- Assets Folder in Android Studio
- How the asset folder is different from the Resource Raw folder?
- But when to use which folder?
- How to Create Assets Folder in Android Studio?
- How to hide files and folders on Android devices without using any third-party app
- Articles
- Open File Manager app on your smartphone
- Look for the option to create a new folder
- Type desired name for the folder
- Add a dot (.) before the folder name to make it a hidden folder.
- Now, transfer all the data to this folder you want to hide
- Assets Folder in Android Studio
- How the asset folder is different from the Resource Raw folder?
- But when to use which folder?
- How to Create Assets Folder in Android Studio?
- Android 11 storage FAQ
- Does Scoped Storage allow apps to access files with file paths, using File API, for example?
- How does the performance of file path access compare to Media Store APIs?
- My app needs broad access to shared storage. Is Storage Access Framework the only option available?
- What categories of apps should request the MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE permission?
- Does using Storage Access Framework require Google Play policy approval?
- Are there any further restrictions to using Storage Access Framework in Android 11 as compared to Android 10?
- How can apps test out Scoped Storage changes?
- Are apps in scoped storage limited to writing files into their app-specific data directories?
- What is the guidance around using the Media Store DATA column since it’s been deprecated?
- For apps that have opted out of Scoped Storage, when will they have to be compatible with Scoped Storage?
- What is the recommended way to migrate data that we currently store outside of Scoped Storage?
- Are there any exceptions for Android/obb directories given that some package installers, like app stores, need access to it?
Assets Folder in Android Studio
It can be noticed that unlike Eclipse ADT (App Development Tools), Android Studio doesn’t contain an Assets folder in which we usually use to keep the web files like HTML. Assets provide a way to add arbitrary files like text, XML, HTML, fonts, music, and video in the application. If one tries to add these files as “resources“, Android will treat them into its resource system and you will be unable to get the raw data. If one wants to access data untouched, Assets are one way to do it. But the question arises is why in the asset folder? We can do the same things by creating a Resource Raw Folder. So let discuss how the assets folder is different from the Resource Raw folder?
How the asset folder is different from the Resource Raw folder?
In Android one can store the raw asset file like JSON, Text, mp3, HTML, pdf, etc in two possible locations:
- assets
- res/raw folder
Both of them appears to be the same, as they can read the file and generate InputStream as below
But when to use which folder?
Below is some guidance that might be helpful to choose
1. Flexible File Name: (assets is better)
- assets: The developer can name the file name in any way, like having capital letters (fileName) or having space (file name).
- res/raw: In this case, the name of the file is restricted. File-based resource names must contain only lowercase a-z, 0-9, or underscore.
2. Store in subdirectory: (possible in assets)
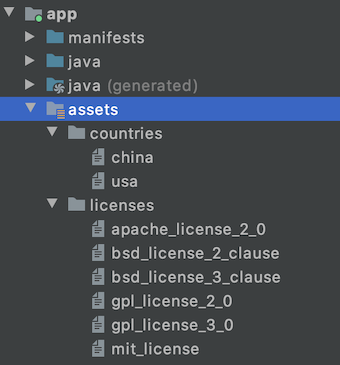
- assets: If the developer wants to categories the files into subfolders, then he/she can do it in assets like below.
3. Compile-time checking: (possible in res/raw)
- assets: Here, the way to read it into InputStream is given below. If the filename doesn’t exist, then we need to catch it.
- res/raw folder: Here, the way to read it into InputStream is:
So putting a file in the res/raw folder will provide ensure the correct file-name during compile time check.
4. List filenames at runtime: (possible in assets)
- assets: If the developer wants to list all the files in the assets folder, he/she has used the list() function and provide the folder name or ” “ on the root folder as given below.
- res/raw: This is not possible in this folder. The developer has to know the filename during development, and not runtime.
So, in assets, one can read the filename during runtime, list them, and use them dynamically. In res/raw, one needs to code them ready, perhaps in the string resources file.
5. Filename accessible from XML: (possible in res/raw)
So if you need to access your file in any XML, put it in the res/raw folder. Let’s make a table to remember the whole scenario easily.
| Res/Raw Folder | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible File Name NO | ||||||
| Store in subdirectory NO | ||||||
| Compile-time checking YES | ||||||
| List filenames at runtime NO | ||||||
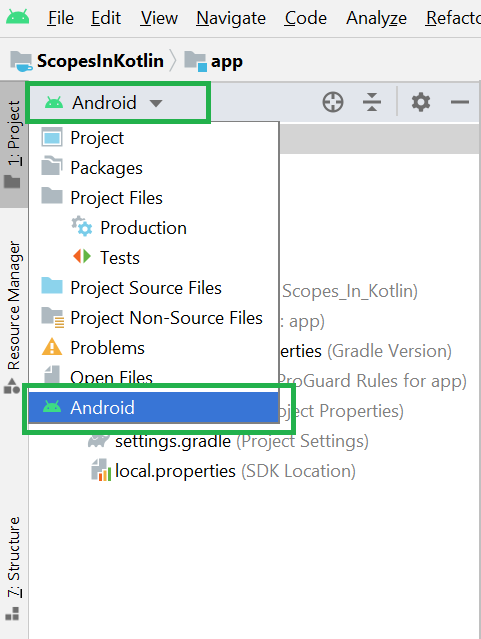
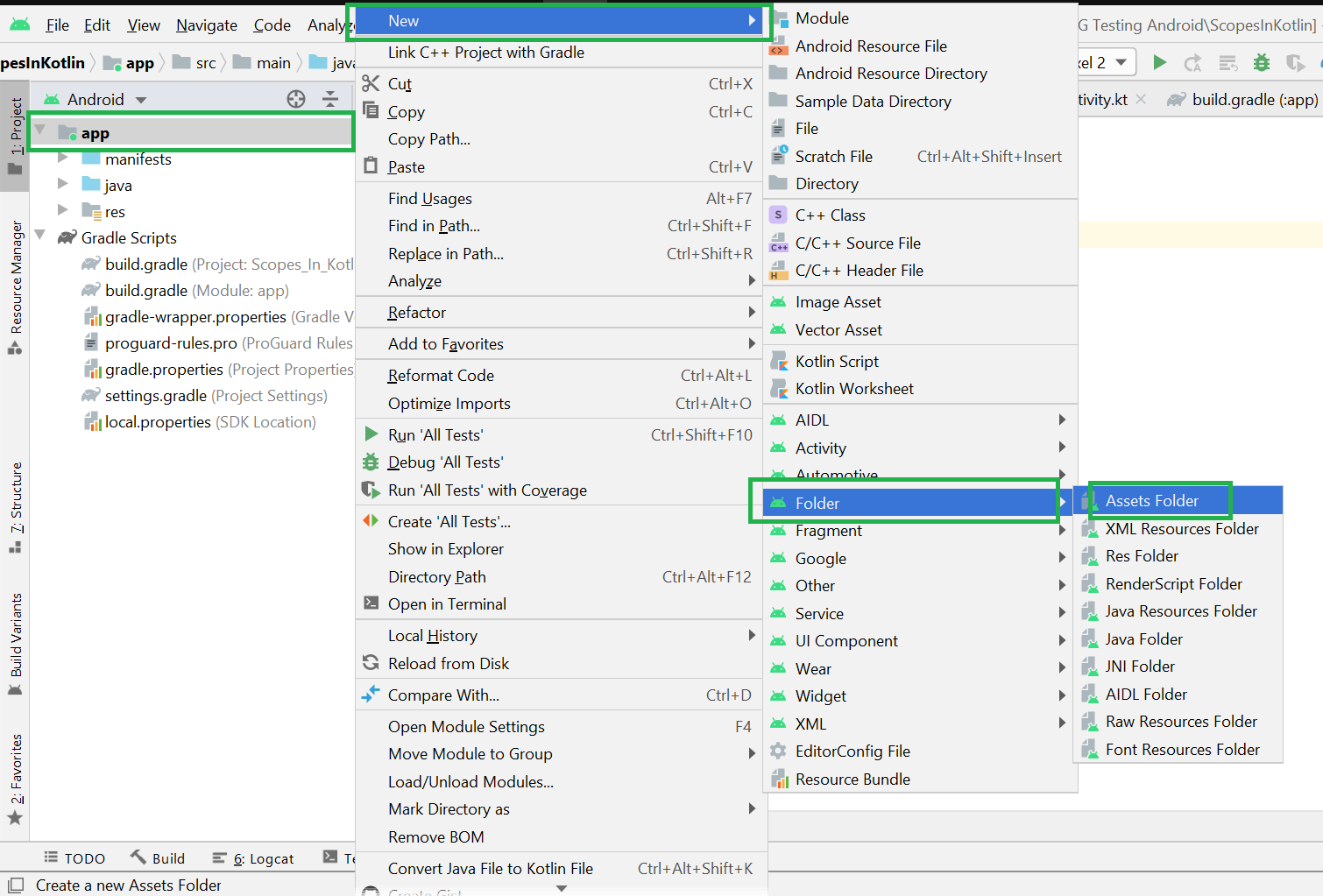
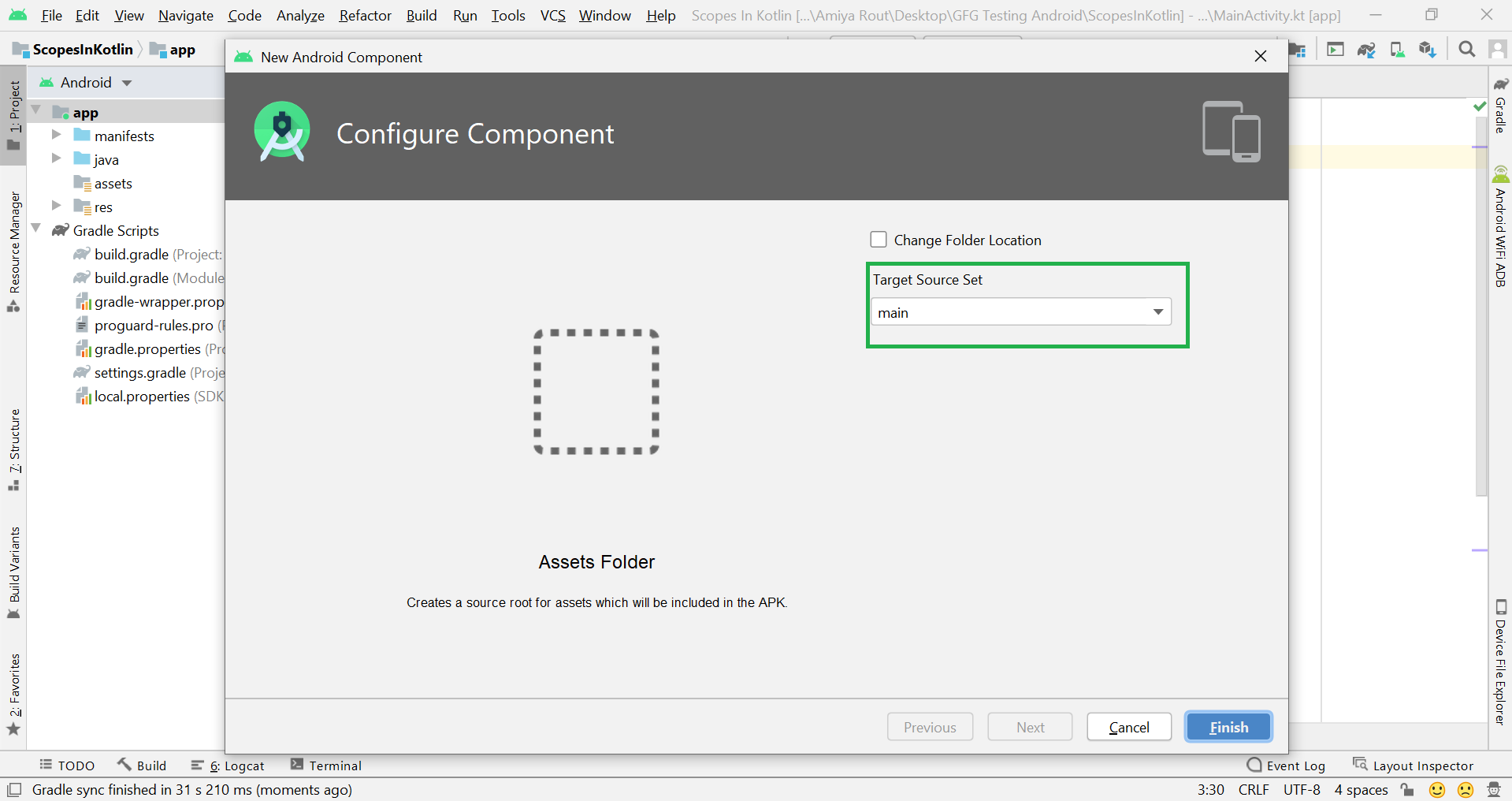
Filename accessible from XML How to Create Assets Folder in Android Studio?Now let’s discuss how to create an assets folder in the android studio. Below is the step-by-step process to create an assets folder in Android studio. Step 1: To create an asset folder in Android studio open your project in Android mode first as shown in the below image. Step 2: Go to the app > right-click > New > Folder > Asset Folder and create the asset folder. Step 3: Android Studio will open a dialog box. Keep all the settings default. Under the target source set, option main should be selected. and click on the finish button. Step 4: Now open the app folder and you will find the assets folder by the name of “assets” as shown in the below image. Источник How to hide files and folders on Android devices without using any third-party appArticlesThere are times when we give our smartphone to our friends or family and there are a few things such as photos, videos and other files on our phone we want to keep out of their sight. As Android operating system is based on Linux, it has some features borrowed directly from the ‘mothership’ such as the ability to create hidden folders so that certain files and folders can only be accessed using the file manager app. Having said that, users no longer have to download any random third party app from Google Play Store. In case you are looking forward to this, here’s our ready-to-use-guide for you. Method 1: Create a dedicated hidden folder The first method is to create a new folder that is automatically hidden so that apps like Gallery, WhatsApp, media players, email clients, office editors, etc. Open File Manager app on your smartphoneLook for the option to create a new folderType desired name for the folderAdd a dot (.) before the folder name to make it a hidden folder.Now, transfer all the data to this folder you want to hideMethod 2: Hide an existing folder To hide an existing folder, follow the steps Источник Assets Folder in Android StudioIt can be noticed that unlike Eclipse ADT (App Development Tools), Android Studio doesn’t contain an Assets folder in which we usually use to keep the web files like HTML. Assets provide a way to add arbitrary files like text, XML, HTML, fonts, music, and video in the application. If one tries to add these files as “resources“, Android will treat them into its resource system and you will be unable to get the raw data. If one wants to access data untouched, Assets are one way to do it. But the question arises is why in the asset folder? We can do the same things by creating a Resource Raw Folder. So let discuss how the assets folder is different from the Resource Raw folder? How the asset folder is different from the Resource Raw folder?In Android one can store the raw asset file like JSON, Text, mp3, HTML, pdf, etc in two possible locations:
Both of them appears to be the same, as they can read the file and generate InputStream as below But when to use which folder?Below is some guidance that might be helpful to choose 1. Flexible File Name: (assets is better)
2. Store in subdirectory: (possible in assets)
3. Compile-time checking: (possible in res/raw)
So putting a file in the res/raw folder will provide ensure the correct file-name during compile time check. 4. List filenames at runtime: (possible in assets)
So, in assets, one can read the filename during runtime, list them, and use them dynamically. In res/raw, one needs to code them ready, perhaps in the string resources file. 5. Filename accessible from XML: (possible in res/raw) So if you need to access your file in any XML, put it in the res/raw folder. Let’s make a table to remember the whole scenario easily.
|