- Jetpack Compose — как легко построить UI на Android
- Преимущества Jetpack Compose
- Подключение к проекту
- Introduction to Android Jetpack
- Key Benefits of Android Jetpack
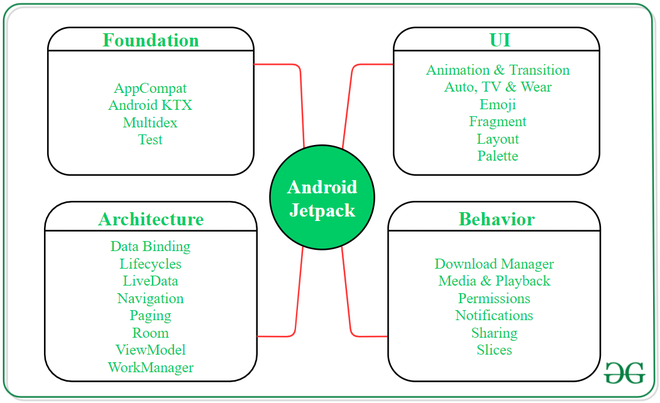
- Android Jetpack Components
- Foundation Components
- Architecture Component
- Behavior Components
- UI Components
- What’s new is there in Android Jetpack
- Jetpack Architecture Components in Android
- Following are the architecture component’s element and their responsibilities
- Ways to include Android Jetpack libraries in the application
- Architecture Components
- 1. Room Component
- 2. WorkManager
- 3. Lifecycle-Aware Components
Jetpack Compose — как легко построить UI на Android
В июле этого года вместе с Android Studio Arctic Fox вышла одна из долгожданных библиотек — Jetpack Compose. Она позволяет создавать пользовательский интерфейс в декларативном стиле и обещает быть революцией в построении UI.
Разбираемся, так ли это на самом деле, какие у библиотеки преимущества и недостатки. Подробности — в статье.
Преимущества Jetpack Compose
Jetpack Compose — это набор инструментов для разработки UI в Android-приложении. Он призван ускорить и упростить разработку пользовательского интерфейса, избавить от лишнего кода и соединить модель реактивного программирования с лаконичностью Kotlin.
Сразу с места в карьер — какие есть преимущества у библиотеки:
1. Меньше кода. Jetpack Compose позволяет писать меньше кода, а значит разработчик может больше фокусироваться на проблеме, с меньшим количеством тестов и дебага, а значит и багов.
2. Интуитивно понятный. Compose использует декларативный API — разработчику нужно лишь сказать, что сделать, а все остальное ляжет на плечи библиотеки.
3. Удобство внедрения. Compose совместим с любым существующим кодом. Например, можно вызвать Compose-код из вьюх (view) и, наоборот, вьюхи из Compose. Многие библиотеки вроде Jetpack Navigation, ViewModel и Coroutines уже адаптированы под Compose, что позволяет сравнительно быстро внедрить его в свой код. Кроме того, Android Studio Arctic Fox поддерживает превью создаваемых вьюх.
4. Имеет обширный инструментарий. Jetpack Compose позволяет создавать красивые приложения с прямым доступом к Android Platform API и build-in поддержкой Material Design, тёмной темы, анимаций и других крутых штук.
Далее пройдёмся по основным аспектам библиотеки и посмотрим, как сильно повышается производительность приложения.
Подключение к проекту
Чтобы подключить Jetpack Compose к проекту, необходимо указать некоторые строки кода в своем build.gradle.
В рутовом объявим переменную с версией Compose:
Здесь мы указываем, что в проекте будем использовать Jetpack Compose и объявляем необходимые зависимости (подробнее про зависимости можно почитать в официальном гайде).
Дальше всё просто. В активити (activity) объявлем Composable-функцию, строим иерархию вьюх с указанием необходимых атрибутов и смотрим результат.
Пройдемся по коду. Я написал две реализации вёрсток различной сложности:
1. Простая реализация
Добавляет TextView в вёрстку с текстом с конкатенацией Hello и аргумента, переданного в Greeting.
Важно отметить, что имена Composable-функций начинаются с заглавной буквы. Это соглашение по наименованию функций, поэтому если писать со строчной, то студия будет подсвечивать неверный нейминг.
2. Более сложная реализация
Этот вариант представляет собой скролящийся экран, который содержит изображение, текст и кнопку. Рассмотрим некоторые особенности:
Необходимо объявить Scroll State. Только не обычный, а тот, который позволяет сохранять состояние скролла сквозь рекомпозицию — rememberScrollState().
Column представляет собой ViewGroup с вертикальным расположением элементов.
Modifier позволяет управлять атрибутами, добавлять декорации и поведение к вьюхам.
Остальное интуитивно понятно. И это как раз одна из ключевых особенностей Jetpack Compose — даже если вы не использовали библиотеку ранее, то всё равно с ней разберётесь.
Добавить вьюхи в активити можно через extension setContent <>, например:
В общем-то, создание UI выглядит действительно просто. Теперь определим, насколько сильно оптимизируется приложение и как быстро пользователь увидит окончательный экран.
Для тестирования воспользуемся библиотекой Jetpack Benchmark, о которой, кстати, тоже рассказывали в отдельной статье. Код теста выглядит так:
Протестируем три версии установки вьюхи в активити:
При передаче ресурса в setContentView.
При передаче вьюхи в setContentView.
Итоги тестирования можно посмотреть в таблице: левый столбец — название теста, правый — время на выполнение:
Источник
Introduction to Android Jetpack
The Android support libraries are used in almost all android applications to overcome the compatibility issues across different Android OS versions and devices. These libraries also facilitate users to add various kinds of updated widgets in the application. Over time, these libraries are updated according to the latest android versions. The problem starts here, the name given to these support libraries are supposed to indicate which Android version is supported by them, for example, com.android.support:support-v7 and com.android.support:support-v13. However, writing version number at the end does not fulfill its purpose because as the libraries have evolved, the minimum version of Android API level increased to 14. Developers also find these names confusing as one cannot say that which all classes are included in a particular library just by looking at its name.
After realizing these challenges faced by the developers, Google launched Android Jetpack in 2018. The existing Support libraries, android architecture components are brought together with an addition of the Android KTX library as a single modular entity and is termed as Android Jetpack. So, Jetpack is nothing but a set of software components, libraries, tools, and guidance to help in developing great Android apps.
Key Benefits of Android Jetpack
- Forms a recommended way for app architecture through its components
- Eliminate boilerplate code
- Simplify complex task
- Provide backward compatibility as libraries like support are unbundled from Android API and are re-packaged to androidx.* package
- Inbuilt productivity feature of the Kotlin Integration
Android Jetpack Components
The software components of Android Jetpack has been divided into 4 categories:
These all components consist of a wide collection of libraries that are built in a way to work together and make robust mobile applications. A brief explanation of each component is given below.
Foundation Components
The core system components of android apps reside in the Foundation area of Jetpack. Kotlin extension for the language support and Testing libraries are also present in it. Moreover, backward compatibility is provided from the libraries present in this component. Following are the list of all foundation components:
- AppCompat: All the components of the v7 library like RecyclerView, GridLayout, CardView, etc are included in the AppCompat library. Further, it contains material design user interface implementation support which helps in degrading the older versions of android.
- Android KTX: This library includes a set of Kotlin extensions that are designed to write concise code and to make the development process smooth when developers use Kotlin language for making apps.
- Multidex: Multidexing capability of Android play a vital role once the number of methods across all classes in an application rise above the mark of 65,536. The system split the classes and make their zip file termed as .dex file. Multidex component provides support for collective dex files of an application.
- Test: This part includes the Espresso UI testing framework for the runtime UI test and AndroidJUnitRunner for the purpose of unit testing in Android.
Architecture Component
This component of Android Jetpack consists of eight libraries and tools that are responsible for building robust and maintainable applications. This component also helps in the proper management of data used by the app as well as in designing app architecture patterns. Following are the components of this area:
- Data Binding: Provide the facility to bind the application data with the XML layout. Data Binding is very helpful in updating the data of Views dynamically.
- Lifecycles: This library manages the activity and fragment lifecycle in the application and also helps in listening to lifecycle events of other components.
- LiveData: Notify the View and automatically updates the UI when there is a change in the database.
- Navigation: Contains all required resources for in-app navigation. With the help of an in-built navigation viewer in Android Studio, developers can visually design the navigation between activities and/or fragments.
- Paging: Load data gradually in the RecyclerView of the application from the data source.
- Room: This library ease the process of accessing the SQLite database in the android application. The Room also performs a compile-time check of SQL code written to perform queries.
- ViewModel: Facilitates the management of data related to UI in a lifecycle-aware manner. Further, it also re-constructs the Activity or Fragment during any configuration change like device rotation.
- WorkManager: Solves the issue of writing different code for managing background tasks in a different version of Android.
Behavior Components
This area of android jetpack covers those libraries that enable users to interact with the application through the UI. This component integrates the standard Android services like notification, downloading, permissions, sharing, assistant, etc. Behavior components are as follows:
- DownloadManager: Helps in downloading files in the background. It self manages and resolves the issues like connection loss, retrying, and system reboots while downloading happens.
- Media & Playback: This library includes the MediaPlayer and AudioManager classes. Moreover, it provides the backward compatible APIs for media playback.
- Permissions: Responsible for providing compatible APIs required for checking and requesting in-app permissions.
- Notifications: It provides API used in the notification and is backward-compatible in nature.
- Sharing: Facilitates sharing and receiving of information/content with other apps. It provides a suitable share action for an application’s action bar in order to share the data.
- Slices: Helps in creating UI elements that are flexible in nature and enables data sharing outside the app.
UI Components
It includes widgets, animations, palettes, etc to improve the user experience. It also provides up-to-date emoji fonts to be used in the apps. Following are the libraries included in this component:
- Animation & Transition: Contains APIs to set up the transition between screens and animations while moving widgets as well as to visualize updates in layout.
- Auto: It includes components for the development of apps for Android Auto. These apps can be tested on the car screen using Desktop Head Unit(DHU).
- Emoji: All kinds of emoji fonts and characters are handled by EmojiCompat. This library keeps the apps updated with the latest emojis.
- Fragment: It is the fragment support class that includes the unit of composable UI such as ListFragment, DialogFragment, and PreferenceFragmentCompat.
- Layout: Contains information regarding the declaration of different kinds of layouts like LinearLayout, RelativeLayout, ContraintLayout.
- Palette: This library allows developers to create a palette and select different colors with the help of Palette.Builder class. Moreover, it helps in pulling the colors from themes and images to make UI compatible with the images present on the screen.
- TV: It includes components for the development of Android TV applications.
- Wear: Contains libraries and classes for the development of applications for wearable Android devices like a smartwatch.
What’s new is there in Android Jetpack
- WorkManager: A powerful new library that provides modern APIs that manage background jobs that need guaranteed execution without writing different code for a different version of Android.
- Navigation: Framework for structuring the in-app UI and to see and manage the navigation properties visually.
- Paging: Easy and effective way to load and present large data sets fast and with infinite scrolling in the RecyclerView. Developers can explicitly define how to load the contents.
- Slices: A very new feature that enables to display of the app’s UI inside the search result of Google Assistant.
- Android KTX (Kotlin Extensions): Transform multiple lines of Kotlin code to a single line which improves the productivity of developers using Kotlin language.
Источник
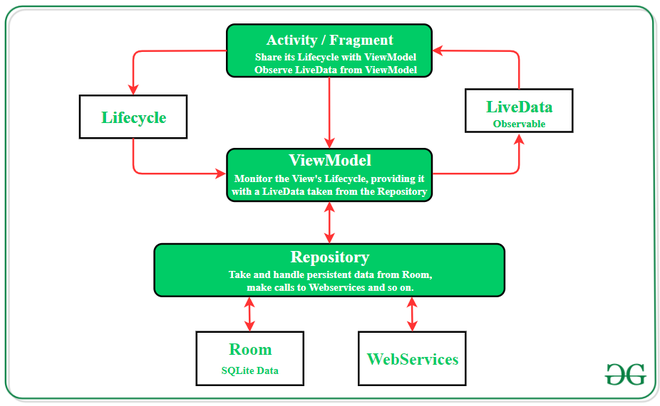
Jetpack Architecture Components in Android
Android Jetpack is a set of software components, libraries, tools, and guidance to help in developing robust Android applications. Launched by Google in 2018, Jetpack comprises existing android support libraries, android architecture components with an addition of the Android KTX library as a single modular entity. Nowadays, nearly 99% of the apps present on the Google Play Store uses Android Jetpack libraries. Moreover, to deal with changes/updates in data and application lifecycle, Google introduced Architecture components. This article explains each and every library of this component in detail. Jetpack consist of a wide collection of libraries that are built in a way to work together and make robust mobile applications. Its software components have been divided into 4 categories:
- Foundation Components
- Architecture Components
- Behavior Components
- UI Components
Further, Architecture Components could be classified as follows:
- Room
- WorkManager
- Lifecycle
- ViewModel
- LiveData
- Navigation
- Paging
- Data Binding
Android Jetpack with its architecture component defines some key principles which one should follow as a secure path to develop good and robust mobile apps. It does not support any particular architecture pattern but suggests a clear separation of concerns and controlling of UI from Model. By following these rules, developers can avoid problems related to lifecycle and it will be easy to test and maintain the application.
Following are the architecture component’s element and their responsibilities
- The View layer is represented by the Activity/Fragment. They only deal with user interaction and observes as well as exhibits the LiveData element which is taken from the ViewModel.
- ViewModel keeps a check on the Lifecycle of View and is responsible for maintaining data consistency during configuration changes in the device or other android lifecycle events.
- The Repository is a class with no proper implementation and is responsible for gathering data from all the sources. It handles all the data and transforms them into observable LiveData and makes it accessible to ViewModel.
- Room is an SQLite mapping library that overcomes the challenges of SQLite database like writing boilerplate codes, and query checking at compile time. It has the ability to return queries directly with observable LiveData.
Ways to include Android Jetpack libraries in the application
- Add google repository in the build.gradle file of the application project.
- All Jetpack components are available in the Google Maven repository, include them in the build.gradle file
Architecture Components
1. Room Component
The requirement of a database in Android is fulfilled by SQLite from the very beginning. However, it comes with some severe drawbacks like not checking the queries at compile-time, it does not save plain-old-Java Objects(commonly referred to as POJOs). Developers also need to write a lot of boilerplate code to make the SQLite database work in the Android OS environment. The Room component comes into the picture as an SQLite Object Mapping Library which overcomes all the mentioned challenges. Room converts queries directly into objects, check errors in queries at the compile-time, and is also capable of persisting the Java POJOs.
Moreover, it produces LiveData results/observables from the given query result. Because of this versatile nature of the Room component, Google officially supports and recommends developers to use it. The Room consists of the following sub-components:
- Entity: It is the annotated class for which the Room creates a table within the database. The field of the class represents columns in the table.
- DAO(Data Access Object): It is responsible for defining the methods to access the database and to perform operations.
- Database: It is an abstract class that extends RoomDatabase class and it serves as the main access point to the underlying app’s relational data.
Advantages of Room Component:
- Reduce boilerplate code
- Simplifies database access mechanism
- Easy to implement migrations
- Test-ability is high
2. WorkManager
WorkManager API provides an optimal solution to manage the background tasks in Android which are deferrable(can be run later and is still useful) as well as guaranteed(runs even if the device restarts) in nature. Its capability to cover the power-saving feature of Android and the ability to run with or without Google Play Services are the reasons for its popularity among developers. Further, it is also backward compatible with API level 14.
The ability of android devices to download a file/document in chunks i.e., occasionally(like user resumes download as per the availability of the WiFi Network) and the feature of saving the downloaded state even if the device restarts is possible only because of WorkManager API. Its execution of tasks depends upon the order of requests made by the user and for each work request, it returns the state which is displayed on the UI of the device.
Advantages of WorkManager Component:
- Provides backward compatibility
- Scheduling and chaining of tasks is possible
- Users can keep track of/status of the tasks.
3. Lifecycle-Aware Components
Details of the lifecycle state of an android component are stored in the Lifecycle class and it permits other components/objects to observe this state. An android component is lifecycle-aware if it has the ability to detect the change in the lifecycle state of other components and respond accordingly. Proper management of application lifecycles is a challenging task for the developers as it can lead to severe issues like memory leaks and app crashing. The android.arch.lifecycle package facilitates the developers by managing the lifecycles attached to the components directly by the system. By implementing the LifecycleObserver interface within the desired class, it can be configured to be lifecycle-aware.
There are 2 ways to create Activity / Fragment which are Lifecycle aware:
- Extend a LifecycleActivity or LifecycleFragment
class MainActivity : LifecycleActivity() <
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) <
Источник