- Modal Bottom Sheet in Kotlin
- Implementation of a Modal Bottom Sheet in Android using Kotlin
- Android BottomSheet Example in Kotlin
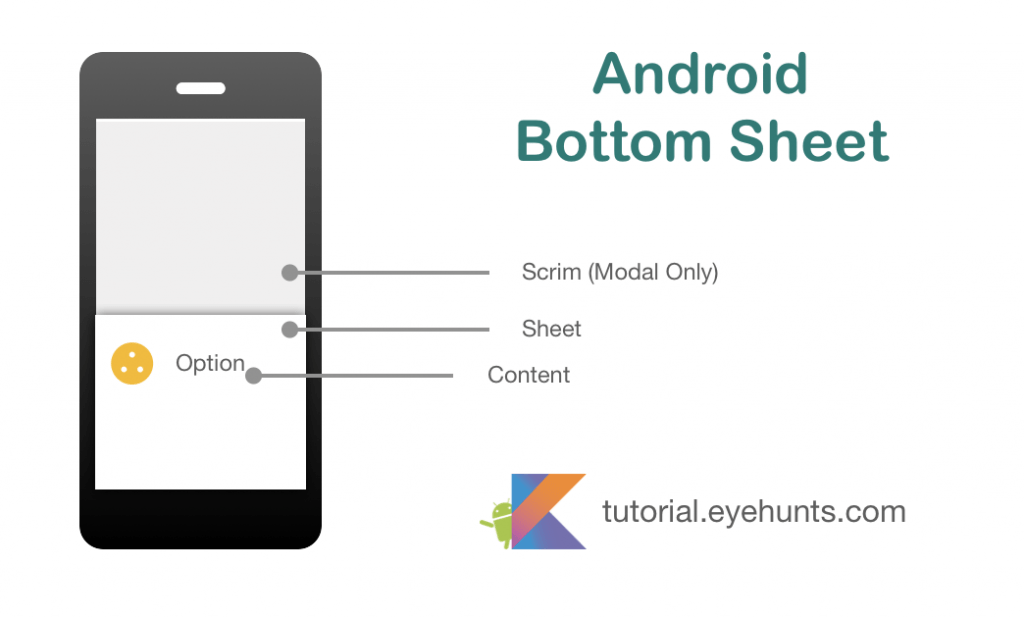
- What is Bottom Sheet?
- Types of Bottom Sheet?
- What we are going to build in this article?
- Step by Step Implementation
- Android BottomSheet Example in Kotlin
- Types of Android BottomSheet
- Adding BottomSheet in Android Application
- Android Bottom Sheet Tutorial with Example in Kotlin
- In this tutorial, you will learn the following:
- Types of Bottom Sheets
- Bottom Sheet behavior and States :
- Let’s Build an Example of Android Bottom Sheet
- Output screenshot Android Bottom Sheet example :
- Video Output
- Download source code Android BottomSheet in kotlin
Modal Bottom Sheet in Kotlin
Implementation of a Modal Bottom Sheet in Android using Kotlin
A modal bottom sheet is a component that slides up from the bottom of the screen to show more content.
Here’s how you can set up a modal bottom sheet in an android application using Kotlin:
We will implement the bottom sheet on the click of a button.
First of all, create a new activity (preferably an Empty Activity) and modify the activity_main.xml file to add a button.
Now our screen looks like this,
Now it’s time to make a new layout file for the bottom sheet dialog.
Make a new layout file(Right-click on res ->New ->Layout Resource File) and name it dialog_layout.xml.
Add the following code in the dialog_layout.xml file,
Now, let’s add a listener to the button in the MainActivity.kt file;
Declare a global variable to access the button
To initialize the global variable write,
Adding a listener to it,
Now in the curly braces add the following code to implement the bottom sheet dialog,
Now Run the application. When you click on the button you can see the bottom sheet coming up.
Now it’s time to make the items as well the cross button image clickable.
When an item is clicked, a Toast should be displayed and when the cross image is clicked, the bottom sheet should go back.
Add the following code to the existing listener,
Now Run the app again and see the changes.
Whenever we click on the Items, we see a Toast message and when the cross image is clicked, the bottom sheet goes back.
To implement the cross image(imgClose)we have used the following dismiss command,
But still, one issue needs to be fixed. Whenever we click on the outside the bottom sheet dialog, the bottom sheet dialog goes back automatically.
In order to fix this issue, add the following code in the ban click.setOnClickListener<>
Now Run the application and the issue is resolved.
The Modal Bottom Sheet has been successfully implemented.
Источник
Android BottomSheet Example in Kotlin
The Bottom Sheet is seen in many of the applications such as Google Drive, Google Maps and most of the applications used the Bottom Sheet to display the data inside the application. In this article, we will take a look at implementing a Bottom Sheet in the Android app using Kotlin in Android Studio.
What is Bottom Sheet?
Bottom Sheet is a component of the Android design support library that is used to display different actions in an expandable UI design. It is an expandable widget that opens from the bottom of the android device on clicking on a specific Button or View.
Types of Bottom Sheet?
There are two different types of Bottom Sheet as
- Persistent Bottom Sheet and
- Modal Bottom Sheet
1. Persistent Bottom Sheet
A Persistent Bottom Sheet will be displayed on the bottom of the screen in our Android application. This sheet will be displayed at the bottom of the screen making some portion of the content visible. The elevation of this bottom sheet is the same as that of the app. Users can be able to navigate to both the app along with the bottom sheet at a time. Below is the example for the Persistent Bottom Sheet.
2. Modal Bottom Sheet
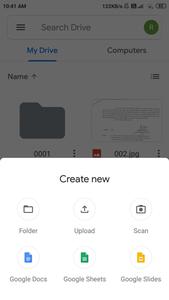
Modal Bottom Sheet will also be displayed on the bottom of the screen, but the difference is the user will not be able to use the app’s background content when the bottom sheet is open. This type of bottom sheet is having an elevation slightly higher than that of the app. When this bottom sheet is the open user will not be able to access the app’s content. Users can at a time use the bottom sheet or the app’s content. Below is the example for the Modal Bottom Sheet.
What we are going to build in this article?
We will be building a simple application in which we will be displaying the course details in our bottom sheets such as Course Name, Course Duration, Course Tracks, and many more. A sample video is given below to get an idea about what we are going to do in this article.
Step by Step Implementation
Step 1: Create a New Project
To create a new project in Android Studio please refer to How to Create/Start a New Project in Android Studio. Note that select Kotlin as the programming language.
Источник
Android BottomSheet Example in Kotlin
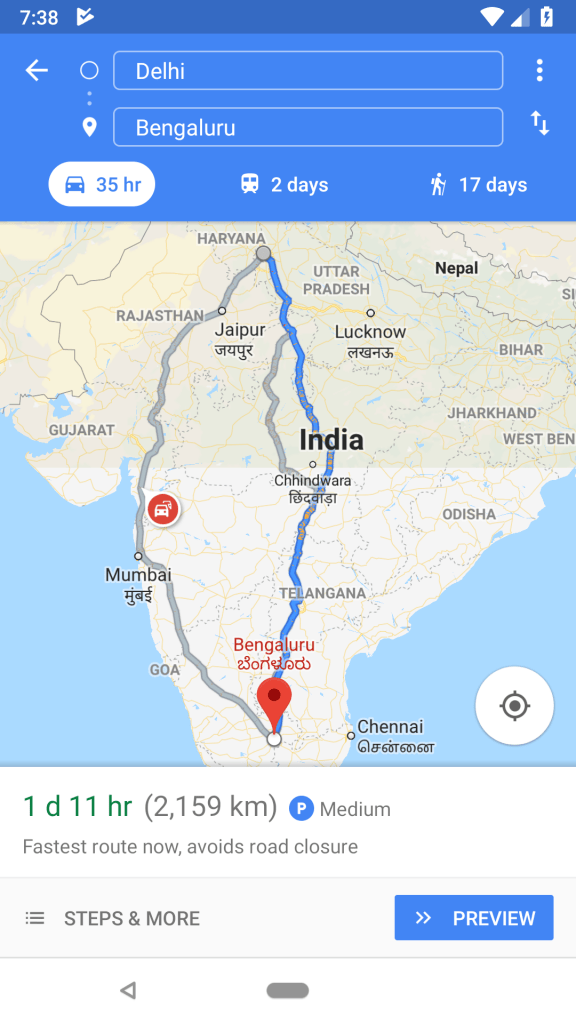
Android BottomSheet is a component that slides from the bottom of the screen to reveal more information. You can see Android BottomSheet in action in Google Maps android app.
In this tutorial we will learn about the types of BottomSheet and how you can integrate it in your Android application using Kotlin.
Types of Android BottomSheet
- Standard BottomSheet or Persistent BottomSheet: This type of BottomSheet remains visible at the bottom along with the primary screen. User can interact with the sheet like sliding it up and down to reveal or hide content.
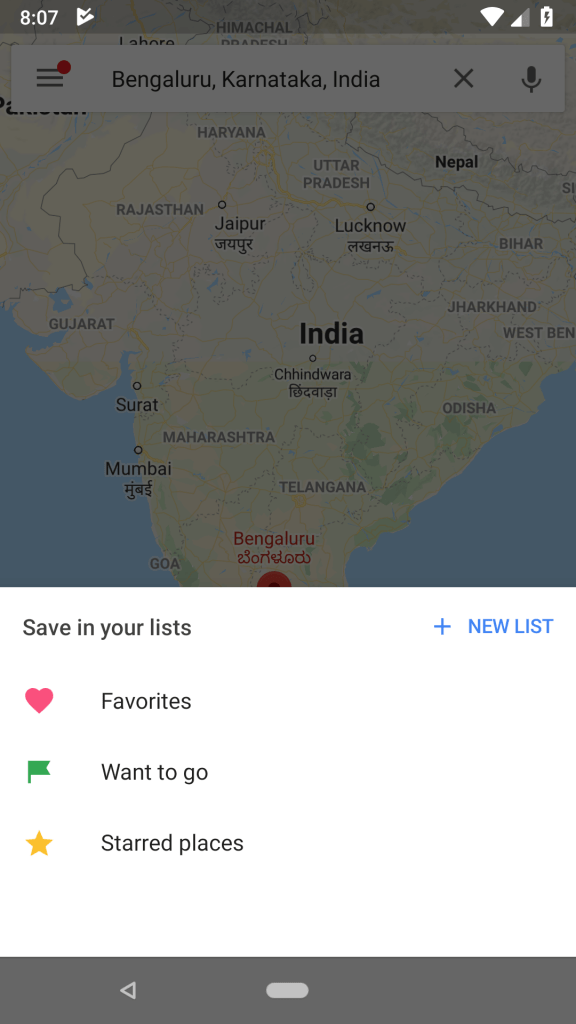
- Modal BottomSheet: This type of sheet opens from the bottom when user performs any action for example showing the sharing option when tap on share button.
Bottom sheets have 5 states:
- STATE_COLLAPSED : The bottom sheet is visible but only showing its peek height. This state is usually the ‘resting position’ of a Bottom Sheet. The peek height is chosen by the developer and should be enough to indicate there is extra content, allow the user to trigger an action or expand the bottom sheet.
- STATE_EXPANDED : The bottom sheet is visible and its maximum height and it is neither dragging or settling (see below).
- STATE_DRAGGING : The user is actively dragging the bottom sheet up or down.
- STATE_SETTLING : The bottom sheet is settling to specific height after a drag/swipe gesture. This will be the peek height, expanded height, or 0, in case the user action caused the bottom sheet to hide.
- STATE_HIDDEN : The bottom sheet is no longer visible.
Adding BottomSheet in Android Application
Let’s create a new Empty Android Project.
In build.gradle file add the latest support design dependency:
We will first start with Persistent Bottom Sheet:
Add a new layout file as persistent_bottom_sheet.xml in the project. This file will contain the layout of the persistent bottom sheet.
Now let’s go to our activity_main.xml file. Here we will add 3 buttons to show different bottomSheet examples and link our persistent_bottom_sheet.xml file.
If you run the application at this point you will be able to see the persistent BottomSheet in action. Now we will bind our persistent bottom sheet with the button we have added and change our button text on the sheet state change.
In your MainActivity.kt file add a variable of type BottomSheetBehavior and pass our persistent_bottom_sheet layout
Let’s add bottomSheet callback to observe bottom sheet states:
To toggle between expand and close state of the sheet we will add click listener to our persistentBtn.
So far, your application will look like this:
Let’s proceed to our other type of Bottom Sheet i.e. Modal BottomSheet
We will create a different layout to showcase Modal BottomSheet. Lets call our new layout as fragment_modal_bottom_sheet.xml
Add 2 more buttons in your activity_main.xml file, one to show Modal BottomSheet using dialog and other to show Modal BottomSheet using fragment.
To show the Modal BottomSheet as fragment lets add a fragment class and bind it with the new layout we just created(you can create a new layout for the fragment, for this demo we will show the same layout for the dialog and the fragment).
Lets wire up our newly added button to show Modal Bottom Sheet. Navigate to your MainActivity.kt
Here is our Modal BottomSheet in action:
You can checkout the complete project on Github
Источник
Android Bottom Sheet Tutorial with Example in Kotlin
Android Bottom Sheet is a component that slides up from the bottom to up in an application. For example, when you have a video to share and you click on the Share button, it will open a one slider from bottom, which contains available apps in your device.
Sometimes it can also have a menu option. In a simple word, the Android Bottom sheet is an area (surface) that containing extra useful content at the bottom of the screen. It’s hidden in the bottom or partial show to the user will be shown to the user on the action.
In this tutorial, you will learn the following:
- What is Android Bottom Sheet and it’s type
- Example and code of Bottom sheet.
Types of Bottom Sheets
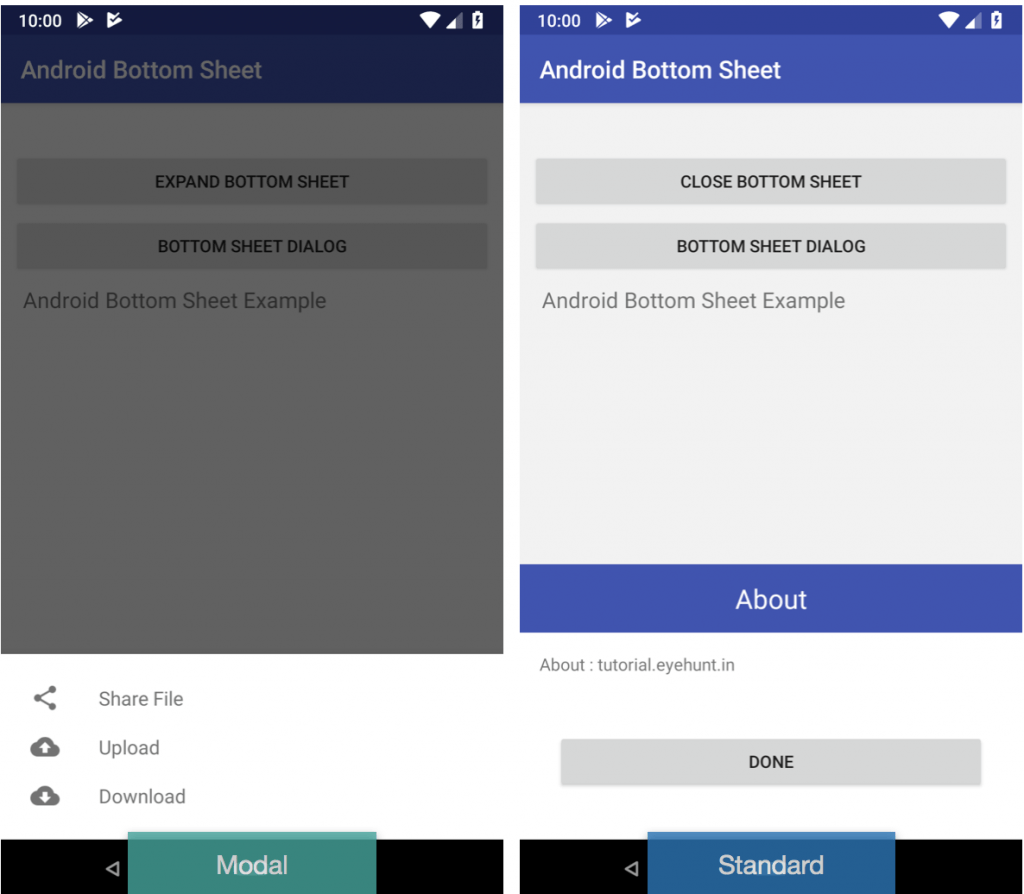
There are two types of bottom sheets, Standard Bottom Sheet and Modal Bottom Sheet.
- Standard bottom sheets: Display content that complements the screen’s primary content. Remain visible screen users can interact with the primary content. Like, google maps are shown at the bottom how much time and km etc detail of the destination from your point. Here user can interact with both the bottom sheet and the remain of screen content.
- Modal bottom sheets: This can be an alternative to inline menus or simple dialogs on mobile, providing room for additional items, longer descriptions, and iconography. They must be dismissed in order to interact with the underlying content. Example share the location in Google Maps.
Bottom Sheet behavior and States :
Bottom sheets have 5 states:
STATE_COLLAPSED : The bottom sheet is visible but only showing its peek height. This state is usually the ‘resting position’ of a Bottom Sheet
STATE_EXPANDED : The bottom sheet is visible and its maximum height and it is neither dragging or settling.
STATE_DRAGGING : The user is actively dragging the bottom sheet up or down.
STATE_SETTLING : The bottom sheet is settling to specific height after a drag/swipe gesture. This will be the peek height, expanded height, or 0, in case the user action caused the bottom sheet to hide.
STATE_HIDDEN : The bottom sheet is no longer visible.
Let’s Build an Example of Android Bottom Sheet
Step 1. Create new project “ Build Your First Android App in Kotlin “
Step 2. Add following color code in “color.xml” layout file
Step 3. Create “bottom_sheet.xml” and Add code
This will be use for standard bottom sheet.
Step 4. Create “bottom_sheet_dialog.xml” and Add code
You must add image in mipmap folder.
» data-medium-file=»https://tutorial.eyehunts.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/baseline_cloud_download_black_24dp.png» data-large-file=»https://tutorial.eyehunts.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/baseline_cloud_download_black_24dp.png» loading=»lazy» width=»48″ height=»48″ src=»https://tutorial.eyehunts.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/baseline_cloud_download_black_24dp.png» alt=»»/>
Step 5. Create “main_content.xml” and Add code
Its your app main content with 2 Button to perform a show and hide Android Bottom Sheet.
Step 6. Add following code in “activity_main.xml“
A holding all xml file (main_content.xml & bottom_sheet.xml) in one place, using . . its a good practice to use if your screen have common or long code.
Step 7. Open the “MainActivity.kt” and add following code
Setting a listener in button and handling behaviour or bottom sheet.
Step 8. Now Run the application, in emulator or On you android device
Output screenshot Android Bottom Sheet example :
Video Output
Download source code Android BottomSheet in kotlin
Do comment if you have any doubt and suggestion on this tutorial.
Note : This example (Project) is developed in Android Studio 3.1.3 . Tested on Android 9 ( Android-P), compile SDK version API 27: Android 8.0 (Oreo)
Degree in Computer Science and Engineer: App Developer and has multiple Programming languages experience. Enthusiasm for technology & like learning technical.
Источник