- Monitor your heart rate with Apple Watch
- How to check your heart rate
- When Apple Watch measures your heart rate
- How Apple Watch measures your heart rate
- For best results
- Apple Watch.
- Helping your patients identify early warning signs.
- Heart rate notifications.
- Irregular rhythm notifications.
- Validation of irregular rhythm notification feature.
- ECG app.
- Get the most accurate measurements using your Apple Watch
- Keep your personal information up to date
- Make sure that you earn Move and Exercise credit
- Make sure that Wrist Detection is on
- Check the fit
- Get the most accurate heart rate measurement
- Choose the best workout
- Calibrate your Apple Watch
- What else affects your heart rate reading
Monitor your heart rate with Apple Watch
Learn how Apple Watch measures your heart rate, and get tips for a more accurate reading.
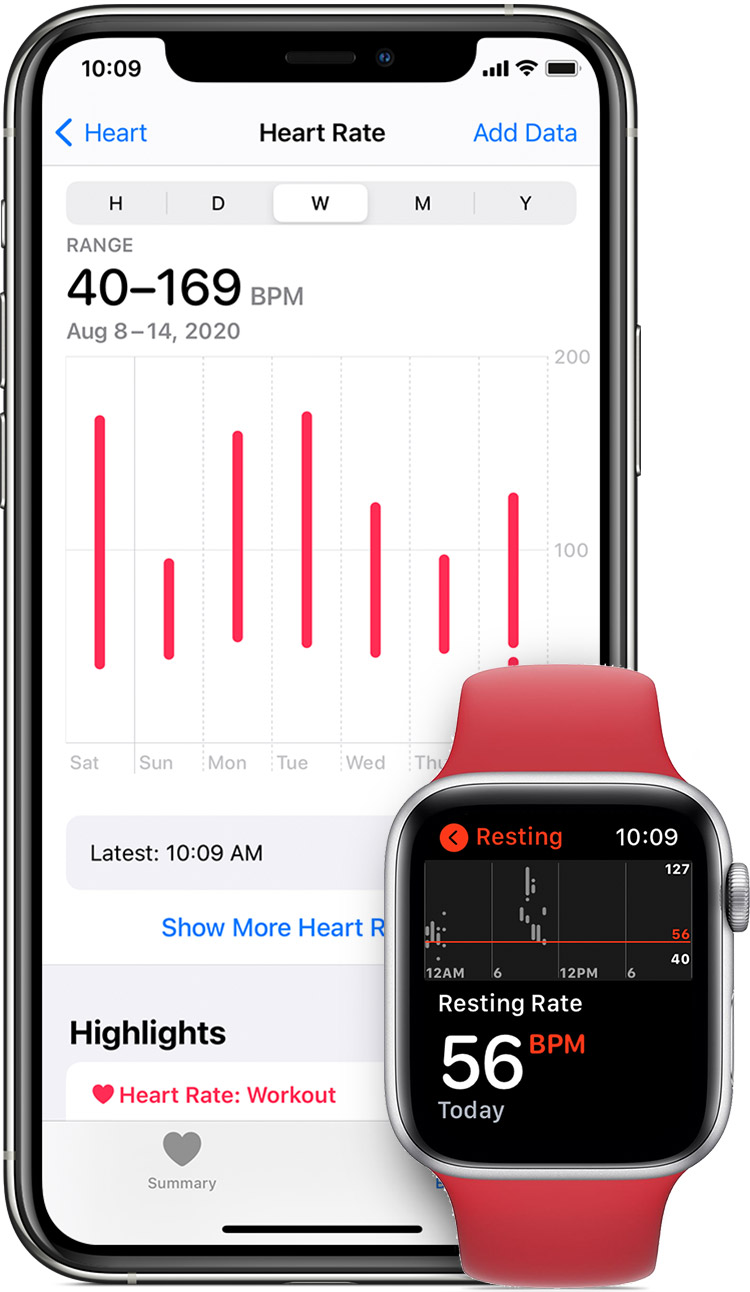
How to check your heart rate
You can check your heart rate any time using the Heart Rate app. Open the app, then wait for Apple Watch to measure your heart rate. You can also view your resting, walking, breathe, workout, and recovery rates throughout the day. To easily open the app, add the Heart Rate complication to your watch face or add the Heart Rate app to the Dock.
You can also turn on heart rate notifications, so you know if your heart rate remains above or below a chosen beats per minute (BPM), or to occasionally check for an irregular heart rhythm.
Irregular rhythm notifications are available only with watchOS 5.1.2 or later. To enable irregular rhythm notifications, the notifications must be available in your country or region and you must be in the country or region where you purchased your device. Learn where irregular rhythm notifications are available.
When Apple Watch measures your heart rate
When you use the Workout app, Apple Watch measures your heart rate continuously during the workout and for 3 minutes after the workout ends to determine a workout recovery rate. If you don’t see your heart rate, check your settings.
This information, as well as other data it collects, helps Apple Watch estimate how many calories you’ve burned. In addition, Apple Watch measures your heart rate throughout the day when you’re still, and periodically when you’re walking (Apple Watch Series 1 or later). Since Apple Watch takes these background readings based on your activity, the time between these measurements will vary. Apple Watch also calculates a daily resting rate and walking average by correlating background heart rate readings with accelerometer data when sufficient background readings are available. You can control which third-party apps have access to your health data from the Health app in Sources.
Some anomalies may appear in the displayed data, resulting in occasional heart rate measurements that are abnormally high or low.
How Apple Watch measures your heart rate
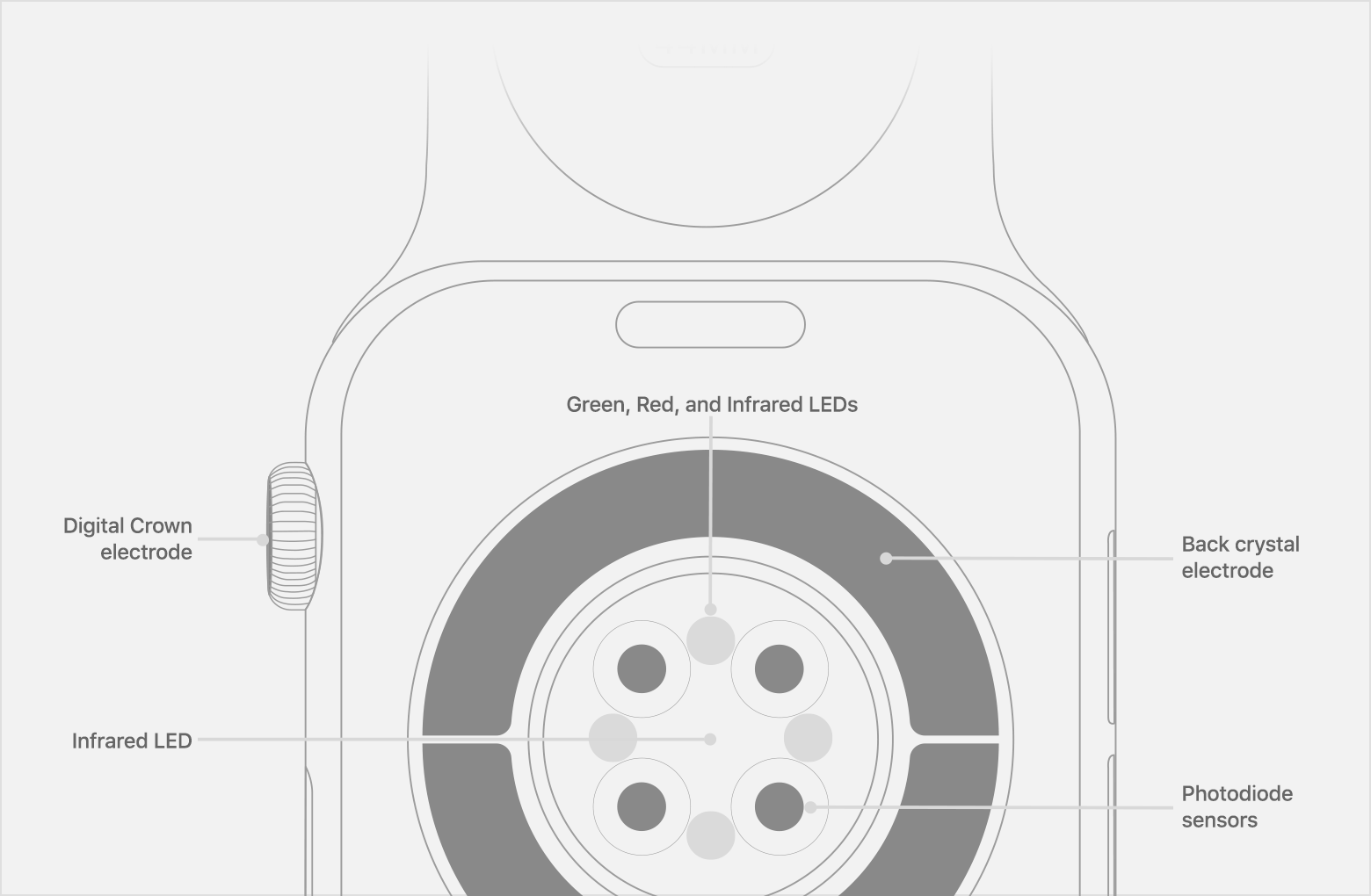
The optical heart sensor in Apple Watch uses what is known as photoplethysmography. This technology, while difficult to pronounce, is based on a very simple fact: Blood is red because it reflects red light and absorbs green light. Apple Watch uses green LED lights paired with light‑sensitive photodiodes to detect the amount of blood flowing through your wrist at any given moment. When your heart beats, the blood flow in your wrist — and the green light absorption — is greater. Between beats, it’s less. By flashing its LED lights hundreds of times per second, Apple Watch can calculate the number of times the heart beats each minute — your heart rate. The optical heart sensor supports a range of 30–210 beats per minute. In addition, the optical heart sensor is designed to compensate for low signal levels by increasing both LED brightness and sampling rate.
The optical heart sensor can also use infrared light. This mode is what Apple Watch uses when it measures your heart rate in the background, and for heart rate notifications. Apple Watch uses green LED lights to measure your heart rate during workouts and Breathe sessions, and to calculate walking average and Heart Rate Variability (HRV).
Apple Watch Series 4, Series 5, Series 6, or Series 7* also have built-in electrodes in the Digital Crown and the back of Apple Watch, which can measure the electrical signals across your heart when used with the Heart Rate app or the ECG app. When you place your finger on the Digital Crown, it creates a closed circuit between your heart and both arms, capturing the electrical impulses across your chest.
To use the electrical heart sensor to measure your heart rate, open the Heart Rate app and place your finger on the Digital Crown. You will get a faster reading with higher fidelity — getting a measurement every second instead of every 5 seconds. You’ll see «ECG» in Heart Rate Context when looking at recorded data for Heart Rate in the Health app. You can also use the electrical heart sensor to take an ECG with the ECG app.
*ECG isn’t supported on Apple Watch SE. The ECG app is currently available only in certain countries and regions. Learn where the ECG app is available.
For best results
Start with a good fit. Even under ideal conditions, Apple Watch may not be able to get a reliable heart rate reading every time for everybody. And for a small percentage of users, various factors may make it impossible to get any heart rate reading at all. But there are things you can do to help Apple Watch get the most consistent and best heart rate readings possible. Learn what else affects your reading.
Источник
Apple Watch.
Helping your patients identify early warning signs.
Apple Watch has powerful apps that make it the ultimate device for a healthy life. Now with new notifications and the ECG app, it can provide you and your patients with important information concerning their heart health.
Heart rate notifications.
Apple Watch checks for unusually high or low heart rates in the background, which could be signs of a serious underlying condition. This could help you and your patients identify situations which may warrant further evaluation.
If a patient’s heart rate is above 120 bpm or below 40 bpm while they appear to have been inactive for 10 minutes, the user will receive a notification. Patients can adjust the threshold bpm or turn these notifications on or off. All heart rate notifications — along with date, time, and heart rate — can be viewed in the Health app on iPhone.
Irregular rhythm notifications.
The irregular rhythm notification occasionally checks for signs of irregular rhythms that may be suggestive of atrial fibrillation (AFib). This feature won’t detect all instances of AFib but may catch something that can provide your patients with an early indication that further evaluation may be warranted.
Irregular rhythm notifications use the optical heart sensor to detect the pulse wave at the wrist and look for variability in beat‑to‑beat intervals when the user is at rest. If the algorithm repeatedly detects an irregular rhythm suggestive of AFib, your patient will receive a notification and the date, time, and beat‑to‑beat heart rate will be recorded in the Health app.
The irregular notification feature has been granted De Novo classification by the FDA for users 22 years and older in the U.S. with no prior history of AFib.
Validation of irregular rhythm notification feature.
In 2017 and 2018, researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine worked with Apple to conduct the Apple Heart Study on the detection of atrial fibrillation, a heartbeat irregularity that is a leading cause of stroke and hospitalization. Over 400,000 Apple Watch users participated and helped validate the ability of wearable technology to aid in the early detection of this condition, which often goes undiagnosed. And the study led to the availability of the irregular rhythm notification that is now on Apple Watch.
ECG app.
With the ECG app on Apple Watch Series 4 or later, patients who experience symptoms such as rapid or skipped heartbeat, or receive the irregular rhythm notification, can capture an ECG and record their symptoms. This real world data can enable you to make more informed and timely decisions regarding further evaluation and care.
The ECG app uses the electrical heart sensor built into the Digital Crown and the back crystal of Apple Watch Series 4 or later to record a single lead ECG similar to a Lead I ECG. The ECG app then provides a result of sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, atrial fibrillation with high heart rate, or poor recording, and prompts the user to enter any symptoms such as rapid or pounding heartbeat, dizziness, or fatigue. The waveform, results, date, time, and any symptoms are recorded and can be exported from the Health app as a PDF to share with a clinician. If the patient notes symptoms that indicate a serious condition, they are prompted to immediately call emergency services.
The updated ECG app with additional rhythm classification received 510(k) clearance from FDA for users 22 years or older.
Источник
Get the most accurate measurements using your Apple Watch
Your Apple Watch uses the personal information that you provide to help calculate metrics for your daily activity. You can further improve its accuracy using these tips.
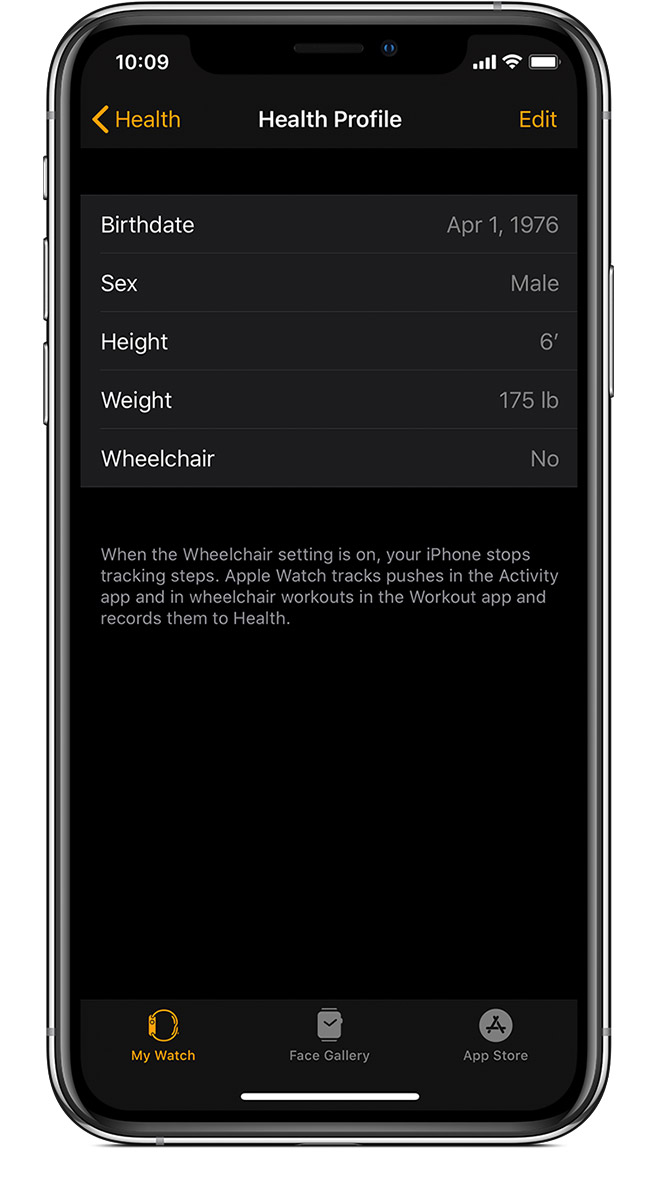
Keep your personal information up to date
Your Apple Watch uses your personal information — such as your height, weight, gender, and age — to calculate how many calories you burn and more.
To update your personal information, open the Apple Watch app on your iPhone. Tap the My Watch tab, then tap Health > Health Profile. Tap Edit, then tap the item that you want to change.
Make sure that you earn Move and Exercise credit
Every full minute of movement that equals or exceeds the intensity of a brisk walk counts toward your daily Exercise and Move goals. With Apple Watch Series 3 or later, your cardio fitness levels are used to determine what is brisk for you. For wheelchair users, this is measured in brisk pushes. Any activity below this level counts only toward your daily Move goal.
To make sure that you earn Exercise credit during walks, allow the arm with your Apple Watch to swing naturally. For example, while walking your pet, let the arm with your watch swing freely while the other holds the leash.
If you need both hands while walking, for example to push a stroller, you can still earn Exercise credit with the Workout app. Open the app on your Apple Watch and tap Outdoor Walk. The Activity app relies on arm motion and an accelerometer to track movement, but the Workout app can use the accelerometer, the heart rate sensor, and GPS.
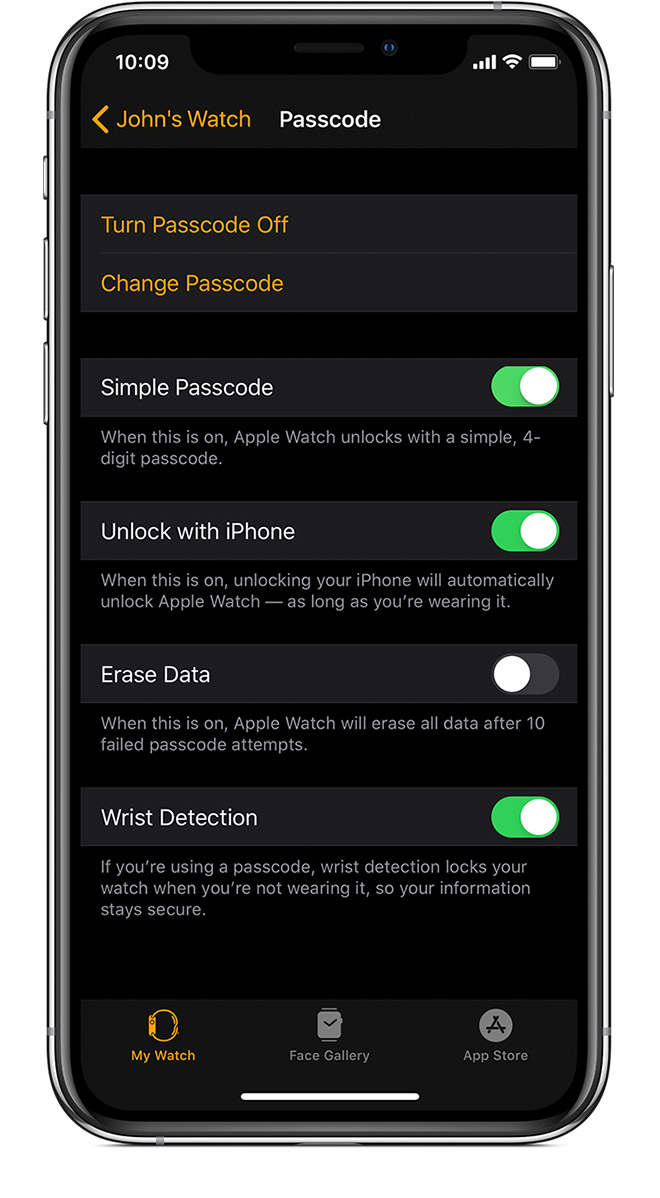
Make sure that Wrist Detection is on
If Wrist Detection is off, you won’t get Stand notifications, and your Apple Watch can’t track your Stand progress. Background heart rate readings (like resting and walking rates) won’t be taken if Wrist Detection is off.
To check the setting, open the Apple Watch app on your iPhone. Tap the My Watch tab, then tap Passcode. Make sure that Wrist Detection is on.
Resting and walking rates are available only on Apple Watch Series 1 or later.
Check the fit
Wearing Apple Watch with the right fit — not too tight, not too loose, and with room for your skin to breathe — keeps you comfortable and lets the sensors do their job.
You might want to tighten your Apple Watch band for workouts, then loosen it when you’re done. In addition, the sensors will work only if you wear your Apple Watch on the top of your wrist.
Get the most accurate heart rate measurement
To get the most accurate heart rate measurement when you use Workout, make sure your Apple Watch fits snugly on top of your wrist. The heart rate sensor should stay close to your skin. Learn about the accuracy and limitations of the heart rate sensor.
If you have an Apple Watch Series 3 or later, set up Cardio Fitness Levels to measure how hard your heart is working during an outdoor walk, run, or hike in the Workout app.
If you turn on Power Saving Mode during a walking or running workout, the heart rate sensor turns off. To see if Power Saving Mode is off or on, open Settings on your Apple Watch, then tap Workout. You can also find this setting in the Apple Watch app on your iPhone.
If you turn off Heart Rate in Privacy settings, you also won’t get a heart rate measurement. To see if Heart Rate is off or on, open the Apple Watch app on your iPhone, then tap Privacy.
Choose the best workout
When you use the Workout app, choose the option that best matches what you’re doing. For example, if you’re running on a treadmill, choose Indoor Run. If you’re doing a workout that isn’t listed, like strength training, choose Other.
Learn about each workout.
Calibrate your Apple Watch
Calibrate your Apple Watch to improve the accuracy of your distance, pace, and calorie measurements. Calibrating your watch can also help it learn your fitness level and stride.
What else affects your heart rate reading
Many factors can affect the performance of the Apple Watch heart rate sensor. Skin perfusion (or how much blood flows through your skin) is one factor. Skin perfusion varies significantly from person to person and can also be impacted by the environment. If you’re exercising in the cold, for example, the skin perfusion in your wrist might be too low for the heart rate sensor to get a reading.
Permanent or temporary changes to your skin, such as some tattoos, can also impact heart rate sensor performance. The ink, pattern, and saturation of some tattoos can block light from the sensor, making it difficult to get reliable readings.
Motion is another factor that can affect the heart rate sensor. Rhythmic movements, such as running or cycling, give better results compared to irregular movements, like tennis or boxing.
If you’re not able to get a consistent reading because of any of these factors, you can connect your Apple Watch wirelessly to external heart rate monitors such as Bluetooth chest straps. Learn how to pair Bluetooth accessories.
Heart rate is one of many factors that Apple Watch uses to measure your activity and exercise. Depending on your workout, it selects the most appropriate inputs for that activity. For example, when you’re running indoors, it also uses the accelerometer. Learn more about how your Apple Watch uses GPS and the heart rate sensor when you use the Workout app.
Источник