- DP/PX Converter
- Calculate pixels (and other units) in DPs
- Android app
- Introspect
- Pixels to dpi android
- How the French Revolution and NASA crash orbiter is connected to this article?
- Let’s see the relation between pixels and density-independent pixels
- What’s the conversion of pixel and dip?
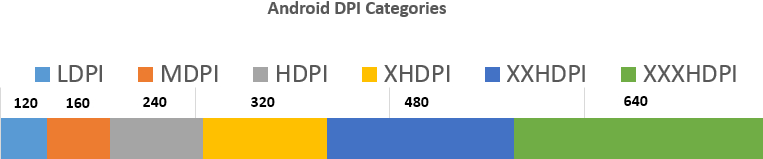
- Density Bucket
- Support different pixel densities
- Use density-independent pixels
- Convert dp units to pixel units
- Kotlin
- Use pre-scaled configuration values
- Kotlin
- Provide alternative bitmaps
- Put app icons in mipmap directories
- Use vector graphics instead
- Advice for uncommon density issues
- Test on all pixel densities
DP/PX Converter
Calculate pixels (and other units) in DPs
This tool helps you convert pixels to and from DPs (density independent pixels).
Enter a value and unit to calculate the dimensions for the various DPI bins (ldpi, mdpi, hdpi, xhdpi, xxhdpi and xxxhdpi).
| at | compensating for user’s font size at |
Launcher Action bar Small / contextual Notification icon Notification action
The values are calculated based on:
| ldpi | 120 dpi |
| mdpi | 160 dpi |
| tvdpi | 213 dpi |
| hdpi | 240 dpi |
| xhdpi | 320 dpi |
| xxhdpi | 480 dpi |
| xxxhdpi | 640 dpi |
Take special note of the nodpi bin; specifying resources using this qualifier specifically instructs the system to not scale resources, regardless of the current screen’s density. The DP/PX converter above behaves slightly different when selecting this bin, as it treats the specified pixel dimension as DP.
Android app
Introspect
If you want to know exactly how many dips you own phone has, and much, much more, get our app Introspect from the Play Store. Completely free, it shows you all there is to know about your phone and has some useful tools for developers.
Источник
Pixels to dpi android
What does the French Revolution have to do with the time NASA accidentally crashed a $200 million orbiter into the surface of Mars?
Crash happened due to a small mistake on the unit conversion between two measurement systems. At the time of French Revolution, France alone has a quarter million different units. Revolutionaries found such system displeasingly irrational and in need of the new system. They switch out to the Metric System. Gradually, everyone accepts this new standard system except few countries like America where they follow the older imperial system where things measured in feet, inches and pounds.
How the French Revolution and NASA crash orbiter is connected to this article?
All the web developers discussions are in pixels whereas android developers discussions are in dp or sp(pronounce as dips). Websites displayed on the screen the same as mobile apps. Does the measurement system is the same?
First, Let’s have a look at the terminologies:
Pixels — (Google Definition) a minute area of illumination on a display screen, one of many from which an image is composed.
Screen Resolution — Resolution is always referred in x*y form, which means x is the number of pixels in horizontal direction and y is the number of pixels in a vertical direction.
Example — HD display 1920*1080 = 2,083,600 is the total pixels on screen
Pixels per inch — This is the measurement of the pixel density(resolution).
Example — I have an image of 100*100 pixel which I need to print on a 1-inch square. Now, it will have a resolution of 100 pixels per inch.
Through this terminologies, we can say that now we can design the UI for Android based on the pixels of the displaying screen. But, this world consists of a variety of display screen sizes which is not possible for us to design with.
Here comes the Density Independent Pixel (dip).
In Android Development, we have seen many developers using dp as a measurement unit for all the views. But, what’s dp? what’s sp? And how this dp/sp helps us to achieve the same size in different screen sizes?
Let’s see the relation between pixels and density-independent pixels
Taking an example of three devices of the same physical size but different resolution.
If I define my Button’s height and width in pixel, this is going to happen in different device resolution. Button covers 2 pixels horizontally and 2 pixels vertically but the pixel density(resolution) is different which makes our button size small.
So, what’s the solution here? Now, I will use dp as a measurement unit.
Here, we can see the size of the button is the same in all the devices. What Android has done here is, map the number of pixels.
There is one more unit called SP. What is sp? And when should we use sp? And when should we use dp?
Scale Independent Pixels —This is same as dp, but by default, android resizes it based on the font size of the user’s phone.
sp is only used for the text, never use it for the layout sizes.
What’s the conversion of pixel and dip?
In Android, we have a baseline density of 160 dots-per-inch(dpi). So, for a 160 dpi screen, we have 1 pixel = 1 dp and 320 dpi screen, we have 2 pixels = 1 dp which is 2x.
Let’s say we have a tablet of 1280*800 pixels, 160 dpi and phone of 800*1280 pixels, 320 dpi. Their pixel resolution is the same. But, what will be in the dp?
Tablet is of 160 dpi which is baseline so, 1280*800 dp but the phone is of 320 dpi which is half, 400*640dp. This helps us to design the layout for a tablet and phone very quickly. We can also think of a screen of 1280 dp versus 400 dp.
Let’s say we have two devices of the same size but different resolution. One is 400*640 pixels, 160 dpi and another is 800*1280 pixels, 320 dpi.
Now, if we convert this in density-independent pixels, we have the same size of 400*640 dp. This makes us design a single layout for both the screens.
Now, we can understand the meaning of Density Independent Pixels, (Pixels not depending on the density)
Density Bucket
Many times we had seen some words like MDPI, HDPI, XHDPI, XXHDPI inside our Android Studio. What are these? These are the Density Bucket. We have different size of size to design for, but to make it simple, all the screens are grouped under density bucket.
This is the screenshot of a StackOverflow answer explaining density bucket. This chart can help us to understand which resolution devices comes in which bucket either mdpi or hdpi etc.
smallestWidth — sw dp
The smallest width is fixed screen size; the device’s smallest width doesn’t change when the screen’s orientation changes.
sw320dp
sw600dp
sw720dp
Available width — w dp
This configuration value changes when the orientation changes between landscape and portrait to match the current actual width.
w720dp
w1024dp
land — This helps us to design for landscape
Thanks for reading! If you find this reading useful, please share to help others find it! Feel free to leave a comment . below. Have feedbac k?
Источник
Support different pixel densities
Not only do Android devices come in different screen sizes (handsets, tablets, TVs, and so on), but their screens also have different pixel sizes. That is, while one device has 160 pixels per square inch, another device fits 480 pixels in the same space. If you don’t consider these variations in pixel density, the system might scale your images (resulting in blurry images) or the images might appear at the completely wrong size.
This page shows you how you can design your app to support different pixel densities by using resolution-independent units of measurements and providing alternative bitmap resources for each pixel density.
Watch the video below for an overview of these techniques.
For more information about designing the actual icons assets, see the material design icon guidelines.
Use density-independent pixels
The first pitfall you must avoid is using pixels to define distances or sizes. Defining dimensions with pixels is a problem because different screens have different pixel densities, so the same number of pixels may correspond to different physical sizes on different devices.
Figure 1. Two screens of the same size may have a different number of pixels
To preserve the visible size of your UI on screens with different densities, you must design your UI using density-independent pixels (dp) as your unit of measurement. One dp is a virtual pixel unit that’s roughly equal to one pixel on a medium-density screen (160dpi; the «baseline» density). Android translates this value to the appropriate number of real pixels for each other density.
For example, consider the two devices in figure 1. If you were to define a view to be «100px» wide, it will appear much larger on the device on the left. So you must instead use «100dp» to ensure it appears the same size on both screens.
When defining text sizes, however, you should instead use scalable pixels (sp) as your units (but never use sp for layout sizes). The sp unit is the same size as dp, by default, but it resizes based on the user’s preferred text size.
For example, when you specify spacing between two views, use dp :
When specifying text size, always use sp :
Convert dp units to pixel units
In some cases, you will need to express dimensions in dp and then convert them to pixels. The conversion of dp units to screen pixels is simple:
Imagine an app in which a scroll or fling gesture is recognized after the user’s finger has moved by at least 16 pixels. On a baseline screen, a user’s must move by 16 pixels / 160 dpi , which equals 1/10th of an inch (or 2.5 mm) before the gesture is recognized. On a device with a high-density display (240dpi), the user’s must move by 16 pixels / 240 dpi , which equals 1/15th of an inch (or 1.7 mm). The distance is much shorter and the app thus appears more sensitive to the user.
To fix this issue, the gesture threshold must be expressed in code in dp and then converted to actual pixels. For example:
Kotlin
The DisplayMetrics.density field specifies the scale factor you must use to convert dp units to pixels, according to the current pixel density. On a medium-density screen, DisplayMetrics.density equals 1.0; on a high-density screen it equals 1.5; on an extra-high-density screen, it equals 2.0; and on a low-density screen, it equals 0.75. This figure is the factor by which you should multiply the dp units in order to get the actual pixel count for the current screen.
Use pre-scaled configuration values
You can use the ViewConfiguration class to access common distances, speeds, and times used by the Android system. For instance, the distance in pixels used by the framework as the scroll threshold can be obtained with getScaledTouchSlop() :
Kotlin
Methods in ViewConfiguration starting with the getScaled prefix are guaranteed to return a value in pixels that will display properly regardless of the current pixel density.
Provide alternative bitmaps
To provide good graphical qualities on devices with different pixel densities, you should provide multiple versions of each bitmap in your app—one for each density bucket, at a corresponding resolution. Otherwise, Android must scale your bitmap so it occupies the same visible space on each screen, resulting in scaling artifacts such as blurring.
Figure 2. Relative sizes for bitmaps at different density sizes
There are several density buckets available for use in your apps. Table 1 describes the different configuration qualifiers available and what screen types they apply to.
Table 1. Configuration qualifiers for different pixel densities.
| Density qualifier | Description |
|---|---|
| ldpi | Resources for low-density (ldpi) screens ( 120dpi). |
| mdpi | Resources for medium-density (mdpi) screens ( 160dpi). (This is the baseline density.) |
| hdpi | Resources for high-density (hdpi) screens ( 240dpi). |
| xhdpi | Resources for extra-high-density (xhdpi) screens ( 320dpi). | xxhdpi | Resources for extra-extra-high-density (xxhdpi) screens ( 480dpi). | xxxhdpi | Resources for extra-extra-extra-high-density (xxxhdpi) uses ( 640dpi). |
| nodpi | Resources for all densities. These are density-independent resources. The system does not scale resources tagged with this qualifier, regardless of the current screen’s density. |
| tvdpi | Resources for screens somewhere between mdpi and hdpi; approximately 213dpi. This is not considered a «primary» density group. It is mostly intended for televisions and most apps shouldn’t need it—providing mdpi and hdpi resources is sufficient for most apps and the system will scale them as appropriate. If you find it necessary to provide tvdpi resources, you should size them at a factor of 1.33*mdpi. For example, a 100px x 100px image for mdpi screens should be 133px x 133px for tvdpi. |
To create alternative bitmap drawables for different densities, you should follow the 3:4:6:8:12:16 scaling ratio between the six primary densities. For example, if you have a bitmap drawable that’s 48×48 pixels for medium-density screens, all the different sizes should be:
- 36×36 (0.75x) for low-density (ldpi)
- 48×48 (1.0x baseline) for medium-density (mdpi)
- 72×72 (1.5x) for high-density (hdpi)
- 96×96 (2.0x) for extra-high-density (xhdpi)
- 144×144 (3.0x) for extra-extra-high-density (xxhdpi)
- 192×192 (4.0x) for extra-extra-extra-high-density (xxxhdpi)
Then, place the generated image files in the appropriate subdirectory under res/ and the system will pick the correct one automatically based on the pixel density of the device your app is running on:
Then, any time you reference @drawable/awesomeimage , the system selects the appropriate bitmap based on the screen’s dpi. If you don’t provide a density-specific resource for that density, the system picks the next best match and scales it to fit the screen.
Tip: If you have some drawable resources that the system should never scale (perhaps because you perform some adjustments to the image yourself at runtime), you should place them in a directory with the nodpi configuration qualifier. Resources with this qualifier are considered density-agnostic and the system will not scale them.
For more information about other configuration qualifiers and how Android selects the appropriate resources for the current screen configuration, see Providing Resources.
Put app icons in mipmap directories
Like all other bitmap assets, you need to provide density-specific versions of your app icon. However, some app launchers display your app icon as much as 25% larger than what’s called for by the device’s density bucket.
For example, if a device’s density bucket is xxhdpi and the largest app icon you provide is in drawable-xxhdpi , the launcher app scales up this icon, and that makes it appear less crisp. So you should provide an even higher density launcher icon in the mipmap-xxxhdpi directory. Now the launcher can use the xxxhdpi asset instead.
Because your app icon might be scaled up like this, you should put all your app icons in mipmap directories instead of drawable directories. Unlike the drawable directory, all mipmap directories are retained in the APK even if you build density-specific APKs. This allows launcher apps to pick the best resolution icon to display on the home screen.
For icon design guidelines, see the material guide for icons.
Use vector graphics instead
An alternative to creating multiple density-specific versions of an image is to create just one vector graphic. Vector graphics create an image using XML to define paths and colors, instead of using pixel bitmaps. As such, vector graphics can scale to any size without scaling artifacts, though they’re usually best for illustrations such as icons, not photographs.
Vector graphics are often provided as an SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) file, but Android does not support this format so you must convert SVGs files to Android’s vector drawable format.
You can easily convert an SVG to a vector drawable from Android Studio using Vector Asset Studio as follows:
- In the Project window, right-click on the res directory and select New > Vector Asset.
- Select Local file (SVG, PSD).
Locate the file you want to import and make any adjustments.
Figure 3. Importing an SVG with Android Studio
You might notice some errors appear in the Asset Studio window, indicating some properties of the file that vector drawables do not support. But this will not prevent you from importing—the unsupported properties are simply ignored.
Click Next.
On the next screen, confirm the source set where you want the file in your project and click Finish.
Because one vector drawable can be used on all pixel densities, this file goes in your default drawables directory (you don’t need to use density-specific directories):
For more information about creating vector graphics, read the Vector Drawable documentation.
Advice for uncommon density issues
This section describes more about how Android performs scaling for bitmaps on different pixel densities and how you can further control how bitmaps are drawn on different densities. Unless your app manipulates graphics or you have encountered problems when running on different pixel densities, you can ignore this section.
To better understand how you can support multiple densities when manipulating graphics at runtime, you should understand that the system helps ensure the proper scale for bitmaps in the following ways:
- Pre-scaling of resources (such as bitmap drawables)
Based on the density of the current screen, the system uses any density-specific resources from your app. If resources are not available in the correct density, the system loads the default resources and scales them up or down as needed. The system assumes that default resources (those from a directory without configuration qualifiers) are designed for the baseline pixel density (mdpi) and will resize those bitmaps to the appropriate size for the current pixel density.
If you request the dimensions of a pre-scaled resource, the system returns values representing the dimensions after scaling. For example, a bitmap designed at 50×50 pixels for an mdpi screen is scaled to 75×75 pixels on an hdpi screen (if there is no alternative resource for hdpi) and the system reports the size as such.
There are some situations in which you might not want Android to pre-scale a resource. The easiest way to avoid pre-scaling is to put the resource in a resource directory with the nodpi configuration qualifier. For example:
When the system uses the icon.png bitmap from this folder, it does not scale it based on the current device density.
Auto-scaling of pixel dimensions and coordinates
You can disable pre-scaling dimensions and images by setting android:anyDensity to «false» in the manifest or programmatically for a Bitmap by setting inScaled to «false» . In this case, the system auto-scales any absolute pixel coordinates and pixel dimension values at draw time. It does this to ensure that pixel-defined screen elements are still displayed at approximately the same physical size as they would be at the baseline pixel density (mdpi). The system handles this scaling transparently to the app and reports the scaled pixel dimensions to the app, rather than physical pixel dimensions.
For instance, suppose a device has a WVGA high-density screen, which is 480×800 and about the same size as a traditional HVGA screen, but it’s running an app that has disabled pre-scaling. In this case, the system will «lie» to the app when it queries for screen dimensions, and report 320×533 (the approximate mdpi translation for the pixel density). Then, when the app does drawing operations, such as invalidating the rectangle from (10,10) to (100, 100), the system transforms the coordinates by scaling them the appropriate amount, and actually invalidate the region (15,15) to (150, 150). This discrepancy may cause unexpected behavior if your app directly manipulates the scaled bitmap, but this is considered a reasonable trade-off to keep the performance of apps as good as possible. If you encounter this situation, read Converting dp units to pixel units.
Usually, you should not disable pre-scaling. The best way to support multiple screens is to follow the basic techniques described in this document.
If your app manipulates bitmaps or directly interacts with pixels on the screen in some other way, you might need to take additional steps to support different pixel densities. For example, if you respond to touch gestures by counting the number of pixels that a finger crosses, you need to use the appropriate density- independent pixel values, instead of actual pixels, but you can easily convert between dp and px values.
Test on all pixel densities
It’s important to test your app on multiple devices with different pixel densities so you can ensure your UI scales correctly. Testing on a physical device is easy but you can also use the Android Emulator if you don’t have access to physical devices for all the different pixel densities.
If you would rather test on a physical device, but don’t want to buy the devices, you can use Firebase Test Lab to access devices in a Google data center.
Content and code samples on this page are subject to the licenses described in the Content License. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Источник