- Detecting Root on Android
- What is root/rooted?
- Why root your device?
- Why is a rooted device potentially dangerous to users/apps?
- Enter the tasty root checking library — RootBeer!
- How Rootbeer works
- Java based checks
- Ndk checks
- Call for more root checks
- Closing thoughts and Disclaimers
- How to Check if Your Android Phone is Rooted
- What is Rooting?
- Check through Settings
- Use the Root Checker App
- Use the Terminal Emulator
- Advantages of a Rooted Android Phone
- More Control
- More Customization Options
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I unroot an Android device?
- Can I see if my phone is rooted without an app?
- Don’t Go too Crazy over Root Access
- Is My Phone Rooted? 7 Effective Methods to Check if Your Device is Rooted
- Section 1. What Is Rooting & Why Is My Phone Rooted?
- What Is Rooting?
- Why Root Your Phone?
- Section 2. Is My Phone Rooted? 7 Ways to Check It
- Way 1: Check Root Status through Settings
- Way 2: Find if There Is a Kinguser or SuperSU Icon
- Way 3: Use a «Systemless Root» Method
- Way 4: Use a Root Checker Application
- Way 5: Install a Terminal Emulator
- Way 6: Install ADB Tools
- Way 7: Check If Phone Is Rooted with Doctor for Android
- Section 3. How to Recover Lost Android Data after Rooting?
- FAQs for Android Rooting
- Concluding Remarks
Detecting Root on Android
Mar 13, 2016 · 5 min read
We’ve recently open sourced a new Android library called rootbeer to detect if your app is running on a rooted device. But what is root? and why is potentially dangerous? Read on for more details.
What is root/rooted?
When we talk about rooting a Android device, it’s really just talking about circumventing a system security to allow us to elevate our permissions to be the root user. Think of it as accessing the devi
ce’s administrative permissio n s. The root user can do ‘anything’ on the device so many of the built-in security services can be circumvented. If you’re sensible and have a grasp of the dangers, rooting doesn’t have to be a big security risk. It reminds me of one of our favourite quotes:
“With great power comes great responsibility” — Uncle Ben Parker
Why root your device?
Users tend to root their device for a number of reasons — but a great level of control and customisation is typically the main driver. For example removing preinstalled bloatware, enabling full system backup with apps such as TitaniumBackup, blocking advertisements/banners in all apps, tweaking system UI beyond that supported in Android or in order to flash a custom rom such as Cyanogenmod.
Why is a rooted device potentially dangerous to users/apps?
In a nutshell when an Android device is rooted the system security and safeguards cannot be guaranteed. One of cornerstones of Android security is that each app is assigned a unique user id (or uid) on installation. This is how the system controls and enforces read/write access to each app’s private data folder (or sandbox). With a rooted device a user or malicious program can elevate their permissions to root and circumvent this protection giving them access to other app’s private data. For example, you might grant an application root access for a legitimate reason, such as listing the wifi passwords stored on your device. However you cannot be certain this app isn’t also accessing all of your device filesystem (including any private info) and sending it to their servers.
At Intohand we believe that verifying the integrity of the device is an important part of app hardening and checking if the device is rooted is one of those verifications. But how do we check if the device is rooted?
Enter the tasty root checking library — RootBeer!
Detecting root is a question often raised when I’ve spoken at conferences about Android Security. The Rootbeer library was born out of a conversation between Mat Rollings and myself about how the rootcloak apps work and whether we could write a root checker to beat some of the popular cloakers. We wanted to create a simple to use Android library that other developers could easily integrate and use to check the device for indications of root. Head over to the project’s github page to see the code. As you’ll see from the readme it’s very simple to use.
We’ve also allowed direct access to each of the checks that make up the final `isRooted` decision to allow developers to customise the level of verification performed.
How Rootbeer works
Rootbeer is a culmination of our own checks and those found on stackoverflow and other? forums brought together into a single easy to use library. More info on contributions can be found in the Rootbeer ReadMe. We recommend thinking of these checks as more of an indication of root rather than foolproof evidence the device is rooted (more on this in the closing thoughts).
Java based checks
- CheckRootManagementApps*, CheckPotentiallyDangerousApps* and CheckRootCloakingApps* — Using the PackageManager we look for installed apps that are typically used for managing superuser/root access, known patching apps and/or apps that specifically try to hide root status. Typically Rootcloaking apps will block some of the other tests, however we can still check if the Rootcloaking is installed.
- CheckTestKeys — Typically the platform system image is signed with production keys, if it’s not this could be a sign of being compromised. This check looks at the Build properties (specifically android.os.Build. TAGS) for test keys.
- checkForDangerousProps — This method looks up several system properties that can only been changed when the device is rooted. If the values don’t match an unrooted device it’ll flag as rooted.
- checkForBusyBoxBinary, checkForSuBinary* — su (super user) and Busybox binaries are often present on rooted devices to perform some of the privilege escalation and utility functions. Using file search look we search of presences of these in various which if found in the Android file system could indicate the device is rooted.
- checkSuExists* — slightly different file system check for the su binary.
- checkForRWPaths — The final java check is to interrogate the file system on the device and look for system folders that should be read only but have read/write permissions.
*The static paths and the package names that rootbeer looks for are defined in a single file. This can be easily edited if you were to fork the github project and there is a future enhancement to allow users of the rootbeer library to add their own packages/paths to root checks. This file would be an ideal candidate to use DexGuard’s String/Class encryption in an attempt to hide these definitions from would-be attackers.
Ndk checks
Native checks tend to be harder for an attacker to intercept and hide against therefore we added a single native/NDK check for the su binary.
Call for more root checks
Do you have any other ways to check for root? we’d be very keen on adding them to the library and giving full credit. Please send us a pull request.
Several commercial Obfuscation/protection tools include root checks such as Arxan’s GuardIT and Guard Square’s DexGuard.
Closing thoughts and Disclaimers
Given system security is more at risk on rooted devices it’s certainly worth verifying this in your apps. However we want to be clear that the Rootbeer library is by no means perfect: it only gives a likely indication of root. What you do with that information is up to you. As mentioned above no root detection code can ever been 100% effective as when the user is root they are basically god on the device.
It’s also worth noting that rooting your device can void warranty and in some cases brick your device.
That’s it, enjoy Rootbeer and we’re interested in your feedback and improvements via github.
Thanks to Mat Rollings for co-authoring this article and rootbeer and Elliot Long for proofing the article.
Источник
How to Check if Your Android Phone is Rooted
A lot of people want to root Android smartphones so that they can install various third-party apps or overcome certain system limitations, usually put in place by hardware manufacturers and carriers.
While some phones may come rooted, the majority of them do not. There are a few simple and free ways to check if you have a rooted phone. In this article you’ll find three methods, two of them foolproof, and one that may be situational, depending on the model of your phone.
What is Rooting?
Not to be confused with jailbreaking (on iOS devices), is a method of unlocking an Android device in order to grant the user privileged control, or root access. It’s a lot like having administrator privileges on a Windows or Linux-based OS.
Check through Settings
Note that this method may not work on all Android phones.
- Go to ‘Settings.’
- Locate and tap ‘About Phone.’
- Go to ‘Status.’
- Check the ‘Device Status.’
Most new smartphones should have an Official device status. Official means that the software has not been tampered with and the device is not rooted.
Seeing a Custom tag under device status usually means that your phone is rooted.
The device status tab may be different from one model to another. Therefore, if you do see an Official tag it’s usually best to check the manufacturer’s website and see if the phone comes rooted or not.
Use the Root Checker App
The Root Checker app is a third-party app that you can download for free off Google Play, or pay for a fancier Pro version. Whichever version you choose, you should be able to determine the root access status on your phone.
- Go to Play Store.
- Tap on the search bar.
- Type “root checker.”
- Tap on the simple result (free) or the root checker pro if you want to pay for the app.
- Tap install and then accept to download and install the app.
- Go to Settings.
- Select Apps.
- Locate and open Root Checker.
- Tap on the “Get Started” button.
- Tap on “Verify Root” once the app has determined the model of your phone.
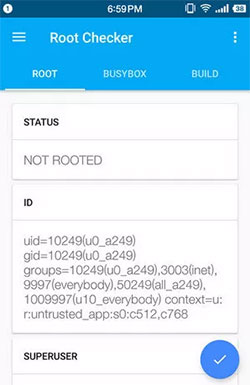
It should only take a few moments for the app to determine the root access status of your phone. Once it knows, a message will be displayed, clearly stating if you have or don’t have root access.
Use the Terminal Emulator
The Terminal Emulator app has been designed to give users a complete Linux terminal emulator on Android devices.
It’s a good way to practice using commands, or to make full use of various commands enabled on rooted phones.
- Go to Play Store.
- Tap the search bar and type “Terminal Emulator”
- Tap Install and Agree.
- Go to Settings and find the Terminal Emulator app.
- Tap the icon to open the app.
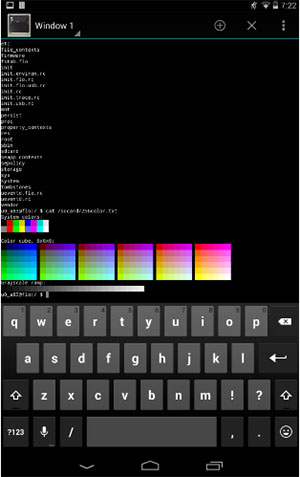
- In the terminal window type “su” and then tap either Search or Enter.
The “su” is the super-user command line. If your phone is rooted, you should be able to see the $ turn into an # in the command line. If not, or if you receive an error with “command not found”, it means that your phone is not rooted.
Note that neither the Terminal Emulator nor the Root Checker apps can root an Android device. There are other third-party apps that let you do that.
Advantages of a Rooted Android Phone
There are some dangers involved with rooting an Android phone. Mostly because when users start to poke and prod through various functions of the phone, it’s possible to cause a complete system malfunction or in other words, you could brick your phone if you don’t know what you’re doing.
This usually happens when users try to squeeze too much performance out of their phones, pushing the components past their limitations, or when installing new firmware that may not be fully supported.
That said, there are some considerable benefits too when it comes to having a rooted phone. If you don’t mess with the essential system processes, there’s a lot you can do to customize and improve the performance of the phone from other areas.
More Control
Imagine a rooted Android phone as a desktop PC. You can pretty much configure a desktop however you want, as long as all the components are compatible. Rooting can even give you access to overclocking or underclocking the phone’s CPU and GPU components. You can beef up the performance or tone it down so that your phone will age slower.
More advantages include full application control. This means being able to backup, restore, remove, and add everything you want, including editing applications in batches.
You can also remove certain unwanted and unnecessary system processes that come pre-installed. These are commonly referred to as bloatware. These types of processes are similar to Windows system processes and pre-installed apps that eat up a large chunk of resources without offering anything of value to the user.
More Customization Options
One of the coolest things about having a rooted phone is the level of customization you can get regarding everything from themes to animations and everything else in between, including icons.
Most smartphones come with limited personalization options. For example, you can’t change your loading screen animations on unrooted phones.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I unroot an Android device?
Absolutely! If you need to perform a system update you’ll need to unroot your device first. Fortunately, it isn’t too difficult. If you want to unroot your device, check out this article.
Can I see if my phone is rooted without an app?
Yes. You can go through the settings as shown above, or you can search the app drawer for a rooting app. These apps are necessary to root the phone in the first place.
Open the app drawer on the Android device and use the search bar to look for ‘SuperSu’ ‘Dr. Fone’ or another rooting app.
Don’t Go too Crazy over Root Access
While it is cool to have a rooted smartphone on which you can theoretically do whatever you want, compared to regular users, it’s best to exercise caution or at least inform yourself of what you should and shouldn’t change.
If you have some tips on how to improve performance by taking advantage of root access, please leave a comment in the comments section below, and don’t forget to specify which model Android smartphone those tips are for.
Источник
Is My Phone Rooted? 7 Effective Methods to Check if Your Device is Rooted
— «Is my phone rootable?»
— «Why is my phone rooted?»
— «How to know if your phone/device is rooted?»
You may want to break out of the constraints of Android OS to gain more permissions. For instance, you’re to install an app from Google Play, but it doesn’t work out as it should. So, a question — is my phone rooted — may come into your mind? Well, since some phones come rooted, some folks care about how to check if your phone is rooted.
As is known to all, most Android smartphones are rootable. However, there might be some risks in doing so. Be that as it may, it’s still a concern to check whether your phone has been rooted and how to do it, if not.
OK, here are seven simple ways to check your Android root status. And they might be situational, depending on your phone models. On top of that, we will share with you more about rooting as well.
Section 1. What Is Rooting & Why Is My Phone Rooted?
You’ve probably heard of people using some Android rooting tools to root their phones. And they thus get more access and fun from the «new phone». So, what is rooting, and why do people root their Android devices? Now, let’s figure them out.
What Is Rooting?
Like jailbreaking on iOS devices, rooting is done on Android devices, granting the users privileged control or root access. That is, it gives you the freedom to bypass Android internal protections and obtain superlative control over the operating system.
Why Root Your Phone?
- Utilize more dominant and powerful applications.
- Change certain settings.
- Level up your battery life.
- Play more exciting games.
- Uninstall useless apps that come with your phone.
- Dispose of maker’s Android UI.
- Extend the usefulness of your device.
- Benefit from the added performance.
Next, how can you tell if your phone is/has been rooted? Indeed, there are at least seven methods to deal with it. And we will talk about them in the following.
You May Also Like:
Section 2. Is My Phone Rooted? 7 Ways to Check It
Way 1: Check Root Status through Settings
Is my phone/tablet rooted or unrooted? The easiest way is to check the root status from the Settings app. Here are the steps:
- Go to your phone’s Settings.
- Locate and tap «About Phone».
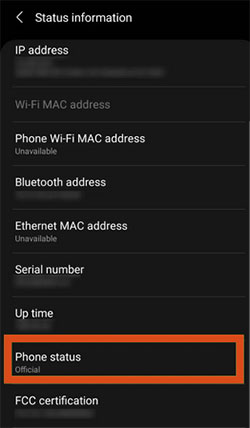
- Go to «Status information».
- Check the «Phone Status».
If it is «Official», it suggests that your software hasn’t been tampered with, and your phone is not rooted.
Seeing a Custom tag under the phone status means your device is rooted.
Way 2: Find if There Is a Kinguser or SuperSU Icon
After checking the root status, you may not be sure whether your Android device is rooted or not. You can get into your device and find if it has installed the Kinguser or Superuser app. These two apps can be used to control your root access. In most cases, they will be installed on your device after rooting.
How did my phone get rooted? Here’s a complete guide on how to root Android phones. Check the link if necessary.
Way 3: Use a «Systemless Root» Method
You can do the «systemless root» with Magisk. One of the most significant features of this tool is that the modifications are saved safely in the boot partition other than modifying the real system files. As the original system files keep unchanged, modifications can go unnoticed by Google SafetyNet.
After everything is done by this tool without an error, you have rooted for all intents and purposes.
Way 4: Use a Root Checker Application
How do I know if my phone is rooted or unrooted? A root checker for Android like Root Checker, SU Root Checker, or Am I Rooted may help. Here, let’s take the Root Checker as an example to explain how to check the status with it:
- Open Google Play, search Root Checker.
- Download and install it on your phone.
- Open the installed Root Checker, tap «ROOT».
- Touch the screen start to check if your phone is rooted or not. It may take you tens of seconds.
Tips: Some root tools might lead to data loss on your phone. Thus, you can back up your Android device without rooting to secure your stuff.
Way 5: Install a Terminal Emulator
How to tell if your Android device is rooted? A Terminal Emulator is another great option to pick. This app gives its users a complete Linux terminal emulator for Android devices.
- Go to Play Store.
- Tap the search bar and then «Terminal Emulator».
- Tap Install > Agree.
- Go to Settings and find the Terminal Emulator app.
- Open the app.
- In the terminal window, type in «su» and tap either Search or Enter.
The «su» is the super-user command line. If your Android phone is rooted, you will see the «$» turn into «#» in the command line. Otherwise, your phone isn’t rooted.
See Also:
Way 6: Install ADB Tools
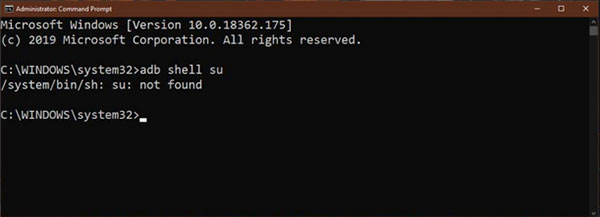
To fix how to check/know if my phone/device is rooted from a PC, you can turn to the Command Prompt. You should have ADB tools and drivers for the Android device installed on your PC. Besides, it’s also necessary to enable USB debugging on your Android device. Subsequently, follow the instruction to check Android root status:
- Make sure your device is powered on.
- Connect Android to your PC via a USB cable.
- Open Command Prompt with admin rights.
- Run the command: adb shell su
- The command will take you to the root status of the connected device.
Way 7: Check If Phone Is Rooted with Doctor for Android
This ultimate way is to use MobiKin Doctor for Android (Win and Mac). This utility can not only help you check if your Android phone has been rooted but gives you an option to securely recover any lost data before/after rooting. Before you know how to check Android root status, let’s get a basic idea of what it is.
Key highlights of MobiKin Doctor for Android:
- Check if an Android phone is rooted easily.
- A dedicated tool to recover data from Android internal memory or SD card.
- Make Android data recovery without root or with root.
- Work for data like contacts, messages, call records, photos, videos, music, documents, and more.
- Let you preview and select the items before recovery.
- Run smoothly on 8000+ Android devices, covering Samsung Galaxy, Huawei, LG, HTC, Motorola, Xiaomi, Sony, Google, Asus, DELL, OPPO, Vivo, etc.
- It won’t give away your privacy.

How to see if your phone is rooted with Doctor for Android?
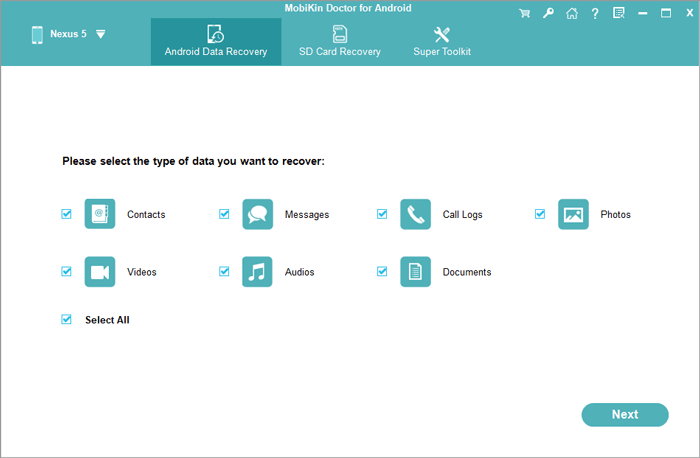
Step 1. Connect Android to a computer via a USB cable. Install and run the tool on the computer. Enable USB debugging on Android to have it recognized by the tool. Afterward, check all the data types and click Next.
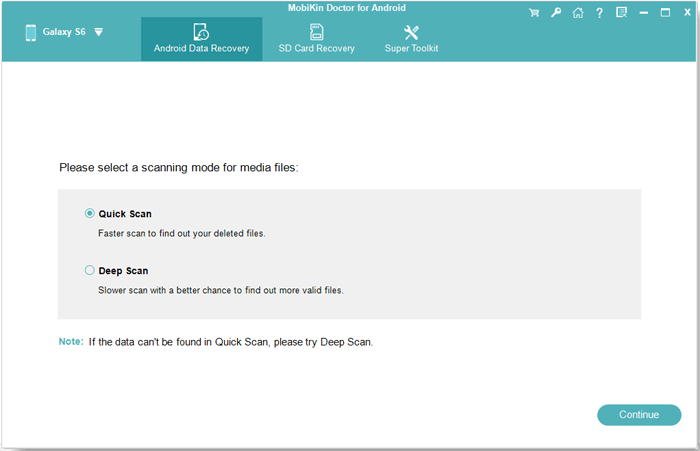
Step 2. Follow the screen prompts to select a scanning mode and then click on «Continue».
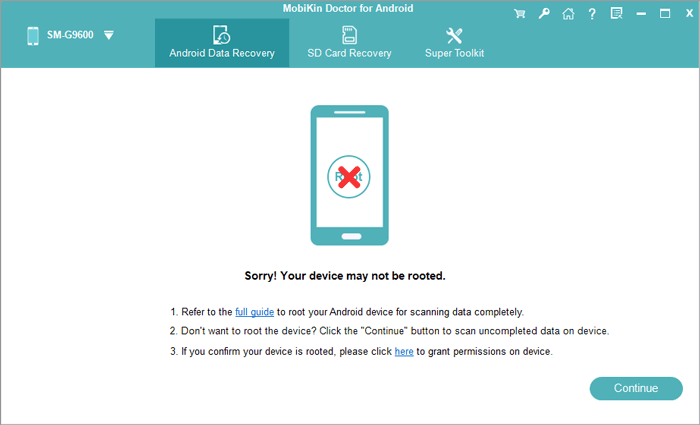
Step 3. If the program shows you an interface as below, it means your device is not rooted. Here, you can tap the «full guide» to root your phone as required.
Section 3. How to Recover Lost Android Data after Rooting?
As we described in the previous section, MobiKin Doctor for Android can help you check if your Android phone is rooted. After rooting your device, you might lose your precious data on it, or you even lost some files before the root. This professional Android data recovery program is right here to let you retrieve all your lost content in simple clicks.
How to retrieve lost/deleted Android data after rooting?
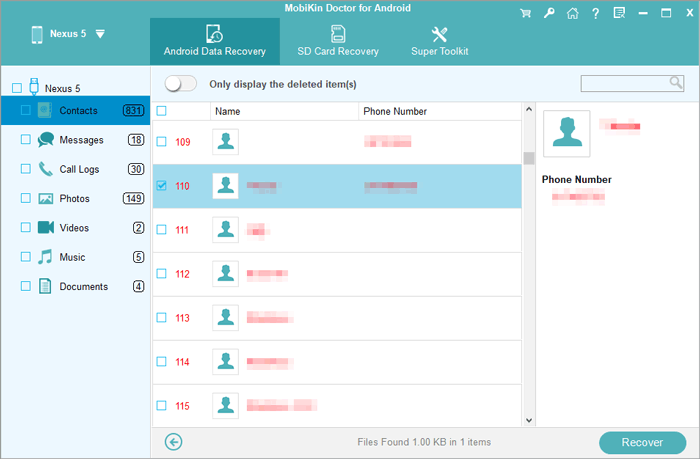
- Follow the drill above to allow the program to run a scan on your device.
- After you get the screen as below, preview and select whatever you want to restore from your device.
FAQs for Android Rooting
1. Is Rooting Android Phone a Security Risk?
Honestly, here are some of the risks your Android phone could face after it is rooted:
- Your phone warranty turns void.
- It may be hard to install official updates.
- You might brick your device simply trying to root it.
- ROMs like Lineage might be difficult to install.
- Malware can easily breach your mobile security.
2. What to Do If My Phone Isn’t Rooted?
Has my phone been rooted? If the answer is no, what can I do to accomplish the job? Well, you know, Android rooting is the key to an unlimited Android experience. On the off chance that your phone is not rooted, do remember to reach out to root specialists for yourself.
3. Can I Unroot an Android Device?
Yeah, definitely! If you’d like to run a system update, unrooting your device could be the first to do. For more, check out the page: how to remove root from Android.
Concluding Remarks
We learned how to see/tell if the phone is rooted, from which we can arrive at the following review:
- Neither the Terminal Emulator nor the Root Checker apps can root any Android device.
- To gain more customization options and control over your device, you can root your Android phone after making a secure backup.
- You can use MobiKin Doctor for Android to check Android root status and recover your lost data as well.
- Don’t go crazy over root access if you are enthralled only by its merits.
Источник