- The 12 Best Android Tutorials for First-Time App Developers
- Building Your First App
- Android Development – Tutorial
- Video Tutorials Series
- An Android Tutorial/Book
- Game Development Series
- Better User Interfaces with the Android Action Bar
- Learning to Parse XML Data in Your Android App
- Android 101 for iOS Developers
- Scheduling Background Tasks in Android
- Android Adventures – Getting Started With Android Studio
- Localizing Android Apps
- Getting Started with Android Library Projects
- Conclusion
- Android App Development Fundamentals for Beginners
- Android Fundamentals
The 12 Best Android Tutorials for First-Time App Developers
This article was updated in January 2017.
Learn more about the official Android IDE with our screencasts A Tour of the Official Android IDE – Android Studio screencast.
When there is so much information and you are a first-time Android developer, it’s easy to get confused about where to start. To make it easy for you and with no illusions that this list of Android tutorials is the best or complete, here are 12 Android tutorials to start with.
Not all the tutorials and their content are strictly beginner beginner focussed. Some of them start out for beginners and then delve into more advanced topics. So if you can’t follow everything in every single tutorial, don’t get desperate or frustrated.
If you encounter a hurdle, just spend more time with the tutorial, reading it a couple of times if necessary. If you are still not on friendly terms with it, there is no drama – just move forward and revisit it later.
Building Your First App
Naturally, we start the list with a tutorial from Google, the creators of Android. The вЂBuilding Your First App†tutorial starts from the very beginning and it’s suitable for absolute beginners. If you have no programming knowledge whatsoever, don’t expect to be able to handle the tutorial but if you have some programming background, it’s easy.
The tutorial has several вЂBest Practice’ sections at the end. This is good because all the important content about the topic in one place and you just have to read it.
Android Development – Tutorial
The reason this tutorial is near the top is that it’s very up-to-date (based on Android 7.0, the latest Android version as of today).
This tutorial has more topics and information than the tutorial from Google, so if you are looking for an in-depth tutorial, this is one the.
It’s not an easy or quick tutorial. If you want to get the most from it, you will need quite a lot of time to read it from start to finish. It can be a great source if you need to consult a given topic in detail.
Video Tutorials Series
I find video tutorials less useful (except when they teach design, animation, or any other visual topic) but for many people they are the preferred way of learning. If you belong to this group, you will love this series of video tutorials.
It’s a comprehensive series of video tutorials ranging from under 5 to 15 minutes in length. Similarly to the previous two tutorials, this series covers everything from absolute beginner level to advanced topics. It’s not uptodate but I couldn’t find a decent video tutorial about a more recent Android version.
An Android Tutorial/Book
It might be old-school, but for me the best way to get a complete idea about something is by reading a book about it. In a book, everything is organized logically, pages are numbered and keep their layout and there is enough text to explain the and code/graphics. The first two tutorials in this list are book-like but if you want something more authentic you could print them. Even better, a pdf tutorial, like this one, is a much better option. Similarly to the previous resource, this one might not be very up to date but it does cover the major principles of Android programming.
This is one more general tutorial that covers Android development from beginner level to advanced.
Game Development Series
If you have some knowledge about Android but you want to delve into games development, this series of video tutorials is a great start. The series starts with the very basics of Android (and Eclipse) but my personal feeling is that if you are a total stranger to Android, the journey will be too hard. Again, this tutorial isn’t about the latest Android version but it does give a solid foundation about Android programming and I couldn’t find a more current one.
From what I saw, the series mentions general Android as well, not only game development. If you don’t know Android basics, my advice is to first read some of the general Android tutorials and then move to specialized topics, such as game development.
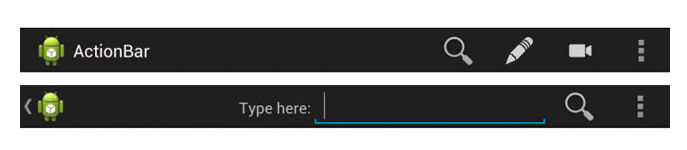
Better User Interfaces with the Android Action Bar
After you have had enough of general Android tutorials, let’s move to tutorials for common tasks. For some of these topics you can find information in the general tutorials as well but if you want more detail, this is for you. The first tutorial is about how to build Better User Interfaces with the Android Action Bar.
In this tutorial you will learn how to set up the action bar, how to add actions, how to split, hide, and overlay it, as well as how to add navigation. You will also learn about action bar interactivity, such as how to handle clicks on its items and to use action views.
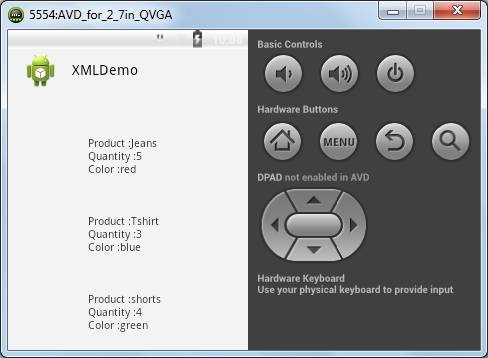
Learning to Parse XML Data in Your Android App
While you could write Android applications that do not involve any data input, often you will need external data. In such cases you need to know how to handle this data. XML can help you a lot and this is why I’ve included a tutorial on how to Parse XML Data in Your Android App.
This tutorial leads you step by step in the world of XML parsing. It also helps you create a parser that will look like the one shown in the next screenshot.
Android 101 for iOS Developers
With the huge popularity of Android, even die-hard iOS developers are likely to consider switching or at least expanding to it. If you are an iOS developer, you are lucky because you are not new to mobile development as a whole. Of course, you could read the general Android tutorials I listed earlier but especially for you, here is a better tutorial. Unfortunately, some of the info in this tutorial might be outdated but with the rapid development of mobile programming technologies this is inevitable. You might want to check a more recent tutorial on the same topic but it isn’t as detailed as the first one.
This tutorial is great because it summarizes the differences between iOS development and Android development, thus making the change easier for you. You might need separate reading on some of the points it mentions but it’s a great tutorial without being overly detailed.
Scheduling Background Tasks in Android
This topic is a bit advanced but since it’s not too difficult and it’s useful, it makes sense to include it on the list. The вЂBackground tasks in Android†tutorial discusses the types of alarms in Android and how to set them.
Android Adventures – Getting Started With Android Studio
I don’t think Android Studio is the most popular method to develop Android apps but since it (supposedly) makes Android development easier, here is a tutorial about Android Studio.
Even if you already use other Android development tools and you wouldn’t change them, it still makes sense to read what Android studio can offer.
The tutorial is a pretty detailed one – it starts with how to install Android Studio, how to create a new project, how to add functionality to it, how to run it, etc. The tutorial isn’t hard to read but if you have no prior Android knowledge, you might not be able to understand everything.
Localizing Android Apps
Android applications are popular all over the world. Your users speak different human languages, which means if you want to reach them, you need to think about localizing your Android apps. This tutorial explains it all.
Getting Started with Android Library Projects
At some point in your Android development career you will get tired of having to re-invent the wheel all the time and you will appreciate the advantages of reusable code. If you are already there, you will certainly want to know more about reusable code. In this case this tutorial will help you get started as quickly as possible.
The вЂGetting Started with Android Library Projects’ tutorial is a bit longer because it’s a three-part series. The first part warms you up with some basic concepts, while the other two delve into more detail about how and when to use Android Library Projects.
Conclusion
I can’t promise that after reading all the tutorials on this list you will become a top Android developer but they are a great start.
Most of these tutorials are for beginners but I am sure that even experienced Android developers will have something new to learn, or find better ways of doing a task they’ve been doing for ages. So, if you have a spare minute, check the tutorials, learn something new and let us know your favorite tutorials.
Learn more about the official Android IDE with our screencasts A Tour of the Official Android IDE – Android Studio screencast.
Источник
Android App Development Fundamentals for Beginners
Android is an operating system that is built basically for Mobile phones. It is based on the Linux Kernel and other open-source software and is developed by Google. It is used for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. But nowadays these are used in Android Auto cars, TV, watches, camera, etc. It has been one of the best-selling OS for smartphones. Android OS was developed by Android Inc. which Google bought in 2005. Various applications (apps) like games, music player, camera, etc. are built for these smartphones for running on Android. Google Play store features more than 3.3 million apps. The app is developed on an application known as Android Studio. These executable apps are installed through a bundle or package called APK(Android Package Kit).
Android Fundamentals
1. Android Programming Languages
In Android, basically, programming is done in two languages JAVA or C++ and XML(Extension Markup Language). Nowadays KOTLIN is also preferred. The XML file deals with the design, presentation, layouts, blueprint, etc (as a front-end) while the JAVA or KOTLIN deals with the working of buttons, variables, storing, etc (as a back-end).
2. Android Components
The App components are the building blocks of Android. Each component has its own role and life cycles i.e from launching of an app till the end. Some of these components depend upon others also. Each component has a definite purpose. The four major app components are:
- Activities
- Services
- Broadcast Receivers:
- Content Provider:
Activities: It deals with the UI and the user interactions to the screen. In other words, it is a User Interface that contains activities. These can be one or more depending upon the App. It starts when the application is launched. At least one activity is always present which is known as MainActivity. The activity is implemented through the following.
Syntax:
To know more Activities please refer to this article: Introduction to Activities in Android
Services: Services are the background actions performed by the app, these might be long-running operations like a user playing music while surfing the Internet. A service might need other sub-services so as to perform specific tasks. The main purpose of the Services is to provide non-stop working of the app without breaking any interaction with the user.
Syntax:
To know more Services please refer to this article: Services in Android with Example
Broadcast Receivers: A Broadcast is used to respond to messages from other applications or from the System. For example, when the battery of the phone is low, then the Android OS fires a Broadcasting message to launch the Battery Saver function or app, after receiving the message the appropriate action is taken by the app. Broadcast Receiver is the subclass of BroadcastReceiver class and each object is represented by Intent objects.
Syntax:
To know more Broadcast Receivers please refer to this article: Broadcast Receiver in Android With Example
Content Provider: Content Provider is used to transferring the data from one application to the others at the request of the other application. These are handled by the class ContentResolver class. This class implements a set of APIs(Application Programming Interface) that enables the other applications to perform the transactions. Any Content Provider must implement the Parent Class of ContentProvider class.
Syntax:
To know more Content Provider please refer to this article: Content Providers in Android with Example
3. Structural Layout Of Android Studio
The basic structural layout of Android Studio is given below:
The above figure represents the various structure of an app.
Manifest Folder: Android Manifest is an XML file that is the root of the project source set. It describes the essential information about the app and the Android build tools, the Android Operating System, and Google Play. It contains the permission that an app might need in order to perform a specific task. It also contains the Hardware and the Software features of the app, which determines the compatibility of an app on the Play Store. It also includes special activities like services, broadcast receiver, content providers, package name, etc.
Java Folder: The JAVA folder consists of the java files that are required to perform the background task of the app. It consists of the functionality of the buttons, calculation, storing, variables, toast(small popup message), programming function, etc. The number of these files depends upon the type of activities created.
Resource Folder: The res or Resource folder consists of the various resources that are used in the app. This consists of sub-folders like drawable, layout, mipmap, raw, and values. The drawable consists of the images. The layout consists of the XML files that define the user interface layout. These are stored in res.layout and are accessed as R.layout class. The raw consists of the Resources files like audio files or music files, etc. These are accessed through R.raw.filename. values are used to store the hardcoded strings(considered safe to store string values) values, integers, and colors. It consists of various other directories like:
- R.array :arrays.xml for resource arrays
- R.integer : integers.xml for resource integers
- R.bool : bools.xml for resource boolean
- R.color :colors.xml for color values
- R.string : strings.xml for string values
- R.dimen : dimens.xml for dimension values
- R.style : styles.xml for styles
Gradle Files: Gradle is an advanced toolkit, which is used to manage the build process, that allows defining the flexible custom build configurations. Each build configuration can define its own set of code and resources while reusing the parts common to all versions of your app. The Android plugin for Gradle works with the build toolkit to provide processes and configurable settings that are specific to building and testing Android applications. Gradle and the Android plugin run independently of Android Studio. This means that you can build your Android apps from within Android Studio. The flexibility of the Android build system enables you to perform custom build configurations without modifying your app’s core source files.
Basic Layout Can be defined in a tree structure as:
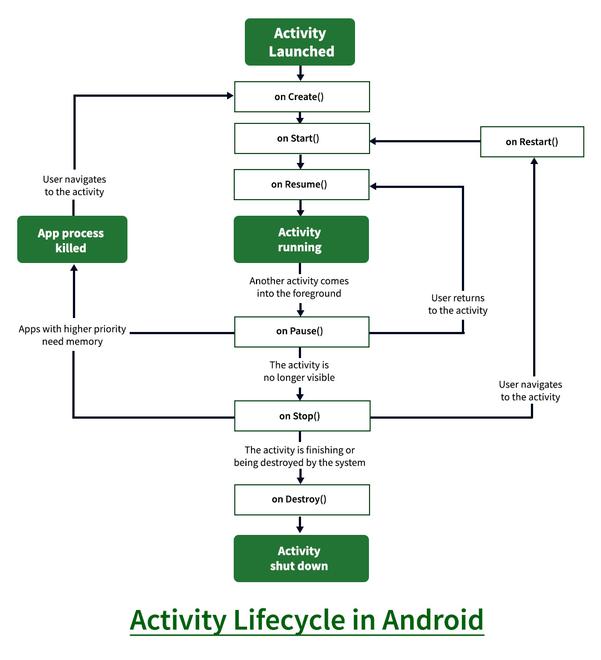
4. Lifecycle of Activity in Android App
The Lifecycle of Activity in Android App can be shown through this diagram:
States of Android Lifecycle:
- OnCreate: This is called when activity is first created.
- OnStart: This is called when the activity becomes visible to the user.
- OnResume: This is called when the activity starts to interact with the user.
- OnPause: This is called when activity is not visible to the user.
- OnStop: This is called when activity is no longer visible.
- OnRestart: This is called when activity is stopped, and restarted again.
- OnDestroy: This is called when activity is to be closed or destroyed.
To know more about Activity Lifecycle in Android Please refer to this article: Activity Lifecycle in Android with Demo App
Источник