- Bluetooth Scanner — поиск Bluetooth — сопряжение v1.1.9 APK+Mod
- Bluetooth Scanner — поиск Bluetooth — сопряжение Mod APK Последняя версия
- Как проводить сканирования Bluetooth на Android
- Сканирование стандартным методом
- Сканирование информации
- Bluetooth Scanner 1.2.1
- (Bluetooth-сканер)
- Скачать
- Create a Bluetooth Scanner With Android’s Bluetooth API
- 1. Enabling Bluetooth
- 2. Obtaining a List of Paired Devices
- 3. Discover Nearby Bluetooth Devices
- 4. Connecting to a Device
- Conclusion
Bluetooth Scanner — поиск Bluetooth — сопряжение v1.1.9 APK+Mod
- Имя файла: com.pzolee.bluetoothscanner
- Версия для загрузки приложения: 1.2.2
- Цена: 0
- Размер apk: 8.91 MB
- Скачать: 1000000
- Время последнего обновления: Dec 5, 2021
- цель: 0
- MD5:
- Подпись:
- SHA256: ROOT: —> 0 —> Предложения покупки в приложении: —> 0 —>
Готовы обнаруживать вокруг себя любые устройства Bluetooth?
Хотите знать всё о подключенных устройствах Bluetooth?
Основные функции:
— Поиск любых устройств Bluetooth, в т.ч. подключенных, сопряженных и неизвестных
— Отслеживание ваших устройств
— Сканер Bluetooth 4.0
— Подключение устройств Bluetooth (TWS-наушники, умные часы и др.)
— Поиск устройств, как с низким энергопотреблением, так и обычных, включая умные часы или браслеты, телевизоры, компьютеры и др.
— Установка и удаление сопряжения с устройствами Bluetooth
— Получение информации об уровне заряда подключенных устройств Bluetooth (только для Android 9 и выше)
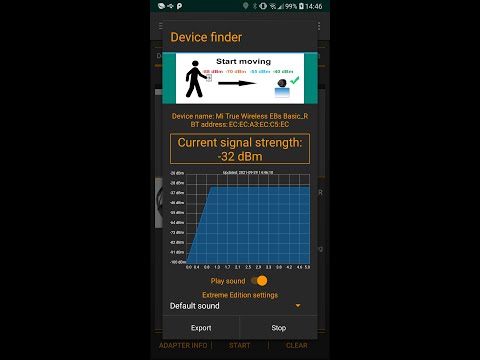
— Получение информации об уровне сигнала
— Отображение информации о кодеках (aptX, LDAC, SBC и др.), смена кодека (только для Android 9 и выше)
— Воспроизведение любого проведенного ранее сканирования, просмотр любых устройств Bluetooth в прошлом
— Настройка устройств (изменение названия и типа устройства)
— Удобные фильтры по типу устройства, названию устройства, времени
— Сортировка по уровню сигнала, адресу, названию, производителю и др.
— Выделение новых устройств вокруг вас
— Формирование графиков на основе полученных данных (распределение устройств по группам и т.п.)
— Экспорт базы данных для последующей обработки
— Функция ‘Найти устройство’
— Переключение между активными устройствами Bluetooth
— Автоматический перезапуск сканирования
Bluetooth Scanner — поиск Bluetooth — сопряжение Mod APK Последняя версия
Источник
Как проводить сканирования Bluetooth на Android
В этой статье поговорим про сканирования Bluetooth на Android. И покажем, как это сделать двумя способами, в одном из которых нашей целью будет дальнейшая работа с устройством; второй способ будет заключаться в том, чтобы отследить информацию о найденных девайсах, узнать их тип, адрес и прочее.
Сканирование стандартным методом
Данную процедуру будем выполнять стандартными функциями, встроенными в ваше мобильное устройство. Как упомянули раньше, этот метод разрешит нам выполнять действия с найденными аппаратами, то есть, ваш, например, смартфон будет взаимодействовать с другим устройством.
Для того чтобы произвести такой поиск, выполните следующие действия:
- Перейдите в настройки смартфона.
После этих действий должно отобразиться окно, в котором будет список найденных устройств. Если же в списке нет ни одного устройства, нужно вручную просканировать находящиеся вблизи вас девайсы.
На вашем дисплее должны появиться названия найденных девайсов, которые находятся поблизости со включенным Bluetooth-приемником.
Чтобы увидеть доступные действия, которые можно сделать с данными девайсами, нужно напротив их названий тапнуть по пиктограмме в виде шестеренки.
После чего должен отобразиться список с вариантами действий над выбранным гаджетом. Могут встретиться такие варианты, как:
- переименовать аппарат;
- подключиться;
- изменить доступ к подключению;
- использовать девайс в качестве беспроводного модема;
- использовать в качестве гарнитуры;
- использовать для звука мультимедиа и т.д.
Сканирование информации
Этот метод стоит использовать для вычисления данных об неизвестном устройстве, находящимся рядом с вами. А именно: узнать тип девайса, адрес и даже местоположение относительно вас.
Для данной цели существует много сторонних приложений, в нашем примере мы рассмотрим программу Bluetooth scanner для Android. Она легка в использовании, не имеет сложных настроек и к тому же бесплатно предоставляется для загрузки. Скачать ее можно с Google Play по ссылке .
Учтите, что программа имеет только англоязычную локализацию.
Рассмотрим, как работает данное приложение:
- Включите беспроводной модуль на вашем телефоне.
- Запустите скачанное приложение.
После запуска сразу начнется сканирование новых устройств. Все найденные аппараты будут показаны на дисплее с информацией о них.
По каждому аппарату будут предоставлены такие данные:
Источник
Bluetooth Scanner 1.2.1
(Bluetooth-сканер)
Скачать
Тут вы можете скачать АПK-файл «Bluetooth Scanner» для Андроид бесплатно, апк файл версии — 1.2.1 для загрузки на ваш андроид просто нажмите эту кнопку. Это просто и безопасно. Мы предоставляем только оригинальные апк файлы. Если какой-либо из материалов на этом сайте нарушает ваши права, сообщите нам
****************************** *******
Информация о кодеках (aptX, SBC и др.) Доступна только в Android 8.0 (Oreo) и только для подключенных устройств .
Если ваше устройство работает под управлением Android 6 или 7, эта информация не будет отображаться.
*************************************
Готовы ли вы обнаружить какие-либо устройства Bluetooth поблизости?
Хотите знать все о подключенных устройствах bt?
Основные функции:
— Найдите все устройства Bluetooth, включая подключенные, сопряженные и неизвестные устройства.
— Следите за своими устройствами
— сканер bluetooth 4.0
— подключение к устройствам bt
— поиск устройств с низким энергопотреблением и классических устройств, включая смарт-часы или браслет, телевизор, компьютер и другие.
— Сопряжение и отключение устройства bt
— Показывать уровень заряда батареи подключенных устройств Bluetooth (только с Android 9)
— Показывать мощность сигнала, информацию о кодеках (aptX, LDAC, SBC и другие)
— Воспроизвести любое сканирование в истории, просмотреть любые устройства bt в прошлом
— Настроить устройство (переименовать, изменить тип устройства)
— Полезные фильтры на основе типа устройства, имени устройства, времени
— Упорядочить по RSSI, адресу, имени, поставщику и т. Д.
— Выделить новые устройства вокруг вас
— Создание диаграмм на основе данных (распределение групп устройств и другие)
— Экспорт базы данных для дальнейшей обработки
— Функция «Найти мое устройство»
— переключение между активными устройствами Bluetooth
— автоматический перезапуск сканирования
Источник
Create a Bluetooth Scanner With Android’s Bluetooth API
Bluetooth has become a very popular technology, especially on mobile devices. It’s a technology to discover and transfer data between nearby devices. Virtually every modern mobile device has Bluetooth capabilities these days. If you want to make an app interface with another Bluetooth enabled device, ranging from phones to speakers, you must know how to use Android’s Bluetooth API.
In this tutorial, we will be making an app that is similar to the built-in Bluetooth app in Android’s settings. It will include the following features:
- enable Bluetooth on a device
- display a list of paired devices
- discover and list nearby Bluetooth devices
We will also go over the basics to connect and send data to another Bluetooth device. I’ve created a project to get us started, which you can download from GitHub. The below screenshot illustrates what the starter project looks like. If you get stuck or run into problems, then you can take a look at the finished project on GitHub.

1. Enabling Bluetooth
Before we can enable Bluetooth on an Android device, we need to request the necessary permissions. We do this in the app’s manifest. The BLUETOOTH permission allows our app to connect, disconnect, and transfer data with another Bluetooth device. The BLUETOOTH_ADMIN permission allows our app to discover new Bluetooth devices and change the device’s Bluetooth settings.
We will use the Bluetooth adapter to interface with Bluetooth. We instantiate the adapter in the ListActivity class. If the adapter is null , this means Bluetooth is not supported by the device and the app will not work on the current device. We handle this situation by showing an alert dialog to the user and exiting the app.
If Bluetooth is available on the device, we need to enable it. To enable Bluetooth, we start an intent provided to us by the Android SDK, BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE . This will present a dialog to the user, asking them for permission to enable Bluetooth on the device. REQUEST_BLUETOOTH is a static integer we set to identify the activity request.
2. Obtaining a List of Paired Devices
In this step, we scan for paired Bluetooth devices and display them in a list. In the context of a mobile device, a Bluetooth device can either be:
It is important to know the difference between a paired and a connected Bluetooth device. Paired devices are aware of each other’s existence and share a link key, which can be used to authenticate, resulting in a connection. Devices are automatically paired once an encrypted connection is established.
Connected devices share an RFCOMM channel, allowing them to send and receive data. A device may have many paired devices, but it can only be connected to one device at a time.
Bluetooth devices are represented by the BluetoothDevice object. A list of paired devices can be obtained by invoking the getBondedDevices() method, which returns a set of BluetoothDevice objects. We invoke the getBondedDevices() method in the DeviceListFragment ‘s onCreate() method.
We use the getName() and getAddress() methods to obtain more information about the Bluetooth devices. The getName() method returns the public identifier of the device while the getAddress() method returns the device’s MAC address, an identifier uniquely identifying the device.
Now that we have a list of the paired devices, we create a DeviceItem object for each BluetoothDevice object. We then add each DeviceItem object to an array named deviceItemList . We’ll use this array to display the list of paired Bluetooth devices in our app. The code for displaying the list of DeviceItem objects is already present in the starter project.
3. Discover Nearby Bluetooth Devices
The next step is to discover devices the device isn’t paired with yet, unknown devices, and add them to the list of paired devices. We do this when the user taps the scan button. The code to handle this is located in DeviceListFragment .
We first need to make a BroadcastReceiver and override the onReceive() method. The onReceive() method is invoked whenever a a Bluetooth device is found.
The onReceive() method takes an intent as its second argument. We can check what kind of intent is broadcasting with by invoking getAction() . If the action is BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND , then we know we have found a Bluetooth device. When this occurs, we create a DeviceItem object using the device’s name and MAC address. Finally, we add the DeviceItem object to the ArrayAdapter to display it in our app.
When the scan button is toggled on, we simply need to register the receiver we just made and invoke the startDiscovery() method. If the scan button is toggled off, we unregister the receiver and invoke cancelDiscovery() . Keep in mind that discovery takes up a lot of resources. If your application connects with another Bluetooth device, you should always cancel discovery prior to connecting.
We also clear the ArrayAdapter object, mAdapter , when discovery begins. When we start scanning, we don’t want to include old devices that may no longer be in range of the device.
That’s it. We have finished our Bluetooth scanner.
4. Connecting to a Device
Bluetooth connections work like any other connection. There is a server and a client, which communicate via RFCOMM sockets. On Android, RFCOMM sockets are represented as a BluetoothSocket object. Fortunately for us, most of the technical code for servers is handled by the Android SDK and available through the Bluetooth API.
Connecting as a client is simple. Your first obtain the RFCOMM socket from the desired BluetoothDevice by calling createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord() , passing in a UUID, a 128-bit value that you create. The UUID is similar to a port number.
For example, let’s assume you are making a chat app that uses Bluetooth to chat with other nearby users. To find other users to chat with, you would want to look for other devices with your chat app installed. To do this, we would look for the UUID in the list of services of the nearby devices. Using a UUID to listen and accept Bluetooth connections automatically adds that UUID to the phone’s list of services, or service discovery protocol.
Once the BluetoothSocket is created, you call connect() on the BluetoothSocket . This will initialize a connection with the BluetoothDevice through the RFCOMM socket. Once our device is connected, we can use the socket to exchange data with the connected device. Doing this is similar to any standard server implementation.
Maintaining a Bluetooth connection is costly so we need to close the socket when we no longer need it. To close the socket, we call close() on the BluetoothSocket .
The following code snippet shows how to connect with a given BluetoothDevice :
Connecting as a server is slightly more difficult. First, from your BluetoothAdapter , you must get a BluetoothServerSocket , which will be used to listen for a connection. This is only used to obtain the connection’s shared RFCOMM socket. Once the connection is established, the server socket is no longer need and can be closed by calling close() on it.
We instantiate a server socket by calling listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord(String name, UUID mUUID) . This method takes two parameters, a name of type String and a unique identifier of type UUID . The name parameter is the name we give the service when it is added to the phone’s SDP (Service Discovery Protocol) entry. The unique identifier should match the UUID the client trying to connect is using.
We then call accept() on the newly obtained BluetoothServerSocket to wait for a connection. When the accept() call returns something that isn’t null , we assign it to our BluetoothSocket , which we can then use to exchange data with the connected device.
The following code snippet shows how to accept a connection as a server:
Reading and writing to the connection is done using streams, InputStream and OutputStream . We can get a reference to these streams by calling getInputStream() and getOutputStream() on the BluetoothSocket . To read from and write to these streams, we call read() and write() respectively.
The following code snippet shows how to do this for a single integer:
You can find both examples in the finished project on GitHub.
Conclusion
We have successfully made our own Bluetooth scanner and learned the following:
- request the necessary Bluetooth permissions
- enable Bluetooth on your phone
- get a list of paired devices
- scan and display a list of nearby Bluetooth devices
- establish a Bluetooth connection between two devices
- send and receive data over a Bluetooth connection
Feel free to use the code in the finished project on GitHub and modify it in your own applications.
Источник