- What Is the Android SDK and How to Start Using It
- What Is the Android SDK?
- How to Install the Android SDK
- What Is the SDK Manager?
- What Are the Components of the Android SDK?
- Android SDK Tools
- SDK Build Tools
- SDK Platform-Tools
- SDK Platform
- Google APIs
- Android Emulator
- Conclusion
- Premium Android App Templates From CodeCanyon
- Installing the Android Development Tools
- Installing the JDK/SDK/NDK
- Handling an Android SDK Manager Issue on Windows 8
- Configuring RAD Studio to Work with Your Installed SDK
- Adding Java as a User Override to Your System Path
What Is the Android SDK and How to Start Using It
Android SDK is a software development kit developed by Google for the Android platform. The Android SDK allows you to create Android apps, and you don’t need to be an expert to use it. In this tutorial, I’ll explain what the Android SDK is and how to get started with it.
Android SDK comes bundled with Android Studio, Google’s official integrated development environment (IDE) for the Android operating system. You can learn about Android Studio and the Android App Development Kit in another of my articles.



In this post, we’ll look at:
- What is the Android SDK?
- How to install the Android SDK
- What is the Android SDK Manager?
- What are the components of the Android SDK?
What Is the Android SDK?

The Android SDK is a collection of software development tools and libraries required to develop Android applications. Every time Google releases a new version of Android or an update, a corresponding SDK is also released which developers must download and install. It is worth noting that you can also download and use the Android SDK independently of Android Studio, but typically you’ll be working through Android Studio for any Android development.
The Android SDK comprises all the tools necessary to code programs from scratch and even test them. These tools provide a smooth flow of the development process from developing and debugging, through to packaging.
The Android SDK is compatible with Windows, macOS, and Linux, so you can develop on any of those platforms.
How to Install the Android SDK
The Android SDK is optimized for Android Studio, and hence to effectively reap its benefits, you will need to install Android Studio. Having the Android SDK managed from within Android Studio is easier since support for languages like Java, Kotlin, and C++ is handled automatically. Not only that, but updates to the Android SDK are handled automatically by Android Studio.
To install the Android SDK from within Android Studio, first start Android Studio.
- From the Android Studio start page, select Configure > SDK Manager.
- If you already have Android Studio open, the SDK Manager icon is found on the top right corner, as shown below.
Install the required Android SDK platform packages and developer tools. A good start is to install:
- Android SDK Build-Tools
- Android Emulator
- Android SDK Platform-Tools
- Android SDK Tools
- Documentation for Android SDK
Click Apply, and Android Studio will install the selected tools and packages.
What Is the SDK Manager?
The Android SDK is composed of modular packages that you can download, install, and update separately using the Android SDK Manager. The SDK Manager helps to update new SDK releases and updates whenever a new Android platform is released. The SDK manager can be found in the top-right corner of the Android Studio screen, as shown below.

All that is required to follow the instructions provided, and the updates will be immediately downloaded to your environment.
What Are the Components of the Android SDK?
The Android SDK consists of an emulator, development tools, sample projects with source code, and the required libraries to build Android applications. Let’s look at the key components one by one.
Android SDK Tools
Android SDK Tools is a component of the Android SDK. It includes a complete set of development and debugging tools for Android, and is included with Android Studio. The SDK Tools also consist of testing tools and other utilities required to develop an app.
SDK Build Tools
Build tools are required for building components for building the actual binaries for your Android app. Always ensure your build tools component is up to date by downloading the latest version in the Android SDK Manager.
SDK Platform-Tools
Android Platform-Tools are used to support the features for the current Android platform and are necessary for Android app development. These tools interface with the Android platform on the device you use for testing. They include:
- Android Debug Bridge (adb): This is a handy command-line tool that lets you communicate with a device. The adb command allows you to perform device actions, such as installing and debugging apps. It also provides access to a Unix shell that you can use to run a variety of commands on a device.
- fastboot: This lets you flash a device with a new system image.
- systrace: This tool helps collect and inspect timing information across all processes running on your device at the system level. It’s crucial for debugging app performance.
SDK Platform-Tools are backward compatible, so you need only one version of the SDK Platform-Tools.
SDK Platform
For each version of Android, there’s one SDK Platform available. These are numbered according to the Android version (e.g. Android 7 Nougat) and an API version (e.g. API Level 24). Before you build an Android app, you must specify an SDK Platform as your build target. Newer SDK Platform versions have more features for developers, but older devices may not be compatible with the newer platform versions.
Google APIs
Google provides a number of exclusive Google APIs to make developing your app easier. They also offer a system image for the emulator so you can test your app using the Google APIs.
Android Emulator
The Android Emulator is a QEMU-based device-emulation tool that simulates Android devices on your computer, allowing developers to test applications on different devices and Android API levels, without needing to have physical devices for each. The emulator comes with configurations for various Android phones, tablets, Wear OS, and Android TV devices.
The Android emulator provides almost all of the capabilities of a real Android device. You can perform the following activities:
- simulate phone calls and text messages
- simulate different network speeds
- specify the location of the device
- simulate hardware sensors such as rotation
- access Google Play Store and much more
Often it is faster and easier to test your app with an emulator instead of using a physical device.
Conclusion
In this post, we looked at some of the basics of the Android SDK. The Android SDK is the only way to develop for Android devices. Fortunately, it contains extensive documentation, tutorials, samples, best practice guidance, and an array of tools for many different development tasks.
Premium Android App Templates From CodeCanyon
Android Studio comes with some default templates to help start an app, but these are very basic and provide minimal, generic functionality.
CodeCanyon is an online marketplace that has hundreds of additional templates, which are way more feature-rich and domain-specific too. You can save days, even months, of effort by using one of them.
An Android app template is a great way to jump-start your app project or to learn some new skills by exploring the source code of a professionally made app.
Take a look at some of our roundups of the best Android app templates:
Источник
Installing the Android Development Tools
Important: You do not need to install the Android tools yourself.
- The installer for RAD Studio installs the current recommended and tested versions of the Android development tools during the RAD Studio product installation.
- The Android development tools are conveniently accessible using Start | All Programs | Embarcadero RAD Studio XE6 | Android SDKs , as shown here:
- The Android AVD Manager menu item opens a command window that invokes the Android SDK Manager, which in turn starts the Android Virtual Device Manager for you.
- The Android Tools menu item opens a command window that invokes the Android SDK Manager.
- The installer gives you the option to not install the Android SDK and NDK. If you opt out in the installer, you can either:
- Use a previously installed Android SDK and NDK.
- Install the Android development tools yourself, following the steps in this topic.
Be aware that you need to use the recommended versions of the Android development tools; alternate versions might introduce changes that cannot be supported by RAD Studio. Note: The JDK is installed if you do not have the recommended version of Java (1.6 or 1.7), regardless of whether the Android development tools are installed for you during product installation.
Having the Android development tools installed on your development system is required for developing Android apps using RAD Studio. To build mobile apps for the Android target platform, you also need to add an Android SDK to the RAD Studio SDK Manager.
Here are the default installed locations of the Android development tools as installed by the RAD Studio installer:
- Java Development Kit (JDK): C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_25
- Android Software Development Kit (SDK): C:\Users\Public\Documents\Embarcadero\Studio\14.0\PlatformSDKs\adt-bundle-windows-x86-20131030\sdk
- Android Native Development Kit (NDK): C:\Users\Public\Documents\Embarcadero\Studio\14.0\PlatformSDKs\android-ndk-r9c
Installing the JDK/SDK/NDK
- Install the JDK (Java development kit):
- On the PC, download and run the JDK installer, which is available here: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
- Install the Android SDK (software development kit):
- In your browser on the PC, open the Android SDK download page and click Download the SDK Tools ADT Bundle for Windows.
- On the Get the Android SDK page, you can select either 32-bit or 64-bit, according to your Windows platform.
- This download includes the SDK tools and the Eclipse IDE. After the download completes, you can safely delete the SDK\adt-bundle-windows-x86-20131030\eclipse folder, unless you want to use the Eclipse IDE.
- From your directory, run SDK Manager.exe. Tips: If the Android SDK Manager does not start, try these suggestions:
- Right-click SDK Manager.exe and choose Run As Administrator.
- Run android.bat from the \tools directory inside your directory.
- In the Android SDK Manager tree, check (enable) the following nodes:
- Tools node
- SDK Platform node within the Android (API ) node, where must be 9 or a higher value (for example, «18»). Note: RAD Studio supports Android 2.3 and later versions regardless of which SDK Platform you download. Android SDK platforms are backward compatible.
- Click Install packages, click Accept License to accept the required licenses, and click Install to install the required software.
- You can close the Android SDK Manager when the installation finishes.
- In your browser on the PC, open the Android SDK download page and click Download the SDK Tools ADT Bundle for Windows.
- Install the Android NDK (native development kit):
- On the PC, download and unzip the NDK for your Windows version (32-bit or 64-bit), available here: http://developer.android.com/tools/sdk/ndk/index.html.
After installing these tools, you need to add an Android SDK to RAD Studio, as described in the next section, and then you can start building mobile applications for the Android platform.
Handling an Android SDK Manager Issue on Windows 8
On Windows 8, you might see errors when you start the Android SDK Manager. If this happens, you might not be able to download any additional SDKs.
The solution is to edit the android.bat file and change the line that launches the Android SDK Manager. Add -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true to the call to Java, as follows:
call %java_exe% -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true %REMOTE_DEBUG% -Dcom.android.sdkmanager.toolsdir=»%tools_dir%» -Dcom.android.sdkmanager.workdir=%work_dir% -classpath «%jar_path%;%swt_path%\swt.jar» com.android.sdkmanager.Main %*
This issue seems to be related to Windows 8 wanting to use Internet Protocol V6.
Configuring RAD Studio to Work with Your Installed SDK
You can use specific versions of the Android SDK simply by pointing the RAD Studio SDK Manager to your installed location.
- Open the Create a New Android SDK wizard by using either Tools Options or Project Manager:
- Choose Tools > Options > Environment Options >SDK Manager | Add | Add new .
- In the Project Manager:
- Right-click the Android target platform and select Properties from the context menu.
- In the SDK field on the Platform Properties dialog box, click Add new in the dropdown list.
- On the Add a New SDK dialog, click Add new in the dropdown list.
- In the Android SDK Base Path and the Android NDK Base Path fields, browse to and select your installed and locations, respectively.
- The Create a new Android SDK wizard now populates the rest of the fields here and on the Android tools locations page. Allow a moment for this process to complete.
- For any fields that are not auto-populated or are marked with
, click the entry field and browse to the installed location of that library on your system.
Adding Java as a User Override to Your System Path
If you installed the JDK yourself, Java might not be in your system path. For example, if Java is not in your system path, you must use android.bat to start the Android SDK Manager (instead of SDK Manager.exe). If you want to optimize for Android development, you should add Java to your system path environment variable.
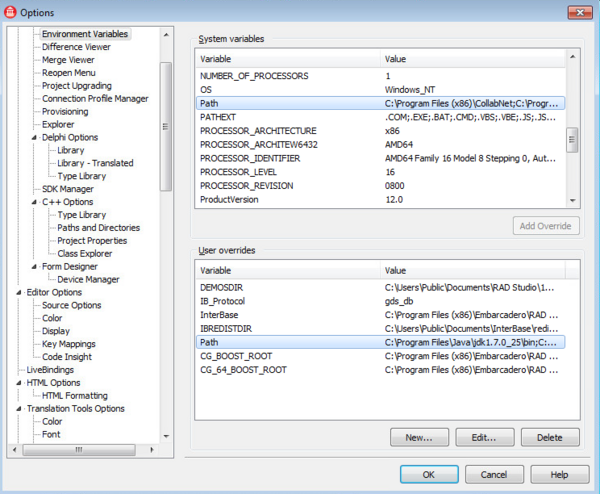
- Choose Tools > Options > Environment Options >Environment Variables .
- In the System variables pane, double-click the Path item.
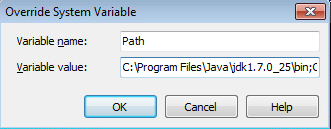
- In the Override System Variable dialog box, click the Home button on your keyboard to bring the focus to the beginning of the path.
- Add the path to Java at the beginning of your system path (it must precede all references to System32). For example, the default installed path to java.exe in RAD Studio is: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_25\bin Note that you should only need to add an override if your Java installation is different from this. End your path entry with a semicolon (;):
- Click OK on the Override dialog box, and click Yes on the Confirm dialog box that follows.
- Verify that you see the path to Java shown at the start of the Path field in the User overrides pane:
- Click OK to close the Tools Options Dialog Box.
Источник













 , click the entry field and browse to the installed location of that library on your system.
, click the entry field and browse to the installed location of that library on your system.