- Drawable. Фигуры и градиенты
- Shape и ShapeDrawable
- Элементы фигуры
- rectangle (Прямоугольник)
- oval (Эллипс)
- ring (Кольцо)
- line (Горизонтальная линия)
- Градиенты: gradient и GradientDrawable
- linear
- radial
- sweep
- Примеры с shape
- Закругляем уголки у компонентов
- Овальный кабинет
- Android Shape, Selector Examples
- 1. Custom Drawable File Overview.
- 2. Shape.
- 2.1 Shape’s Sub Element.
- 3. Selector.
- 3.1 View Component’s State.
- 3.2 Selector Definition.
- border-bottom-right-radius
- Краткая информация
- Версии CSS
- Описание
- Синтаксис
- Значения
- Браузеры
- border-bottom-right-radius
- Syntax
- Values
- Formal definition
- Formal syntax
- Examples
- Arc of a circle
- Arc of an ellipse
Drawable. Фигуры и градиенты
Shape и ShapeDrawable
Фигуры являются подмножеством Drawable-ресурсов.
Данный вид ресурсов на основе класса ShapeDrawable позволяет описывать простые геометрические фигуры, указывая их размеры, фон и контур с помощью тега .
Можно создавать ресурсы фигур на основе стандартных фигур вроде прямоугольника, эллипса, линии. Для использования ресурсов фигур нужно создать в подкаталоге res/drawable XML-файл, в котором будет присутствовать тег , который в свою очередь может содержать дочерние элементы , ,
Имя файла без расширения будет служить идентификатором (ID): R.drawable.filename в Java-коде и @[package:]drawable/filename в XML-файлах.
Элементы фигуры
— отступы. Возможные атрибуты: android:left, android:top, android:right, android:bottom
rectangle (Прямоугольник)
shape_rect.xml — Атрибут android:shape здесь необязателен: rectangle — это значение по умолчанию.
Пример с градиентным прямоугольником в качестве разделителя
Создадим файл separator.xml:
В разметке приложения добавим код:
У первого разделителя ширина 1dp, у второго — 3dp. Получили красивую полоску.
У прямоугольников можно скруглить углы при помощи тега corners
Можно закруглить углы по отдельности:
oval (Эллипс)
Другой вариант с пунктиром:
ring (Кольцо)
shape_ring.xml — Для кольца имеются дополнительные атрибуты:
innerRadius Внутренний радиус innerRadiusRatio Отношение между внешним и внутренним радиусами. По умолчанию равно 3 thickness Толщина кольца (т.е. разница между внешним и внутренним радиусами) thicknessRatio Отношение ширины кольца к его толщине. По умолчанию равно 9
line (Горизонтальная линия)
shape_line.xml — Линия может быть только горизонтальной
Градиенты: gradient и GradientDrawable
Тег gradient (класс GradientDrawable) позволяет создавать сложные градиентные заливки. Каждый градиент описывает плавный переход между двумя или тремя цветами с помощью линейного/радиального алгоритма или же используя метод развертки.
Тег gradient внутри тега shape. Основные атрибуты: type, startColor (обязателен), endColor (обязателен) и middleColor (необязателен). Также иногда оказывается полезным атрибут centerColor.
Используя атрибут type, вы можете описать свой градиент:
linear
- android:type=»linear» можно опустить, он так и есть по умолчанию. Отображает прямой переход от цвета startColor к цвету endColor под углом, заданным в атрибуте angle.
- Атрибут android:angle используется только линейным градиентом и должен быть кратным значению 45.
Дополнительный материал: Android Dev Tip #3 — помните о прозрачности, который может привести к другому результату.
Также можно задействовать атрибуты centerX и centerY.
radial
Интересный эффект получается при использовании множества радиальных градиентов.
sweep
Рисует развёрточный градиент с помощью перехода между цветами startColor и endColor вдоль внешнего края фигуры (как правило, кольца).
Можно использовать атрибуты android:centerX и android:centerY.
Попробуйте также такой вариант.
А почему бы не повращать?
Примеры с shape
Закругляем уголки у компонентов
Создадим отдельный файл res/drawable/roundrect.xml и с его помощью скруглим уголки у LinearLayout, ImageView, TextView, EditText:
В разметке активности пишем следующее:
Овальный кабинет
В Белом доме есть Овальный кабинет. Если вам придётся писать приложение для администрации президента США, то все элементы нужно сделать овальными. Создадим файл res/drawable/oval.xml:
Заменим в предыдущем примере android:background=»@drawable/roundrect» на android:background=»@drawable/oval».
Источник
Android Shape, Selector Examples
Shape, selector, and layer-list are usually used to create custom drawable resources in android development. Those three XML elements can save a lot of UI resources and time if being used properly. This article will show you how to use them correctly.
1. Custom Drawable File Overview.
- All the three XML elements should be defined in an XML file under the app/res/drawable folder. The file name is just the drawable resource id.
- For example, if app/res/drawable/my_layer_list.xml is just the file. Then you can refer to it in both java code or other XML files.
- Refer to the my_layer_list.xml in Java Code: R.drawable.my_layer_list.
- Refer to the my_layer_list.xml in Xml Code : Android:background=”@drawable/my_layer_list”.
2. Shape.
The shape is used to define custom shapes in android drawable resources. It is used in both selector and layer-list elements. It has the below properties.
- Android:shape : Value can be “line“, “rectangle“, “oval” or “ring“.
2.1 Shape’s Sub Element.
2.1.1 .
- The gradient XML element is used to define color gradual change style. It has the below attributes.
- Android:startColor: Start color value.
- Android:endColor: End color value.
- Android:angle: Gradient angle, 0 means from left to right, 90 means from bottom to top, the value should be an integer that is multiple of 45, the default value is 0.
- Android:type: linear, radial, and sweep.
- Below is an example of the gradient XML element.
- Below is the above example’s XML source code.
- The solid XML element is used to define shape internal fill color. It will override the attributes effect. It has the below attributes.
- Android:color: The color value that is used to fill the shape.
- Below is an example of the solid XML element.
- Below is the above example’s XML source code.
- The stroke XML element is used to define shape bolder style. It has the below XML attributes.
- Android:width : Border width.
- Android:color: Border color.
- Android:dashWidth : Dash border width.
- Android:dashGap: Gap between two dashes of the border.
- Below is an example of the stroke XML element.
- Below is the above example’s XML source code.
- The corners XML element is used to define shape corner style. It has the below XML attributes.
- Android:radius: The radius of the corner. The bigger the radius value, the round-shaped the corner.
- Android:topRightRadius: Top right corner radius value.
- Android:bottomLeftRadius: Bottom left radius value.
- Android:topLeftRadius: Top left radius value.
- Android:bottomRightRadius: Bottom right radius value.
- Below is an example of the corners XML element.
- Below is the above example’s XML source code.
- The padding XML element is used to define the padding values. It has the below XML attributes.
- android:top: Top padding value.
- android:bottom: Bottom padding value.
- android:left: Left padding value.
- android:right: Right padding value.
- Below is an example of the corners XML element. There are two custom shapes in the below example. The green shape is drawn at the top because it is defined at last in the layer-list definition.
- Below is the above example’s XML source code.
- The size XML element is used to define the shape width and height value.
3. Selector.
The selector is used to define the view component’s background color or background image by it’s various states.
3.1 View Component’s State.
A view component has various state. For example, a button has following states:
- android:state_pressed : Boolean value, true means button is pressed, false means button is not pressed.
- android:state_enabled : Boolean value, true means button is enabled, false means button is disabled.
- android:state_focused : Boolean value, true means button is focused, false means button lost focus.
- android:state_window_focused : Boolean value, this is the button default state. It is same as do not specify button state.
3.2 Selector Definition.
You should define a selector in a xml file under app / res / drawable folder. Such as my_selector.xml
You can define several items in the selector definition xml file. Each item include a drawable object (color or image) that will be used for a button state.
Android system will check each item in the selector by it’s list order, if one item match current button state, then use that drawable object. If no state match, then use default item.
Please Note : The default state item should be written in the end of the selector xml. If you put it at the beginning of selector xml, no other state will take effect.
From above example, we can see below default state item at the end of the xml.
It behaves same as below default state item.
If we apply above selector drawable to a button as background.
We can see below screen effect. When the button is pressed, the background color is green, when not pressed the background color change to orange.
If you can not watch the above video, you can see it on the youtube URL https://youtu.be/t-D2511VoYg
Above example use some custom color variables, if you do not know, please read How To Define Custom Color Variables In Android Studio.
Источник
border-bottom-right-radius
| Internet Explorer | Chrome | Opera | Safari | Firefox | Android | iOS |
| 9.0+ | 1.0+ | 10.5+ | 3.0+ | 1.0+ | 2.1+ | 1.0+ |
Краткая информация
| Значение по умолчанию | 0 |
|---|---|
| Наследуется | Нет |
| Процентная запись | Да, относительно ширины блока |
| Применяется | Ко всем элементам |
| Ссылка на спецификацию | http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-background/#border-bottom-right-radius |
Версии CSS
Описание
Устанавливает радиус скругления правого нижнего уголка рамки. Если рамка не задана, то скругление также происходит и с фоном.
Синтаксис
border-bottom-right-radius: [значение | проценты] [значение | проценты]
Значения
В качестве радиуса указывается любое допустимое в CSS значение (px, cm, in, em и др.), а также проценты, в этом случае радиус скругления считается от ширины блока.
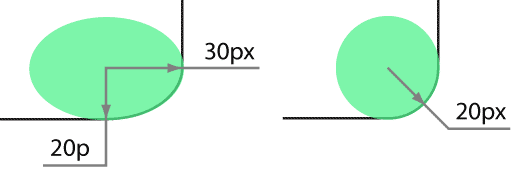
Необязательное второе значение предназначено для создания эллиптического уголка, первое значение при этом устанавливает радиус по горизонтали, а второе — радиус по вертикали (рис. 1).
Рис. 1. Радиус скругления для создания разных типов уголков
HTML5 CSS2.1 CSS3 IE Cr Op Sa Fx
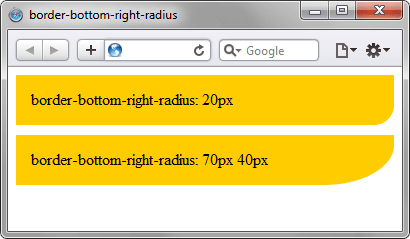
Результат данного примера показан на рис. 2.
Рис. 2. Радиус скругления в браузере Safari
Браузеры
Chrome до версии 4.0, Safari до версии 5.0, iOS используют нестандартное свойство -webkit-border-top-left-radius .
Firefox до версии 4.0 использует нестандартное свойство -moz-border-radius-topleft.
Источник
border-bottom-right-radius
The border-bottom-right-radius CSS property rounds the bottom-right corner of an element by specifying the radius (or the radius of the semi-major and semi-minor axes) of the ellipse defining the curvature of the corner.
The rounding can be a circle or an ellipse, or if one of the value is 0 no rounding is done and the corner is square.
A background, being an image or a color, is clipped at the border, even a rounded one; the exact location of the clipping is defined by the value of the background-clip property.
Note: If the value of this property is not set in a border-radius shorthand property that is applied to the element after the border-bottom-right-radius CSS property, the value of this property is then reset to its initial value by the shorthand property.
Syntax
- the value is a or a
denoting the radius of the circle to use for the border in that corner.
With two values:
- the first value is a or a
denoting the vertical semi-major axis of the ellipse to use for the border in that corner.
Values
Denotes the size of the circle radius or the semi-major and semi-minor axes of the ellipse. As absolute length it can be expressed in any unit allowed by the CSS data type. Percentages for the horizontal axis refer to the width of the box, percentages for the vertical axis refer to the height of the box. Negative values are invalid.
Formal definition
| Initial value | 0 |
|---|---|
| Applies to | all elements; but User Agents are not required to apply to table and inline-table elements when border-collapse is collapse . The behavior on internal table elements is undefined for the moment.. It also applies to ::first-letter . |
| Inherited | no |
| Percentages | refer to the corresponding dimension of the border box |
| Computed value | two absolute s or s |
| Animation type | a CSS data type are interpolated as real, floating-point numbers.»>length, CSS data type are interpolated as real, floating-point numbers.»>percentage or calc(); |
Formal syntax
Examples
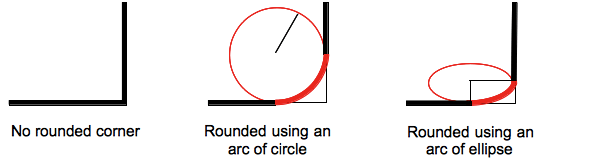
Arc of a circle
A single value produces an arc of a circle.
Arc of an ellipse
Two different values produce an arc of an ellipse.
Источник