- Installing the Android SDK
- Download
- Terms and Conditions
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Accepting this License Agreement
- 3. SDK License from Google
- 4. Use of the SDK by You
- 5. Your Developer Credentials
- 6. Privacy and Information
- 7. Third Party Applications
- 8. Using Android APIs
- 9. Terminating this License Agreement
- 10. DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES
- 11. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
- 12. Indemnification
- 13. Changes to the License Agreement
- 14. General Legal Terms
- Android Studio
- Intelligent code editor
- Code templates and GitHub integration
- Multi-screen app development
- Virtual devices for all shapes and sizes
- Android builds evolved, with Gradle
- More about Android Studio
- System Requirements
- Windows
- Mac OS X
- Linux
- Install and configure the NDK and CMake
- Install NDK and CMake automatically
- Install the NDK and CMake
- Configure a specific version of CMake
- Groovy
- Kotlin
- Install a specific version of the NDK
- Configure specific versions of the NDK in your project
- Groovy
- Kotlin
- Default NDK version per AGP version
Installing the Android SDK
Android Studio provides everything you need to start developing apps for Android, including the Android Studio IDE and the Android SDK tools.
If you didn’t download Android Studio, go download Android Studio now, or switch to the stand-alone SDK Tools install instructions.
Before you set up Android Studio, be sure you have installed JDK 6 or higher (the JRE alone is not sufficient)—JDK 7 is required when developing for Android 5.0 and higher. To check if you have JDK installed (and which version), open a terminal and type javac -version . If the JDK is not available or the version is lower than 6, go download JDK.
To set up Android Studio on Windows:
- Launch the .exe file you just downloaded.
- Follow the setup wizard to install Android Studio and any necessary SDK tools.
On some Windows systems, the launcher script does not find where Java is installed. If you encounter this problem, you need to set an environment variable indicating the correct location.
Select Start menu > Computer > System Properties > Advanced System Properties. Then open Advanced tab > Environment Variables and add a new system variable JAVA_HOME that points to your JDK folder, for example C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_21 .
The individual tools and other SDK packages are saved outside the Android Studio application directory. If you need to access the tools directly, use a terminal to navigate to the location where they are installed. For example:
To set up Android Studio on Mac OSX:
- Unzip the downloaded zip file, android-studio-ide- -mac.zip .
- Drag and drop Android Studio into the Applications folder.
- Open Android Studio and follow the setup wizard to install any necessary SDK tools.
Depending on your security settings, when you attempt to open Android Studio, you might see a warning that says the package is damaged and should be moved to the trash. If this happens, go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy and under Allow applications downloaded from, select Anywhere. Then open Android Studio again.
The individual tools and other SDK packages are saved outside the Android Studio application directory. If you need access the tools directly, use a terminal to navigate into the location where they are installed. For example:
To set up Android Studio on Linux:
- Unpack the downloaded Tar file, android-studio-ide- -linux.zip , into an appropriate location for your applications.
- To launch Android Studio, navigate to the android-studio/bin/ directory in a terminal and execute studio.sh .
You may want to add android-studio/bin/ to your PATH environmental variable so that you can start Android Studio from any directory.
If the SDK is not already installed, follow the setup wizard to install the SDK and any necessary SDK tools.
Note: You may also need to install the ia32-libs, lib32ncurses5-dev, and lib32stdc++6 packages. These packages are required to support 32-bit apps on a 64-bit machine.
Android Studio is now ready and loaded with the Android developer tools, but there are still a couple packages you should add to make your Android SDK complete.
The stand-alone SDK Tools package does not include a complete Android development environment. It includes only the core SDK tools, which you can access from a command line or with a plugin for your favorite IDE (if available).
If you didn’t download the SDK tools, go download the SDK now, or switch to the Android Studio install instructions.
To get started on Windows:
Your download package is an executable file that starts an installer. The installer checks your machine for required tools, such as the proper Java SE Development Kit (JDK) and installs it if necessary. The installer then saves the Android SDK Tools to a specified the location outside of the Android Studio directories.
- Double-click the executable ( .exe file) to start the install.
- Make a note of the name and location where you save the SDK on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later when using the SDK tools from the command line.
- Once the installation completes, the installer starts the Android SDK Manager.
To get started on Mac OSX:
Unpack the ZIP file you’ve downloaded. By default, it’s unpacked into a directory named android-sdk-mac_x86 . Move it to an appropriate location on your machine, such as a «Development» directory in your home directory.
Make a note of the name and location of the SDK directory on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later when using the SDK tools from the command line.
To get started on Linux:
Unpack the .zip file you’ve downloaded. The SDK files are download separately to a user-specified directory.
Make a note of the name and location of the SDK directory on your system—you will need to refer to the SDK directory later when using the SDK tools from the command line.
Troubleshooting Ubuntu
- If you need help installing and configuring Java on your development machine, you might find these resources helpful:
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Java
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/JavaInstallation
- Here are the steps to install Java:
-
If you are running a 64-bit distribution on your development machine, you need to install additional packages first. For Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) and above, install the libncurses5:i386 , libstdc++6:i386 , and zlib1g:i386 packages using apt-get :
For earlier versions of Ubuntu, install the ia32-libs package using apt-get :
The Android SDK tools are now ready to begin developing apps, but there are still a couple packages you should add to make your Android SDK complete.
Then, select which SDK bundle you want to install:
Источник
Download
Before installing Android Studio or the standalone SDK tools, you must agree to the following terms and conditions.
Terms and Conditions
1. Introduction
2. Accepting this License Agreement
3. SDK License from Google
4. Use of the SDK by You
5. Your Developer Credentials
6. Privacy and Information
7. Third Party Applications
8. Using Android APIs
9. Terminating this License Agreement
10. DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES
11. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
12. Indemnification
13. Changes to the License Agreement
14. General Legal Terms
You’re just a few steps away from building apps for Android!
In a moment, you’ll be redirected to Installing the Android SDK.
I have read and agree with the above terms and conditions
Android Studio
The official Android IDE
- Android Studio IDE
- Android SDK tools
- Android 5.0 (Lollipop) Platform
- Android 5.0 emulator system image with Google APIs
Download Android Studio
To get Android Studio or stand-alone SDK tools, visit developer.android.com/sdk/
Intelligent code editor
At the core of Android Studio is an intelligent code editor capable of advanced code completion, refactoring, and code analysis.
The powerful code editor helps you be a more productive Android app developer.
Code templates and GitHub integration
New project wizards make it easier than ever to start a new project.
Start projects using template code for patterns such as navigation drawer and view pagers, and even import Google code samples from GitHub.
Multi-screen app development
Build apps for Android phones, tablets, Android Wear, Android TV, Android Auto and Google Glass.
With the new Android Project View and module support in Android Studio, it’s easier to manage app projects and resources.
Virtual devices for all shapes and sizes
Android Studio comes pre-configured with an optimized emulator image.
The updated and streamlined Virtual Device Manager provides pre-defined device profiles for common Android devices.
Android builds evolved, with Gradle
Create multiple APKs for your Android app with different features using the same project.
Manage app dependencies with Maven.
Build APKs from Android Studio or the command line.
More about Android Studio
For more details about features available in Android Studio, read the overview at Android Studio.
If you have been using Eclipse with ADT, be aware that Android Studio is now the official IDE for Android, so you should migrate to Android Studio to receive all the latest IDE updates. For help moving projects, see Migrating to Android Studio.
System Requirements
Windows
- Microsoft® Windows® 8/7/Vista/2003 (32 or 64-bit)
- 2 GB RAM minimum, 4 GB RAM recommended
- 400 MB hard disk space
- At least 1 GB for Android SDK, emulator system images, and caches
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 7
- Optional for accelerated emulator: Intel® processor with support for Intel® VT-x, Intel® EM64T (Intel® 64), and Execute Disable (XD) Bit functionality
Mac OS X
- Mac® OS X® 10.8.5 or higher, up to 10.9 (Mavericks)
- 2 GB RAM minimum, 4 GB RAM recommended
- 400 MB hard disk space
- At least 1 GB for Android SDK, emulator system images, and caches
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 6
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 7
- Optional for accelerated emulator: Intel® processor with support for Intel® VT-x, Intel® EM64T (Intel® 64), and Execute Disable (XD) Bit functionality
On Mac OS, run Android Studio with Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 6 for optimized font rendering. You can then configure your project to use Java Development Kit (JDK) 6 or JDK 7.
Linux
- GNOME or KDE desktop
- GNU C Library (glibc) 2.15 or later
- 2 GB RAM minimum, 4 GB RAM recommended
- 400 MB hard disk space
- At least 1 GB for Android SDK, emulator system images, and caches
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
- Oracle® Java Development Kit (JDK) 7
Tested on Ubuntu® 14.04, Trusty Tahr (64-bit distribution capable of running 32-bit applications).
Источник
Install and configure the NDK and CMake
To compile and debug native code for your app, you need the following components:
- The Android Native Development Kit (NDK): a set of tools that allows you to use C and C++ code with Android.
- CMake: an external build tool that works alongside Gradle to build your native library. You do not need this component if you only plan to use ndk-build.
- LLDB: the debugger Android Studio uses to debug native code. By default, LLDB will be installed alongside Android Studio.
This page describes how to install these components automatically, or by using Android Studio or the sdkmanager tool to download and install them manually.
Install NDK and CMake automatically
Android Gradle Plugin 4.2.0+ can automatically install the required NDK and CMake the first time you build your project if their licenses have been accepted in advance. If you’ve already read and agree to the license terms, then you can pre-accept the licenses in scripts with the following command:
Install the NDK and CMake
When you install the NDK, Android Studio selects the latest available NDK. For most projects, installing this default version of the NDK is sufficient. If your project needs one or more specific versions of the NDK, though, you can download and configure specific versions. Doing so helps you ensure reproducible builds across projects that each depend on a specific version of the NDK. Android Studio installs all versions of the NDK in the android-sdk /ndk/ directory.
To install CMake and the default NDK in Android Studio, do the following:
With a project open, click Tools > SDK Manager.
Click the SDK Tools tab.
Select the NDK (Side by side) and CMake checkboxes.
Figure 1: The SDK Tools window showing the NDK (Side by side) option
Click OK.
A dialog box tells you how much space the NDK package consumes on disk.
Click OK.
When the installation is complete, click Finish.
Your project automatically syncs the build file and performs a build. Resolve any errors that occur.
Configure a specific version of CMake
The SDK Manager includes the 3.6.0 forked version of CMake and version 3.10.2. Projects that don’t set a specific CMake version are built with CMake 3.10.2. To set the CMake version, add the following to your module’s build.gradle file:
Groovy
Kotlin
If you want to use a CMake version that is not included by the SDK Manager, follow these steps:
- Download and install CMake from the official CMake website.
- Specify the CMake version you want Gradle to use in your module’s build.gradle file.
Either add the path to the CMake installation to your PATH environment variable or include it in your project’s local.properties file, as shown. If Gradle is unable to find the version of CMake you specified in your build.gradle file, you get a build error.
If you don’t already have the Ninja build system installed on your workstation, go to the official Ninja website, and download and install the latest version of Ninja available for your OS. Make sure to also add the path to the Ninja installation to your PATH environment variable.
Install a specific version of the NDK
To install a specific version of the NDK, do the following:
With a project open, click Tools > SDK Manager.
Click the SDK Tools tab.
Select the Show Package Details checkbox.
Select the NDK (Side by side) checkbox and the checkboxes below it that correspond to the NDK versions you want to install. Android Studio installs all versions of the NDK in the android-sdk /ndk/ directory.
Figure 2: The SDK Tools window showing the NDK (Side by side) options
Click OK.
A dialog box tells you how much space the NDK package(s) consumes.
Click OK.
When the installation is complete, click Finish.
Your project automatically syncs the build file and performs a build. Resolve any errors that occur.
Configure each module with the version of the NDK you want it to use. When using Android Studio 3.6 or higher, if you do not specify the version, the Android Gradle plugin chooses a version that it is known to be compatible with.
Configure specific versions of the NDK in your project
You may need to configure the version of the NDK in your project if one of the following is true:
- Your project is inherited and you need to use specific versions of the NDK and the Android Gradle plugin (AGP). For more information, see Configure the NDK for the Android Gradle plugin.
You have multiple versions of the NDK installed and you want to use a specific one. In this case, specify the version using the android.ndkVersion property in the module’s build.gradle file, as shown in the following code sample.
Groovy
Kotlin
Default NDK version per AGP version
Before release, each AGP version is thoroughly tested with the latest stable NDK release at that time. For AGP version 3.6 and above, that NDK version will be used to build your projects if you do NOT specify an NDK version in the build.gradle file. The default NDK version is documented inside the AGP release notes. The current default NDK versions are listed in the following table:
Android Studio/Gradle Plugin Version 7.0 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.6 3.5 3.4 Default NDK version
specified for the version of AGP21.4.7075529 21.4.7075529 21.1.6352462 21.0.6113669 20.0.5594570 No default specified Content and code samples on this page are subject to the licenses described in the Content License. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Источник
-






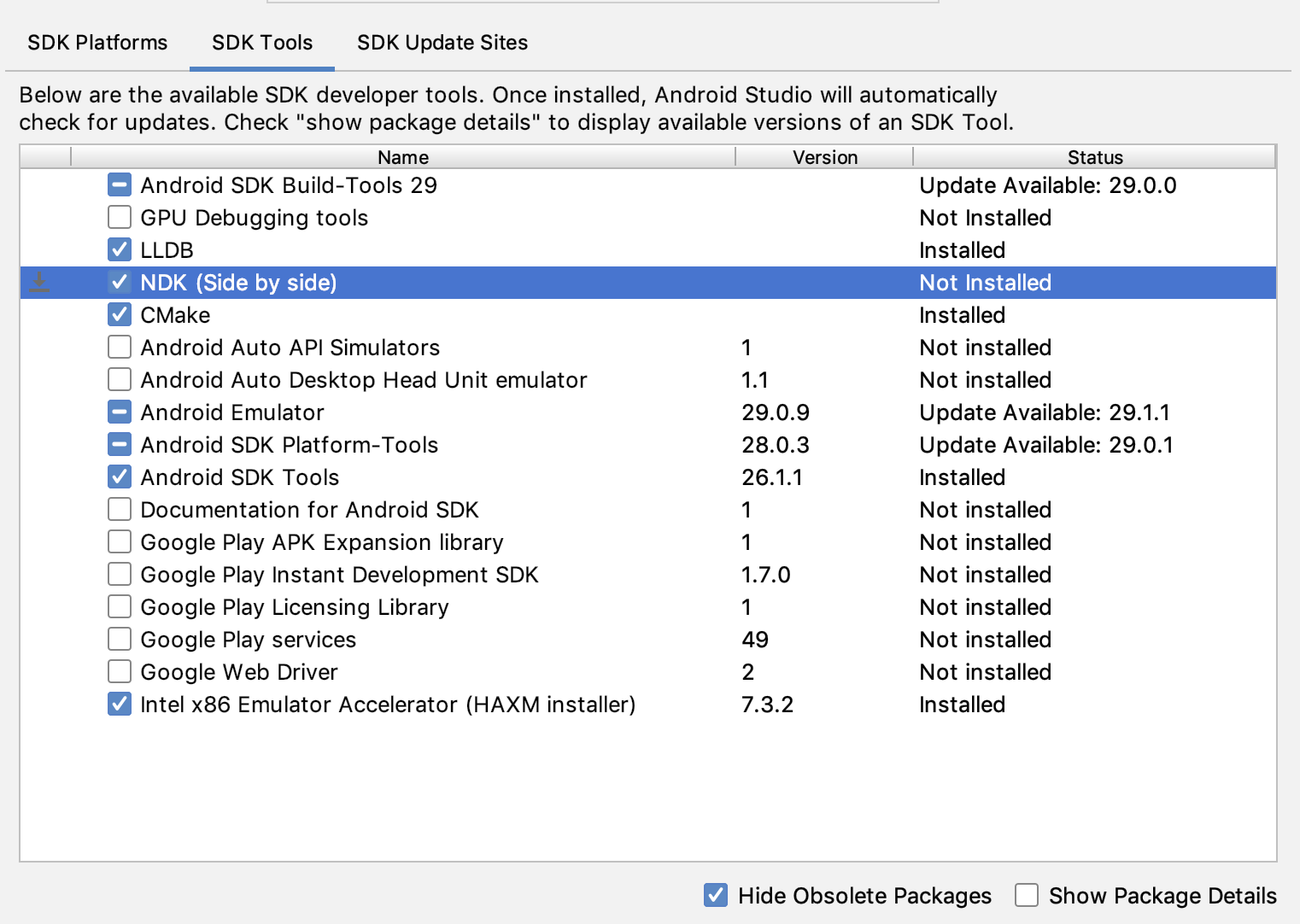 Figure 1: The SDK Tools window showing the NDK (Side by side) option
Figure 1: The SDK Tools window showing the NDK (Side by side) option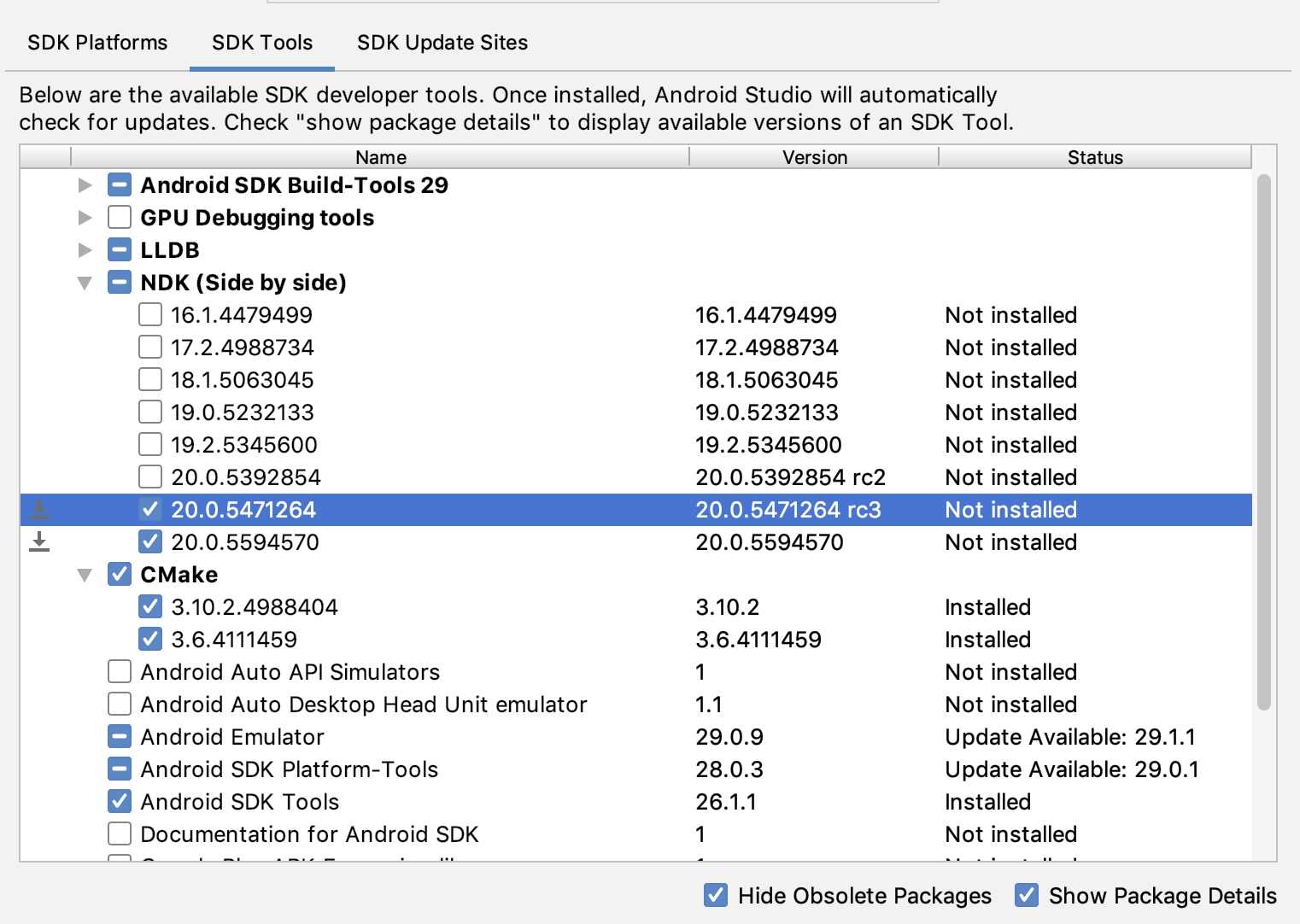 Figure 2: The SDK Tools window showing the NDK (Side by side) options
Figure 2: The SDK Tools window showing the NDK (Side by side) options


