- Ungapps
- Monday, December 23, 2019
- Missing system image Android Studio solution
- Неочевидные вещи при старте разработки под Android под Windows 7
- Методы лечения различных ошибок в Android Studio при разработке проекта
- How to install Android SDK and setup AVD Emulator without Android Studio
- Understanding the Android SDK
- Installing the Android SDK
- Step 1 — Download the tools package
- Step 2— You need Java 8!
- Step 3 — Download the essential packages
- Step 4 — Set your environmental variables
- Step 5 — Download the platform specific packages you want
- Step 5 — Create a AVD device
- Step 6 — Run the Android Emulator
Ungapps
Sharing my experiences.
Monday, December 23, 2019
Missing system image Android Studio solution
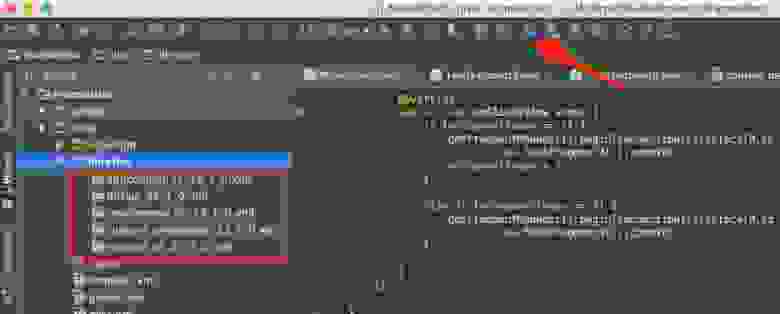
Happy holidays guys, this is december with long weekend haha. I still have a problem with Android Studio. After I update my emulator and suddenly I got a issue that is so weird. You can see picture above I need to redownload emulator from android studio.
If you got a issue like me, don’t worry and don’t uninstall your android studio. It’s not complicated to resolve it. You just need to redownload the emulator go to Tools -> AVD Manager. You can see the issue of your emulator and redownload or resolve it. And you will be like image above.
Just wait the download and your emulator will be fine again. If you still have the issue, please comment below and let me know what’s the problem. I’m happy if i can help you guys. I’m not expert but it’s fun when i can solve programming issues.
I need to make atleast 5 paragraph for good articale. So I will tell a story a little bit, I’m using Pixel 2 XL API 28 for only emulator that I do for testing. You know emualtor itself have much memory, my emulator size is 6.2GB. It’s so big for mac user like that have only 128GB memory SSD. So I need to consider what’s data inside my mac.
I have this mac only for working. It’s macbook air not too heavy when I place it on my leg and I’m in bedroom. So I really enjoy it. Thanks for visiting my simple blog, I hope I can share more knowledge and expierences to you guys.
Источник
Неочевидные вещи при старте разработки под Android под Windows 7
Добрый день, друзья! Захотелось мне изучить react native под Windows7 64. На мою беду, у меня процессор AMD, который не поддерживает VT-x or SVM.
В результате гугления выяснилось, что нужно в биосе активировать виртуализацию, причём в моём случае это сработало с N-ного раза, естественно каждый раз после изменения параметра значение в биосе сохранялось и всё перезапускалось.
Однако, это практически не помогло, поэтому пришлось еще ставить Genymotion. Это программа, которая должна устанавливаться вместе с Oracle VM Virtual Box и позволяет эмулировать android устройства на вашем компьютере. Причём делает это довольно шустро.
Далее в android studio пришлось установить в sdk manager >
android SDK > выбрать необходимую версию, внизу поставить галочку в чекбоксе Show package details
и скачать всякие ARM EABI v7a System Image, Google APIs ARM EABI v7a System Image.
После этого, самое интересное, это рендеринг нашего приложения, потому что во всех в мануалах идёт — запусти Android Studio, нажми сделать приложение «Hello World» — нажми «Play»)).
В нашем случае все будет немного сложнее.
Для начала надо привязать Genymotion к Android Studio. Для этого идем File → Settings → Plugins → в поисковой строке genymotions и устанавливаем плагин
Под строкой меню после иконки помощи (вопрос) должна появиться красная иконка Genymotion device manager.
Теперь нам надо указать Android Studio, куда конкретно выводить результат работы приложения, для этого идём по вкладке app → Edit configuration → Deployment Target Options → Target → USB Device.
Запускаем Genymotion. Выбираем устройство, которое хотим эмулировать.
Двойным кликом или кнопкой Play наверху запускаем наше устройство.
Дожидаемся полной загрузки до такого состояния экрана:
Затем в Android Studio запускаем наше приложение нажатием кнопки play.
Надеюсь никого не оскорбил, просто чтобы запустить приложение, пришлось потратить порядка 5 часов.
Не знаю, даже где напихать тегов, чтобы новички нашли этот пост, поскольку как показало гугление наших и зарубежных ресурсов, тема довольно-таки распространённая, поэтому напихаю тегов тут: «Не запускается genymotion windows 7», «Android studio и AMD», «Genymotion и oracle virtual box».
Источник
Методы лечения различных ошибок в Android Studio при разработке проекта
Сегодня хотел бы поделиться своим анализом и способами лечением разных ошибок при разработке своего продукта в Android Studio. Лично я, не раз сталкивался с различными проблемами и ошибками при компиляции и/или тестировании мобильного приложения. Данный процесс, всегда однообразный и в 99% случаев и всегда нужно тратить n-колличество времени на его устранение. Даже, когда ты уже сталкивался с данной проблемой, ты все равно идешь в поисковик и вспоминаешь, как же решить ту или иную ситуацию.
Я для себя завел файлик, в котором отметил самые частые ошибки — потратив на это несколько часов и перечислил самые популярные ошибки (в дальнейшем планирую просто их запомнить), чтоб сократить свое время в дальнейшем.
Итак, начну по порядку с самой распространенной проблемы и дальше буду перечислять их по мере появления:
1) Если подчеркивает красным код, где используются ресурсы: R. — попробовать (но вероятно не поможет): Build -> Clean Project.
В принципе на Build -> Clean Project можно не терять времени, а лучше всего — слева переключиться на Project, открыть каталог .idea, затем каталог libraries и из него удалить все содержимое. Затем нажать кнопку Sync Project. А затем (если все еще красное, но скорее всего уже будет все ок ) Build -> Clean Project.
2) После внезапного выключения компьютера, после перезапуска может быть во всех проектах весь код красным. Перед этим может быть ошибка: Unable to create Debug Bridge: Unable to start adb server: Unable to obtain result of ‘adb version’. Есть три решения — первое помогло, второе нет (но может быть для другого случая), а третье — не пробовал:
а) File — Invalidate Caches/Restart — Invalidate and Restart
б) Закрыть студию. В корне папки проекта удалить файл(ы) .iml и папку .idea. Вновь запустить студию и импортировать проект.
в) Нажать Ctrl-Alt-O и запустить оптимизацию импорта.
Кстати, adb сервер можно проверить на версию (и работоспособность) и затем перезапустить:
3) Если Android Studio выдает приблизительно такую ошибку: Error:Execution failed for task ‘:app:dexDebug’.
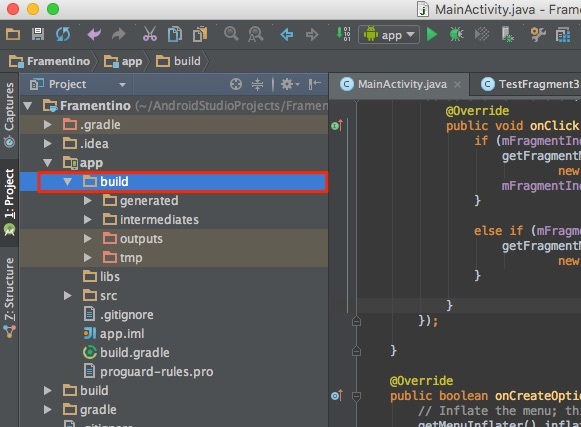
Надо слева переключиться на опцию Project, найти и удалить папку build которая лежит в папке app, т.е. по пути app/build. Затем перестроить весь проект заново: Build -> Rebuild Project.
Такое же решение если ошибка типа: «не могу удалить (создать) папку или файл» и указан путь, который в ведет в app/build. Тоже удаляем папку build и ребилдим проект.
4) В сообщении об ошибке упоминается heap — виртуальная память. А ошибка обычно вызвана ее нехваткой, т.е. невозможностью получить запрашиваемый объем. Поэтому этот запрашиваемый объем надо уменьшить, т.е. переписать дефолтное значение (обычно 2048 MB которое можно изменить в настройках), на меньшее 1024 MB.
В файле проекта gradle.properties пишем:
5) Android Studio пришет примерно такую ошибку: Plugin is too old, please update to a more recent version, or set ANDROID_DAILY_OVERRIDE environment variable to «83648b99316049d63656d7276cb19cc7e95d70a5»
Возможные причины (кроме необходимости регулярного обновления SDK):
а) Загруженный проект был скомпилирован с помощью уже несовместимого старого gradle плагина. В этом случае надо найти и подключить в своем build.gradle проекта этот более старый плагин. т.е. попробовать более старые версии, например: 1.1.3 (часто именно 1.1.x и подходит).
Найти все версии можно здесь.
б) Если в build.gradle проекта используется beta-версия плагина — это означает, что срок ее истек. Посмотреть последние релизы (продакшн и бета) можно также здесь:
6) Иногда при подключении сторонних библиотек могут дублироваться некоторые файлы (обычно связанные с лицензированием). В сообщении будет что-то содержащее слова: duplicate files. Решение — надо посмотреть в сообщении об ошибке или в документации подключенной сторонней библиотеки — какие именно файлы стали избыточными, и перечислить их в build.gradle модуля для исключения (exclude) из билда.
Это делается в директиве packagingOptions (которая, в свою очередь, находится в директиве android).
Источник
How to install Android SDK and setup AVD Emulator without Android Studio
If you are trying to develop to Android, you probably will end up installing the Android Studio to get the Android SDK and the AVD Emulator working properly.
But if you are using another code editor, like Sublime Text or VSCode, installing the Android Studio will just mess up with your setup and consume your precious RAM for no good reason.
I had a hard time figuring out how to properly do this setup due the lack of documentation about it, so i hope this article helps you. 🙂
Recommended previous knowledge:
- SDK (Standard Development Kit); Read about on Wikipedia;
- AVD (Android Virtual Device); Read about on docs;
- CLI (Command Line Interface); Read about on Wikipedia;
- Android API levels; Read about on Vanderbilt University;
- How to open, navigate and execute files in your OS terminal;
- Know what are environmental variables;
Understanding the Android SDK
Basically, the Android SDK is a bunch of packages necessary to develop for Android.
These packages stays in subfolders of a folder called “sdk” (or “android-sdk” sometimes). You do not need to know how these packages really work, just what they do.
The picture below is my Android SDK folder, these are the basic packages you will need in order to get everything working properly.
Here is a brief explanation of each package:
- tools: This package is mainly used to manage the other packages and to create AVD’s;
- emulator: As the name suggest, this is the Android emulator;
- platform-tools: Some tools to communicate with Android devices when you plug then in your computer;
- patcher: This package is automatically downloaded by the SDK. I didn’t find what exactly this is for, so just leave it as it is;
The folders bellow contain sub-folders with the packages for each Android API level.
- platforms: The platform packages are required to compile your app for the specified API level.
- system-images: These are the android images used in the emulator.
- build-tools: These are necessary to build your Android apps
Installing the Android SDK
In order to install the SDK we will use the Command Line Tools. These are some quite simple CLI’s used to manage the Android SDK. You can read the documentation here for more details.
Step 1 — Download the tools package
First, you need to download the tools package. And with this package you can download the others.
- First, go to the Android Studio download page: https://developer.android.com/studio;
- Then click in “ Download Options”;
- There you will find a table named “ Command line tools only”;
- This table contain some zip files. Download the appropriate file for your system ( Windows, Mac or Linux);
- Extract this zip and you will get a folder called tools: This is the tools package i explained earlier;
Create a folder anywhere you prefer to place your SDK. I recommend you to stick with one of these commonly used places:
- Globally: C:\Android\sdk or C:\android-sdk (this is not default, but i usually set my SDK here on Windows)
- One user only: C:\Users\ \AppData\Local\Android\sdk
- Globally: /Library/Android/sdk
- One user only: /Users/ /Library/Android/sdk
And move the tools folder to this new sdk folder. Make sure you have admin access to this folder and any sub-folders inside it, or the tools package will fail to download new packages.
Note: You can also download a pre-build package for your SO (like the one available on Ubuntu repository). But i do not recommend you do to so, because they probably will not be updated and will be harder to manage, since it was automatically installed.
Step 2— You need Java 8!
The Android SDK packages require Java 8. If you do not have it, you need to download. If you are using a newer version, you have to downgrade to Java 8 or you will eventually get some errors, because it is not compatible.
If you do not have the Java 8 SDK, here is how you can install it:
On Ubuntu run these commands:
- # sudo apt-get update
- # sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk
Sorry for MacOS users, i don’t know how to install it on this OS.
Step 3 — Download the essential packages
Now, download the platform-tools and the emulator packages, because they contain some CLI binary files you will need later. I decided to download these packages first in order to set all the necessary environment variables at once and make the rest of the process easier.
Open a terminal window (you need to use a terminal, not the file explorer), go to your sdk folder and navigate to the /tools/bin directory.
This folder contain the SDKManager binary: this is a CLI used to list the available packages in the Google’s repository and download, update or remove them from your SDK folder.
The bellow command will list all packages installed (the first items on the list) and all packages available to download:
To download the packages, simply copy the package names and pass it as a parameter to the SDKManager CLI using the terminal:
# ./sdkmanager platform-tools emulator
If you open your sdk folder you should see these packages folders there.
Step 4 — Set your environmental variables
You need to set the below environmental variables containing the path to our SDK, so any running program can find it in your pc:
ANDROID_SDK_ROOT = Path to your SDK folder
ANDROID_HOME = The same as ANDROID_SDK_ROOT. This variable is now deprecated, but i recommend setting it because some programs still using it to locate your sdk.
And add these folders to the PATH variable, making their binary files accessible from everywhere:
To add the environment variables on WIndows, just follow these steps:
- Open the “Control Panel”;
- Go to “ System and Security” option in the side menu;
- In the window “ System Properties” open the tab “ Advanced”;
- Click in the button “ Environment Variables” in the bottom of the page;
- In the “ Environment Variables” window you will see two tables: “User Variables” and ” System Variables”.
- If you created your sdk folder for one user only, set the variables in the “ User Variables” table;
- But, if you create your sdk folder globally, set the variables in the “ System Variables” table instead;
On Linux, you can set your environment variables in many places. So i choose the ones I found the most appropriate:
- If you created your sdk folder for one user only, set your environment variables in the file
/.bashrc;
Here is how i set these variables in my Ubuntu, using the file /etc/environment:
And sorry again, no MacOS instructions for this task.
You can find more about these environmental variables in the oficial docs here.
Now your SDK is ready! If you do not need to run the emulator there’s no need to follow the next steps.
Step 5 — Download the platform specific packages you want
You need more three packages: The platform, the system-image and the build-tools. You can download these packages for any Android version you prefer. In this article, i will download the packages for the API Level 28.
Use the “ sdkmanager — list” command to find these packages and download them using the command “ sdkmanager
Here’s an example:
Step 5 — Create a AVD device
Creating a AVD device is a simple task: run the AVDManager command (this is a binary file located in the tools/bin folder of your sdk) with the create avd option, a name for the new AVD and the image you want to use.
Here is a example:
# avdmanager create avd — name android28 — package “system-images;android-28;default;x86”
You will be asked if you want to alter some configurations. You can also modify these configurations later in the file config.ini, located in the avd folder (this folder usually is created in your user folder, under the android directory). The currently active configurations can be find in the file hardware-qemu.ini (this file just will be created after the emulator runs for the first time).
Step 6 — Run the Android Emulator
Now you just need to run the emulator command (remember that we added this package to the environmental variables?):
The emulator take some time to init for the first time. But if you done everything correctly you should see this screen:
Источник