- Android Clipboard – Copy and Paste Text Example in Kotlin
- In this tutorial, you will learn the following:
- Android Clipboard Framework
- Some Important Points about Android clipboard
- Let’s Build Android Clipboard – Copy and Paste Text Example in Kotlin
- Output screenshot Android Clipboard – Copy and Paste Text
- Download source code Android Clipboard Text- Copy and Paste
- Android Clipboard with Examples
- Android Copying Data to Clipboard
- Android Pasting Data from Clipboard
- Android Clipboard App Example
- activity_main.xml
- MainActivity.java
- Output of Android Clipboard App Example
- Android TextView Copy Paste Using Clipboard
- Android Tutorial
- Andorid Clipboard – Copy Paste
- Copying Text To Clipboard
- Pasting Text To Clipboard
- Project Structure
- Output
- Download Links
Android Clipboard – Copy and Paste Text Example in Kotlin
Android Clipboard Text – Copy and Paste Android: Android provides a powerful clipboard-based framework for copying and pasting. It supports both simple and complex data types, including text strings, complex data structures, text and binary stream data, and even application assets.
Simple text data is stored directly in the clipboard and complex data is stored as a reference that the pasting application resolves with a content provider. Copying and pasting work both within an application and between applications that implement the framework.
In this tutorial, you will learn the following:
- Overview of Android Clipboard
- An Example of Android Clipboard – Copy and Paste Text in kotlin.
Android Clipboard Framework
The clip object can take one of three forms:
Text
Returns a ClipData object whose single ClipData. Item object contains a text string.
URI
newUri(resolver, label, URI)
Returns a ClipData object whose single ClipData.Item object contains a URI.
Intent
Returns a ClipData object whose single ClipData. Item object contains an Intent.
Some Important Points about Android clipboard
- The clipboard holds only one clip object at a time. When an application puts a clip object on the clipboard, the previous clip object disappears.
- If You want to allow paste data in your app, then you don’t need to handle all types of data. You can example the clipboard data, before giving an option to app users.
- Clip object also contains Metadata, which has what MIME type or types are available. This Metadata helps you handle data.
- If you have an application that primarily handles text, you may want to ignore clip objects that contain a URI or Intent.
Let’s Build Android Clipboard – Copy and Paste Text Example in Kotlin
In this tutorial, you will learn How to store simple text data in Clipboard and get the value.
Step 1. Create a new project “ Build Your First Android App in Kotlin“
Step 2. In res layout file “activity_main.xml” – Add following code in the layout file
In the User interface using 2 Buttons – One button for copy, the text from EditText and another one paste the test in TextView.
Step 3. Open the “MainActivity.kt” and add following code
Handling the action on click button methods which mentioned in the XML file and showing action information in TOAST.
Step 4. Now Run the application, in an emulator or On your Android device
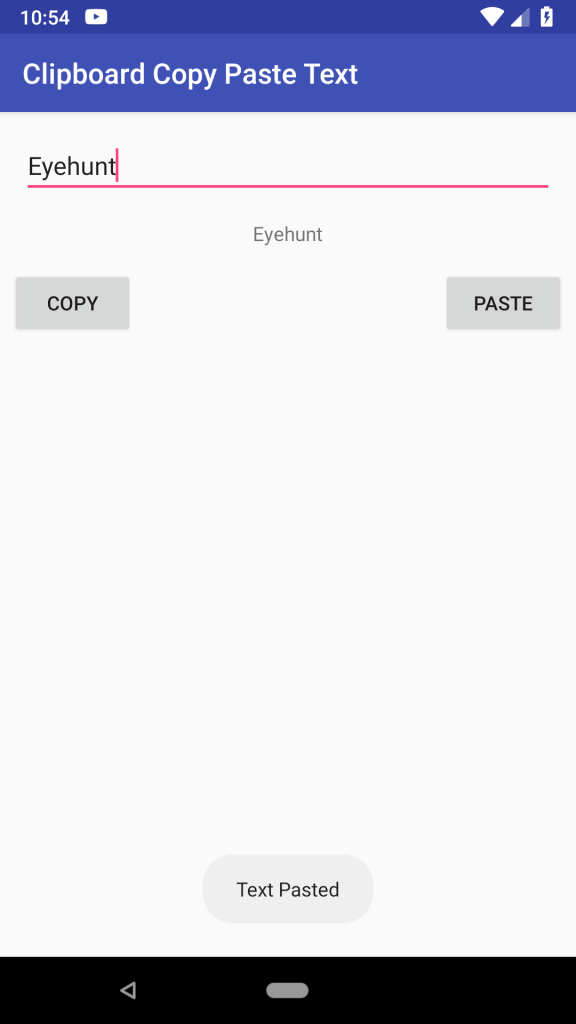
Output screenshot Android Clipboard – Copy and Paste Text
Download source code Android Clipboard Text- Copy and Paste
Do comment if you have any doubt and suggestion on this tutorial.
Note: This example (Project) is developed in Android Studio 3.1.3. Tested on Android 9 ( Android-P), compile SDK version API 27: Android 8.0 (Oreo)
Degree in Computer Science and Engineer: App Developer and has multiple Programming languages experience. Enthusiasm for technology & like learning technical.
Источник
Android Clipboard with Examples
In android, Clipboard is a framework that is useful for copying and pasting the different types of data such as text strings, images, binary stream data, and other complex data types.
Generally, the android Clipboard framework will store the simple text data directly in the clipboard and the complex data is stored as a reference that the pasting application resolves with a content provider.
In android, the clipboard copying and pasting works within an application and between the applications that implement the framework.
To use the android clipboard framework, we need to put the data into a clip object, and then put the clip object on the system-wide clipboard.
The clip object in android can take one of three forms to copy and paste data in android applications.
| Clip Data Form | Description |
|---|---|
| Text | It’s a text string. We can put the string directly into the clip object, and then put the clip object on the clipboard. To paste the string, we can get the clip object from the clipboard and copy the string to our application’s storage. |
| URI | It represents any form of URI and it’s primarily for copying the complex data from a content provider. To copy the data, we need to put a Uri object into a clip object, and then put the clip object onto the clipboard. To paste the data, we need to get the clip and Uri objects, resolve it to a data source such as a content provider, and copy the data from the source into our application’s storage. |
| Intent | To copy data, we need to create an Intent object, put it into a clip object, and then put the clip object onto the clipboard. To paste the data, we need to get the clip object and then copy the Intent object into our application’s memory area. |
In android, the clipboard can hold only one clip object at a time. When an application puts a clip object on the clipboard, the previous clip object disappears.
To use the clipboard in our applications, we need to create an instance of ClipboardManger class by calling the getSystemService() method.
Following is the syntax of creating an instance of ClipboardManager by calling the getSystemService() method.
If you observe above code snippet, we created an instance of ClipboardManager by calling getSystemService() method.
Android Copying Data to Clipboard
As discussed, to copy the data to clipboard we need to create an instance of ClipData object by calling the respective type of data method of ClipData class. In case if it is text type, then newPlainText method will be called, and add the finished ClipData object to the ClipboardManager object using the setPrimaryClip method.
Following is the code snippet of copying the text data to clipboard in android applications.
ClipboardManager clipboardManager ;
ClipData clipData ;
String txtcopy = «Welcome to tutlane» ;
clipData = ClipData.newPlainText( «text» ,txtcopy);
clipboardManager .setPrimaryClip( clipData );
If you observe above code snippet, we copied text type of data to ClipData object and added ClipData object to the ClipboardManager object using setPrimaryClip method to copy the data to clipboard.
Android Pasting Data from Clipboard
As described previously, you paste data from the clipboard by getting the global clipboard object, getting the clip object, looking at its data, and if possible copying the data from the clip object to your own storage.
As discussed, to paste the data from clipboard we need to create an instance of ClipData object to get the clip data from ClipboardManager object using the getPrimaryClip() method. If data available, get the data from clip data using ClipData.Item object. After that copy its text to your own storage using getText().
Following is the code snippet to pasting the data from the clipboard in android applications.
ClipData pData = clipboardManager .getPrimaryClip();
ClipData.Item item = pData.getItemAt( 0 );
String txtpaste = item.getText().toString();
If you observe above code snippet, we are getting the clip data from ClipboardManager object using getPrimaryClip() method. After that, we are getting the data from ClipData object using ClipData.Item and getText() method.
Now we will see how to use the clipboard for copying and pasting text type data in the android application with examples.
Android Clipboard App Example
Following is the example of copying the text type data into the clipboard from edittext on button click and pasting the clipboard data into another edittext control on button click in android application.
Create a new android application using android studio and give names as ClipboardExample. In case if you are not aware of creating an app in android studio check this article Android Hello World App.
Once we create an application, open activity_main.xml file from \res\layout folder path and write the code like as shown below.
activity_main.xml
xml version= «1.0» encoding= «utf-8» ?>
LinearLayout xmlns: android = «http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
android :orientation= «vertical» android :layout_width= «match_parent»
android :layout_height= «match_parent» >
TextView
android :id= «@+id/fstTxt»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :layout_marginTop= «150dp»
android :text= «Enter Text to Copy»
/>
EditText
android :id= «@+id/txtCopy»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :text= «Welcome to Tutlane»
android :ems= «10» >
EditText >
Button
android :id= «@+id/btnCopy»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :text= «Copy Data to Clipboard»/>
TextView
android :id= «@+id/secTxt»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :text= «Show Copied Data»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
/>
EditText
android :id= «@+id/txtShow»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :ems= «10»/>
Button
android :id= «@+id/btnShow»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :text= «Show Clipboard Data»/>
LinearLayout >
Now open your main activity file MainActivity.java from \java\com.tutlane.clipboardexample path and write the code like as shown below
MainActivity.java
package com.tutlane.clipboardexample;
import android.content.ClipData;
import android.content.ClipboardManager;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity <
private EditText ctxt ;
private EditText ptxt ;
private Button btncpy ;
private Button btnpst ;
private ClipboardManager clipboardManager ;
private ClipData clipData ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) <
super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout. activity_main );
ctxt =(EditText)findViewById(R.id. txtCopy );
ptxt = (EditText)findViewById(R.id. txtShow );
btncpy = (Button)findViewById(R.id. btnCopy );
btnpst = (Button)findViewById(R.id. btnShow );
clipboardManager = (ClipboardManager)getSystemService(Context. CLIPBOARD_SERVICE );
btncpy .setOnClickListener( new View.OnClickListener() <
@Override
public void onClick(View v) <
String txtcopy = ctxt .getText().toString();
clipData = ClipData.newPlainText( «text» ,txtcopy);
clipboardManager .setPrimaryClip( clipData );
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), «Data Copied to Clipboard» , Toast. LENGTH_SHORT ).show();
>
>);
btnpst .setOnClickListener( new View.OnClickListener() <
@Override
public void onClick(View v) <
ClipData pData = clipboardManager .getPrimaryClip();
ClipData.Item item = pData.getItemAt( 0 );
String txtpaste = item.getText().toString();
ptxt .setText(txtpaste);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), «Data Pasted from Clipboard» ,Toast. LENGTH_SHORT ).show();
>
>);
>
>
If you observe above code snippet, we used ClipboardManager, ClipData, ClipData.Item objects to copy a data into clipboard and paste a data from clipboard based on our requirements.
Output of Android Clipboard App Example
When we run above program in android studio we will get the result like as shown below.
If we enter text in the first edittext and click on Copy Data to Clipboard button, the text will be copied to the clipboard and when we click on Show Clipboard Data, the clipboard data will be pasted into second edittext control.
This is how we can use clipboard framework in android applications to copy and paste the data based on our requirements.
Источник
Android TextView Copy Paste Using Clipboard
Android Tutorial
In this tutorial, we’ll implement the copy-paste feature on a TextView in our Android Application.
At the end of this article, you’d be able to copy a text to the Android System’s Clipboard and then paste that Clipboard data.
Andorid Clipboard – Copy Paste
You must have noticed that EditText has a built in Clipboard Manager for Copy Paste functionality.
But a TextView doesn’t. So in order to allow Copy Pasting TextViews, we need to register the ContextMenu.
Hence in order to receive the menu events, we need to registerForContextMenu .
Once this is done, you can long-press on the TextView to display the menu.
But where’s the menu?
The menu is created in the onCreateContextMenu() method.
The menu items actions are set in the onContextItemSelected method.
Copying Text To Clipboard
It’s easy to copy TextView text onto the Clipboard. You just need to set the ClipData type as newPlainText and pass the string.
Pasting Text To Clipboard
Now that you have copied the text onto the Clipboard, just paste it using the following piece of code:
Here we’re pasting the first data from the Clipboard. If we have multiple copied texts, they can be pasted using pasteData.getItemAt(1) and so on.
Now let’s jump onto the implementation part of this article.
In the next section, we’ll be developing a simple Android Application in which you can copy-paste text from one TextView to another.
Project Structure
Android Textview Copy Paste Project Structure
The code for the activity_main.xml layout is given below:
The code for the MainActivity.java class is given below:
getItemCount() is used to get the items present in the clipboard.
You can also set the clipboard data to be copied in the onContextItemSelected copy menu item action.
Output
The output of the above application in action is given below:
Android Textview Copy Paste Output
That sums up this tutorial. Can you add a Cut Menu option? Post your code snippets in the comment sections!
Download Links
You can do ahead and download the full source code from the link below or visit our Github Repository.
Источник