This results in three files being downloaded — lato.xml, font_certs.xml and preloaded_fonts.xml.
This file contains the font attributes for loading a Typeface from the Google Fonts Provider Application.
The system uses these certificates to verify the font provider’s identity, to avoid getting fonts from an unknown source. If using the steps above, Android Studio should have automatically generated the string certificates for dev and prod in font_certs.xml below.
preloaded-fonts.xml
This file is referenced in the Android manifest which helps the framework pre-load fonts to avoid delays when the app is launched.
- Make sure this line is added to your app’s Manifest file, Android Studio should have done this automatically:
- Great, now you are ready to apply the fonts in XML!
All I had to do was set the font family in the app’s theme to get TextViews throughout the app to change to Lato, including parts that were bold or italicized. However, if you want to configure the weights, you can follow the same steps to get Lato Bold using Android Studio, and change the weight manually in lato_bold.xml that you can then apply in XML layouts:
That’s all about the custom and downloadable fonts in android. Hope you like the blog.
Источник
Fonts in XML
Android 8.0 (API level 26) introduces a new feature, Fonts in XML, which lets you use fonts as resources. You can add the font file in the res/font/ folder to bundle fonts as resources. These fonts are compiled in your R file and are automatically available in Android Studio. You can access the font resources with the help of a new resource type, font . For example, to access a font resource, use @font/myfont , or R.font.myfont .
To use the Fonts in XML feature on devices running Android 4.1 (API level 16) and higher, use the Support Library 26. For more information on using the support library, refer to the Using the support library section.
To add fonts as resources, perform the following steps in the Android Studio:
- Right-click the res folder and go to New > Android resource directory.
The New Resource Directory window appears.
In the Resource type list, select font, and then click OK.
Note: The name of the resource directory must be font.
Figure 1. Adding the font resource directory
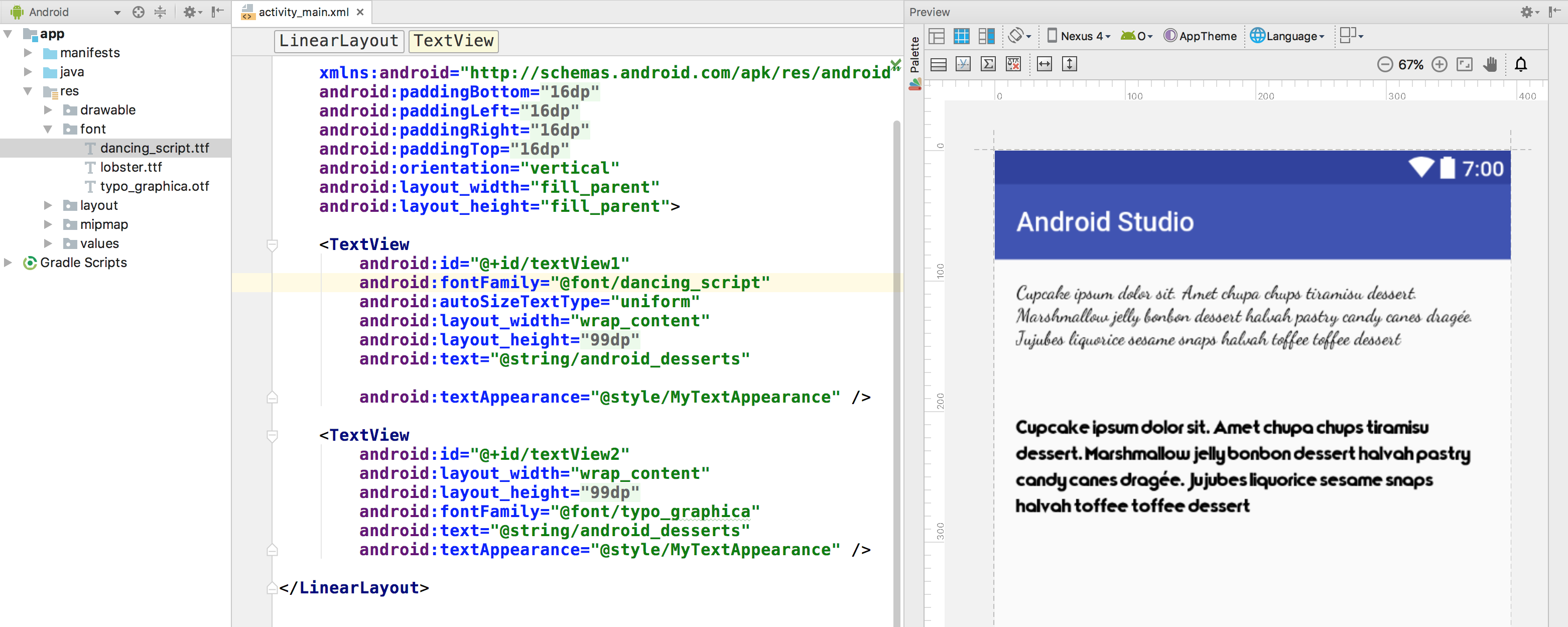
Add your font files in the font folder.
The folder structure below generates R.font.dancing_script , R.font.lobster , and R.font.typo_graphica .
Figure 2. Adding the font files in the resource directory
Double-click a font file to preview the file’s fonts in the editor.
Figure 3. Previewing the font file
Creating a font family
A font family is a set of font files along with its style and weight details. In Android, you can create a new font family as an XML resource and access it as a single unit, instead of referencing each style and weight as separate resources. By doing this, the system can select the correct font based on the text style you are trying to use.
To create a font family, perform the following steps in the Android Studio:
- Right-click the font folder and go to New > Font resource file. The New Resource File window appears.
- Enter the file name, and then click OK. The new font resource XML opens in the editor.
- Enclose each font file, style, and weight attribute in the element. The following XML illustrates adding font-related attributes in the font resource XML:
Using fonts in XML layouts
Use your fonts, either a single font file or a font from a font family, in a TextView object or in styles. To add fonts to the TextView or in styles, use the fontFamily attribute.
Note: When you use a font family, the TextView switches on its own, as needed, to use the font files from that family.
Adding fonts to a TextView
To set a font for the TextView , do one of the following:
- In the layout XML file, set the fontFamily attribute to the font file you want to access.
- Open the Properties window to set the font for the TextView .
- Select a view to open the Properties window.
Note: The Properties window is available only when the design editor is open. Select the Design tab at the bottom of the window.

Figure 4. Selecting the font from the Properties window
The Android Studio layout preview, shown in the rightmost pane of Figure 5, allows you to preview the font set in the TextView .
Figure 5. Previewing fonts in layout preview
Adding fonts to style
Open the styles.xml , and set the fontFamily attribute to the font file you want to access.
Using fonts programmatically
To retrieve fonts programmatically, call the getFont(int) method and provide the resource identifier of the font you want to retrieve. This method returns a Typeface object. Although the system picks the best style for you from the fonts information, you can use the setTypeface(android.graphics.Typeface, int) method to set the typeface with specific styles.
Note: The TextView already does this for you.
Kotlin
Using the support library
The Support Library 26.0 provides support to the Fonts in XML feature on devices running Android 4.1 (API level 16) and higher.
Note: When you declare font families in XML layout through the support library, use the app namespace to ensure your fonts load.
To retrieve fonts programmatically, call the ResourceCompat.getFont(Context, int) method and provide an instance of Context and the resource identifier.
Kotlin
Content and code samples on this page are subject to the licenses described in the Content License. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Источник
Совет: Работаем со своими шрифтами в Android O
Russian (Pусский) translation by Ellen Nelson (you can also view the original English article)
А вот и первая предварительная версия Android O!
В этой серии мы рассмотрим некоторые из современных функций пользовательского интерфейса, с которыми вы можете начать экспериментировать сегодня, в версии Android O для предварительного ознакомления разработчиками.
В первом совете я показал вам, как настроить свою разработку для поддержки этого раннего предварительного просмотра O, и как создать текст, который автоматически масштабируется в соответствии с текущей конфигурацией экрана. В этом совете мы увидим, как Android O сделает работу с пользовательскими шрифтами беззаботной.
Добавление ваших шрифтов в проект
Вы когда-нибудь хотели выделить отдельный фрагмент текста? Или, может быть, вы были убеждены, что ваш шрифт станет отличным способом добавить в ваше приложение дополнительную индивидуальность?
Хотя есть много преимуществ при использовании пользовательских шрифтов, работа с ними на Android традиционно была болезненным опытом, требуя, чтобы вы либо использовали библиотеку, либо создали пользовательский View .
К счастью, работа с пользовательскими шрифтами в Android будет намного проще, так как пользовательские шрифты станут полностью поддерживаемым типом ресурсов в Android O. Это означает, что добавление пользовательского шрифта в ваше приложение будет таким же простым, как добавление любого другого ресурса, например изображения и текста.
Чтобы следовать этому руководству, вам понадобятся несколько файлов шрифтов, которые вы можете добавить в проект с Android O, который мы создали в первой части.
Android O поддерживает оба формата: .otf (OpenType) и .ttf (TrueType). Существует множество веб-сайтов, предлагающих такие шрифты бесплатно, поэтому потратьте несколько минут на поиск в Google, пока не найдете нужный шрифт.
Поскольку мы просто экспериментируем с новыми функциями Android O, не имеет особого значения, какой шрифт вы используете, но если вы ищете шрифты для использования в релизах вашего приложения, вы всегда должны смотреть условия использования этого шрифта. Только потому, что файл доступен для загрузки, не означает автоматически, что нет ограничений на то, как вы можете использовать и обращаться с этим файлом, поэтому всегда читайте мелкий текст!
Вы также должны задуматься о цели, содержании и целевой аудитории вашего приложения, так как разные шрифты передают разные сообщения. Если вы разрабатываете приложение, помогающее людям заполнять их налоговые декларации, то ваша аудитория с трудом сможет серьезно отнестись к финансовым и юридическим советам в вашем приложении, если оно поставляется со непонятным и странным шрифтом!
Как только вы найдете шрифт, с которым хотите работать, загрузите и разархивируйте его. На этом этапе вы должны проверить имя файла шрифта на наличие недопустимых символов — по сути это, что угодно, что не входит в строчные a-z, 0-9 или символ подчеркивания. Попробуйте использовать любые другие символы и Android Studio выдаст ошибку, как только вы попытаетесь сослаться на этот ресурс.
Так как у вас есть файл(ы) шрифтов, вам надо будет где-то их хранить:
- Правый клик по папке app/res вашего проекта и выберите New > Android resource directory.
- Откройте выпадающее меню и выберите font.
- Введите font в File name.
- Нажмите OK.
- Убедитесь, что вы добавили все файлы шрифта в папку res/font вашего проекта.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по папке res/font вашего проекта и выберите New > Font resource file.
- Дайте этому файлу имя и нажмите OK.
- Откройте этот XML-файл и определите все различные версии этого шрифта, а также их атрибуты стиля и веса, например:
Переместите файлы вашего шрифта в новую папку res/font.
Использование своих шрифтов
Вы можете применить свой шрифт к тексту, используя новый XML атрибут android:fontFamily :

Вы можете добавить пользовательский шрифт к любым стилям, которые вы создали в приложении.
Если вы хотите использовать свой шрифт программно, когда вы можете извлечь ваш шрифт используя метод getFont(int) , например:
Создание семейства шрифта
Иногда при распаковке папки со шрифтом вы можете обнаружить несколько версий одного и того же шрифта, например, курсивную версию, или шрифты с различной толщиной.
Если вы используете несколько версий одного и того же шрифта, вы можете сгруппировать их вместе в семейство шрифтов. Семейство шрифтов по существу является отдельным XML-файлом, в котором вы определяете каждую версию шрифта со всеми связанными с ним атрибутами стиля и веса.
Чтобы создать семейство шрифтов:
Затем вы можете ссылаться на любой из шрифтов в этом семействе, используя атрибут android:fontFamily . Например:
Не забудьте протестировать!
В то время, как легко увлечься новыми функциями, не заходите за рамки пользовательских шрифтов! Согласованные UI легче в навигации и понимании, а если ваше приложение постоянно переключается между шрифтами, тогда ваши пользователи скорее обратят больше внимание на то, как выглядит ваш текст, а не на то, что о чем он говорит.
Если вы добавляете пользовательские шрифты в свой проект, важно проверить, как этот шрифт отображается в широком диапазоне различных конфигураций экрана, поскольку вашим главным приоритетом всегда должна быть удобочитаемость текста.
Заключение
В этом совете я показала вам, как создать более стильный и уникальный текст, добавив пользовательские шрифты в свои проекты. В заключительном посте этой серии мы переведём наш фокус с текста на изображения, так как я покажу вам, как создавать адаптивные значки запуска, которые автоматически адаптируют свою форму в соответствии с текущим устройством.
В то же время ознакомьтесь с некоторыми из наших других руководств по разработке приложений для Android!
Источник