- How To Install a Linux OS On Your Android Phone
- What Is Root?
- Use Apps to Root Your Android Device
- BusyBox
- Linux Deploy
- VNC Viewer
- Install a Linux OS On Your Android Mobile Phone With UserLAnd
- Install linux desktop on android
- Guide: Installing and Running a GNU/Linux Environment on Any Android Device
- Setting Up GNU/Linux on Android
- Step-by-Step Guide
- Installing Linux Applications
How To Install a Linux OS On Your Android Phone
Carry your desktop in your pocket
The general trend for technology is to become smaller and smaller. From desktops to watches, users see value in having a mobile computer without having to carry around a bag of wires and adapters.
This article will show you how to install a fully functioning Ubuntu Linux operating system (OS) on your mobile phone. The first method we will describe requires you to root your device.
What Is Root?
Android phones use Linux file-system ownership and permissions. The root is the superuser.
When you log into your device, there are certain functions you can perform on your phone based on user permissions. The root user or superuser has permissions to do anything to any file such as uninstall an application.
Before you can grant yourself superuser permissions, you must unlock the bootloader and install a custom recovery.
Rooting your device adds a standard Linux function that was removed by placing a small file su (switch user) with permissions in the system.
When you run a file without any other parameters, your permissions and credentials are switched from a regular user to a superuser with complete control.
Use Apps to Root Your Android Device
For this method, you will need to install three apps from the Google Play Store.
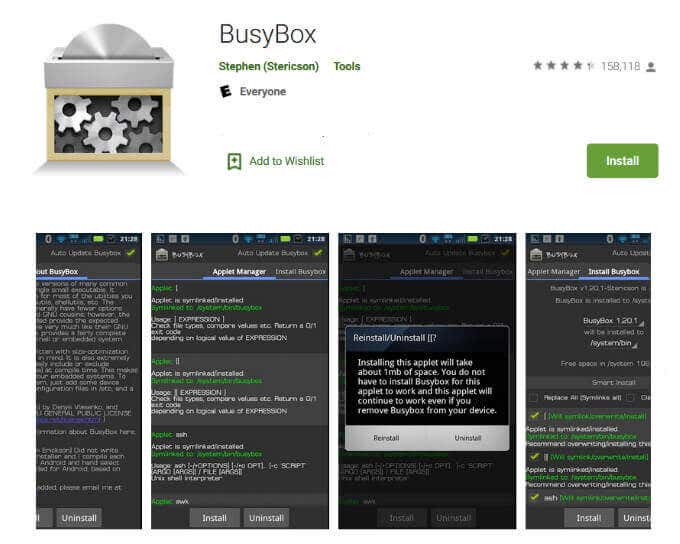
BusyBox
BusyBox gives your phone access to Linux commands that you wouldn’t typically have. It is necessary to enable many root apps to work.
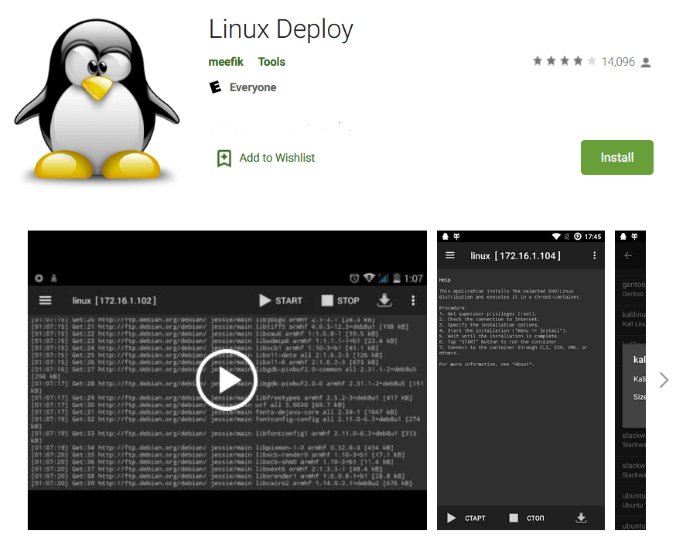
Linux Deploy
Linux Deploy is an open-source program used to easily and quickly install Linux OS on your Android mobile phone.
It works by creating a disk image on a flashcard, mounting it, and installing an OS distribution.
Open the app to make sure you have root access (you should after installing BusyBox). Click the download button on the top or bottom right-hand side of your screen.
- You will now see the options menu. Leave most of the settings as the default. Under Properties: Linux, select your distribution.
- Change the flavor of Linux by selecting an option from the Distribution suite.
- Select the desktop you want under Desktop environment to change the look and feel of the app.
- Under the GUI setting, tick off Enable to ensure your device will have a graphical interface. Go into the GUI settings to change options such as the screen resolution.
- Under Properties, give yourself superuser privileged access by setting your Username to root.
To open the menu, click the three dots at the top right-hand side of your screen. Select Install and click OK to start installing the app on your phone.
The process takes a little time as it is installing the entire Linux distribution on your Android device.
After the installation is complete, click START to open fruit (a sub-compartment), then hit STOP when finished.
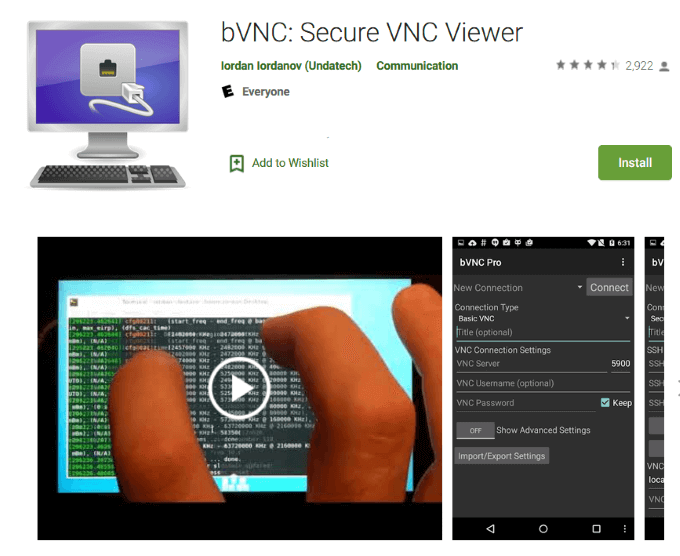
VNC Viewer
The final app to install is VNC Viewer. It will turn your Android device into a remote desktop and allow you to view the GUI.
Open the app, add a new connection, use localhost:5900 for Address, and click Create. This will open a new window for localhost. Click CONNECT.
Enter the password you set earlier when asked for Authentication and click Done. You will now be able to see Linux and use it.
Install a Linux OS On Your Android Mobile Phone With UserLAnd
Another way to install a Linux OS on your Android mobile phone is to use the UserLAnd app. With this method, there is no need to root your device.
Go to the Google Play Store, download, and install UserLAnd. The program will install a layer on your phone, enabling you to run the Linux distribution you choose.
Launch the app, we will choose Ubuntu, and then tap OK. Grant app permissions by clicking ALLOW.
Provide user login details. Enter a Username, Password, and VNC Password for the Ubuntu session, then tap CONTINUE > VNC > CONTINUE.
UserLand will download all the required assets for Ubuntu. The process will vary in length depending upon your Internet speed.
You will use this for VNC and ssh access. Wait for the installation to complete, progress will be displayed.
At this point, UserLAnd will download all the necessary assets for the Ubuntu session. How long the process takes will depend upon the speed of your connection.
When the installation is complete, you will be redirected to the Google Play Store to download bVNC.
Click Install, then Back to return to the UserLAnd app. Give permission to bVNC to access your files if asked and then click Allow.
If an option is available for Ubuntu, tap on it to start a Linux session. If there is no option, click on Sessions at the bottom of your screen, then tap the + sign at the top right-hand corner.
Name the new session Ubuntu > select apps:Ubuntu for Filesystem > choose ssh for Service Type > Done.
To launch a Linux session, tap Sessions on the bottom of your screen. The new session will open to a desktop environment.
To open applications, tap the start menu located at the bottom-left side of your screen. Install new Linux programs using the command terminal by tapping System Tools > LXTTerminal.
If you want to close the desktop, tap anywhere on your screen > the three vertical dots > Disconnect.
The methods above show you how to install a Linux OS on your smartphone. Linux is more flexible than Android by enabling users to perform functions such as advanced image editing, app development, and working in a real desktop environment.
The downside is that you are working on a tiny screen. However, if you want the ability to carry your desktop in your pocket, give it a try.
David has a background in small business and lives in Australia. He is a WordPress and Ubuntu Developer who enjoys design, CSS and tech tool integration. Read David’s Full Bio
Источник
Install linux desktop on android
Краткое описание:
Установка Linux на Android в Termux без рут-прав
Andronix lets you install a Linux system on your Android Device without root. We found out that using Linux on Android is quite useful and lets you do many heavy tasks on your Android device.
This app lets you install various popular Linux distributions on your Android device by using Termux and PRoot functionality on the Android system. The application also provides you a graphics layer or Desktop environment (Xfce, MATE, LXDE, LXQT and KDE) on the top of the Linux shell which makes the user experience much better than working on a Linux command line.
* Manjaro is now available with xfce, lxqt, lxde and mate.
* Ubuntu KDE is now available which is great success.
* KDE Performance optimization — Better performance.
* Added multiple Window manager — Better look in KDE.
* Prinstalled softwares and themes — Makes a better aesthetic.
* AndroNix Premium — We have released AndroNix Premium with tons of features.
* Dark Mode — Use AndroNix at night comfortably.
* AndroNix Commands — A special addition to the family of AndroNix. It’s all you need to manage your commands throughout your life. Just copy and paste!
* AndroNix Web App — We have also released our web app to compliment AndroNix commands on Android, so you can now access Commands on any internet connected device.
* AndroNix Feed — We saw that since the last release you guys were really happy about the blogs we posted. So now we have a dedicated blog feed to make a better use of Linux and the power it offers.
* Offline Downloads — Internet can be unpredictable sometimes, but don’t worry we’re introducing offline support of Linux distros, though you’ll be still needing internet to download some files depending upon your device at the time of installing.
* Robust Documentation — We’ve been working on writing some documentations for weeks now. This will enable you to help yourself without waiting for us to reply.
* Priority Support — AndroNix Premium bring priority support with it at no extra cost. IF you’re an AndroNix Premium member just enjoy the blazing fast support, on the platform you like!
* Communities budding — We now support official AndroNix communities on Telegram and WhatsApp. We will soon expand to other platforms as well.
* UI overhaul — We’ve redisgned almost every element the our app and worked on user experience more than ever
* Automation Added — If you choose AndroNix Premium, we’ll handle everything for you. Just login and forget the rest.
* Profile Tab Added — Profile let’s you see your current status (Premium or not). If you’re a premium member, profile section has many things for you.
* Termux is now available offline — We now offer an offline copy of Termux within
AndroNix.
If you are new to Linux, we provide you easy and hassle-free instructions which makes your first impression of Linux a lot better. In case you still face some issues you can easily contact us on various platforms mentioned in the app. We ensure you that we will contact you as soon as possible.
— No root permissions required.
— Distros we support:
* Manjaro
* Ubuntu
* Kali Linux
* Debian
* Parrot OS
* Fedora
* Arch Linux
— Desktop environments we support:
* KDE
* LXDE
* LXQT
* MATE
* XFCE
— One click install/uninstall feature.
— Features multiboot linux system.
— Termux in required.
— Android version should be at least 5.1
— Device architecture supported: ARMv7, ARM64, x64.
Требуется Android: 5.1 и выше
Русский интерфейс: Нет
Источник
Guide: Installing and Running a GNU/Linux Environment on Any Android Device
As many of you may well be aware, the Android operating system is powered by the Linux kernel underneath. Despite the fact that both Android and GNU/Linux are powered by the same kernel, the two operating systems are vastly different and run completely different types of programs.
Sometimes, however, the applications available on Android can feel a bit limited or underwhelming, especially when compared to their desktop counterparts. Fortunately, you can get a GNU/Linux environment up and running on any Android device, rooted or non-rooted. (The following instructions assume a non-rooted device.)
For those power users on Android tablets, or other Android devices that have large screens (or can plug into a bigger screen), the ability to run desktop Linux software can go a long way towards increasing the potential that an Android device has for productivity.
Setting Up GNU/Linux on Android
To get a GNU/Linux environment set up on your Android device, you only need to install two applications from the Google Play store: GNURoot Debian and XServer XSDL. After you do that, you will only need to run a small handful of Linux commands to complete the installation.
GNURoot Debian provides a Debian Linux environment that runs within the confines of the Android application sandbox. It accomplishes this by leveraging a piece of software called proot, a userspace re-implementation of Linux’s chroot functionality, which is used to run a guest Linux environment inside of a host environment. Chroot normally requires root access to function, but by using proot you can achieve similar functionality without needing root privileges.
GNURoot comes with a built-in terminal emulator for accessing its Debian Linux environment. This is sufficient for running command-line software, however, running graphical software requires an X server to be available as well. The X Window System was designed to have separate client and server components in order to provide more flexibility (a faster, more powerful UNIX mainframe could act as the client to X server instances running on much less powerful and less sophisticated terminals).
In this case, we will use a separate application, XServer XSDL, that GNURoot applications will connect to as clients. XServer XSDL is a complete X server implementation for Android powered by SDL that has many configurable options such as display resolution, font size, different types of mouse pointer behavior, and more.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Install GNURoot Debian and XServer XSDL from the Play Store.
2. Run GNURoot Debian. The Debian Linux environment will unpack and initialize itself, which will take a few minutes. Eventually, you will be presented with a “root” shell. Don’t get misled by this – this is actually a fake root account that is still running within the confines of the Android application sandbox.
3. Run apt-get update and apt-get upgrade to ensure you have the most up-to-date packages available on your system. Apt-get is Debian’s package management system that you will use to install software into your Debian Linux environment.
4. Once you are up-to-date, it’s time to install a graphical environment. I recommend installing LXDE as it is simple and light-weight. (Remember, you’re running Debian with all the overhead of the Android operating system in the background, so it’s best to conserve as many resources as you can.) You can either do apt-get install lxde to install the desktop environment along with a full set of tools, or apt-get install lxde-core to only install the desktop environment itself.
5. Now that we have LXDE installed, let’s install a few more things to complete our Linux setup.
• XTerm – this provides access to the terminal while in a graphical environment
• Synaptic Package Manager – a graphical front-end to apt-get
• Pulseaudio – provides drivers for playing back audio
Run apt-get install xterm synaptic pulseaudio to install these utilities.
6. Finally, let’s get the graphical environment up and running. Start XServer XSDL and have it download the additional fonts. Eventually you will get to a blue screen with some white text – this means that the X server is running and waiting for a client to connect. Switch back to GNURoot and run the following two commands:
Then, switch to XServer XSDL and watch the LXDE desktop come up onto your screen.
I recommend putting the above two commands into a shell script so that you can easily restart LXDE if you close the session or if you need to restart your device.
Installing Linux Applications
Congrats! You’ve successfully gotten Debian Linux up and running on your Android device, but what good is running Linux without apps? Fortunately, you’ve got a massive repository of Linux applications at your fingertips just waiting to be downloaded. We’ll use the Synaptic Package Manager, which we installed earlier, to access this repository.
Click the “start” button at the lower-left hand corner, click Run, and then type synaptic . The Synaptic Package Manager will load. From here, simply press the Search button at the top and then type the name of the application you’d like to install. Once you’ve found an application, right click it and select “Mark for Installation”. When you are finished marking packages, click the Apply button at the top to start the installation. Uninstalling packages follows the same procedure, except by right-clicking and selecting “Mark for Removal” instead.
Of course, since this isn’t a real Linux installation but rather a Linux environment running on top of, and within the constraints of, Android, there are a couple of limitations to be aware of. Some applications will refuse to run or will crash, usually due to the fact that some resources that are usually exposed on GNU/Linux systems are kept hidden by Android. Also, if a regular Android app can’t do something, then usually a Linux application running within Android can’t as well, so you won’t be able to perform tasks such as partitioning hard drives. Lastly, games requiring hardware acceleration will not work. Most standard everyday apps, however, will run just fine. Some examples include Firefox, LibreOffice, GIMP, Eclipse, and simple games like PySol.
I hope that you find this tutorial useful. While I personally performed these steps on my Google Pixel C, you can do this on most Android devices. Preferably on a tablet device with access to keyboard and mouse peripherals, of course. If you already run a GNU/Linux distribution on your Android device, let us know what you are using it for below!
Источник