- Android-x86
- Run Android on your PC
- Installation
- Introduction
- Step by Step
- Upgrade
- Auto Installation
- Auto Update
- Other boot options
- Advanced
- Create a bootable USB stick for Android-x86
- Multi-Boot
- Updated (2010)
- Issues
- VMware
- Android-x86
- Advertisement
- Advertisement
- Downloads
- Description
- Android-x86 Review
- Documentation of Operating Systems and Developers
- Android operating system
- Android OS
Android-x86
Run Android on your PC
Installation
Introduction
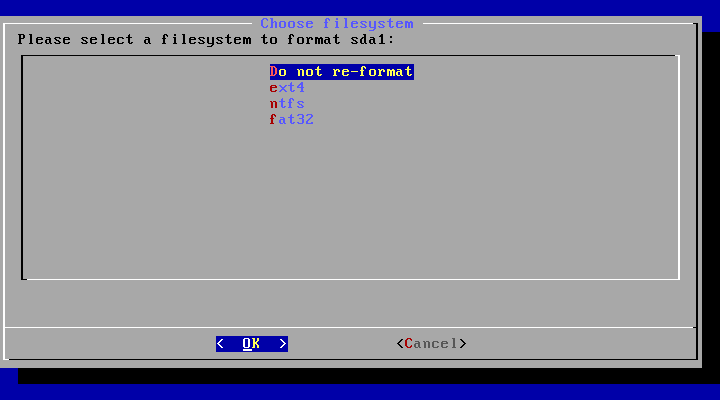
In particular, you can install Android-x86 to an NTFS filesystem to co-exist with Windows. See the Advanced Section for more details.
Step by Step
- Download an iso image from a mirror site. Usually you should just use the latest image.
- Burn the iso image to cdrom, or create a bootable USB disk (recommended). See the Advanced Section for details.
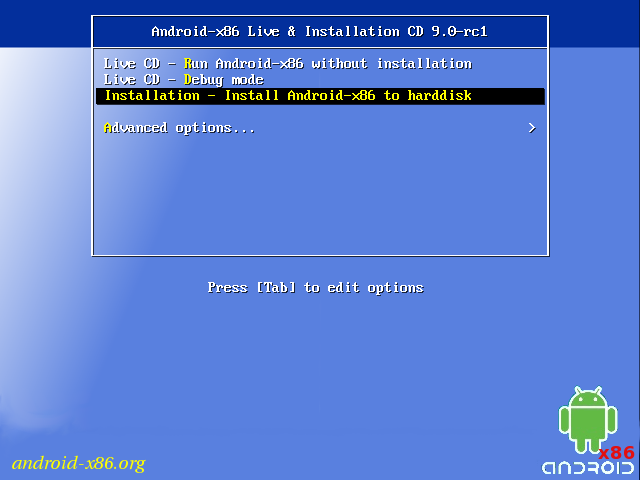
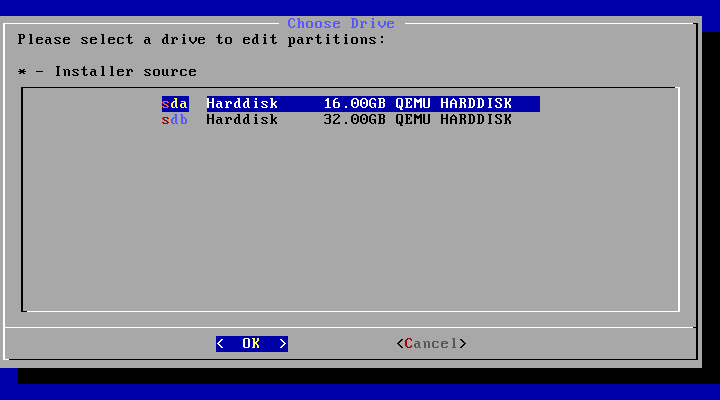
- Boot from the Android-x86 installation CD/USB, choose the ‘Install Android-x86 to harddisk’ item, as shown below:
Upgrade
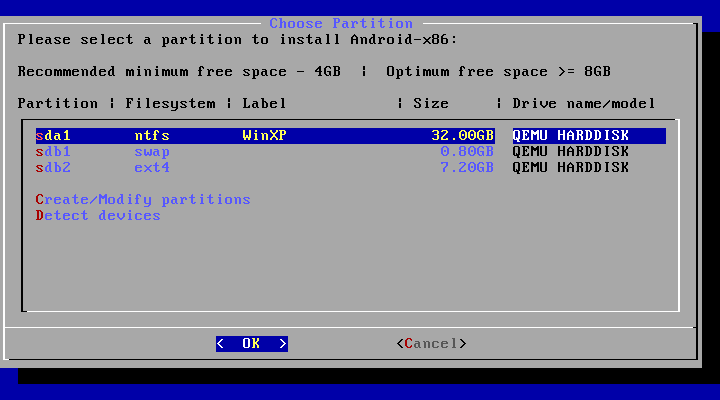
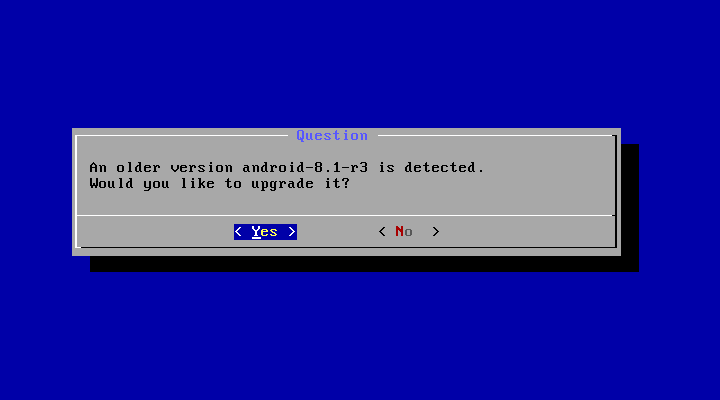
You may upgrade an older Android-x86 installation by the installer. Just select the partition containing the older installation. The installer will prompt if you’d like to upgrade it:
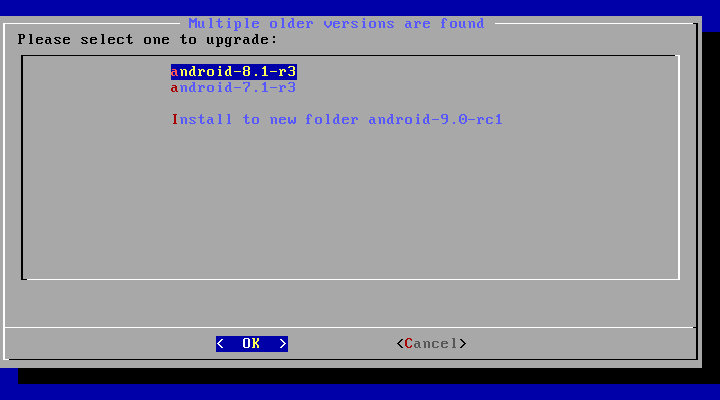
If there are multiple older versions in the same partition, the installer will ask which version to upgrade:
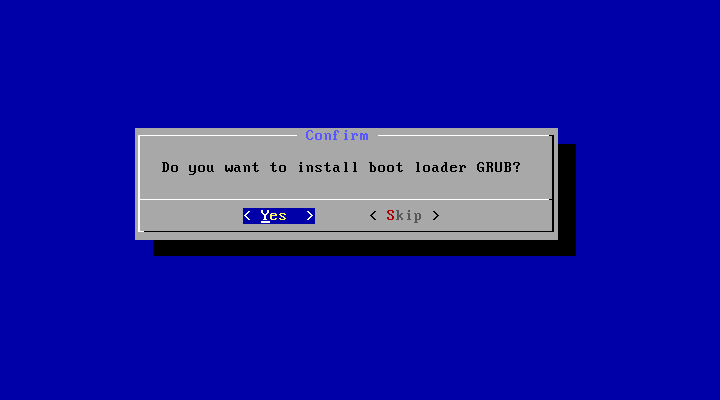
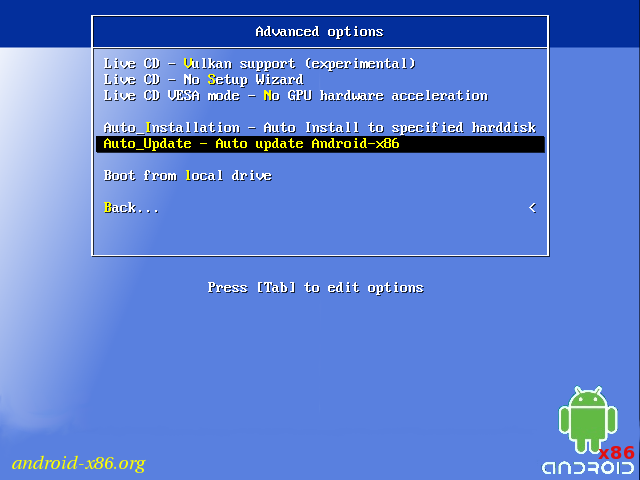
Auto Installation
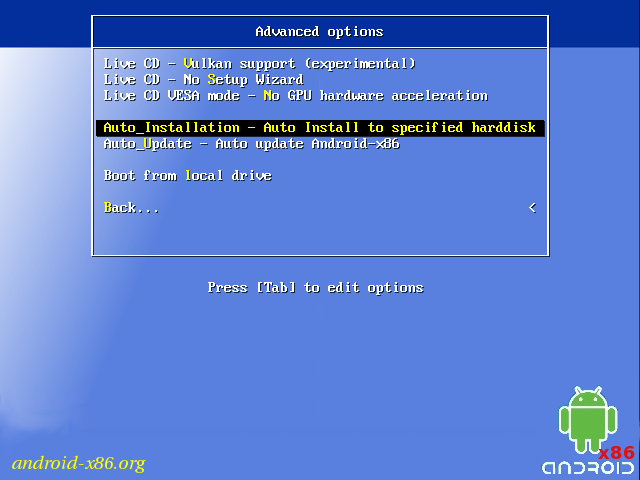
If you want to use Android-x86 as the only OS in your device, you may choose «Auto Installation» under the «Advanced options».
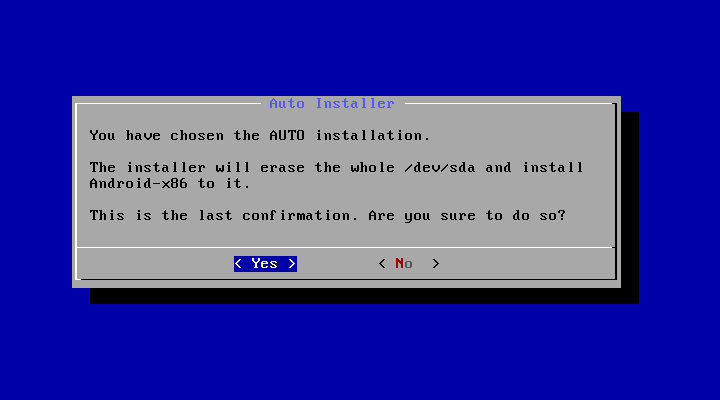
The installer will prompt you to confirm:
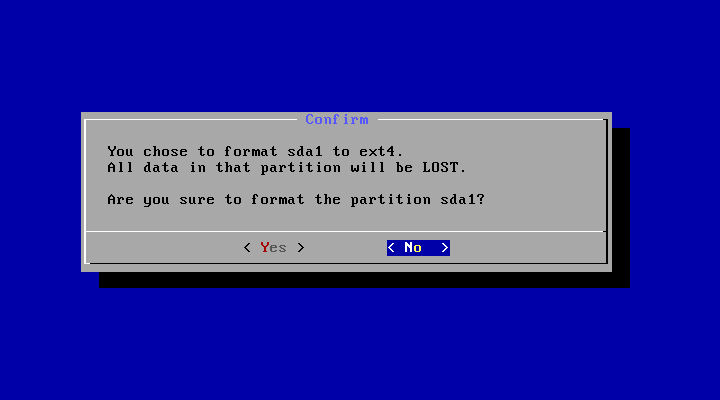
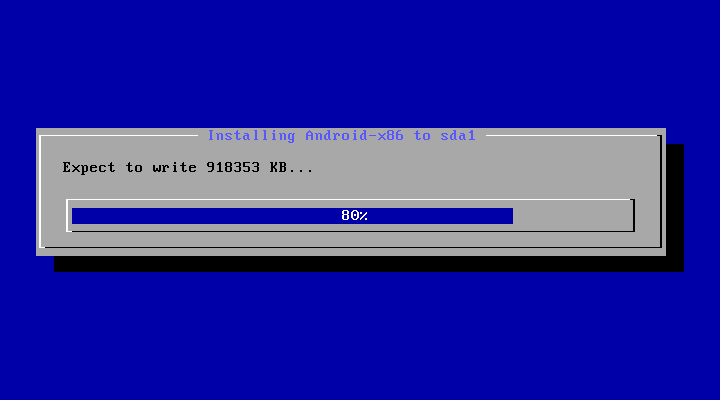
After you select ‘Yes’, the installer will erase the whole content of the hard disk, partition and install Android-x86 to it.
If you have multiple hard drives, the installer will let you choose which one to use. Be careful to choose the correct one.
Auto Update
By choosing «Auto Update» under the «Advanced options», the installer could update an older installation automatically.
In this mode, the installer searches a partition named «Android-x86» or the first ext4 partition, and update the older installation in it automatically. If no such a partition is found, the auto update mode will be cancelled.
Other boot options
- Live CD — Run Android-x86 without installation
The item means to boot Android-x86 directly. This is useful to check if your hardware is compatible with Android-x86 quickly. All data is stored in RAM (tmpfs) and will lose after poweroff.
Live CD — Debug mode
See the debug howto for more details.
Live CD — Vulkan support (experimental)
Enable the experimental Vulkan support. Not all GPUs support it.
Live CD — No Setup Wizard
Skip the Setup Wizard. It’s useful if you want to test some apps quickly in live mode.
Live CD VESA mode — No GPU hardware acceleration
Disable GPU hardware acceleration. If you encounter black screen after booting, you may try this mode to see if it’s bootable.
Advanced
Create a bootable USB stick for Android-x86
There are several tools which could be used to create a bootable USB stick for Android-x86. The following tools are available for Windows users:
- Win32 Disk Imager — see demo video.
- UNetbootin — see demo video.
- Rufus — see demo video.
- Linux Live USB Creator (LiLi) — Obsolete software, but used to officially support Android-x86 until v4.4.
For Linux users, just use the standard dd command like:
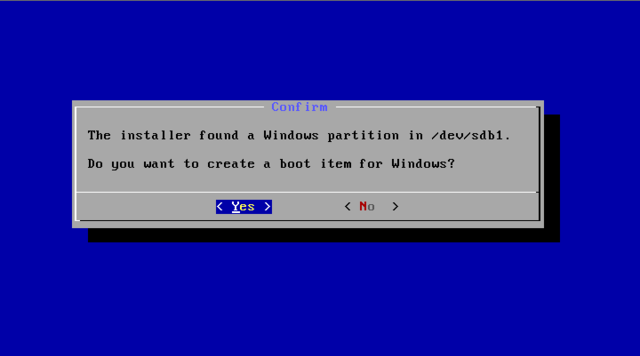
Multi-Boot
To boot other operating systems, you have to add items for them to /grub/menu.lst. For example, to boot Windows, add the following:
This assumes Windows is installed to the first partition of the first hard disk. Alternatively, you need to change rootnoverify to the appropriate value. See Grub Manual for details.
Updated (2010)
Issues
VMware
You have to change your virtual disk type to be IDE because the default type in VMware is SCSI, and Android-x86 kernel is not configured to support SCSI. You can follow these steps:
- Create a virtual machine.
- Edit virtual machine settings after the virtual machine created.
- Choose the hard disk and remove it.
- Add a hard disk to create a new virtual disk, then you can choose IDE as your virtual disk type.
- When finished, you can install android-x86 normally.
Источник
Android-x86
Advertisement
Advertisement
Downloads
Description
Android-x86 (formely known as «patch hosting for android x86 support») is a free, open source project that allows you to run Androidв„ў on x86 operating systems.
It is a port of the well-known «Android Open Source Project» led and offered for free.
Trademark Note: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google Inc. Android is a trademark of Google Inc. Please note that Android-x86 project is not affiliated with Google Inc or other registered trademarks such as Androidв„ў.
Android-x86 Review
The new Android-x86 software helps people use the Android operating system on a laptop or desktop computer. Though the software has its merits, it is also somewhat flawed. Let’s dig into the details of Android-x86.
Who It is For
The Android-x86 software allows the mobile Google Androidв„ў operating system to function on devices that are powered by AMD x86 / Intel processors rather than RISC-based ARM chips. Those who would like a single Linux-based operating system to run on all of their devices will find that Android-x86 is a solid alternative.
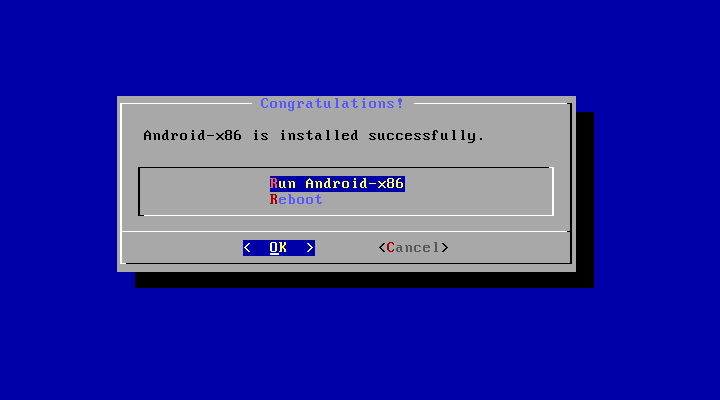
The Installation Process
Android-x86 contains two files. The first is the ISO file that can be booted on any device with legacy BIOS. The second is an EFI image that one can be used on contemporary computing devices that have UEFI firmware. Select the one that is appropriate for your hardware. You will be taken to a screen where you can run the software in a live session without actually installing it or choose a direct installation. You can even install Android-x86 onto a USB drive so you have a bootable USB stick at your disposal. Opting for this installation route is quite convenient as it will allow your USB drive to save some of its memory capability. All in all, the Android-x86 installation process is quite easy. The one minor fault with the installation process is that the installer is not capable of formatting ext3 file systems.
Ease of Use
Run Android-x86 on all of your computers and you will likely be fairly impressed with its performance. The software requires that you create / sign into your Google account when first using it on a PC. However, a plan vanilla Android will load if you fail to sign in through a Google account. This allows you to access the world wide web through the standard Android web browser. You will also have to configure your WiFi. When the program is up and running, you will use a ring-shaped mouse-like pointer as the indicator for clicks. Certain navigation functions require that the user holds down a key on the keyboard or click to transition from one desktop to another. Go ahead and access the Google Playв„ў store as well as your Google Chrome / mobile Android settings to populate your PC’s new operating system.
The software features two home screens and six different wallpapers. Both home screens have a Google search box and a voice input icon toward the center of the screen. The bottom of the screen has a see-through dock row with the typical “home”, “return” and “recent apps” buttons. Above this row are five conveniently placed icons.
Benefits
The benefit to running Android on each device is that it allows you to keep all of your apps, settings and Google services aligned. Thankfully Android-x86 makes this happen without too many major obstacles. The new version of Android-x86 is fairly intuitive and easy to learn. It runs much faster than previous versions of Androidв„ў on dedicated hardware. Use it on a variety of computing devices from netbooks to tablets and beyond and you’ll likely be content with its performance Hardware acceleration is now available for Vmware ad Nvidia chips. A new Hal sensor even supports GPS.
Drawbacks
The software’s download page isn’t the easiest to use as it shows earlier versions of the software. Many users have complained that they had to resort to the «release notes web page» to access the download. Some users have reported that there are issues with the software’s suspend and resume features. Others have complained about the software being limited to strictly the Androidв„ў web browser.
In some instances when a live session is occurring, the web browser will fail to start and an error window will pop up. Yet some users have stated that after they rebooted the same hardware, this browser problem goes away. Many users have complained that the app has failed to launch or completely failed to even open at all. Some report that the apps open but crash shortly afterward. If this occurs, go ahead and reboot your computer. It just might provide a temporary fix until Android-x86 developers come up with a permanent solution to this widely reported problem.
The Verdict
Android-x86 should be lauded for its ability to seamlessly run the Android operating system on a laptop or desktop powered by AMD x86 / Intel processors. However, some users will be frustrated with the software’s flaws and unreliability. If you aren’t in any hurry to use your Androidв„ў system on your traditional computers, it might be prudent to wait until the next version of Android-x86 is released.
Источник
Documentation of Operating Systems and Developers
Android operating system
Android OS

The Eclipse IDE with an official plugin is used for the development. The operating system Android for Smartphones is supported by the Open Handset Alliance. Including more than 30 communication provider, equipment and semiconductor manufacturers as well as software companies. Because Android is an open platform in the meaning of the software and product development the source code shall be available completely at a later time and is in opposite with the market leading closed operating systems Symbian, Palm OS and Windows Mobile.
Android include C/C++ function libraries used by different parts of the operating system.
- Surface manager for 2D and 3D even overlay display
- System C library, specialized for Linux-based devices (BSD implementation)
- SGL, 2D graphic system
- 3D libraries, based on OpenGL ES 1.0 APIs with hardware or software accelerated 3D display
- Media libraries for playback and record of audio, graphic and video formats (MPEG4, H.264, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, PNG)
- LibWebCore, Android internet browser
- FreeType, for representing of bitmap and vector fonds
- SQLite, an efficient and slim relational database for all applications
The Android SDK is available for Linux, MacOS and Windows. It contains an emulator with the surface of Android to try applications. After unpacking the SDK the emulator can be found in the subdirectory » oolsemulator.exe» that shows a HTC Smartphone with keyboard.
Standard programs for e-mail, SMS, contacts, calendar, road maps, internet browser and others are preinstalled.
The first Google Android Developer Challenge (ADC) started in April 2008 for engaged programmers to realize and present ideas. Approximately 1,800 programmes were submitted and 20 honoured with a price money under the best 50. Part of the best applications are for example cab4me by combination of Google Maps, GPS signal and a database to send a taxi in the simplest mode by click to the current position on the map. Or GoCart which reads the bar code of goods with the mobile telephone camera and looks over onlineshops and registered shops in the circumference for the best price.
Google creates a sales platform for Smarthone applications with Android Market. At first the market place is provided free of charge. The first Android mobile telephone cames from the taiwanese manufacturer HTC with the T-Mobile G1 smartphone starting at October 22nd, 2008 in the USA and at the beginning of 2009 in Germany. The Android Market was renamed in Google Play on 6th March 2012.
The market research group Gartner, Inc. released a press news about the worldwide market share of smartphone ventors and operating systems on 19th August 2016. In the 2nd quarter 2016, 296.9 million Android units have been sold, this represents a market share of 86.2%. The Android operating system increased his share, in 2nd quarter 2015 the market share was 82.2% with 271.6 million units sold.
Источник