- Работа с XML в Android
- Шаг 1.
- Шаг 2.
- Шаг 3.
- Шаг 4.
- Android Binary XML Format¶
- Decode the AndroidManifest.xml¶
- Decode any other XML file¶
- Decode information from the resources.arsc¶
- Working with AXML and Resource files from python¶
- A Complete Guide to Learn XML For Android App Development
- Basics of User Interface(UI)
- Different Types of XML Files Used in Android Studio
- Processing and Parsing XML in Android
- What is XML?
- XML elements
- XML Parsing
- Steps involved in XML parsing
- XML parsing example
- Conclusion
Работа с XML в Android
Очень часто приходится хранить информацию форм и для этого можно использовать xml файлы. В данном уроке мы это и рассмотрим, как можно работать с файлами XML.
Библиотеки Android имеют набор классов для работы с XML-документами с произвольной структурой и содержанием.
Шаг 1.
Для того чтобы упаковать статический XML файл вместе с вашим приложением, вам нужно поместить его в папку: res/xml/
В каталоге res/ создайте подкаталог xml/ в котором будет располагаться наш ХМL-файл.
После чего вы получите возможность обращаться в коде программы к этому документу.
Шаг 2.
Рассмотрим загрузку XML-документа произвольной структуры из ресурсов в код программы.
Создадим приложения, которое будет уметь способность читать список имен, фамилий и телефонов, определенных в XML-файле.
Теперь создадим XML файл который будет хранить Имена, Фамилии и номера телефонов сотрудников фирмы и сохраним его в res/xml/ под именем contacts.xml.
Вот как будут выглядеть XML файл contacts.xml
Шаг 3.
Создадим View состоять она будет с LinearLayout и ListView и назовем main.xml:
Шаг 4.
Загружаем файл contacts.xml, созданный ранее:
Метод getXml() возвращает XmlPullParser, используя который можно прочитать загруженный XML-документ в цикле while:
В конечном итоге ваше приложение должно выглядеть так:

Обратите внимание что наследуется MyActivity не от Activity а от ListActivity.
Источник
Android Binary XML Format¶
Android uses a special format to save XML and resource files. Also resource files are XML files in the source folder, but all resources are packed into a single resource file called resources.arsc . The underlying format is chunk based and is capable for storing several different information.
The most common AXML file is the AndroidManifest.xml . This file must be part of every APK, and contains the meta-information about the package.
Androguard is capable of decoding such files and two different tools exists for decoding:
androguard arsc for decoding resources.arsc .
androguard axml for decoding AndroidManifest.xml and all other XML files
Decode the AndroidManifest.xml¶
Let’s use one of the example files provided by androguard. To decode the AndroidManifest.xml of an APK file, simply give androguard axml the APK file as an argument:
The output will look like this:
You can check with the original, uncompiled, XML file, which can be found here:
The original file will print:
Note, that the overall structure is equal but there are certain differences.
Resource labels are hex numbers in the decompiled version but strings in the original one
Newlines and whitespaces are different.
Due to the compilation, this information is lost. But it does not matter, as the structure of the Manifest does not matter. To get some information about the resource IDs, we need information from the resources.arsc .
To retrive information about a single ID, simply run the following:
You can see, that the ID 7F040001 was successfully resolved to the same string from the source file. To understand how Android handles resource configurations, you should read HandlingResources.
Decode any other XML file¶
Also layout files or other XML files provided with the APK are compiled. To decompile them, just give the path inside the APK as an argument, or specify the binary XML file directly:
Decode information from the resources.arsc¶
To get XML resource files out of the binary resources.arsc , use androguard arsc .
For example, get all string resources of an APK:
will give the following output:
You can also list all resource types:
Working with AXML and Resource files from python¶
To load an AXML file, for example the AndroidManifest.xml , use the AXMLPrinter :
In order to use resources, you need the ARSCParser :
© Copyright 2012-2018, Anthony Desnos, Geoffroy Gueguen, Sebastian Bachmann Revision eef97351 .
Источник
A Complete Guide to Learn XML For Android App Development
XML stands for Extensible Markup Language. XML is a markup language much like HTML used to describe data. It is derived from Standard Generalized Markup Language(SMGL). Basically, the XML tags are not predefined in XML. We need to implement and define the tags in XML. XML tags define the data and used to store and organize data. It’s easily scalable and simple to develop. In Android, the XML is used to implement UI-related data, and it’s a lightweight markup language that doesn’t make layout heavy. XML only contains tags, while implementing they need to be just invoked.
The simple syntax of XML is
So in this article, there is a deep discussion on how to learn and understand what XML is for Android Development.
Basics of User Interface(UI)
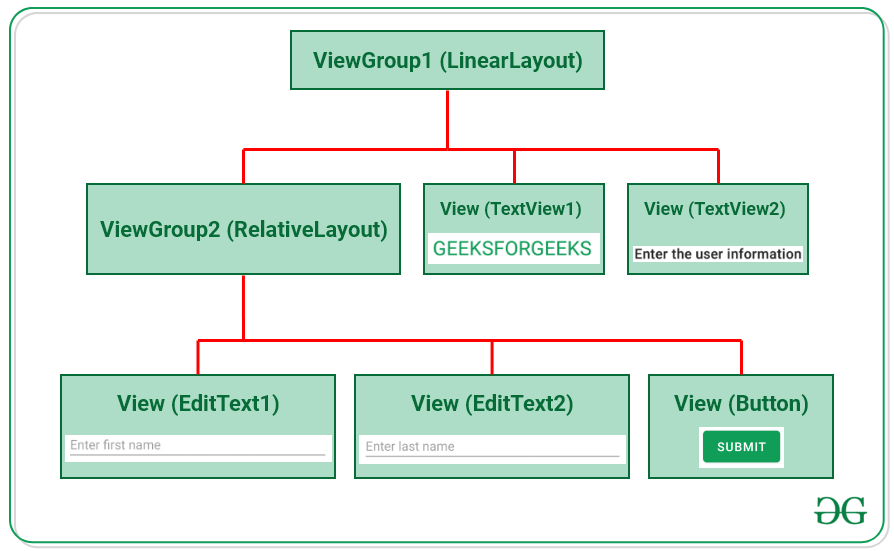
Basically in Android XML is used to implement the UI-related data. So understanding the core part of the UI interface with respect to XML is important. The User Interface for an Android App is built as the hierarchy of main layouts, widgets. The layouts are ViewGroup objects or containers that control how the child view should be positioned on the screen. Widgets here are view objects, such as Buttons and text boxes. Considering the following simple example of the activity_main.xml file.
Output UI:
In the above example of XML file, There are 2 view groups one is LinearLayout and another is RelativeLayout and the TextView1 and TextView2 is child widgets under the ViewGroup1 that is LinearLayout. EditText1, EditText2, and Button are the child widgets under ViewGroup2 that is RelativeLayout. ViewGroup2(RelativeLayout) is nested under the ViewGroup1 which produces the following hierarchy.
From the hierarchy, it’s been observed that every widget like EdtText, TextView, or Button is one of the View. These Views are contained inside the ViewGroup, like RelativeLayout, LinearLayout, FrameLayout, etc.
Different Types of XML Files Used in Android Studio
Different XML files serve different purposes in Android Studio. The list of various XML files in Android Studio with their purposes is discussed below.
1. Layout XML files in android
The Layout XML files are responsible for the actual User Interface of the application. It holds all the widgets or views like Buttons, TextViews, EditTexts, etc. which are defined under the ViewGroups. The Location of the layout files in Android is:
app -> src -> main -> res -> layout
Источник
Processing and Parsing XML in Android
Sharing data over the internet is very popular. We share our information with the other users over the internet. Let’s take a very common example, since we all are developers and to be more precise, we all are Android Developers and we all must have visited the StackOverflow website whenever we are stuck into some problem in our projects and in every 99 out of 100 cases, we find the solution to our problem. The answer that we get from the StackOverflow website consists of various parts that we are less bothered about. In general, the answers or the questions present on the website contains the id of the question, type of the question, author name of the article or question, publishing data, URL and many other things are there on the website. But we want only meaningful data i.e. we want answers and the authors and nothing else.
The problem arises when you want to access the data of a particular website in your Android Application. This is because the data present on the websites are in JSON format or in XML format. So, in order to use that data or to extract the meaningful information from that data, you have to parse that XML file or a JSON file.
So, in this blog, we will learn how to process and parse the XML data in Android. So, let’s get started.
What is XML?
XML stands for Extensible Markup Language. It is a set of rules that are used to encode data or documents in a Machine-readable language. There are many websites that use an XML format to share data on the internet. For example, many blogging websites use an XML format to share data between users. So, XML parsing and processing become an important task to use that data in our Android Application.
XML elements
In general, an XML file consists of a number of elements that together make an XML file. They are the basic building blocks of XML document. These elements are used to store some text elements, attributes, media, etc. Below is the syntax of XML element:
Here, element-name is the name of the element and attributes are used to define the property of XML element. Following is an example of an XML document that is used to describe the data of the student:
We can broadly divide the XML elements in four parts:
- Prolog: It is the first line that contains the information about the XML file i.e. it is the first line of the XML file.
- Events: An XML file contains a number of events like document start, document end, Tag start, Tag end, etc.
- Text: In between the tags(opening and closing), there can be some text. For example, in the above example, “John” is the text.
- Attributes: These are the properties of XML elements.
XML Parsing
So, we have seen the introduction of XML and our next task is, How to parse the XML in Android? So, let’s find out.In Android, there are various parsers that can be used to parse the XML file in Android. Some of these are:
- XMLPullParser
- DOM Parser
- SAX Parser
Among these three parsers, XMLPullParser is the most commonly and most widely used parsers in Android. This is because XMLPullParser is very efficient and easy to use. Also, unlike the DOM Parser which loads the whole file in the memory and then parses it, the XMLPullParser consumes less memory.
Steps involved in XML parsing
Following are the steps that are involved in XML parsing:
- Analyze the feed: There are many cases when you will be provided with a number of data but you need only few of them. SO, before parsing the XML, your first step should be to find the desired element in the XML data. For example, here is example of XML file of StackOverflow:
Here, if you want to extract the data present in the entry tag and the data of its sub tags then you should keep note of these things.
- Create XMLPullParser object: Our next step is to create the object of XMLPullParser and specify the file name for the XMLPullParser that contains XML. You can use a file or a stream. Following is the code to create an object of the XMLPullParser and then passing the file name for the XMLPullParser:
- Read the desired data: Our last step is to parse the data of the XML file. The following readFeed() function is used to parse the XML file and extract only the values of entries and store it into a list:
Here, XMLPullParser.END_TAG is used to find if the parser has reached to the last tag of the file or not. If it has reached then return and it has not reached then we will check for the entry tag and if found then will add the value to the entries list. If the values are not found be to of entries type then we can skip the parser. At last, we return entries.
Following are the methods that can be used while parsing an XML file:
- getEventType(): This method is used to get the event type. For example, Document start, Document End, Tag start, Tag end, etc.
- getName(): This is used to get the tag name in a file. For example, in the above code, the tag name is entry.
- getAttributeValue(): This method is used to get the attribute value of a particular tag.
- getAttributeCount(): It returns the total number of attributes of the current tag.
- getAttributeName(int index): It returns the attribute name at a particular index.
- getColumnNumber(): It returns the current column number using a 0 based indexing.
- getName(): It returns the name of the tag.
- getText(): It returns the text present in a particular element.
XML parsing example
Now, let’s do one example to understand the concept of XML parsing ina very easy and clear manner.
Open Android Studio and create a project with Empty Activity template.
The very first step is to create the XML file. Either you create your own XML file or you can use mine. To create an XML file, go to java folder and then right click on it. Then click on New > Folder > Assets folder and then OK. One assets folder will be created for you. Now right click on that folder and create a file and name it as example.xml. Following is the XML content of example.xml file:
This is a simple example of student data containing the name, surname, mobile and section of the student. In this example, we will extract the name, surname and section of the student. We will ignore the mobile number.
Now, let’s code for the UI part of our application. Here we will display the desired data on a TextView. So, open the activity_main.xml file and add the below code:
So, we are done with the UI part. Now, let’s write the code for the XML parsing. Below is the code for the MainActivity.kt file:
Now, run the application on your mobile phone and try to add more data to your XML file i.e. the example.xml file.
Conclusion
In this blog, we learned about XML parsing in Android. We learned how to parse the data present in the XML format in Android Application. We saw how to use XMLPullParser to do XML parsing. At last, we did one example of XML parsing. You can get more contents about XML parsing at the Android Developer Website.
Источник