- AccountManager
- Авторизация через Google в Android и проверка токена на сервере
- Небольшая подготовка
- Добавляем действие на кнопку
- Необходимые области доступа
- Регистрация нашего приложения.
- Код получения токена
- Проверяем токен на сервере. (PHP)
- Integrating Google Sign-In into Your Android App
- Before you begin
- Configure Google Sign-in and the GoogleSignInClient object
- Check for an existing signed-in user
- Add the Google Sign-in button to your app
- Start the sign-in flow
- Login with Google Using Firebase Authentication in Android Studio (Tutorial)
- How Does It Work? (Video)
- Login with Google Using Firebase in Android Studio (Step by Step)
- Create a new project in Android Studio
- Adding Firebase to Android Project
- Building UI
- Adding functionality
- Running the application
AccountManager
Иногда разработчик хочет отслеживать пользователя. Первый вариант, который приходит в голову — попросить его ввести какие-то данные о себе и сохранить их где-нибудь. Но просить пользователя повторять эту процедуру при покупке нового устройства не самая лучшая идея. Кроме того, вы не можете гарантировать уникальность данных. Второй вариант — запомнить идентификатор телефона. Но пользователи иногда пользуются двумя телефонами, планшетами и т.д. и тут одним идентификатором не обойдёшься. Опять проблема.
Третий вариант – использовать класс AccountManager. С разрешения пользователя, вы можете использовать AccountManager для извлечения имён учетных записей, которые пользователь хранит на устройстве. Имея полученную информацию, вы можете, например, автоматически заполнить форму с адресом электронной почты.
Само устройство может хранить несколько аккаунтов от разных сервисов. Вы можете отфильтровать результат по типам аккаунтов. Например, у Гугла аккаунт имеет тип «com.google», Twitter использует тип «com.twitter.android.auth.login».
Для извлечения информации требуется разрешение:
В приложении вы сначала получаете экземпляр AccountManager через метод get(), а затем можете вызвать список аккаунтов определённого типа через getAccountsByType().
Метод getAccountsByType() возвращает массив учётных записей. Если в массиве более одной учётной записи, то покажите пользователю диалоговое окно с запросом для выбора одного аккаунта.
Объект Account содержит имя учетной записи, для учетных записей Google – это адрес электронной почты, который вы можете использовать для автоматического заполнения полей или в качестве ключа в базе данных и т.д.
В других учётных записях в имени не обязательно может содержаться электронный адрес. Например, это может быть часть электронного адреса или просто имя пользователя.
На эмуляторе скорее всего нет никаких аккаунтов, поэтому лучше проверять на устройстве. В большинстве случаев на телефоне есть аккаунт для Гугла. В логах я проверил количество аккаунтов, а в текстовом поле вывел имя аккаунта, который оказался моим электронным адресом.
Метод getAccounts() выводит все учётные записи, которые есть на устройстве.
На моём устройстве оказалось три учётные записи. Чтобы понять, кому они принадлежат, я заменил account.name на account.toString() и получил следующий результат.
Теперь стало понятно.
Мы рассмотрели только базовый пример работы с AccountManager. На самом деле, у класса много других возможностей. Например, вы можете добавить новую учётную запись и управлять ею.
Источник
Авторизация через Google в Android и проверка токена на сервере
Недавно мне захотелось создать личный проект на андроиде, и основной вопрос был такой: как однозначно идентифицировать пользователя заставляя его делать как можно меньше телодвижений? Конечно же это аккаунт Google. Я пытался пробовать множество примеров в сети — однако API несколько раз обновилось за время своего существования, многие методы не работали, мои вопросы в Google+ по этому поводу либо были вообще никак не восприняты окружением, либо были вроде «Никогда такое не делал».
В этой статье я постараюсь как можно более просто для новичков (вроде меня) описать мой метод авторизации в Google на андроид, получения токена и проверке этого самого токена на сервере.
Небольшая подготовка
Для начала — у вас должны быть установлены Google Play Services в SDK. После их установки можно будет импортировать все необходимые библиотеки. Статья пишется с расчетом на Android Studio — он сам подсказывает, что необходимо импортировать.
У вас должно быть создано активити с кнопкой.
Чтобы было привычнее пользователю можете создать стандартную кнопку Google+ Sing-In
Выглядеть она будет вот так: 
Просто добавьте в ваш Layout:
Добавляем действие на кнопку
Пишем в нашем активити:
Собственно присвоим кнопке действие — вызов интенда выбора аккаунта. Если вы работаете в Android Studio он сам вам подскажет, какие библиотеки нужно импортировать, так что это подробно тут я расписывать не буду.
startActivityForResult(intent, 123); — задает код с которым произойдет возврат. 123 это код возврата, он может быть каким угодно. Это необходимо, когда вы делаете несколько интендов, и вам надо обработать их по разному.
Необходимые области доступа
Обьявите эти переменные в классе. Это необходимые нам области доступа. Первый написано в google: «Позволяет определить аутентифицированного пользователя. Для этого при вызове API необходимо указать me вместо идентификатора пользователя Google+. » Второе разрешение нам необходимо для получения личных данных пользователя (Имя, Фамилия, адрес G+ страницы, аватар), и последнее для получения E-mail. Я посчитал это важным, ведь это вполне неизменный идентификатор для записи в бд.
Регистрация нашего приложения.
Изначально забыл этот пункт — исправляюсь.
Нам необходимо зайти на code.google.com/apis/console создать там проект, зайти в Credentials и создать новый Client ID для OAuth выбрав пункт Installed Application -> Android. Там нам необходимо ввести название нашего пакета и SHA1 сумму нашего ключа.
С этим у меня на самом деле было много проблем решил достаточно костыльным способом.
Нашел debug.keystore в %USERPROFILE%\.android\debug.keystore поместил в папку с проектом и прописал в build.grandle:
После чего нам нужно выполнить команду:
keytool -exportcert -alias androiddebugkey -keystore
/.android/debug.keystore -v -list
Сам keytool можно найти в SDK. Из вывода копируем SHA1 в нужное поле.
Как я понимаю метод временный, и для нормальной работы надо создать нормальный ключ. Но для тестирования этого достаточно.
Код получения токена
Где 123 — ваш код, который вы указали ранее, где AcrivityName — название вашего актитивити. Грубо говоря — мы скармливаем функции получения токена необходимые разрешения и имя аккаунта. И заметьте — это все происходит в фоновом режиме, после чего полученный токен передается в написанную мною функцию reg. Она уже отправляет токен и все необходимые данные на сервер.
Так как разрабатываю недавно, с исключениями пока что беда, если есть предложение — напишите в личку или в комментарии.
Проверяем токен на сервере. (PHP)
Хочу обратить внимание, полученный нами токен имеет тип Online. И действует он лишь 10 минут. Для получения offline токена (чтобы дольше работать с ним с сервера) обратитесь к этой инструкции developers.google.com/accounts/docs/CrossClientAuth
Собственно скармливаем токен в googleapis и забираем полученный JSON ответ.
Источник
Integrating Google Sign-In into Your Android App
To integrate Google Sign-In into your Android app, configure Google Sign-In and add a button to your app’s layout that starts the sign-in flow.
Before you begin
Configure Google Sign-in and the GoogleSignInClient object
In your sign-in activity’s onCreate method, configure Google Sign-In to request the user data required by your app. For example, to configure Google Sign-In to request users’ ID and basic profile information, create a GoogleSignInOptions object with the DEFAULT_SIGN_IN parameter. To request users’ email addresses as well, create the GoogleSignInOptions object with the requestEmail option.
If you need to request additional scopes to access Google APIs, specify them with requestScopes . For the best user experience, on sign-in, only request the scopes that are required for your app to minimally function. Request any additional scopes only when you need them, so that your users see the consent screen in the context of an action they performed. See Requesting Additional Scopes.
Then, also in your sign-in activity’s onCreate method, create a GoogleSignInClient object with the options you specified.
Check for an existing signed-in user
In your activity’s onStart method, check if a user has already signed in to your app with Google.
If GoogleSignIn.getLastSignedInAccount returns a GoogleSignInAccount object (rather than null ), the user has already signed in to your app with Google. Update your UI accordingly—that is, hide the sign-in button, launch your main activity, or whatever is appropriate for your app.
If GoogleSignIn.getLastSignedInAccount returns null , the user has not yet signed in to your app with Google. Update your UI to display the Google Sign-in button.
Add the Google Sign-in button to your app

Optional: If you are using the default sign-in button graphic instead of providing your own sign-in button assets, you can customize the button’s size with the setSize method.
In the Android activity (for example, in the onCreate method), register your button’s OnClickListener to sign in the user when clicked:
Start the sign-in flow
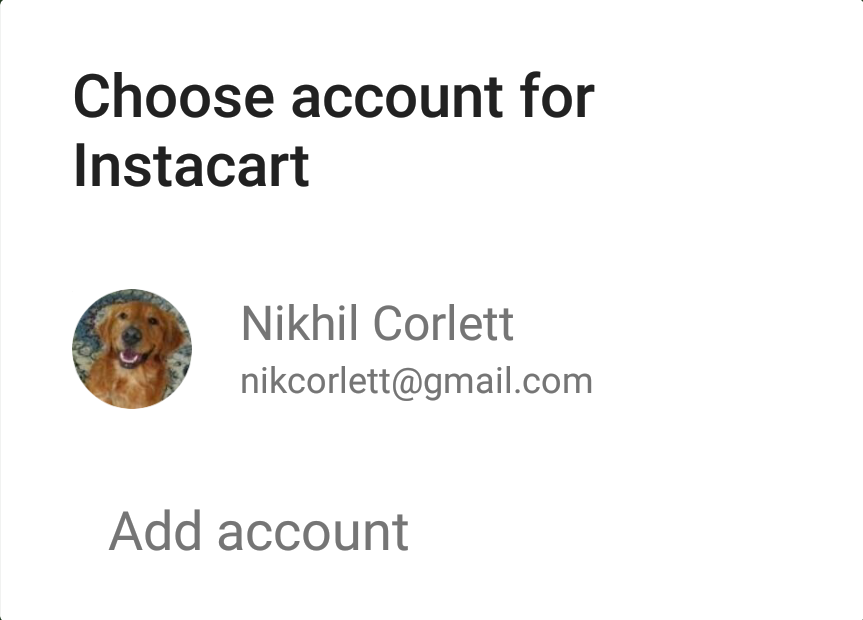
Starting the intent prompts the user to select a Google account to sign in with. If you requested scopes beyond profile , email , and openid , the user is also prompted to grant access to the requested resources.
After the user signs in, you can get a GoogleSignInAccount object for the user in the activity’s onActivityResult method.
The GoogleSignInAccount object contains information about the signed-in user, such as the user’s name.
You can also get the user’s email address with getEmail , the user’s Google ID (for client-side use) with getId , and an ID token for the user with getIdToken . If you need to pass the currently signed-in user to a backend server, send the ID token to your backend server and validate the token on the server.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under the Apache 2.0 License. For details, see the Google Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Источник
Login with Google Using Firebase Authentication in Android Studio (Tutorial)
Do you want to make your users fall in love with your app by creating a smooth UX through login Google account using Firebase? If yes, go ahead to read on.
I don’t need to emphasize what modern users have become — they want the fastest mobile, fastest internet, and fastest pizza delivery.
You might be thinking what’s wrong on asking the critical pieces of information like email, first and last name, and password.
The problem is that users are addicted to the apps that allow instant sign in with Google.
Furthermore, you must understand one fundamental rule in your life to be good at anything. You have to follow the best competitors in the world.
What does it mean?
It means you’ll need to follow the same standards, frameworks, and techniques that the best competitors implement in their apps since they’ve hired the best CRO, ASO and copywriter experts.
TL;DR of the feature is that it:
- Saves time for both the developers and the end-users.
- Gets all the information that you need like: name & emails
How Does It Work? (Video)
More than a billion users are already signed in with Google Play with their Google accounts. When an app authenticates and gets all the information from Google Play.
If a user isn’t signed in with Google Play, it’s essential to sign in to enjoy the app that is an unlikely cause.
Login with Google Using Firebase in Android Studio (Step by Step)
Create a new project in Android Studio
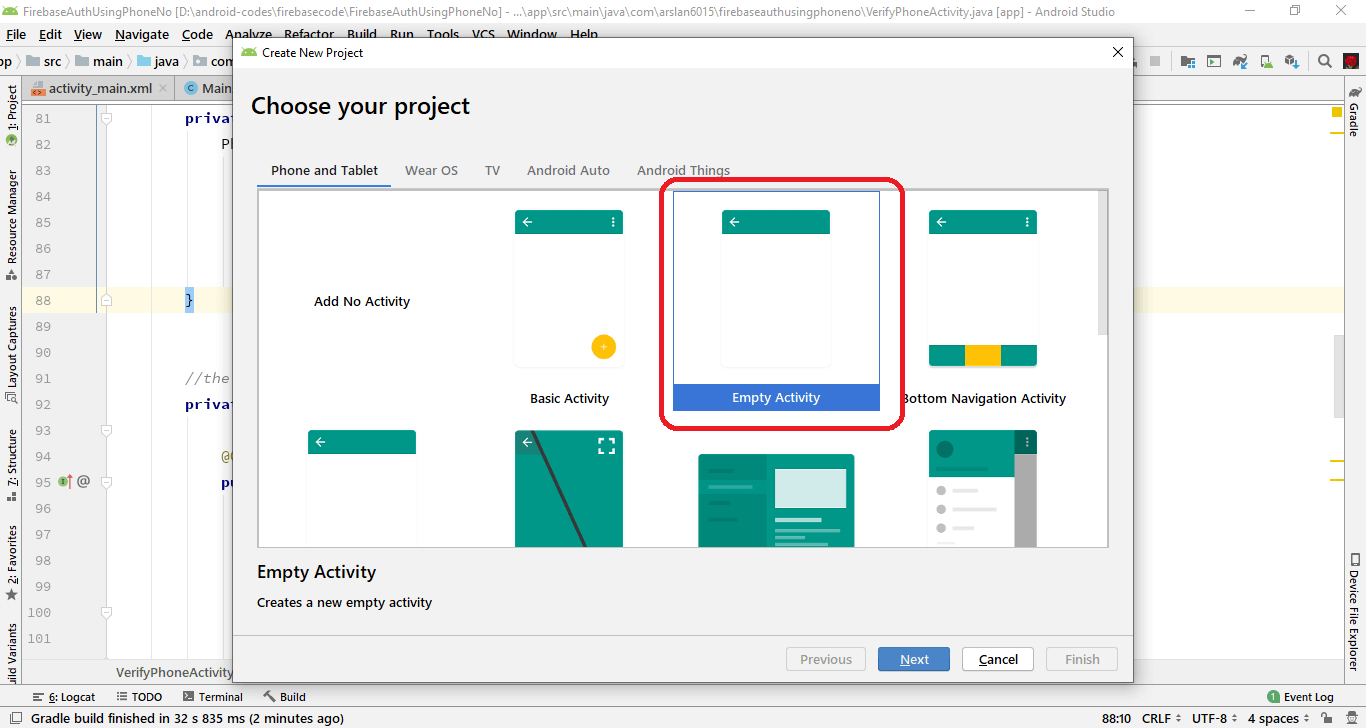
Create a New Project in Android Studio. How? You need to click on File -> New -> New Projects.
Click on Empty Activity -> Next
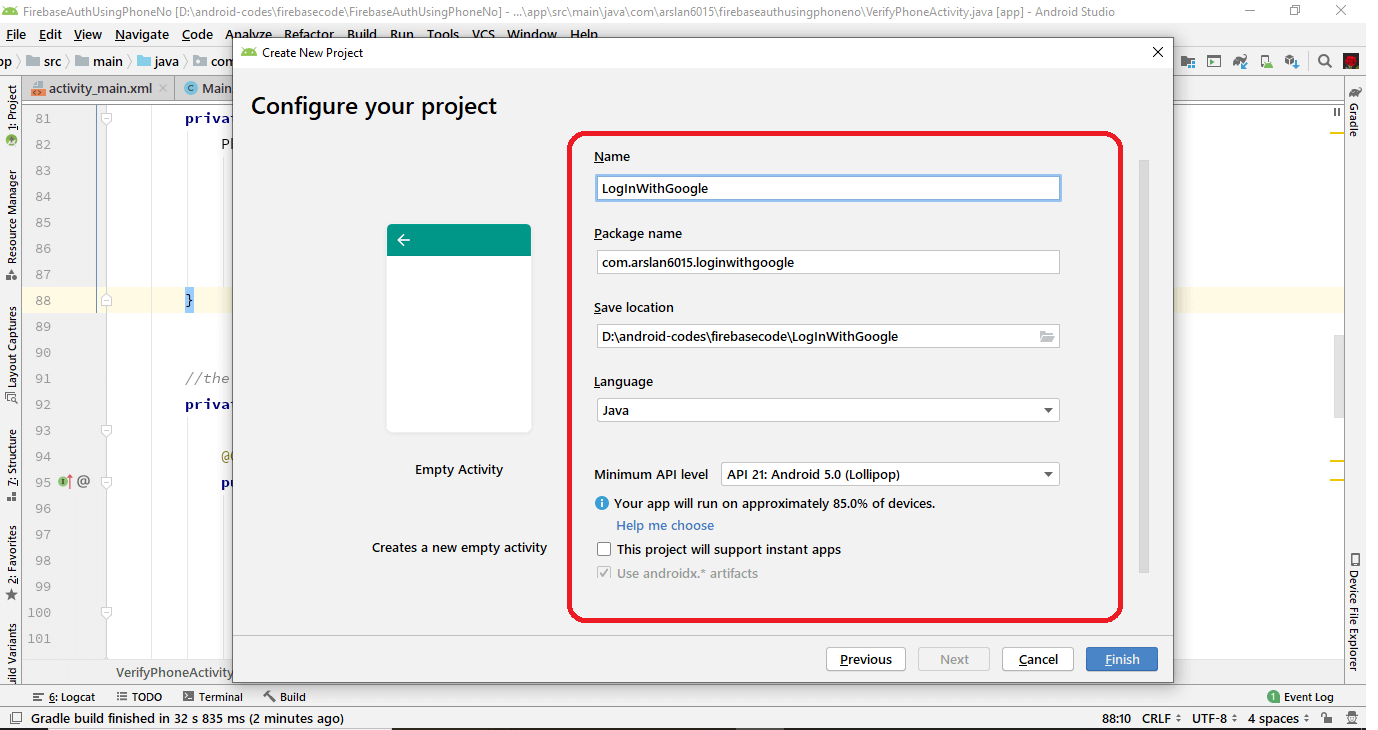
Enter Name -> and Click Next
Adding Firebase to Android Project
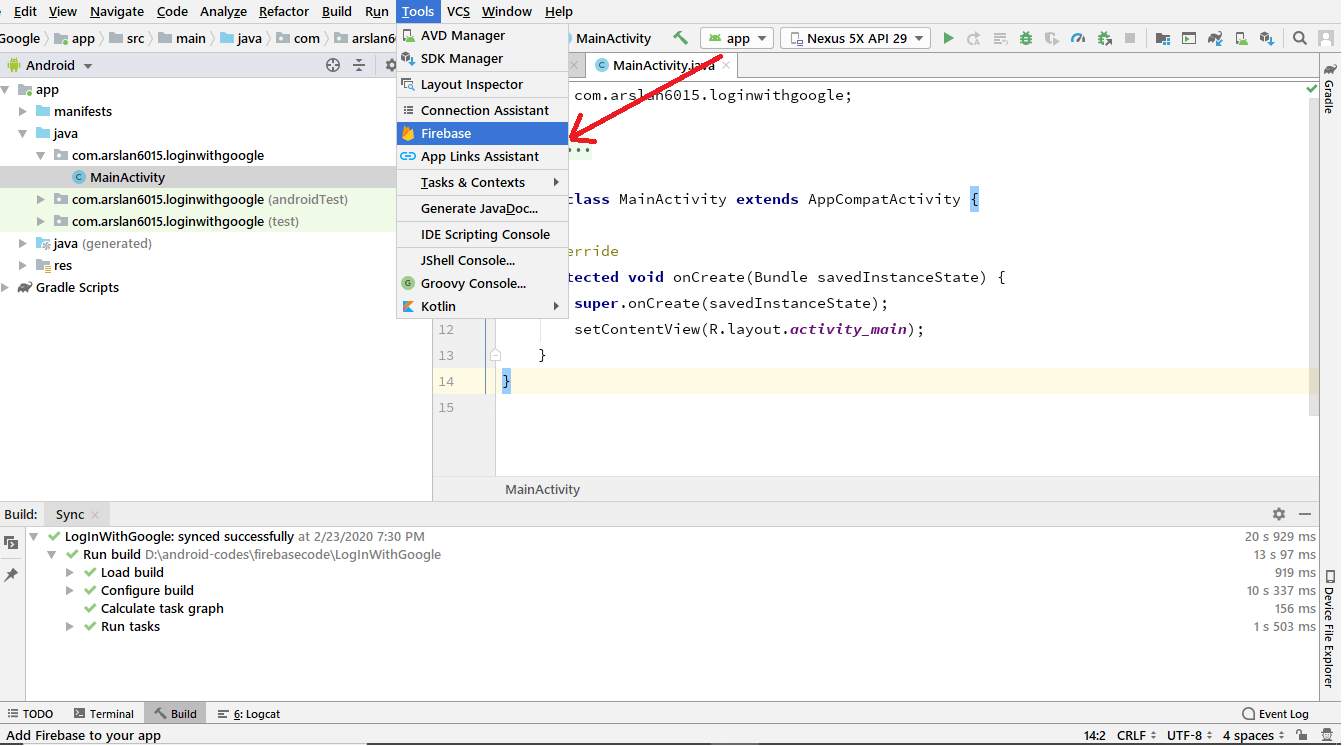
Add Firebase to your project.
by clicking on Tools -> Firebase
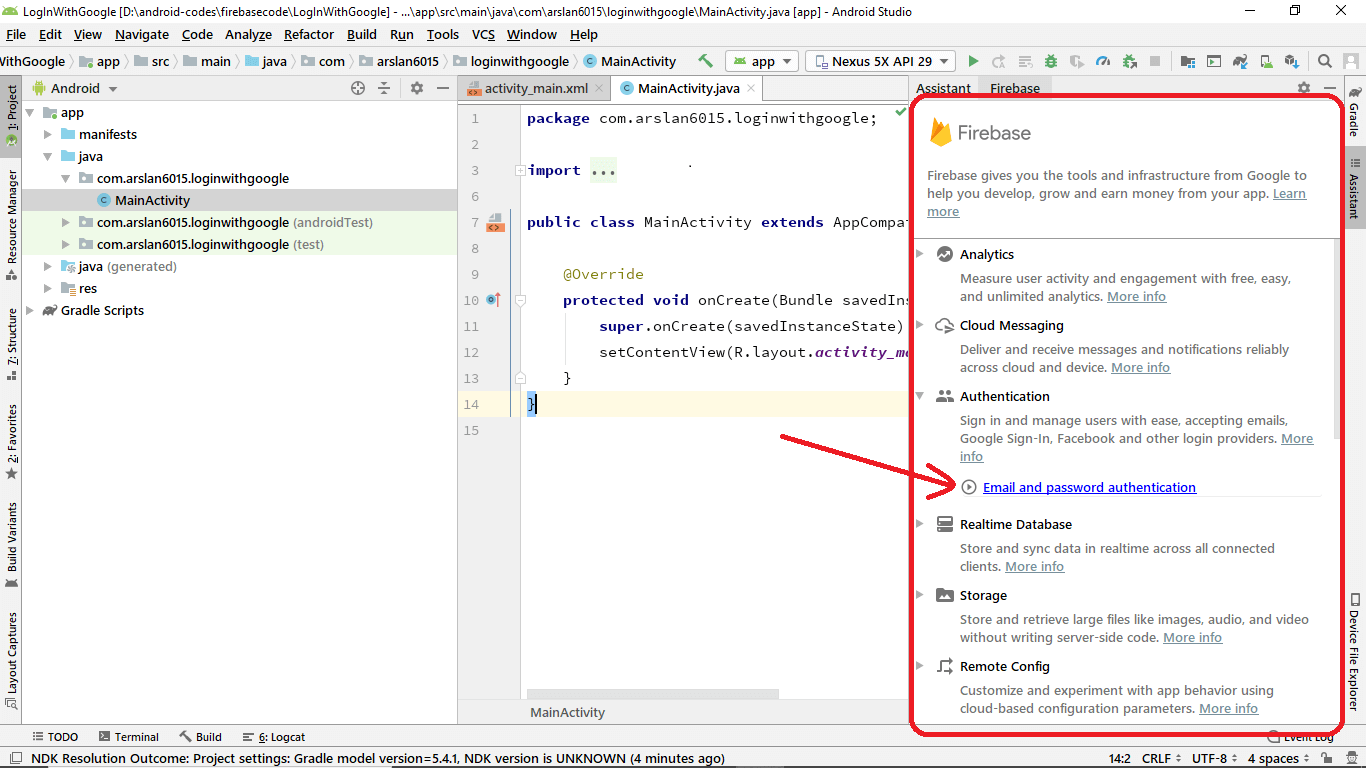
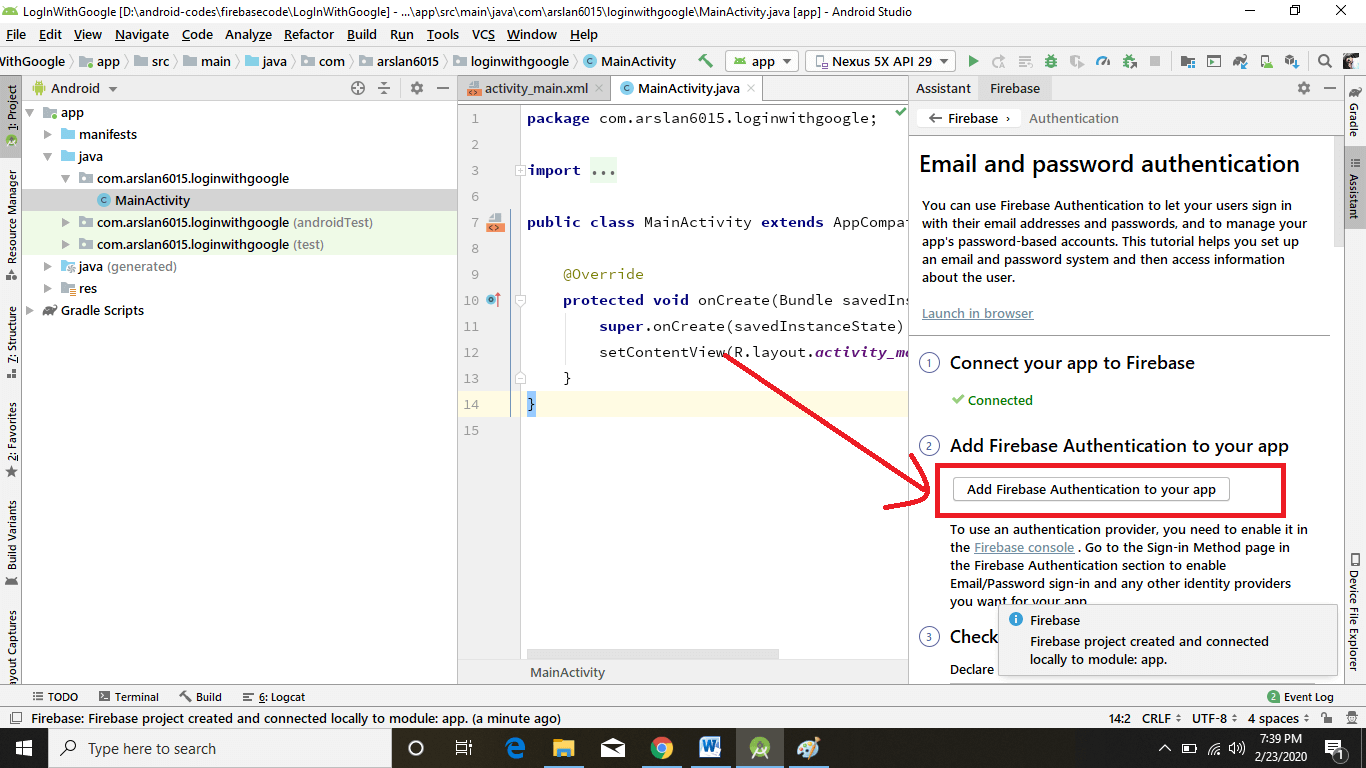
Now Firebase Assistant is open on the right side as you can see in the image below, then click on Email and Password Authentication.
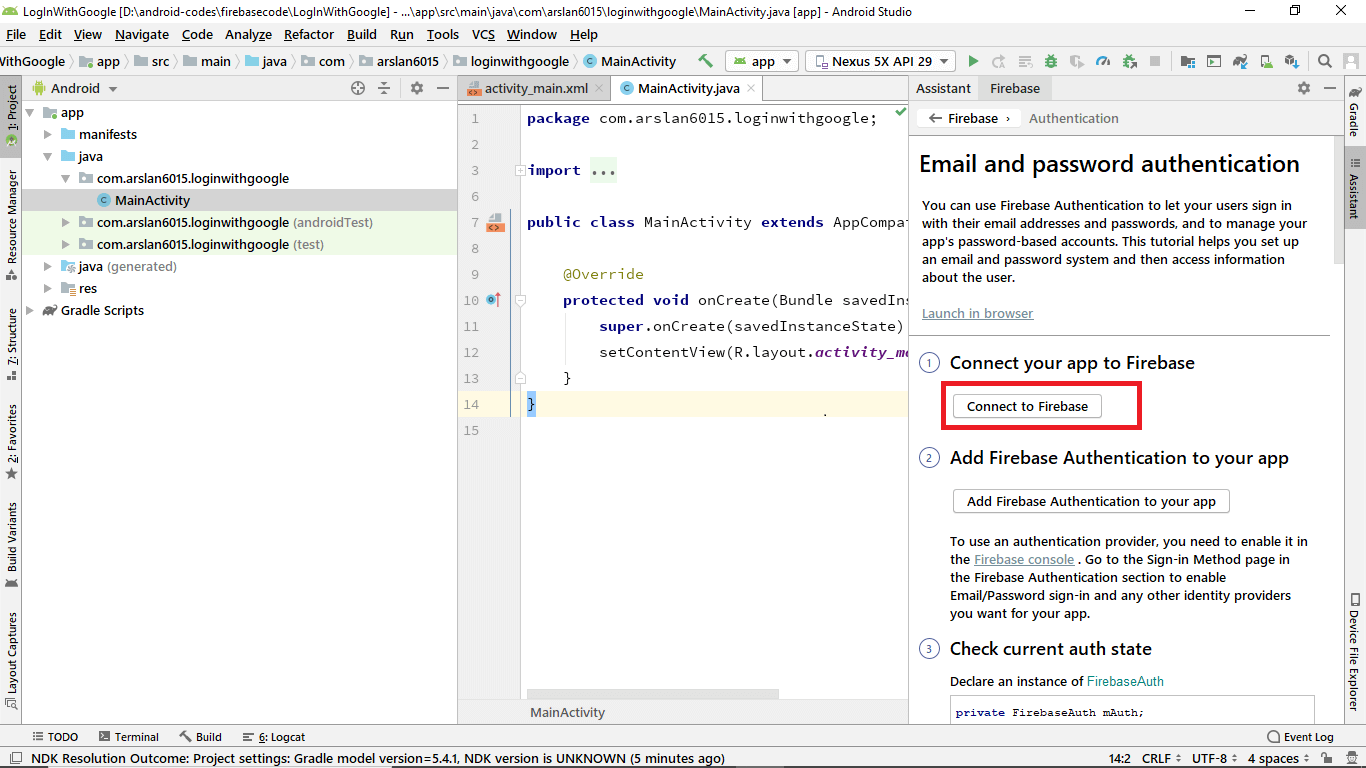
Now click Connect to Firebase
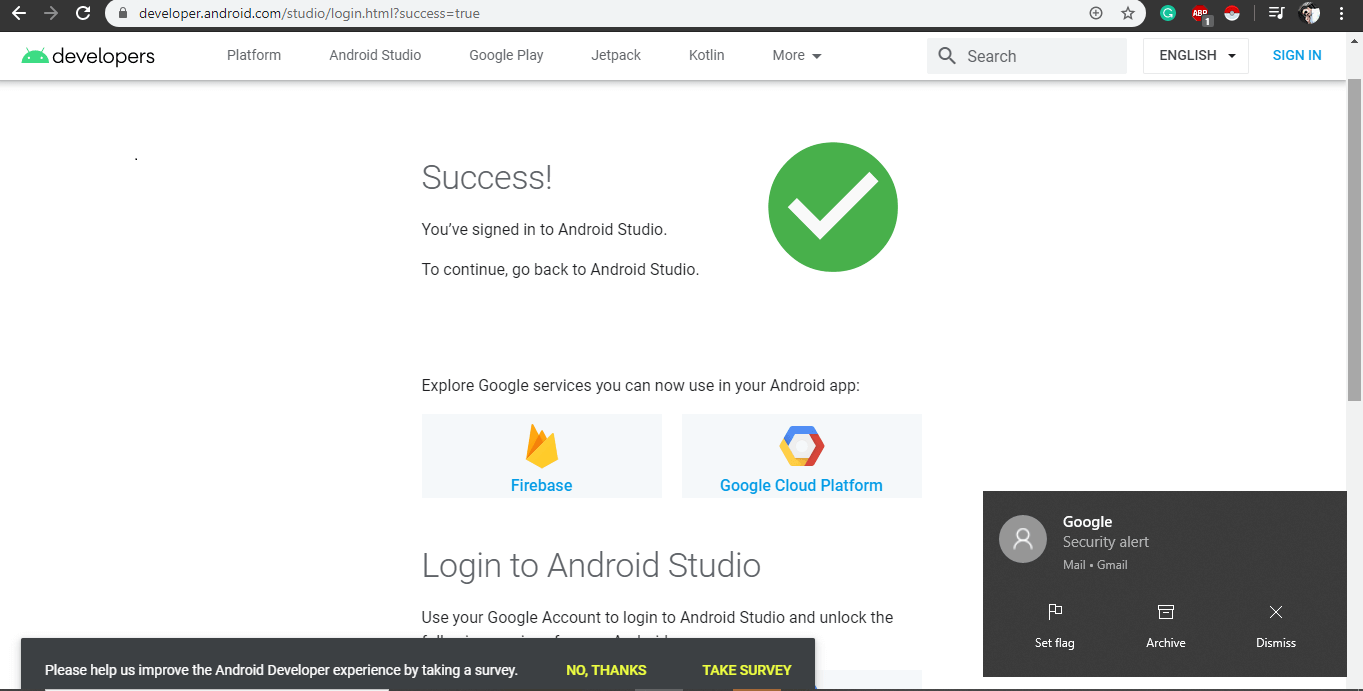
Now if you are not signed with Android Studio then a window appears in the browser where you’ll need sign in to Google account.
Then click Next.
Now you are logged in on Android Studio and an email is also sent through google to your computer stating that “You’ve signed in with Android Studio“.
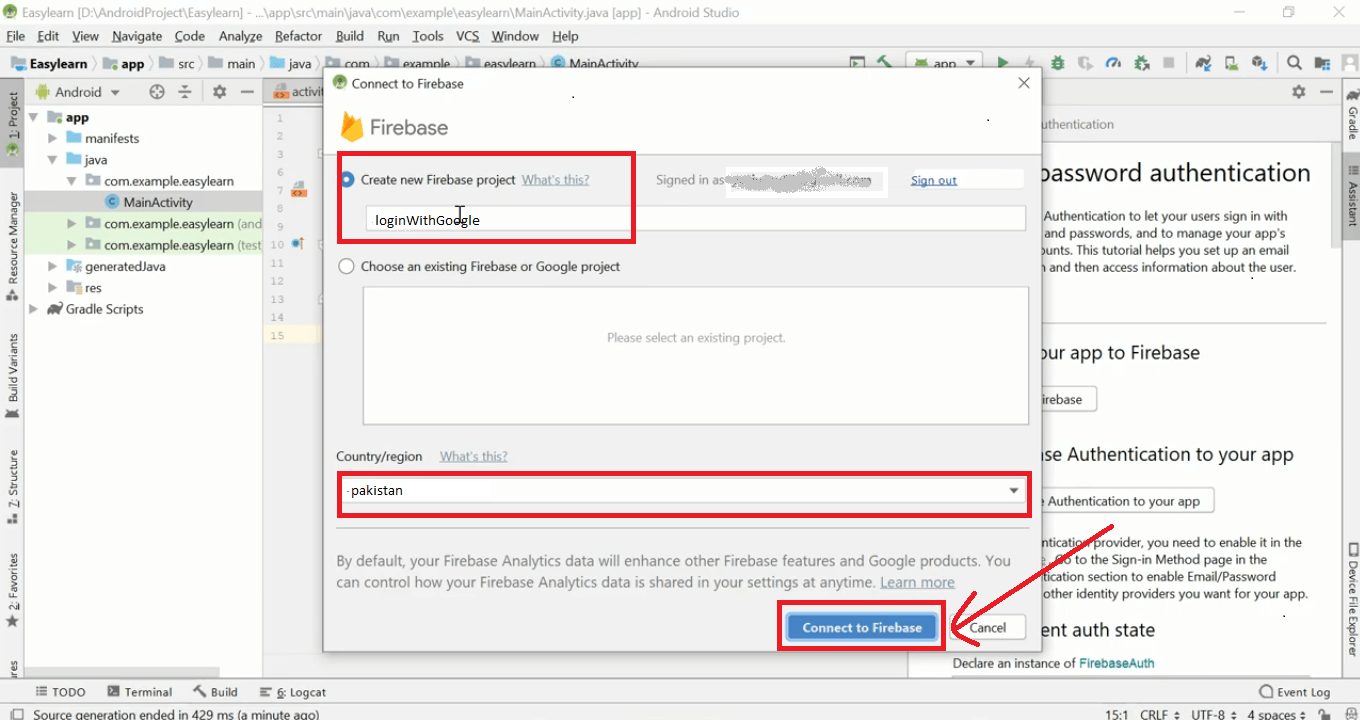
Now open Android Studio you can see a popup box appear just like below. Enter ProjectName (if you want to change) then Select Country and click Connect to Firebase.
You’re good to go if you see a green color text ✔️ Connected on the bottom right side of the screen. Now click on Add Firebase Authentication to your app.
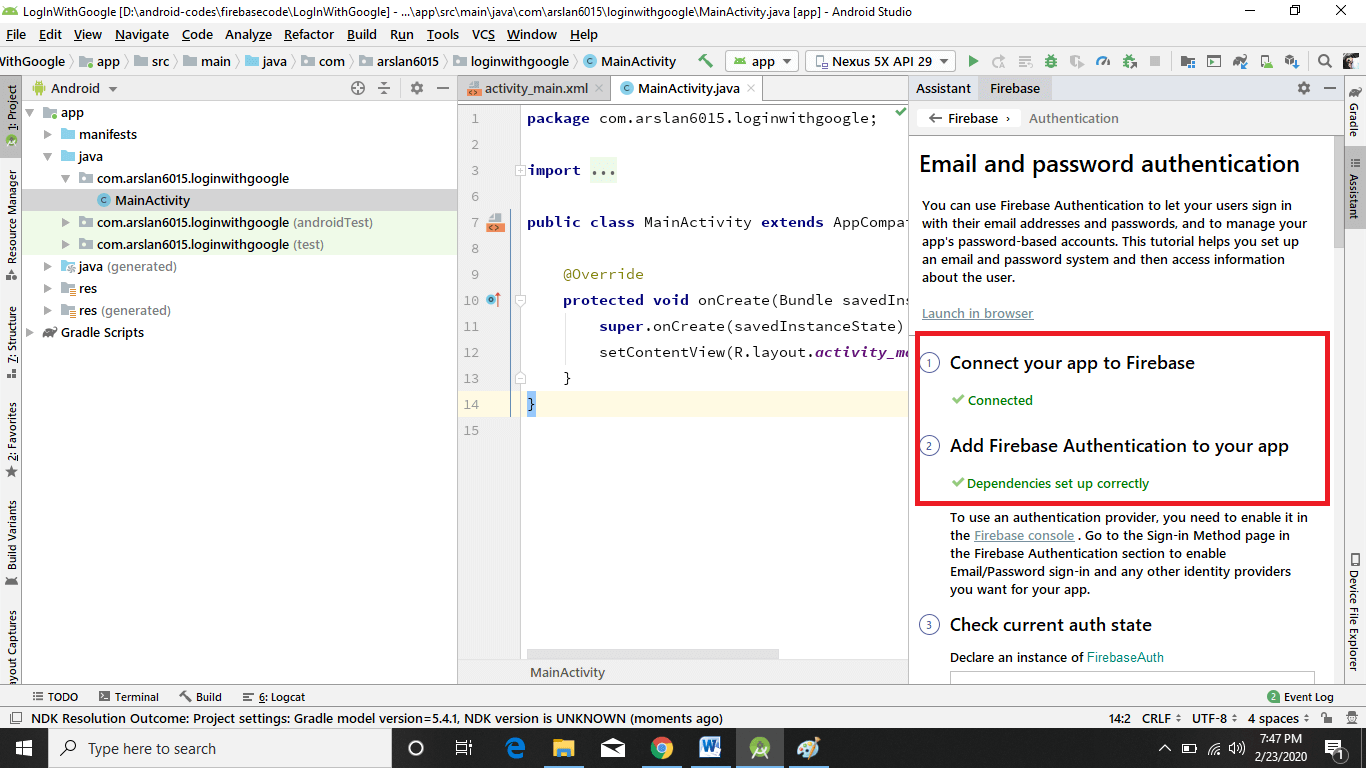
A popup box appears now click Accept Changes. This will add some dependencies to your project at the app-level and the Project-level.
Now you can see dependencies set up correctly.
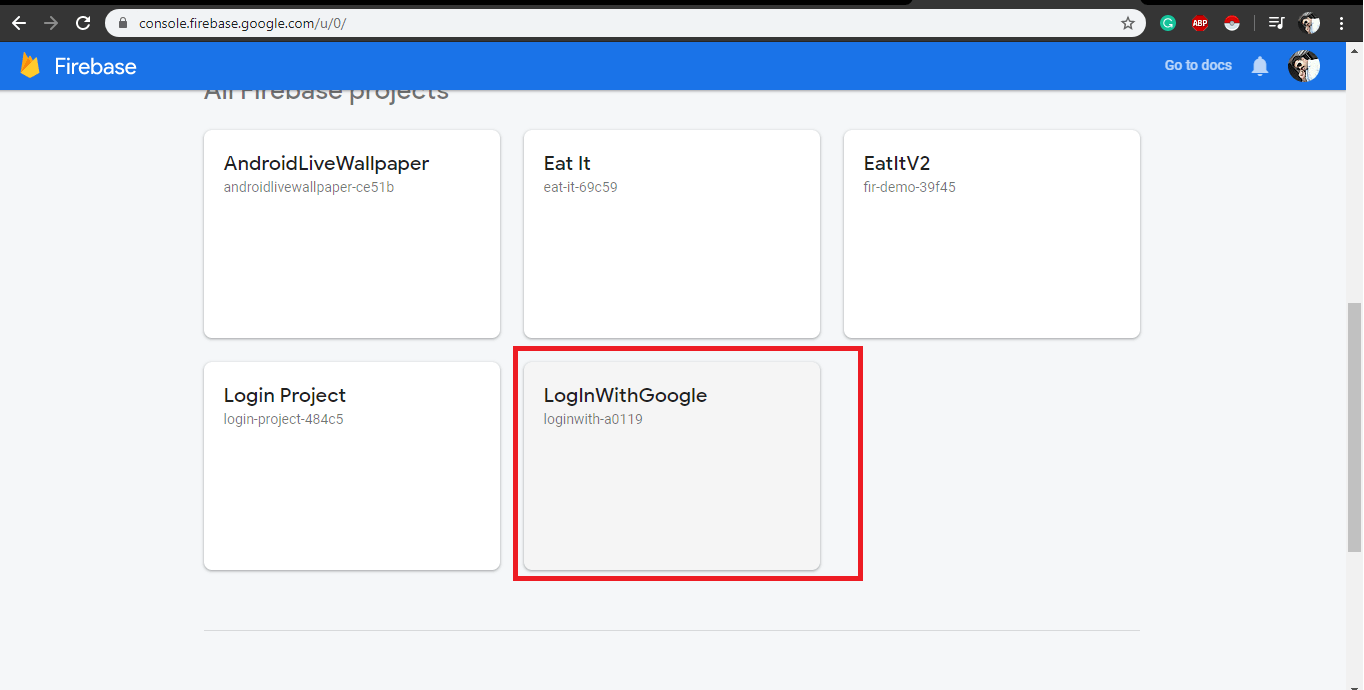
Now open https://console.firebase.google.com/ and log in here with the same account that you are logged in with Android Studio. Now you can see your project has been added. Click on it.
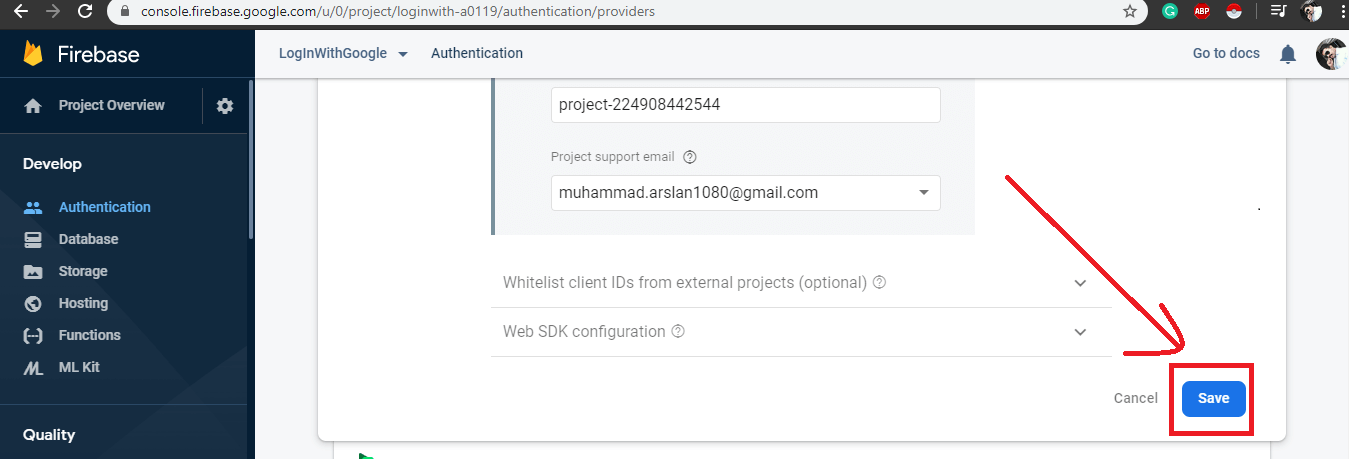
Now click on Authentication Tab -> Sign-In method -> click Google -> Enable Toggle button -> Select Email Address .
Click Save.
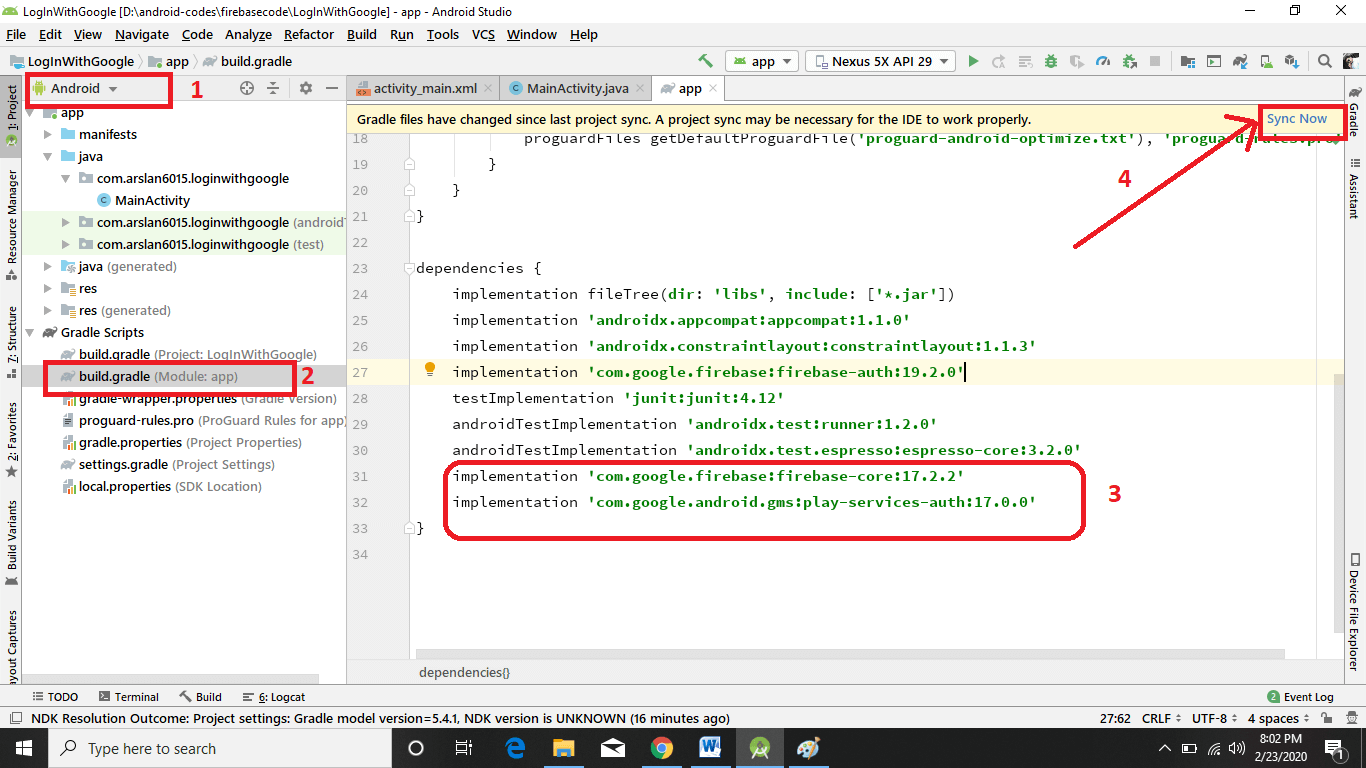
Now open Android Studio -> Select Android -> Gradle Script -> Open build.Gradle file
Now add these two dependencies and click Sync Now.
Building UI
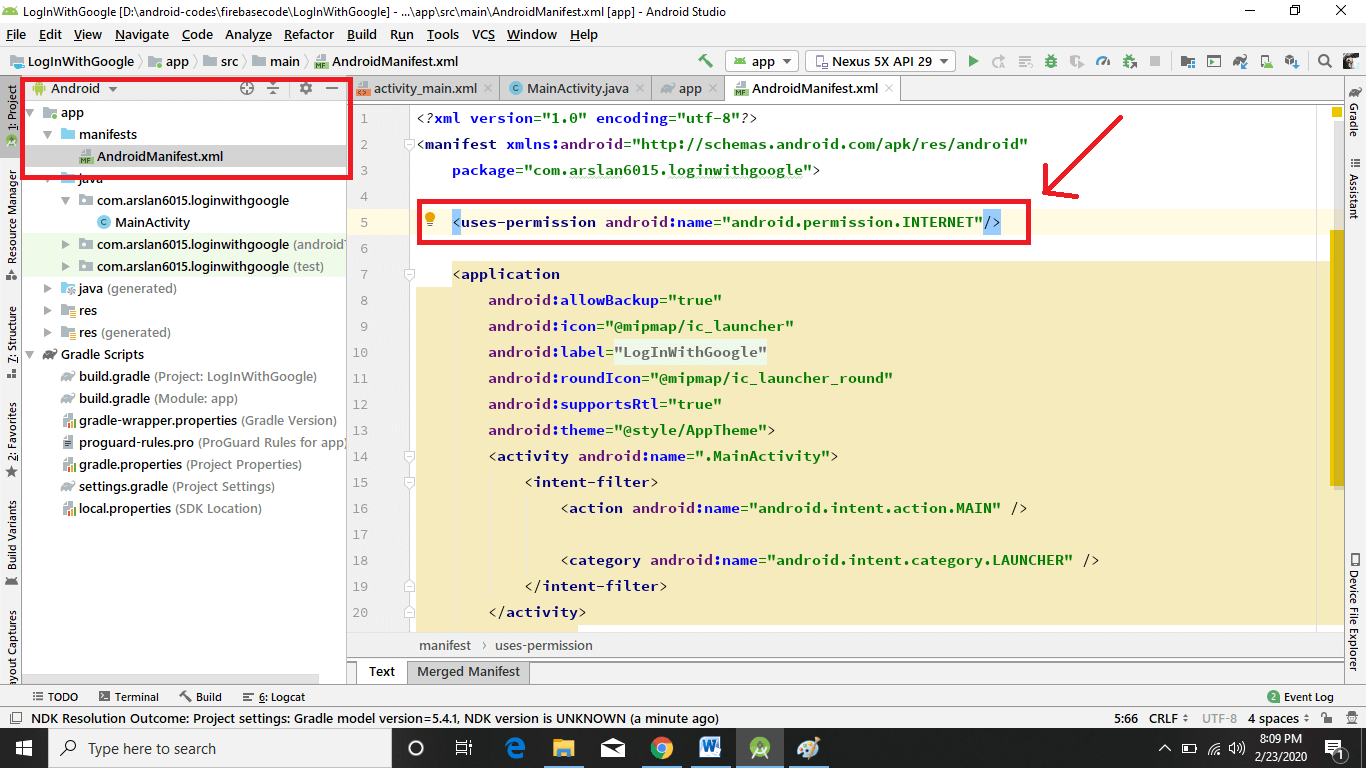
Before we start building the interface and start coding the functionality, we need to add internet permission in the Android Manifest file. I am doing it at the very beginning because I often forget to add it and then start scratching my head that why the code is not working!
Add Internet permission in AndroidManifest.xml
Enter code in activity_main.xml
Adding functionality
Enter code in MainActivity.java
Running the application
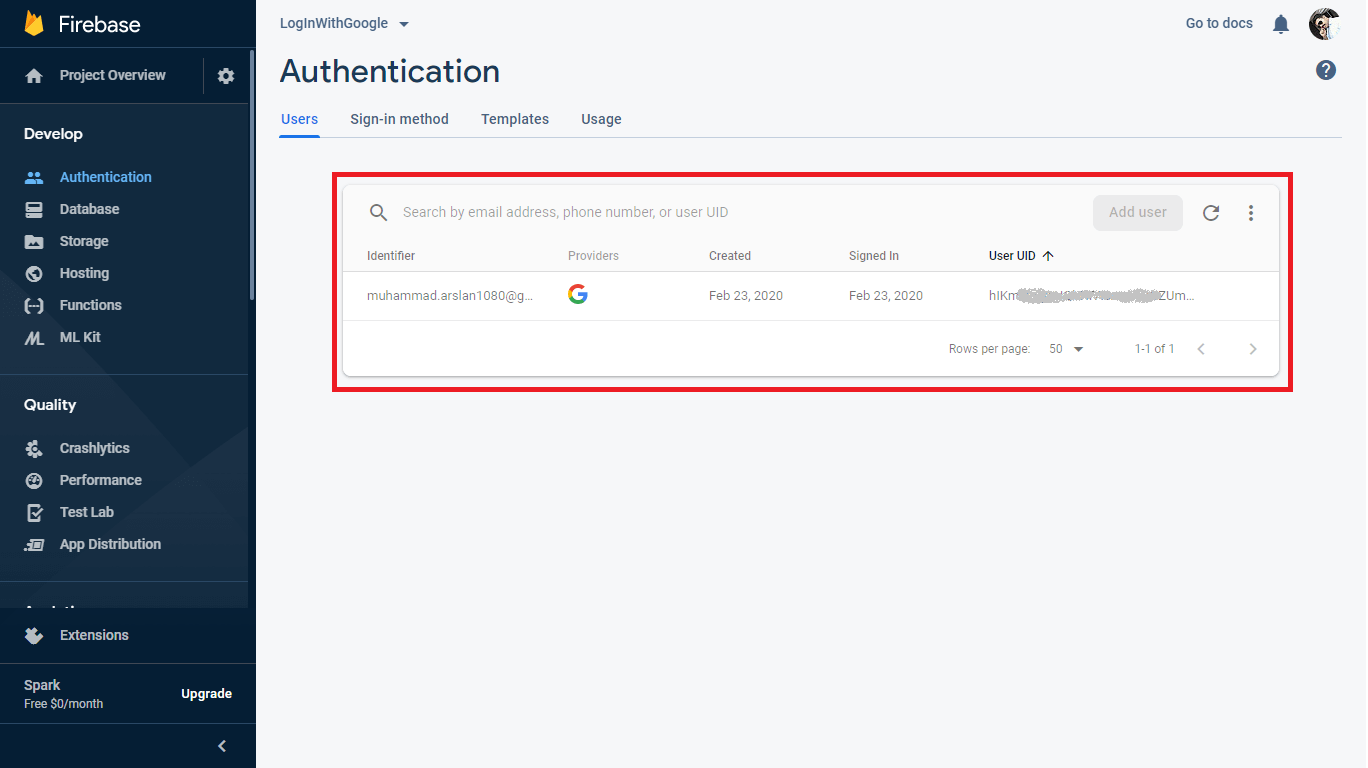
Run the app and now you can see the output as shown above in the video and you can also see in Firebase console that a new user is added
I hope you have understood how the Firebase Authentication works with Google, and how you can provide the “Continue with Google” button to your Android App.
Not interested in Google Sign in? You can:
Don’t forget to ask a question. I understand many people feel being an idiot in asking a question, please don’t feel hesitation. I’ll be delighted to answer your simplest or hardest question.
Источник