- How to Create Drawable Resource XML File in Android Studio?
- Step by Step Process to Create a New Drawable Resource XML in Android Studio
- A Complete Guide to Learn XML For Android App Development
- Basics of User Interface(UI)
- Different Types of XML Files Used in Android Studio
- How to create a Layout xml file in Android?
- Adding Views to a layout File
- Edit the properties of the Views in your layout file
- About Krishna Srinivasan
- Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Follow Us
- Processing and Parsing XML in Android
- What is XML?
- XML elements
- XML Parsing
- Steps involved in XML parsing
- XML parsing example
- Conclusion
How to Create Drawable Resource XML File in Android Studio?
A drawable resource is a common concept for a graphic that can be drawn to the screen and which one can retrieve with APIs such as getDrawable(int) or apply to another XML resource with attributes such as android:drawable and android:icon. There are several different types of drawable resources files and let’s discuss all the types in a tabular manner.
Drawable Resources Files
As it is known to all that Android Studio is the official integrated development environment for Google’s Android operating system, built on JetBrains’ IntelliJ IDEA software and designed specifically for Android development. So as a beginner in android app development , the developer should know about the tools vividly before building some awesome projects in Android. So in this article let’s learn to create a drawable resource XML file in Android Studio. Drawable Resource XML is mostly created in the drawable folder and is used in Android to add more customization for views. Here is the step by step process to create a new Drawable Resource XML in Android Studio.
Step by Step Process to Create a New Drawable Resource XML in Android Studio
Step 1: Go to the app > res > drawable and right-click on it. Please refer to the screenshot below to get a clear cut view of the steps.
Step 2: After right-clicking on the drawable file go to New > Drawable resource file as shown in the figure below.
Step 3: When you click on the Drawable resource file a dialog box will open on your compute screen. Enter the file name in the text box and then click on OK.
Note: File names must start with a lowercase letter.
Step 4: After that the drawable resource XML file will be created and one can find the file in app > res > drawable as shown in the figure below. In this case, we have named the file as round_button as shown in the above image.
Step 5: Now click on the file name and one can customize the views by writing the necessary codes inside this file.
After doing all the steps the important questions arise are why to create a drawable resource XML file in Andoird? What’s its application? To get the answer to these questions please refer to this article to get a clear-cut idea about its real usage.
Источник
A Complete Guide to Learn XML For Android App Development
XML stands for Extensible Markup Language. XML is a markup language much like HTML used to describe data. It is derived from Standard Generalized Markup Language(SMGL). Basically, the XML tags are not predefined in XML. We need to implement and define the tags in XML. XML tags define the data and used to store and organize data. It’s easily scalable and simple to develop. In Android, the XML is used to implement UI-related data, and it’s a lightweight markup language that doesn’t make layout heavy. XML only contains tags, while implementing they need to be just invoked.
The simple syntax of XML is
So in this article, there is a deep discussion on how to learn and understand what XML is for Android Development.
Basics of User Interface(UI)
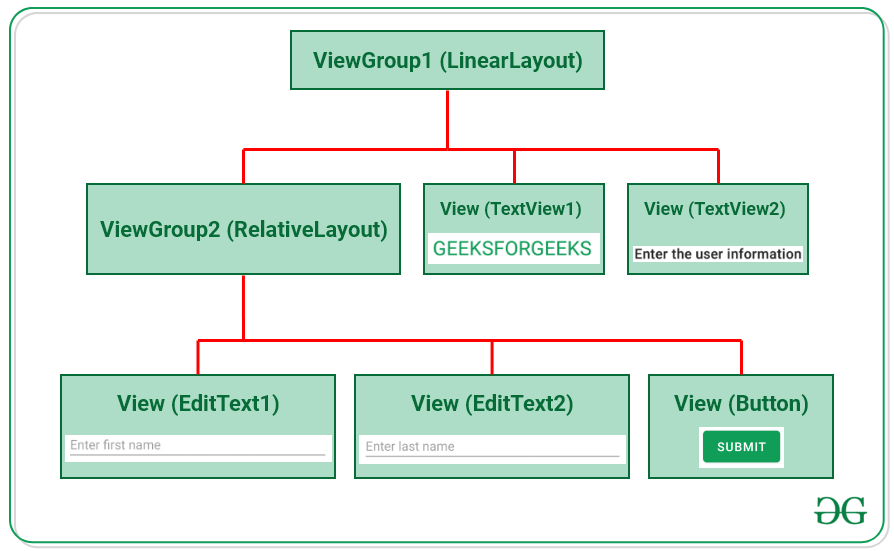
Basically in Android XML is used to implement the UI-related data. So understanding the core part of the UI interface with respect to XML is important. The User Interface for an Android App is built as the hierarchy of main layouts, widgets. The layouts are ViewGroup objects or containers that control how the child view should be positioned on the screen. Widgets here are view objects, such as Buttons and text boxes. Considering the following simple example of the activity_main.xml file.
Output UI:
In the above example of XML file, There are 2 view groups one is LinearLayout and another is RelativeLayout and the TextView1 and TextView2 is child widgets under the ViewGroup1 that is LinearLayout. EditText1, EditText2, and Button are the child widgets under ViewGroup2 that is RelativeLayout. ViewGroup2(RelativeLayout) is nested under the ViewGroup1 which produces the following hierarchy.
From the hierarchy, it’s been observed that every widget like EdtText, TextView, or Button is one of the View. These Views are contained inside the ViewGroup, like RelativeLayout, LinearLayout, FrameLayout, etc.
Different Types of XML Files Used in Android Studio
Different XML files serve different purposes in Android Studio. The list of various XML files in Android Studio with their purposes is discussed below.
1. Layout XML files in android
The Layout XML files are responsible for the actual User Interface of the application. It holds all the widgets or views like Buttons, TextViews, EditTexts, etc. which are defined under the ViewGroups. The Location of the layout files in Android is:
app -> src -> main -> res -> layout
Источник
How to create a Layout xml file in Android?
As we have discussed in one of our previous posts Layouts in android layouts are the containers that hold the components of UI that you want to display in your application. When you compile your application,each xml layout file is compiled into a View resource. This tutorial describes how you can add a layout file to a newly created activity.
also read:
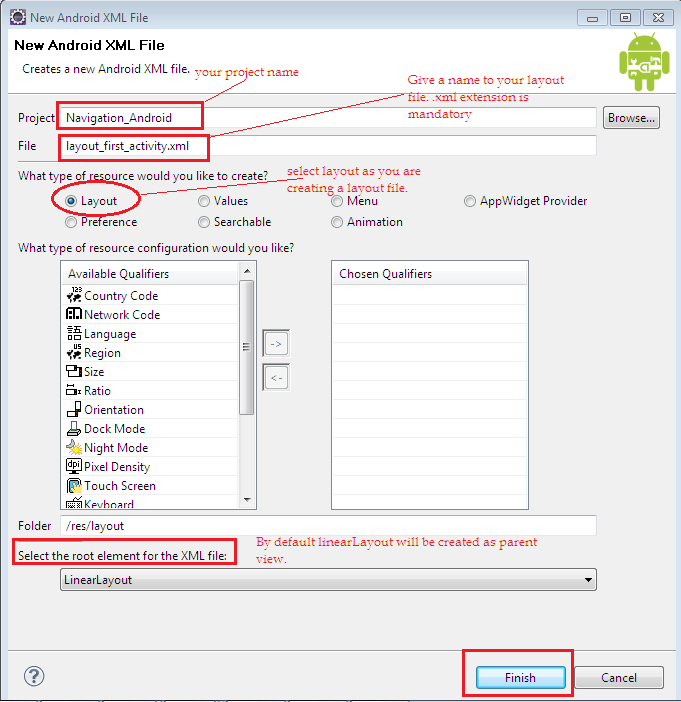
To create a layout file, follow the steps:
- Open eclipse (Read: how to setup android in eclipse?)
- File->New->Android XML File
- The above steps open up the below window
Once you fill up all required details in the above screen click on “Finish” button. This creates your layout xml file in res/layout directory. The initial code of the created layout “layout_first_activity.xml” is as below.
[java]
xmlns:android=»http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
android:layout_width=»wrap_content»
android:layout_height=»wrap_content»>
[/java]
When you create a layout file,by default it contains only one linear layout. You have to add views that you want to display in your activity.
Adding Views to a layout File
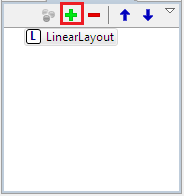
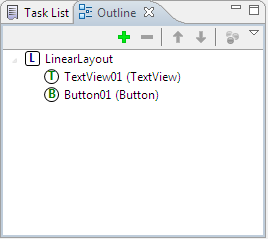
Add the views that you want to display in your Activity. Lets now add a Textview and a Button. You can find the below pane called outline when you create a layout. If you don’t find it open window->Show View->Outline
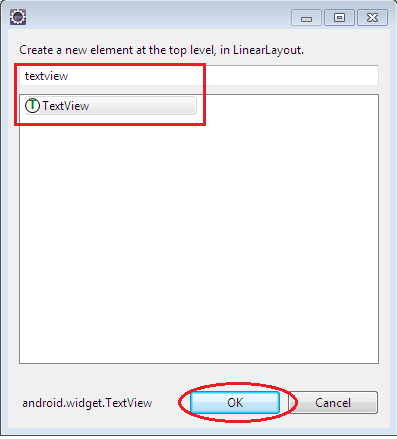
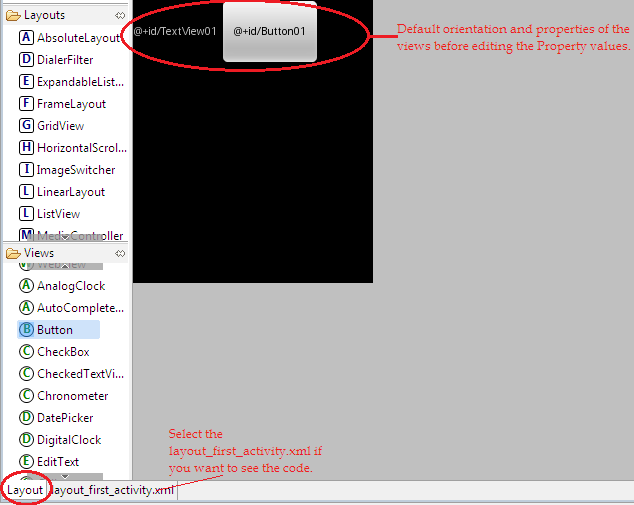
click on the highlighted “+” symbol to create new views. This takes you to the below screen.
Select the view that you want to add. I have selected textView. Then click “OK” button. Let us now add a button to our layout file. Again click on the “+” symbol in the outline pane to add a button and select the button and click “OK” to add it. Then your “layout_first_activity” file contains a LinearLayout which inturn contains a textview and a button. The structure of the layout file as seen in the outline is as below:
You can always remove the view that you have added by clicking on the “-” symbol present on right side of the “+” symbol.
To view the layout that you have created before you run the project, select the layout section in your layout window.
Edit the properties of the Views in your layout file
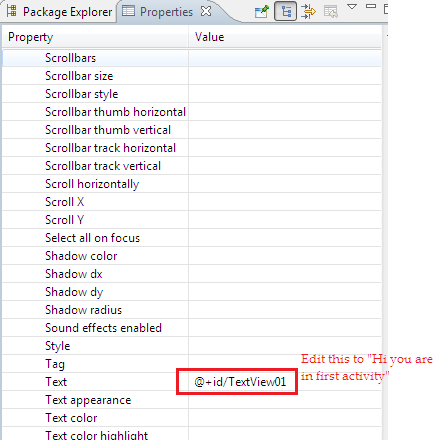
Edit the properties of the newly created views. To the Edit the properties of a particular view, double click on that view which opens up a pane called “Properties”. Lets us edit the Textview text as “Hi you are in first activity”. The property Window is as below.
Double click on the Button view to Edit the properties of the button.Let us edit the text property of the button to “Click to Navigate”.
You can customize your views by editing various properties present in the Property pane. For example: text size,Text color, orientation of the views etc. By default when you add views to your linear layout the orientation will be “Horizontal”. Now change the Orientation property of the LinearLayout to vertical.
The layout code after editing the required property values is as below.
[java]
android:orientation=»vertical» android:layout_height=»fill_parent»
android:layout_width=»fill_parent»>
android:layout_height=»wrap_content» android:textStyle=»bold» android:layout_gravity=»center»
android:layout_marginTop=»30dip» android:text=»Hi you are in first activity»>
You should load the created layout file from your application code,in your Activity.onCreate() callback implementation. You can do that by calling setContentview(), passing it the reference to your layout file in the form of R.layout.layouy_first_activity. The code of your activity is as below.
[java]
package my.app;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class First_activity extends Activity <
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) <
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.layout_first_activity);
>
>
[/java]
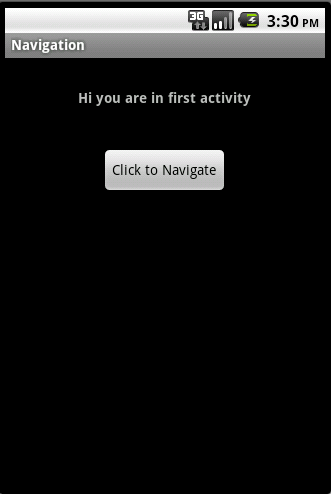
Now run your application. The output is as below.
This is how you can create a layout xml file in android. If you have any queries,please post in it comment section.
also read:
About Krishna Srinivasan
He is Founder and Chief Editor of JavaBeat. He has more than 8+ years of experience on developing Web applications. He writes about Spring, DOJO, JSF, Hibernate and many other emerging technologies in this blog.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Follow Us
As a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, this site may earn from qualifying purchases. We may also earn commissions on purchases from other retail websites.
Источник
Processing and Parsing XML in Android
Sharing data over the internet is very popular. We share our information with the other users over the internet. Let’s take a very common example, since we all are developers and to be more precise, we all are Android Developers and we all must have visited the StackOverflow website whenever we are stuck into some problem in our projects and in every 99 out of 100 cases, we find the solution to our problem. The answer that we get from the StackOverflow website consists of various parts that we are less bothered about. In general, the answers or the questions present on the website contains the id of the question, type of the question, author name of the article or question, publishing data, URL and many other things are there on the website. But we want only meaningful data i.e. we want answers and the authors and nothing else.
The problem arises when you want to access the data of a particular website in your Android Application. This is because the data present on the websites are in JSON format or in XML format. So, in order to use that data or to extract the meaningful information from that data, you have to parse that XML file or a JSON file.
So, in this blog, we will learn how to process and parse the XML data in Android. So, let’s get started.
What is XML?
XML stands for Extensible Markup Language. It is a set of rules that are used to encode data or documents in a Machine-readable language. There are many websites that use an XML format to share data on the internet. For example, many blogging websites use an XML format to share data between users. So, XML parsing and processing become an important task to use that data in our Android Application.
XML elements
In general, an XML file consists of a number of elements that together make an XML file. They are the basic building blocks of XML document. These elements are used to store some text elements, attributes, media, etc. Below is the syntax of XML element:
Here, element-name is the name of the element and attributes are used to define the property of XML element. Following is an example of an XML document that is used to describe the data of the student:
We can broadly divide the XML elements in four parts:
- Prolog: It is the first line that contains the information about the XML file i.e. it is the first line of the XML file.
- Events: An XML file contains a number of events like document start, document end, Tag start, Tag end, etc.
- Text: In between the tags(opening and closing), there can be some text. For example, in the above example, “John” is the text.
- Attributes: These are the properties of XML elements.
XML Parsing
So, we have seen the introduction of XML and our next task is, How to parse the XML in Android? So, let’s find out.In Android, there are various parsers that can be used to parse the XML file in Android. Some of these are:
- XMLPullParser
- DOM Parser
- SAX Parser
Among these three parsers, XMLPullParser is the most commonly and most widely used parsers in Android. This is because XMLPullParser is very efficient and easy to use. Also, unlike the DOM Parser which loads the whole file in the memory and then parses it, the XMLPullParser consumes less memory.
Steps involved in XML parsing
Following are the steps that are involved in XML parsing:
- Analyze the feed: There are many cases when you will be provided with a number of data but you need only few of them. SO, before parsing the XML, your first step should be to find the desired element in the XML data. For example, here is example of XML file of StackOverflow:
Here, if you want to extract the data present in the entry tag and the data of its sub tags then you should keep note of these things.
- Create XMLPullParser object: Our next step is to create the object of XMLPullParser and specify the file name for the XMLPullParser that contains XML. You can use a file or a stream. Following is the code to create an object of the XMLPullParser and then passing the file name for the XMLPullParser:
- Read the desired data: Our last step is to parse the data of the XML file. The following readFeed() function is used to parse the XML file and extract only the values of entries and store it into a list:
Here, XMLPullParser.END_TAG is used to find if the parser has reached to the last tag of the file or not. If it has reached then return and it has not reached then we will check for the entry tag and if found then will add the value to the entries list. If the values are not found be to of entries type then we can skip the parser. At last, we return entries.
Following are the methods that can be used while parsing an XML file:
- getEventType(): This method is used to get the event type. For example, Document start, Document End, Tag start, Tag end, etc.
- getName(): This is used to get the tag name in a file. For example, in the above code, the tag name is entry.
- getAttributeValue(): This method is used to get the attribute value of a particular tag.
- getAttributeCount(): It returns the total number of attributes of the current tag.
- getAttributeName(int index): It returns the attribute name at a particular index.
- getColumnNumber(): It returns the current column number using a 0 based indexing.
- getName(): It returns the name of the tag.
- getText(): It returns the text present in a particular element.
XML parsing example
Now, let’s do one example to understand the concept of XML parsing ina very easy and clear manner.
Open Android Studio and create a project with Empty Activity template.
The very first step is to create the XML file. Either you create your own XML file or you can use mine. To create an XML file, go to java folder and then right click on it. Then click on New > Folder > Assets folder and then OK. One assets folder will be created for you. Now right click on that folder and create a file and name it as example.xml. Following is the XML content of example.xml file:
This is a simple example of student data containing the name, surname, mobile and section of the student. In this example, we will extract the name, surname and section of the student. We will ignore the mobile number.
Now, let’s code for the UI part of our application. Here we will display the desired data on a TextView. So, open the activity_main.xml file and add the below code:
So, we are done with the UI part. Now, let’s write the code for the XML parsing. Below is the code for the MainActivity.kt file:
Now, run the application on your mobile phone and try to add more data to your XML file i.e. the example.xml file.
Conclusion
In this blog, we learned about XML parsing in Android. We learned how to parse the data present in the XML format in Android Application. We saw how to use XMLPullParser to do XML parsing. At last, we did one example of XML parsing. You can get more contents about XML parsing at the Android Developer Website.
Источник