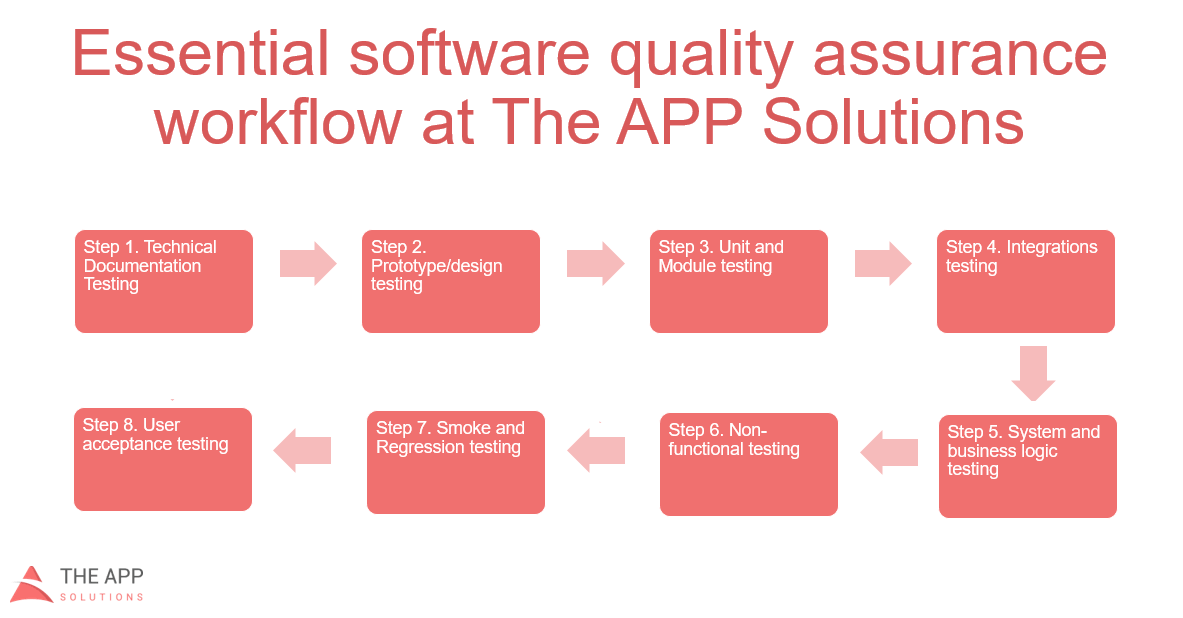
- Mobile Application Development
- What is mobile application development?
- Choose a platform
- Develop for both Android and iOS: Native apps or hybrid apps?
- Think light: Building for a mobile platform
- Offload processing to the cloud
- Extend your app with advanced cloud services
- Join a developer program
- Mobile application development and IBM Cloud
- Android Apps vs. iOS apps — What and Why is Better in 2021?
- Tech Stack
- Pros and Cons
- Android vs. iOS App Development: Which is better for you?
- Market share
- Demographics
- Development cost
- Testing
- App Updates
- Revenue Models
- Engagement
- Comparing Android vs Apple Development
- iOS or Android: What to choose?
- The APP Solutions experience
- Download Free E-book with DevOps Checklist
- Android vs. Apple: Which Platform to Develop for First
Mobile Application Development
What is mobile application development?
Mobile application development is the process to making software for smartphones and digital assistants, most commonly for Android and iOS. The software can be preinstalled on the device, downloaded from a mobile app store or accessed through a mobile web browser. The programming and markup languages used for this kind of software development include Java, Swift, C# and HTML5.
Mobile app development is rapidly growing. From retail, telecommunications and e-commerce to insurance, healthcare and government, organizations across industries must meet user expectations for real-time, convenient ways to conduct transactions and access information. Today, mobile devices—and the mobile applications that unlock their value—are the most popular way for people and businesses to connect to the internet. To stay relevant, responsive and successful, organizations need to develop the mobile applications that their customers, partners and employees demand.
Yet mobile application development might seem daunting. Once you’ve selected the OS platform or platforms, you need to overcome the limitations of mobile devices and usher your app all the way past the potential hurdles of distribution. Fortunately, by following a few basic guidelines and best practices, you can streamline your application development journey.
To learn more about the specifics of mobile application development on either platform, read our articles on iOS app development and Android app development.
Choose a platform
Many independent application development teams choose to build their apps for Android first. Why? The vast majority—around 70 percent—of smartphones run Android, and the Google Play Store has fewer restrictions than the Apple App Store. On the other hand, mobile applications developed for iOS have far fewer devices that need support, making optimization simpler. And user retention is typically higher for iOS applications.
Depending on the intended use case and target audience for the mobile application you are developing, you might have other considerations. For example, if you’re designing an app for your organization’s employees, you’ll need to support the platforms they use, which may mean developing cross-platform apps that work for both Android and iOS. Or if you’re building a mobile application for your customers and you know the majority of them use iPhones, then developing iOS applications should be a top priority. Additional considerations when developing your mobile applications include monetization strategies and anticipated user behavior, which can be influenced by geographical and cultural factors.
Enhance efficiency and tighten security by integrating the development platform and device management tool
Develop for both Android and iOS: Native apps or hybrid apps?
Let’s say you need to do mobile application development for both the Android operating system and iOS. What is the best software development approach?
You could develop two native applications. Taking advantage of native APIs and OS-specific programming languages can help you build a powerful app. Most enterprise apps, especially ones that require substantial API traffic, benefit from native development.
If you decide to develop native applications one at a time, you’ll likely want to begin with Android—for some of the same reasons that independent app developers often focus on Android. You’ll probably have better luck developing the full application as an MVP on Android and then converting and optimizing it to iOS after release.
You will still need to debug and rewrite the code for the native language and redesign the front-end user interface, because the two operating systems function very differently, making cross-platform operation impossible.
So why not start completely from scratch? While you can’t simply translate the code into a new programming language, much of the back end can be replicated cross-platform. Frameworks, libraries and third-party extensions often function identically in both environments, allowing you to avoid costly reworking. You can also use a prebuilt mobile cloud service, such as IBM Mobile Foundation, to manage the web back end.
Another option is to go hybrid, taking a write-once-run-anywhere approach. Hybrid apps use a single codebase that can function on either platform. They’re typically coded in a programming language that’s universally recognized, such as Java, JavaScript, HTML or CSS. Because you’re denied access to the operating system’s native APIs, hybrid mobile application development works best for simple web applications—three- or four-page mobile applications with limited functionality.
Think light: Building for a mobile platform
Whether you choose native or hybrid mobile application development, one of the first hurdles you’ll need to overcome is the relatively limited resources on mobile devices. Your target mobile device will have much less processing power and memory than desktop computers or enterprise servers. These constraints might seem like a significant challenge, especially if you’re more familiar with the comparatively boundless resources for conventional software development for web apps.
Limited mobile platform resources mean you need to adjust your goals for your app design.
Throughout the mobile application development process, developers must work to ensure that their mobile app is less resource intensive than a typical desktop application.
Delivering a great user experience is vital. That starts with understanding that your user interface for a mobile app should be simpler than a desktop application interface. By creating a straightforward UX design that is focused on critical functions, you can provide a better user experience while consuming fewer resources.
Your mobile app interface should be designed for touch. Mobile users must be able to navigate your app easily and provide input without excessive typing.
Fortunately, these requirements for efficient, simple touch-based apps map well to user expectations. Mobile users generally want to accomplish tasks simply, with just a few taps. They want apps that are above all fast, convenient and easy to use on their mobile devices.
Offload processing to the cloud
What if your mobile application requires more processing than a typical mobile platform can support? Consider offloading that processing to the cloud.
Through the judicious use of APIs, you can connect your app to cloud-based services and databases to provide advanced functionality without slowing your application or straining the device it is running on. You can even offload data storage and caching to a cloud-based server, leaving very little data on the device.
Extend your app with advanced cloud services
The cloud can offer additional advantages beyond performance boosts. Connect your mobile application to powerful cloud services to add features and improve usability. Employ APIs to integrate new features, such as advanced cloud-based services that can help you enhance your mobile apps. These include push notifications, IBM Watson®-powered AI analytics, Internet of Things (IoT) smart device integration and more.
Join a developer program
Neither Android nor iOS is a completely open environment. Before your application can be officially distributed, you’ll need to join the appropriate developer program.
The Android mobile application development program lets you use your existing Google account to create a developer account, pay the USD 25 fee and submit your application. Google Play, the official Android store, does have quality standards that must be met prior to publication, but they’re more guidelines than actual rules. As part of your app development process, you can also distribute your applications outside the Google Play store and allow users to directly download and install them.
By contrast, the Apple mobile application development program sets a high barrier to entry. You need to pay a program fee of USD 99 per year and adhere to high standards. Once you’re a member of the program, you get early access to beta versions of the operating systems and proprietary frameworks or APIs. Meeting the high standards for the App Store also signifies to the world that you’ve developed a high-quality app.
Mobile application development and IBM Cloud
Mobile application development is necessary for most enterprises. When you build your application with both operating systems in mind, try to make judicious use of APIs and understand the specifics of the required developer programs. That approach will help you deliver to your users an app that’s flexible, convenient and lightweight—the perfect way to serve information or services—along with an excellent user experience.
To help mobile app developers, IBM Cloud offers a variety of solutions, including IBM Cloud App ID, which allows you to add authentication and back-end security, and IBM Push Notifications, which lets you send personalized real-time messages to mobile applications.
To learn more about the specifics of mobile application development on either platform, read our articles on iOS app development and Android app development.
To help you explore mobile application development, IBM offers a simple tutorial on building a voice-enabled Android-based chatbot.
Learn about the features and capabilities of the IBM Mobile Foundation, in addition to IBM Push Notifications through the Introduction to Mobile Foundation course in the IBM Cloud Professional Developer curriculum.
If you are ready to start using IBM Cloud today, sign up here.
Источник
Android Apps vs. iOS apps — What and Why is Better in 2021?
Websites are no longer the best way to access information, products, and services.
Android and iOS devices with mobile applications more convenient for these tasks compared with traditional websites.
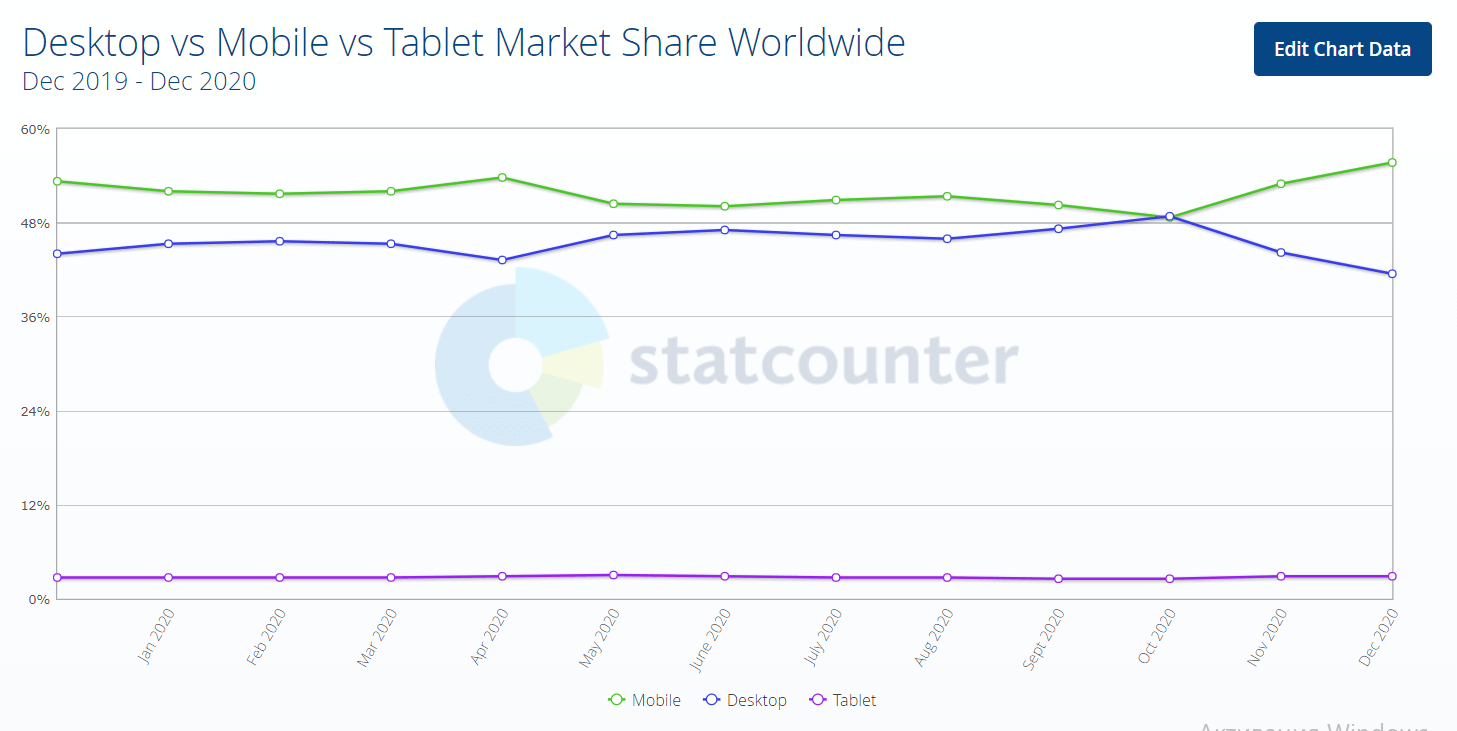
- As for December 2020, mobile currently accounts for 55.73% of all internet traffic worldwide, while desktop has 41.46%, says StatCounter.
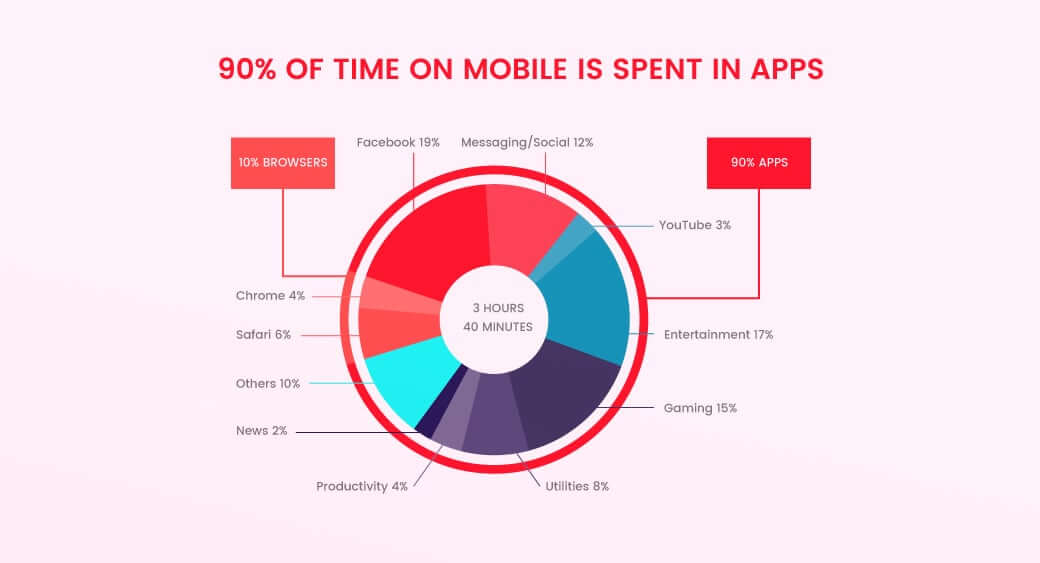
- App Annie reveals that mobile apps now account for 10 out of every 11 minutes we spend using mobile devices, while web browsing is only responsible for 10% of our mobile time.
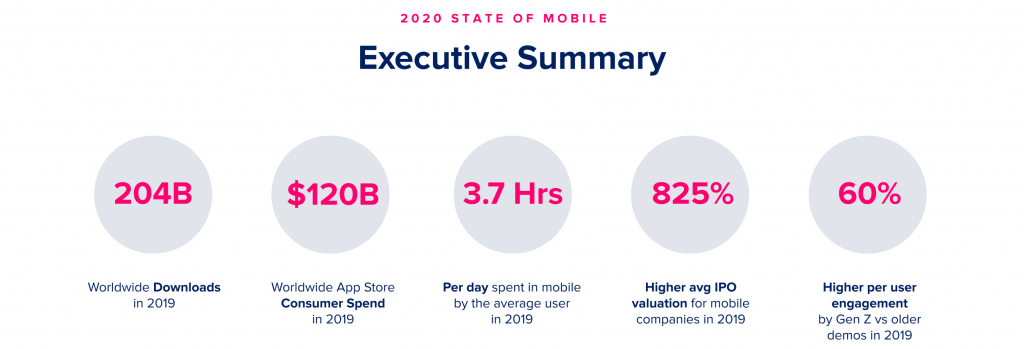
- App Annie also reports that the world’s smartphone users downloaded more than 200 billion mobile apps in 2019, spending a total of US$120 billion on apps and app-related purchases over the past 12 months.
- Recent data from Ericsson tells that the average user now spends an annual average of more than US$21 per connected smartphone.
Apart from growing popularity among users, mobile applications also work perfectly as an engaging business tool. Why? Mobile applications can leverage native mobile device functionality, such as Push-notifications, geolocation, camera, etc.
That’s why smart entrepreneurs, who want to stay connected with clients in the distractive digital world, can’t ignore mobile applications. The same strategy works for start-ups who prefer building mobile-first versions of their products while using websites and landing pages as a marketing tool.
But before asking a mobile app development company for a free quote, you need to decide which of the operating systems you are going to hit: iOS or Android. The first thing to do for dealing with the «Android apps vs iOS apps» dilemma, is identifying your app’s target market. To be on the safe side, learn also about differences in both platforms’ tech stack, how much each app will cost you, and how much time the project will take.
We’ve decided to create this article to help you make the right decision for iOS or Android application development. In this article, we’ve dug deeper into the tech stack of both platform use and listed the pros and cons of iOS and Android application development. We’ve also highlighted other factors that impact stakeholders’ decisions when choosing between Android and Apple and our experience of creating both iOS and Android projects.
Ready? Let’s start!
Tech Stack
Let’s see what technologies mobile developers use to build projects for different platforms.
Developing Android projects
To create Android apps, developers use Java, C++, and Kotlin programming languages. Furthermore, Android developers use the following advanced Google development tools:
- Android Jetpack, a set of pre-build Android components
- Firebase is known as a comprehensive mobile app development platform
- Android SDK development kit, connected with Android Studio, an integrated development environment
Now, let’s compare iOS advantages and disadvantages.
Developing iOS projects
While the Android operating system has an open-source code, iOS has closed source code. Closed source code means that iOS works on Apple devices only. The development team might use Swift or Objective-C. Also, iOS developing tools include:
- iOS SDK, or Software Development Kit, is integrated with the Cocoa Touch UI framework. The framework provides graphical elements, user interface controls, and others.
- XCode is the official integrated development environment (IDE) for iOS development.
- Swift Playgrounds is a development environment for Swift.
- TestFlight is an online service for over-the-air installation and testing. This online service allows developers to test apps and collect valuable feedback before the app release.
Pros and Cons
Below, we have gathered the pros and cons of Android and iOS development. You will also find a platform comparison to help you make the right decision.
Advantages of developing Android
- Open system. Android developers receive access to more features restricted in iOS applications.
- Design. Developers use extensive Google design guidelines for developing an intuitive user interface.
- Fragmentation. On the one hand, we may consider fragmentation as a disadvantage, but you can develop apps not only for an Android smartphone, but also for a broader range of devices, including wearables, TVs, in-car systems, and others.
- Release. In comparison to iOS, Android apps are easier to publish to Google Play. The whole process may take just a few hours.
Disadvantages of Android
- Fragmentation. As we said, fragmentation may also be an Android drawback. Nowadays, Android devices come in different screen sizes, resolutions, etc. The development team might need more time to adjust the app’s features for particular devices.
- Testing. Android versions and devices might vary. Thus, it might take more time for QA specialists to test your app.
- Costly. The more time the development and testing stage takes, the higher will be the Android app price. But the price also depends on the app’s features and complexity.
Advantages of iOS
- Revenue. As you may already know, Apple users spend more money on app purchases compared to Android users.
- The number of devices. As we said, iOS powers only Apple products. For that reason, your app should fit a limited number of screens and devices.
- UI design. Apple provides developers with a detailed style guide for the app UI. The team needs less time, making it more affordable in the app design stage.
Disadvantages of iOS
- App release. Keep in mind that the App Store has quite strict review guidelines. The marketplace can reject your app due to security issues, a lack of valuable content, or poor performance. Besides, the developer should submit your app for real-life testing, which usually takes a few days.
- Flexibility. iOS apps are usually hard to customize because the platform has many restrictions.
Now, it’s time to compare both platforms.
Android vs. iOS App Development: Which is better for you?
To identify your target market for your mobile application, you should consider the following factors:
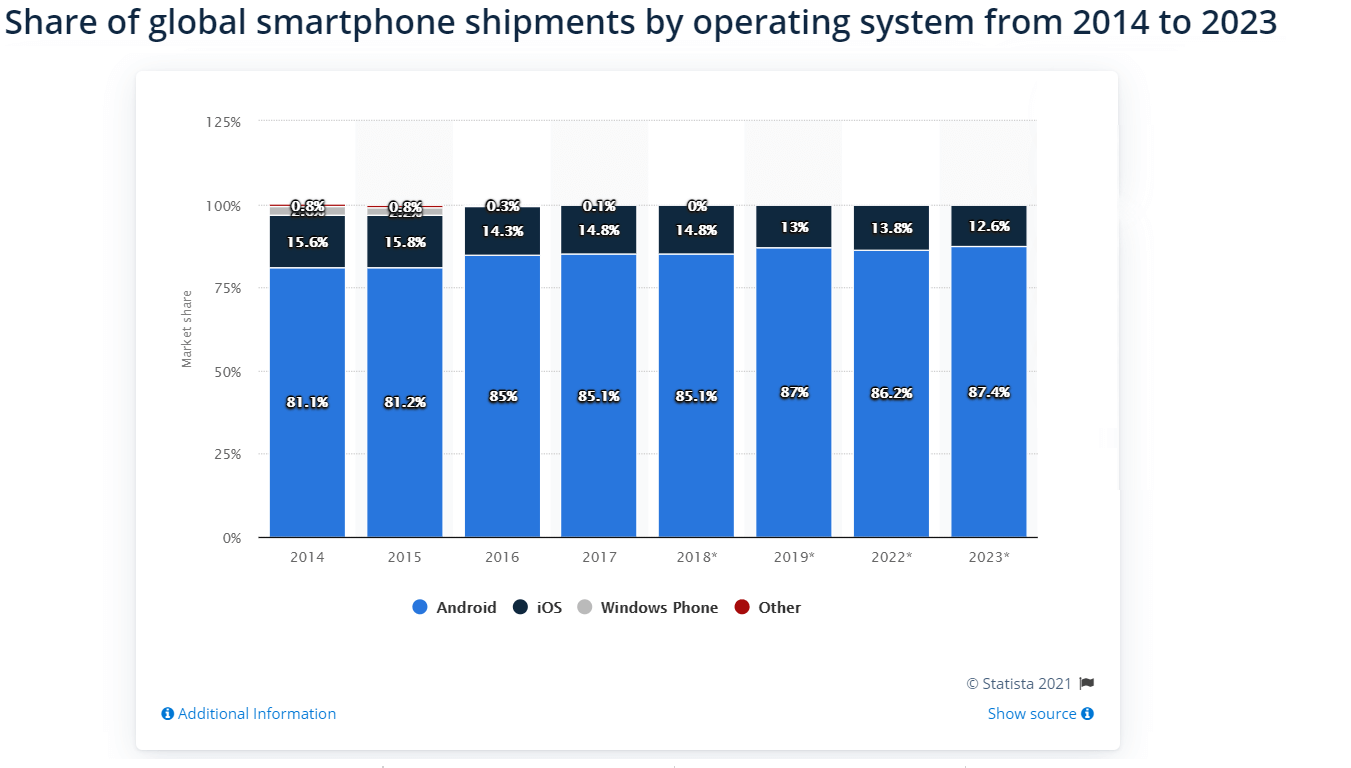
Market share
The amount of smartphones that support one or another mobile platform shows us how many potential users your application can have. Sure, those figures are just theory, but they still matter.
Statista, a company specializing in market and consumer data, reports the following data:
- In 2019, smartphones running the Android operating system held an 87 percent share of the global market and will increase over the forthcoming years.
- The same year, iOS devices developed by Apple, had a 13 percent share of the market.
[Share of global smartphone shipments by operating system from 2014 to 2023]
Thus, by developing an Android-first project and uploading your Android project to Google Play Store, you can receive more users, compared to the results after building an iOS app.
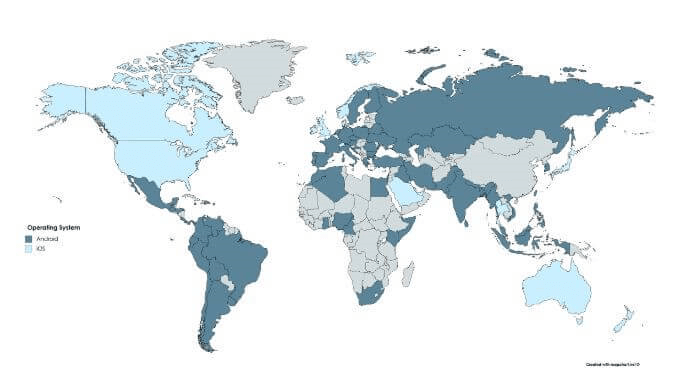
Demographics
Demographics tell us a lot about Android and iOS users. For example, their country:
Android currently holds the most significant global platform share. This market share comes from developing countries and lower-income areas.
iOS users are younger, with a higher education level, greater engagement, and earn more money. Thus, they spend more per app.
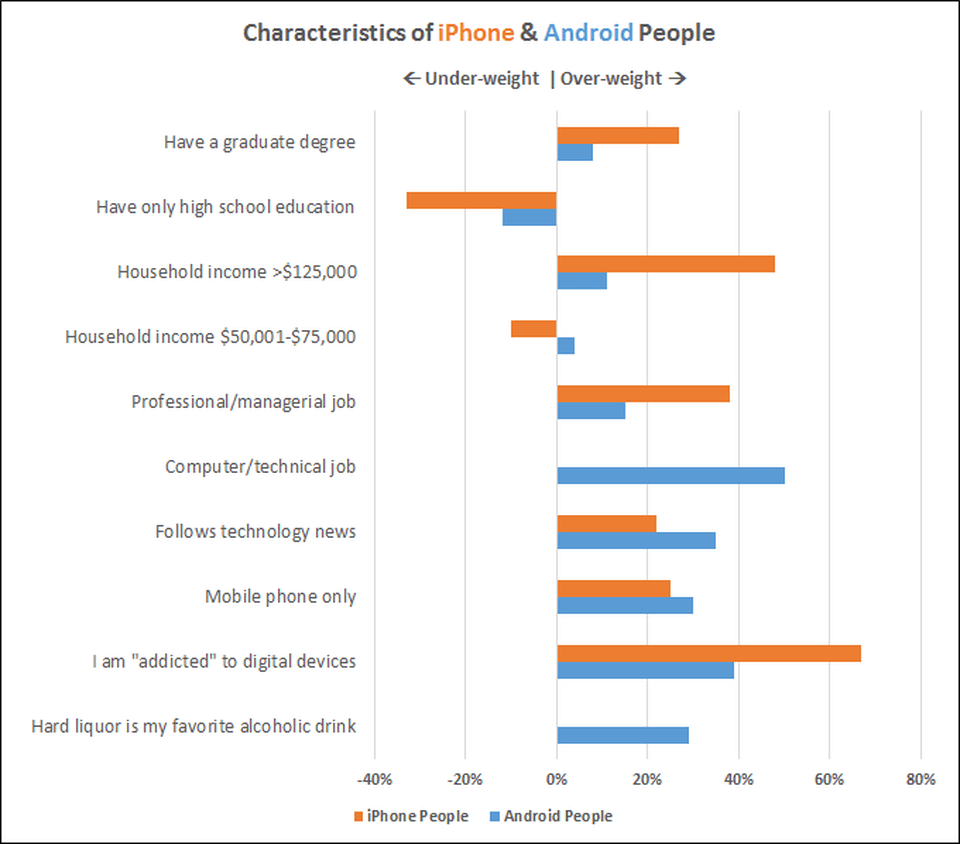
iPhone Users
Android Users
37% more likely to have a graduate degree
80% more likely to have only a high school diploma
29% more likely to be older women (35+)
More likely to be younger men (34 and younger)
14% more likely to be extroverted
12% more likely to be introverted
67% more likely to make over $200K and enjoy spending it
24% more likely to earn $100K or less
More likely to be in Media/Marketing/Business
More likely to be in IT/Energy/Utilities
39% more likely to be high-maintenance
12% more likely to be pet lovers
50% more likely to have visited more than 5 countries
71% more likely to have never traveled abroad
Now that you know about Apple and Android users, it is time to learn about other important factors for successful decision-making:
Development cost
When choosing between iOS vs. Android development, consider that the estimated app prices might be higher for Android development. As previously mentioned, Android OS powers many devices with different screen sizes. This fact increases the development time, as well as the costs. On the other hand, iOS has a limited amount of devices, which also speeds up the development process. However, iOS vs. Android development costs depend on the number of features and app complexity.
Based on our previous projects, we share the following mobile projects estimations :
- Basic app for an Android phone with basic features will cost from $15k and take two or three months to develop
- Medium complexity apps with third-party integrations, like payment gateways, might cost from $30K and take three months to build.
- Complex applications, such as social networks or taxi-hailing apps, with database and API integrations, will cost from $50K and take five+ months.
When comparing iOS and Android for developing an app, consider that both Google Play Store and Apple App Store have their publishing apps fees. In the case of Android apps, you will need to pay a one-time registration fee of $25. To publish your app in the Apple marketplace, you need to pay $99 annually.
Testing
iOS and Android OS have their simulators for app testing. However, there are some differences between them. TestFlight, the iOS testing environment, is faster than the Android emulator. But the Android emulator virtual machine is more effective and has a more realistic representation.
App Updates
Both operating systems release new OS updates once a year. Thus, consider that updating the iOS apps for the new OS release may take up to two weeks and impact your product roadmap and business strategy. As for Android, it will take several hours to publish the new app release.
Revenue Models
Another factor you need to consider when deciding on the platform is where the majority of your audience is. Android has a higher percentage of ad-supported apps, while the iOS development platform relies predominantly on purchases.
Even though iOS makes you pay for apps, they still earn more revenue with that model. In the first quarter of 2017, iOS made 70% more than Android app developers:
Engagement
When choosing between iOS vs. Android app development, consider that it is more important to have higher amounts of users or fewer users who frequently engage. This choice will depend highly on how you’ll decide to monetize an app. Android has a broader audience in general, whereas iOS has more engaged users.
Comparing Android vs Apple Development
To see the differences between iOS development vs Android development, check the table below:
Key aspects
iOS-based platform
Android-based platform
Development language
Integrated development environment
The target audience
Design philosophy
Development complexity
Development time
Depends on complexity
Depends on complexity
Apple Store and Play Store Acceptance and Deployment speed
Long app review by app stores
(7 days on average)
Short app reviews process
iOS or Android: What to choose?
When choosing between Android and iOS development, take into account the advantages and disadvantages of these two platforms. But it would be best if you based your choice on your budget, business idea, time to market, and other factors we have discussed in this article.
Chose iOS-first development in the following cases:
- You want to generate higher revenue per user
- You are looking for a less complicated development process
- Your priorities are user data security and privacy.
Choose Android when:
- You want to reach a wider audience
- You are in tight deadlines to get the app to the Store
- You want to customize the app
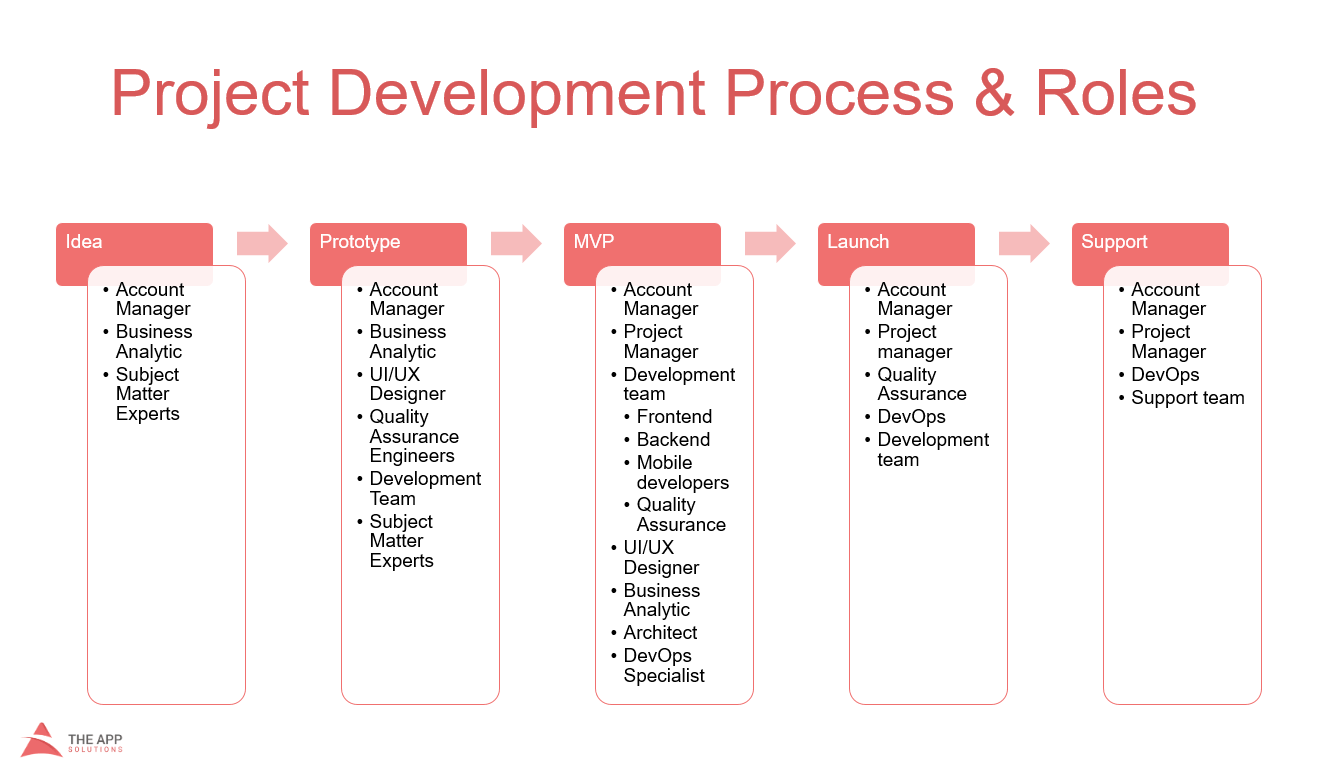
The APP Solutions experience
Our development department includes both Android and iOS specialists as well as QA managers, who test ready code.
At The APP Solutions, we deliver projects in time thanks to a well-organized workflow.
We developed several mobile platform products and want to share Android and iOS development insider information from the developer’s perspective.
Download Free E-book with DevOps Checklist
Android applications are easy to build, upload to the marketplace, and maintain. But they don’t support advanced features for the authorization security, such as Face ID, that iOS provides.
Thus, if you want to create an application with ultimate security, you’ll need to integrate additional authorization solutions from third-party providers, which increases the development cost.
[The APP Solutions Android project Emberlow]
iOS applications are also easy in development. But the official app marketplace for iOS applications has strict rules. For example, it doesn’t allow applications to read SMS and log calls, which some HR and staff management applications require.
[The APP Solutions iOS project Nuwbii]
One example is a casino management application we developed for our client from Las Vegas. To find out more about the solutions we used in this project, read a full case study.
Android vs. Apple: Which Platform to Develop for First
The decision to create an iOS or Android project depends on your target market, areas where you will launch your app, the portrait of target users you want to attract, and the business functionality your app needs. The development timeline and budget are also important factors to consider.
If you want to launch your business application as a minimum viable product in tight deadlines and with a limited budget, the iOS app may be the way to go.
But in case you’re targeting global markets, including Asia and Latin America, and your business idea requires features that Apple doesn’t support, then launching a project for Android devices will be your best bet.
Despite the platform you select, you can build another version of your application for the other platform with time. In this way, you’ll enhance more users on both operating systems who want to use your app.
To receive a free consultation from an app developer considering your business application, drop us a line.
Источник