- How to Get App Package Name on Android [3 Methods]
- Method 1: Get Android App Package Name via Play Store URL
- On PC
- On Mobile
- Method 2: Get Android App Package Name via a Third-Party App
- Method 3: Get Android App Package Name via ADB Commands
- About Chief Editor
- Sadique Hassan
- How do I get an apk file from an Android device?
- 24 Answers 24
- How do I get my application Version
- 11 Answers 11
- How to get a list of installed android applications and pick one to run
- 20 Answers 20
- Clean solution that filter successfuly out system apps
How to Get App Package Name on Android [3 Methods]
In this guide, we will share three different methods to get the package name of all the installed apps on your Android device. The apps installed on your device are labeled via two different methods. The first one is the general name that you usually come across such as Facebook, WhatsApp, etc. These are the name that the everyday users deals with and searches for on Play Store.
On the other hand, there’s an associated application ID or app package name, which acts as a unique identifier for each app. For example, Facebook has the package name com.facebook.katana and WhatsApp has com.whatsapp. These are the names used by backend people and developers alike. Furthermore, while you may come across many apps on the Play Store by the name of Facebook, but none could have the com.facebook.katana as their package.
So if you have ever any doubt regarding the app’s authenticity, then you may count on this factor. With that said, how could you get hold of the package name of all the installed apps on your Android device? Well, there are three different methods for the same, and in this guide, we will make you aware of all these three approaches. So without further ado, let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Method 1: Get Android App Package Name via Play Store URL
This method is extremely easy to execute. However, if you are looking to get the name of various installed apps in one go, then it would require quite a lot of manual effort. But for a few apps, this should be your go-to method. Here’s how to use it:
On PC
- First off, head over to the Play Store website on your PC.
- Now search for the desired app (as an example, let’s go with Facebook)
- Then head over to its search bar and check out its URL, it will be something along this line:
- As an example, in the case of Facebook, the URL will be
- Now the portion after be the app’s package name. So for Facebook, it turns out to be com.facebook.katana.
So this was the first method to get the app package name via Play Store and PC. Let’s see how to try out this Play Store trick on your phone.
On Mobile
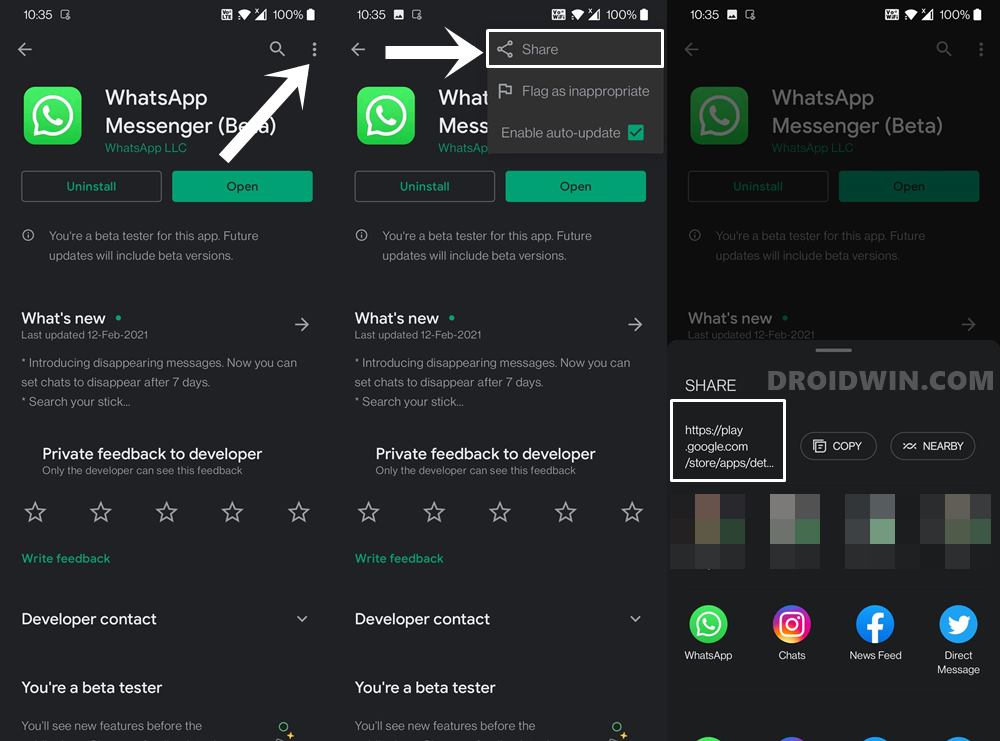
- Open the Play Store app on your device and search for the desired app (let’s say WhatsApp).
- Under the app listing’s page, tap on the overflow icon situated at the top right and select Share.
- Now just share/save this URL anywhere you wish. The URL will be of the same format as mentioned above, i.e.
- As an example, in the case of WhatsApp, the URL turns out to be
- As before the app package name will be the portion after So for WhatsApp, it turns out to be com.whatsapp.
The other method involves opening the Play Store website on your smartphone browser, changing its view to Desktop Mode, and then getting hold of the URL. With that, we round off this first method to get the package name of all the installed apps on your Android device. Let’s now turn our attention towards the other two methods.
Method 2: Get Android App Package Name via a Third-Party App
The benefit of this method is the fact that you require minimal effort. Furthermore, it is able to display both the user installed as well as system apps. The UI is also user-friendly. However, I have never been in favor of using third-party apps and giving them access to my device, unless it is of paramount importance. With that said, if you wish to try it out, then follow the below instructions:
- To begin with, download the App Package Viewer 2.0 from Play Store.
- Then launch it and select the desired app from the list.
- Now tap on that app’s name and you should get its associated package name.
That’s it. This is perhaps the easiest method to get the package name of all the installed apps on your Android device. Now let’s check out the third and final method to carry out this task.
Method 3: Get Android App Package Name via ADB Commands
The benefit of this method is the fact that apart from getting the app’s package name, you could even remove the user-installed and system-installed apps on your device via these ADB Commands. Without Root! On the flip side, this method requires a few prerequisites and some level of technicalities as well. But if you are ready to challenge your inner-geek, then this method is tailored made for you. Follow along.
- To begin with, download and install the Android SDK Platform Tools on your PC. These are the official ABD binary files provided by Google.
- Extract its content to any convenient location on your PC and you should get the platform-tools folder.
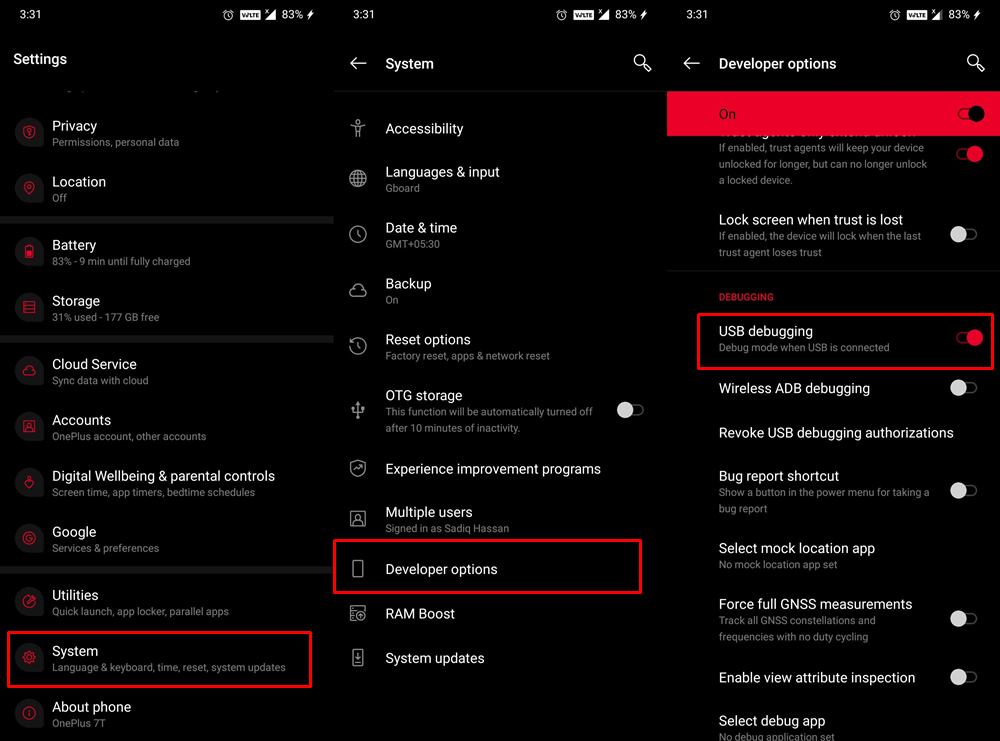
- Now head over to your Android device and enable USB Debugging. This will make your device recognizable by your PC in ADB mode. So head over to Settings > About Phone > Tap on Build Number 7 times > Go back to Settings > System > Developer Options > Enable USB Debugging.
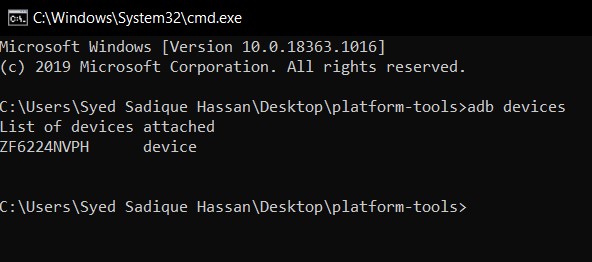
- When that is done, connect your device to the PC via USB cable. Make sure USB Debugging is enabled.
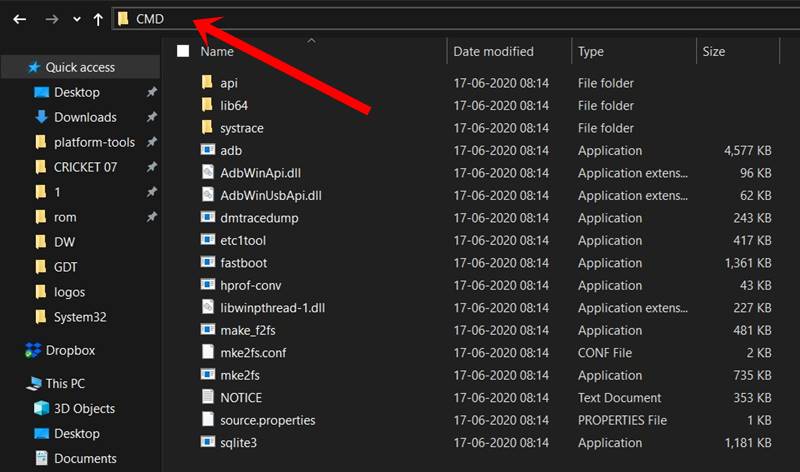
- Then head over to the platform-tools folder, type in CMD in the address bar, and hit Enter. This will launch the Command Prompt.
- Now type in the below command in the CMD window and hit Enter:

Then type in the below command and you should get a list of all the installed apps:

That’s it. With this, we conclude the guide on how to get the package name of all the installed apps on your Android device. We have shared three different methods for the same, do let us know in the comments which one you ultimately settled for.
About Chief Editor
Sadique Hassan
A technical geek by birth, he always has a keen interest in the Android platform right since the birth of the HTC Dream. The open-source environment always seems to intrigue him with the plethora of options available at his fingertips. “MBA by profession, blogger by choice!”
Источник
How do I get an apk file from an Android device?
How do I get the apk file from an android device? Or how do I transfer the apk file from device to system?
24 Answers 24
None of these suggestions worked for me, because Android was appending a sequence number to the package name to produce the final APK file name. On more recent versions of Android (Oreo and Pie), an unpredictable random string is appended. The following sequence of commands is what worked for me on a non-rooted device:
1) Determine the package name of the app, e.g. «com.example.someapp». Skip this step if you already know the package name.
Look through the list of package names and try to find a match between the app in question and the package name. This is usually easy, but note that the package name can be completely unrelated to the app name. If you can’t recognize the app from the list of package names, try finding the app in Google Play using a browser. The URL for an app in Google Play contains the package name.
2) Get the full path name of the APK file for the desired package.
The output will look something like
package:/data/app/com.example.someapp-2.apk
or
package:/data/app/com.example.someapp-nfFSVxn_CTafgra3Fr_rXQ==/base.apk
3) Using the full path name from Step 2, pull the APK file from the Android device to the development box.
Источник
How do I get my application Version
Can anyone tell me how to get applcation version in Android?
11 Answers 11
This page has a tips on how to do it from java:
I am using Android Studio, I realized I could use one line code to get this.
Edited:
If you are using other android libraries, make sure you import BuildConfig from your application package. This is similar to the automatically generated R class for identifying resources.
More info on this link
To get application information:
The easiest and best answer I found is to just import your BuildConfig
If you are using eclipse try this:
In Android Studio :
make sure you have mansion version code in your module-level build.gradle file
In you (Module : app) gradle define version name and version code
versionCode
The versionCode is integer value used to easily differentiate between app versions.
App developers must increment this value when they release updates to their apps in Android Market, so it can determine if users are using an old version of the app, and offer them to update it.
versionName
The versionName is a string containing a regular “release version” as seen in other desktop applications, such as “1.4.5” or “3.7”.
The versionName is just a “human readable” version code.
Источник
How to get a list of installed android applications and pick one to run
I asked a similar question to this earlier this week but I’m still not understanding how to get a list of all installed applications and then pick one to run.
and this only shows application that are preinstalled or can run the ACTION_MAIN Intent type.
I also know I can use PackageManager to get all the installed applications, but how do I use this to run a specific application?
20 Answers 20
Here’s a cleaner way using the PackageManager
Following is the code to get the list of activities/applications installed on Android :
You will get all the necessary data in the ResolveInfo to start a application. You can check ResolveInfo javadoc here.
Another way to filter on system apps (works with the example of king9981):
Here a good example:
Getting list of installed non-system apps
To filter on sytem based apps :
To get al installed apps you can use Package Manager..
To run you can use package name
You can Find the List of installed apps in Android Device by using below code, «packageInfo» Contains Installed Application Information in Device. we can retrive Intent for the application installed from the packageinfo object and by using startactivity(intent), can start application. it is up to you how you organize the UI either Listview or Gridview. so on click event based on position, you can retrive intent object and start activity intent.
I had a requirement to filter out the system apps which user do not really use(eg. «com.qualcomm.service», «update services», etc). Ultimately I added another condition to filter down the app list. I just checked whether the app has ‘launcher intent’.
So, the resultant code looks like.
If there are multiple launchers in a one package above code has a problem. Eg: on LG Optimus Facebook for LG, MySpace for LG, Twitter for LG contains in a one package name SNS and if you use above SNS will repeat. After hours of research I came with below code. Seems to work well.
@Jas: I don’t have that code anymore, but I’ve found something close. I’ve made this to search for «components» of my application, they are just activities with a given category.
I’ve commented the part where it gets the activity name, but it’s pretty straightforward.
Clean solution that filter successfuly out system apps
The idea behind this solution is that the main activity of every system app does not have a custom activity icon. This method gives me an excellent result:
context.getPackageManager().getInstalledApplications(PackageManager.GET_META_DATA); Should return the list of all the installed apps but in android 11 it’ll only return the list of system apps. To get the list of all the applications(system+user) we need to provide an additional permission to the application i.e
Since Android 11 (API level 30), most user-installed apps are not visible by default. You must either statically declare which apps and/or intent filters you are going to get info about in your manifest like this:
Or require the QUERY_ALL_PACKAGES permission.
After doing the above, the other answers here still apply.
Источник