- Context actions
- Apply context actions
- Configure context actions
- Apply context actions in wider scope
- TypeScript
- Android Studio Editor IntelliJ Intention / Context Actions (Alt+Enter) not functioning #4686
- Comments
- SadSack963 commented Jul 4, 2020
- Context в Android приложении
- Что такое Context?
- Контекст приложения
- Контекст Activity
- getContext() в ContentProvider
- Когда нельзя использовать getApplicationContext()?
- Правило большого пальца
Context actions
Context actions are code transformations helpers available right in the editor. In contrast to quick-fixes, context actions do not aim to resolve a problem or improve your code, instead, they allow you to quickly introduce minor changes like changing access modifiers, generating code that checks for null, convert ‘foreach’ to ‘for’, etc.
For larger transformations of your codebase, JetBrains Rider provide several dozens of automated refactorings.
JetBrains Rider provides hundreds of context actions in all supported languages. You can find the full list in the Context actions reference.
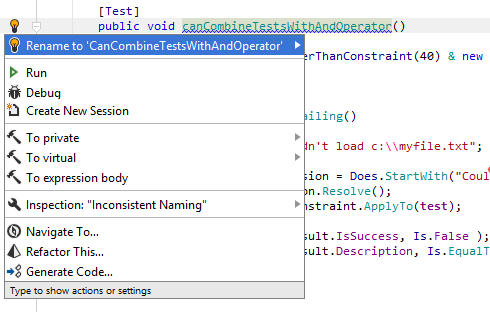
Apply context actions
As soon as a context action becomes available for the current caret position, JetBrains Rider displays the corresponding action indicator to the left of the caret. Sometimes however, JetBrains Rider provides several contextually available features for the current caret position. In this case, the action indicator corresponding to the action with the highest priority is shown, and all other actions only appear when you expand the action list by clicking on the action indicator or pressing Alt+Enter Context actions have the lowest priority, therefore, they often appear at the bottom of the action list.
In most cases, a context action is applied immediately. However, some actions require user interaction to choose how exactly they transform your code. In these cases, a Hot spot session is deployed in the editor, where you can select one of the suggested values or provide your own values in the active input positions.
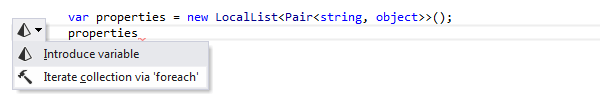
For example, here is what happens when you apply the Iterate collection via ‘foreach’ context action:
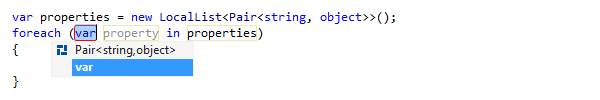
After creating the foreach statement, a hot spot session helps you complete editable parameters of the generated statement:
To complete the hot spot session:
If JetBrains Rider suggests some values for the current parameter, use Up and Down arrow keys to navigate through the list of suggested values, or just type in a desired value.
Press Tab or Enter to accept the value and move to the input position of the next parameter. If this is the last parameter, the hot spot session completes and the caret moves to the end position defined for the session.
Press Shift+Tab to move the input focus to the input position of the previous parameter.
Press Esc to exit the hot spot session. In this case, all session parameters will be initialized with default values.
Configure context actions
By default, most of the context actions are enabled, but you can easily disable those that you consider unhelpful.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S or choose File | Settings (Windows and Linux) or JetBrains Rider | Preferences (macOS) from the menu.
Use the search box in the Settings/Preferences dialog to find specific context action.
Alternatively, open the Editor | Context Actions page and look for the context actions that you want to disable.
Clear the checkbox next to a context action to disable it.
Click Save in the Settings dialog to apply the modifications and let JetBrains Rider choose where to save them, or save the modifications to a specific settings layer using the Save To list. For more information, see Layer-based settings.
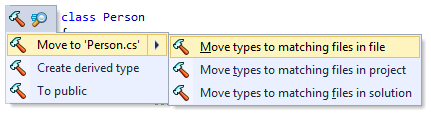
Apply context actions in wider scope
Some context actions can automatically find and change similar code items in a larger scope — in the current file, in the current project or in the whole solution. These context actions work the same as Fix in scope. For example, you can move all types from the current file to new matching files:
The full list of context actions that can be applied in wider scopes includes:
Add another accessor
Add block braces to switch section statements
Add deconstruct pattern component name
Add name to argument
Add tuple component name
Change between ‘set’ and ‘init’ accessor
Convert collection initializer into ‘Add’ method calls
Convert explicit to implicit implementation
Convert expression body member to statement body
Convert ‘if’ statement to ‘switch’ expression
Convert ‘if’ statement to ‘switch’ statement
Convert implicit to explicit interface implementation
Convert integer literal to binary form
Convert integer literal to hexadecimal form
Convert integral literal to decimal form
Convert object initializer into assignment statements
Convert object initializer into constructor invocation
Convert string interpolation to ‘string.Format’ call
Convert ‘switch’ expression to conditional ?: expression(s)
Convert ‘switch’ expression to ‘if’ statements
Convert ‘switch’ expression to ‘switch’ statement
Convert ‘switch’ statement to ‘if’ statements
Convert ‘switch’ statement to ‘switch’ expression
Converts member value check expression to recursive pattern
Converts not null check into object pattern check
Create explicit array creation from ‘params’ parameter arguments
Create explicit constructor declaration for primary constructor
Create explicit property declaration for positional parameter
Fully qualify reference to type, static member or namespace
Include member access into object pattern
Inline temporary variable
Inlines variable into condition expression using this variable
Insert digit separators in integer literal
Insert digit separators in real literal
Insert generic method invocation type arguments
Invoke extension method as static
Join attributes into single section
Merge sequential checks into null-propagating expression
Merge sequential null/pattern checks into single pattern check
Move type to another file to match its name
Qualify static members imported via ‘using static’ directive
Remove #region, #endregion directives
Remove argument name
Remove digit separators from numeric literal
Remove redundant parenthesis
Remove tuple component name
Replace ‘?:’ conditional operator with null-propagating expression
Replace array initializer with expression
Replace auto-property with property and backing field
Replace explicit type specification with ‘var’
Replace null-propagating expression with ‘?:’ conditional operator
Replace separate deconstruction declarations with single declaration
Replace ‘var’ with explicit type declaration
Specify enum member values
Split ‘and’ patterns into multiple ‘is’ expressions or guard expression
Split attributes into separate sections
Split null-propagating expression into sequential checks
Split ‘or’ patterns into multiple ‘is’ expressions or ‘switch’ cases
Split recursive pattern into several consecutive checks
To named property patterns
Use ‘ConfigureAwait(false)’ call
Use explicit discard declaration
Use implicit discard declaration
Use object/collection initializer instead of assignments/.Add() method calls
Use positional deconstruction pattern
Use separate declarations in deconstruction declaration/patterns
Use string interpolation
TypeScript
Move type to another file to match its name
Источник
Android Studio Editor IntelliJ Intention / Context Actions (Alt+Enter) not functioning #4686
Comments
SadSack963 commented Jul 4, 2020
Suspected error in Flutter Plugin version 47.1.2 (My Windows 10 system).
Flutter Plugin version 46.0.2 works correctly (My Linux system).
If the cursor caret is placed at or inside a widget name, there is no yellow intention bulb, and Alt+Enter does not bring up the list of suggestions as stated here: https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/intention-actions.html
Right-clicking the widget name allows you to select Show Context Actions from the context menu, but then a message is shown «No context actions available at this location».
Right clicking on the widget in the Flutter Outline does bring up a context menu allowing to wrap with certain widgets (though there is no option to «Wrap with widget»).
The red bulb does appear if there are errors on the line.
The yellow bulb does not appear when the cursor caret is within a widget name.
The yellow bulb does appear when the cursor caret is placed after the last «),» in a descending tree.
It also appears if the cursor is inside a text comment, and sometimes after the comma at the end of a parameter line, for example in the default project:
The yellow bulb appears when the cursor is at the end of the onPressed: and tooltip: lines only. The only context action is to Flip.
File menu -> Settings: 
=========================================================================
System: Windows 10
The context actions do not work.
flutter doctor -v
[√] Flutter (Channel stable, v1.17.5, on Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.18362.295], locale en-GB)
• Flutter version 1.17.5 at E:\Flutter
• Framework revision 8af6b2f038 (3 days ago), 2020-06-30 12:53:55 -0700
• Engine revision ee76268252
• Dart version 2.8.4
[√] Android toolchain — develop for Android devices (Android SDK version 30.0.0)
• Android SDK at D:\Users\John\AppData\Local\Android\sdk
• Platform android-30, build-tools 30.0.0
• Java binary at: C:\Program Files\Android\Android Studio\jre\bin\java
• Java version OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_242-release-1644-b01)
• All Android licenses accepted.
[√] Android Studio (version 4.0)
• Android Studio at C:\Program Files\Android\Android Studio
• Flutter plugin version 47.1.2
• Dart plugin version 193.7361
• Java version OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_242-release-1644-b01)
[√] VS Code (version 1.46.1)
• VS Code at D:\Users\John\AppData\Local\Programs\Microsoft VS Code
• Flutter extension version 3.12.0
[!] Connected device
! No devices available
! Doctor found issues in 1 category.
=========================================================================
System: Linux Mint
The context actions work correctly.
flutter doctor -v
[✓] Flutter (Channel stable, v1.17.3, on Linux, locale en_GB.UTF-8)
• Flutter version 1.17.3 at /home/john/Programs/flutter
• Framework revision b041144f83 (4 weeks ago), 2020-06-04 09:26:11 -0700
• Engine revision ee76268252
• Dart version 2.8.4
[✓] Android toolchain — develop for Android devices (Android SDK version 30.0.0)
• Android SDK at /home/john/Android/Sdk
• Platform android-30, build-tools 30.0.0
• Java binary at: /home/john/Programs/android-studio/jre/bin/java
• Java version OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build
1.8.0_242-release-1644-b3-6222593)
• All Android licenses accepted.
[✓] Android Studio (version 4.0)
• Android Studio at /home/john/Programs/android-studio
• Dart plugin version 193.7361
• Java version OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build
1.8.0_242-release-1644-b3-6222593)
[!] Connected device
! No devices available
! Doctor found issues in 1 category.
Context Actions work correctly in Linux with Flutter Plugin version 46.0.2
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Источник
Context в Android приложении
Что такое Context?
Как следует из названия, это контекст текущего состояния приложения или объекта. Это позволяет вновь созданным объектам понять, что вообще происходит. Обычно его вызывают, чтобы получить информацию о другой части программы.
Кроме того, Context является проводником в систему, он может предоставлять ресурсы, получать доступ к базам данных, преференсам и т.д. Ещё в Android приложениях есть Activity . Это похоже на проводник в среду, в которой выполняется ваше приложение. Объект Activity наследует объект Context . Он позволяет получить доступ к конкретным ресурсам и информации о среде приложения.
Context присутствует практически повсюду в Android приложении и является самой важной его частью, поэтому необходимо понимать, как правильно его использовать.
Неправильное использование Context может легко привести к утечкам памяти в Android приложении.
Существует много разных типов контекста, поэтому давайте разберёмся, что каждый из них представляет из себя, как и когда их правильно использовать.
Контекст приложения
Это singleton-экземпляр (единственный на всё приложение), и к нему можно получить доступ через функцию getApplicationContext() . Этот контекст привязан к жизненному циклу приложения. Контекст приложения может использоваться там, где вам нужен контекст, жизненный цикл которого не связан с текущим контекстом или когда вам нужно передать контекст за пределы Activity .
Например, если вам нужно создать singleton-объект для вашего приложения, и этому объекту нужен какой-нибудь контекст, всегда используйте контекст приложения.
Если вы передадите контекст Activity в этом случае, это приведет к утечке памяти, так как singleton-объект сохранит ссылку на Activity и она не будет уничтожена сборщиком мусора, когда это потребуется.
В случае, когда вам нужно инициализировать какую-либо библиотеку в Activity , всегда передавайте контекст приложения, а не контекст Activity .
Таким образом, getApplicationContext() нужно использовать тогда, когда известно, что вам нужен контекст для чего-то, что может жить дольше, чем любой другой контекст, который есть в вашем распоряжении.
Контекст Activity
Этот контекст доступен в Activity и привязан к её жизненному циклу. Контекст Activity следует использовать, когда вы передаете контекст в рамках Activity или вам нужен контекст, жизненный цикл которого привязан к текущему контексту.
getContext() в ContentProvider
Этот контекст является контекстом приложения и может использоваться аналогично контексту приложения. К нему можно получить доступ через метод getContext() .
Когда нельзя использовать getApplicationContext()?
Правило большого пальца
В большинстве случаев используйте контекст, доступный непосредственно из компонента, в котором вы работаете в данный момент. Вы можете безопасно хранить ссылку на него, если она не выходит за пределы жизненного цикла этого компонента. Как только вам нужно сохранить ссылку на контекст в объекте, который живет за пределами вашей Activity или другого компонента, даже временно, используйте ссылку на контекст приложения.
Источник