- Run/Debug Configuration: Xamarin.Android
- Common settings
- Toolbar
- Before launch
- Xamarin
- Xamarin SDK
- JetBrains Xamarin SDK
- Before you start
- Create and open Xamarin projects
- Xcode integration on macOS
- How it works under the hood
- When you create a new Xamarin macios project
- When you made changes in Xcode and then switch to Rider
- Run and debug Xamarin applications
- Debug a Xamarin project, which was not created with JetBrains Rider
- Webinar recording: Better Xamarin Development with Rider for Mac
Run/Debug Configuration: Xamarin.Android
Run | Edit Configurations | | Xamarin.Android
Use this configuration to run/debug Xamarin.Android applications.
If your solution contains multiple Xamarin projects, you can choose which one should be started.
Select how to deploy your application when you run or debug it:
Default APK — Create an APK as specified in your build configuration.
Nothing — Don’t install an APK on a device. For example, if you prefer to install it manually.
Use this field to pass any adb am start options to the application.
By default, JetBrains Rider will display a dialog where you can choose the target device/emulator each time you run or debug your application.
You can avoid this dialog by choosing Emulator or Connected device in this selector. If you do so, the Name selector appears below it, where you can specify which emulator or device should be used for running/debugging your application.
Common settings
When you edit a run configuration (but not a run configuration template), you can specify the following options:
Specify a name for the run/debug configuration to quickly identify it when editing or running the configuration, for example, from the Run popup Alt+Shift+F10 .
Allow parallel run
Select to allow running multiple instances of this run configuration in parallel.
By default, it is disabled, and when you start this configuration while another instance is still running, JetBrains Rider suggests to stop the running instance and start another one. This is helpful when a run/debug configuration consumes a lot of resources and there is no good reason to run multiple instances.
Store as project file
Save the file with the run configuration settings to share it with other team members. The default location is .idea/runConfigurations . However, if you do not want to share the .idea directory, you can save the configuration to any other directory within the project.
By default, it is disabled, and JetBrains Rider stores run configuration settings in .idea/workspace.xml .
Toolbar
The tree view of run/debug configurations has a toolbar that helps you manage configurations available in your solution as well as adjust default configurations templates.
Create a run/debug configuration.
Delete the selected run/debug configuration. Note that you cannot delete default configurations.
Create a copy of the selected run/debug configuration. Note that you create copies of default configurations.
The button is displayed only when you select a temporary configuration. Click this button to save a temporary configuration as permanent.
Move into new folder / Create new folder. You can group run/debug configurations by placing them into folders.
To create a folder, select the configurations within a category, click , and specify the folder name. If only a category is in focus, an empty folder is created.
Then, to move a configuration into a folder, between the folders or out of a folder, use drag or and buttons.
To remove grouping, select a folder and click .
Click this button to sort configurations in the alphabetical order.
Before launch
In this area, you can specify tasks to be performed before starting the selected run/debug configuration. The tasks are performed in the order they appear in the list.
Click this icon to add one of the following available tasks:
Run External tool : select to run an external application. In the dialog that opens, select one or multiple applications you want to run. If it is not defined in JetBrains Rider yet, add its definition.
Run Another Configuration : select to execute another run/debug configuration. In the dialog that opens, select the configuration to be run.
Build solution : select this option to build the solution before launching the configuration.
Run File Watchers : select this option to have JetBrains Rider apply all the currently active File Watchers.
Run Grunt task : select this option to run a Grunt task.
In the Grunt task dialog that opens, specify the Gruntfile.js where the required task is defined, select the task to execute, and specify the arguments to pass to the Grunt tool.
Specify the location of the Node.js interpreter, the parameters to pass to it, and the path to the grunt-cli package.
Run gulp task : select this option to run a Gulp task.
In the Gulp task dialog that opens, specify the Gulpfile.js where the required task is defined, select the task to execute, and specify the arguments to pass to the Gulp tool.
Specify the location of the Node.js interpreter, the parameters to pass to it, and the path to the gulp package.
Run npm script : select this option to execute an npm script.
In the NPM Script dialog that opens, specify the npm run/debug configuration settings.
Compile TypeScript : select to run the built-in TypeScript compiler and thus make sure that all the changes you made to your TypeScript code are reflected in the generated JavaScript files. In the TypeScript Compile Settings dialog that opens, select or clear the Check errors checkbox to configure the behaviour of the compiler in case any errors are detected:
If the Check errors checkbox is selected, the compiler will show all the errors and the run configuration will not start.
If the Check errors checkbox is cleared, the compiler will show all the detected errors but the run configuration still will be launched.
Generate CoffeeScript Source Maps : select this option to generate the source maps for your CoffeeScript sources. In the dialog that opens, specify where your CoffeeScript source files are located.
Upload files to Remote Host : select this option to have the application files automatically uploaded to the server according to the default server access configuration .
Run Remote External Tool : adds a remote SSH external tool.
Click this icon to remove the selected task from the list.
Click this icon to edit the selected task. Make the necessary changes in the dialog that opens.
/
Click these icons to move the selected task one line up or down in the list. The tasks are performed in the order that they appear in the list.
Select this checkbox to show the run/debug configuration settings prior to actually starting the run/debug configuration.
Activate tool window
By default this checkbox is selected and the Run or the Debug tool window opens when you start the run/debug configuration.
Otherwise, if the checkbox is cleared, the tool window is hidden. However, when the configuration is running, you can open the corresponding tool window for it yourself by pressing Alt+4 or Alt+5 .
Источник
Xamarin
JetBrains Rider supports creating and working with Xamarin applications for both Android and iOS. Although currently JetBrains Rider does not provide a designer or a previewer for Xamarin forms, you can still benefit from code analysis, coding assistance, and debugging features in C#, VB.NET, and other languages, as well as from general IDE features, such as the integrated VCS client.
If other tools that Xamarin relies on (for example, Android SDK, Android Emulator) are configured properly, you will be able to build and run your Xamarin application right from the JetBrains Rider IDE.
Xamarin SDK
To develop Xamarin Applications you need to have a Xamarin SDK on your machine. There are two different Xamarin SDKs — for iOS/Mac and for Android .
Xamarin SDK consists of two parts:
Assemblies with .NET types for the target platform. For example, a .NET type to represent the base OSX NSObject . Using these assemblies, IDE and compiler resolve and build user code.
Tools that transform .NET projects into native applications, which can be deployed and executed on the emulator or a physical device. For example, using these tools .apk packages for Android are built.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK
JetBrains Rider can use different Xamarin SDKs, for example the one from Visual Studio. However, if you do not have Visual Studio on your machine, you can use JetBrains Xamarin SDK prepared and packed by the JetBrains Rider team.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK is a custom build of Xamarin GitHub sources with some improvements and additional code.
Currently JetBrains Xamarin SDK lacks some features compared to Visual Studio Xamarin SDK, but it is in the process of constant improvement.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK is available for Windows and macOS:
There are two JetBrains Xamarin SDK builds available on Windows targeting the following platforms:
Apple platform (iOS, Mac, tvOS, watchOS)
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for iOS development provides a limited feature set on Windows. For example, currently it does not support connecting to a remote Mac and perform full build/deploy.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Apple platforms on Windows ships as a .zip file (
60Mb) and installs into the JetBrains MsBuild directory:
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android development provides a solid feature set. However, fast deployment is currently not supported.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android platforms on Windows ships as a .zip file (
700Mb) and installs into the JetBrains MsBuild directory:
There are two JetBrains Xamarin SDK builds available on macOS targeting the following platforms:
Apple platform (iOS, Mac, tvOS, watchOS)
On macOS, JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Apple platforms provides almost the same feature set as Visual Studio SDK, all known scenarios are supported.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for iOS development on macOS ships as a .dmg file (
700Mb) and installs into:
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android development provides a solid feature set. However, fast deployment is currently not supported.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android development on macOS ships as a .dmg file (
700Mb) and installs into:
Before you start
Xamarin aims to be executed on a variety of different platforms and therefore Xamarin development relies on several different tools for building and running your applications.
On Windows, you can develop Xamarin applications for any platform, but local build and run/debug is limited to Android devices and emulators.
If you use Visual Studio Xamarin SDK, you will be able to build and run your application on iOS and macOS. To do so, configure a Mac agent accessible on the network, and then connect to it ( Tools | iOS | Xamarin Mac Agent ).
Install a Xamarin SDK for iOS on your machine in one of the following ways.
Install Xamarin in Visual Studio. Note that you can use Visual Studio Community, which is free. If you already have Visual Studio installed, you have to add Xamarin support to it.
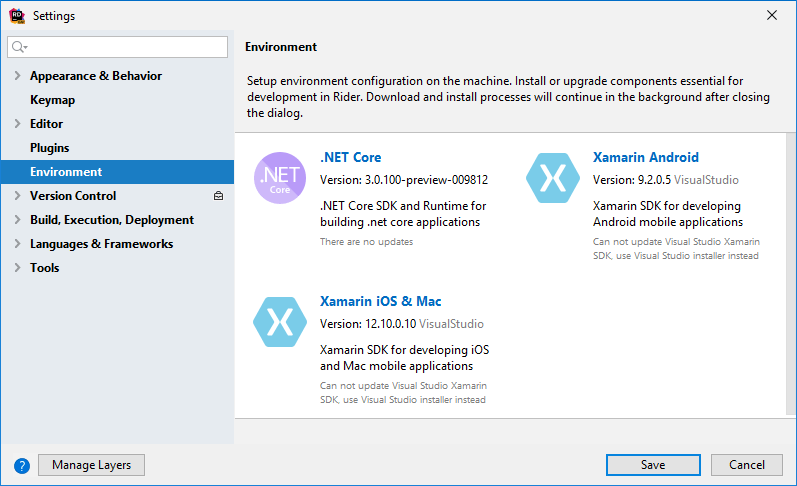
Start installation of Xamarin iOS & Mac on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S and follow the installation wizard. This way JetBrains Rider will automatically download and install JetBrains Xamarin SDK for iOS & Mac.
Alternatively you can clone the Xamarin open-source repo from GitHub, build it and install on the machine. This way is quite complicated and we do not recommend it.
Install Android development tools in one of the following ways:
Start installation of Xamarin Android on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S and follow the installation wizard. This way JetBrains Rider will automatically download and install JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android.
Alternatively, all components that are automatically installed on the the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S , could be also installed manually:
Rider Xamarin Android Support plugin. It has all necessary features, like Android SDK manager.
Android SDK developed and provided by Google. You can install it from Visual Studio, Android Studio, Rider (with Rider Xamarin Android Support plugin), or downloaded as a set of command line tools.
On macOS, you can develop, build and run fully cross-platform Xamarin applications.
Install a Xamarin SDK on your machine in one of the following ways.
Start installation of Xamarin iOS & Mac on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S and follow the installation wizard. This way JetBrains Rider will automatically download and install JetBrains Xamarin SDK for iOS & Mac.
Alternatively you can clone the Xamarin open-source repo from GitHub, build it and install on the machine. This way is quite complicated and we do not recommend it.
For iOS and Mac development, install Xcode. You will need an Apple ID for installing and signing into Xcode. If you do not already have it, you can create a new one at https://appleid.apple.com.
JetBrains Rider will detect Xcode automatically. If you have several Xcode versions, you can choose which one to use on the Build, Execution, Deployment | iOS page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S .
Install Android development tools in one of the following ways:
Start installation of Xamarin Android on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S and follow the installation wizard. This way JetBrains Rider will automatically download and install JetBrains Xamarin SDK for Android.
Alternatively, all components that are automatically installed on the the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S , could be also installed manually:
Rider Xamarin Android Support plugin. It has all necessary features, like Android SDK manager.
Android SDK developed and provided by Google. You can install it from Visual Studio, Android Studio, Rider (with Rider Xamarin Android Support plugin), or downloaded as a set of command line tools.
You can check the status of Xamarin tools and install or update them on the Environment page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S :
Create and open Xamarin projects
JetBrains Rider supports creating new and working with existing projects. Project templates are available, too.
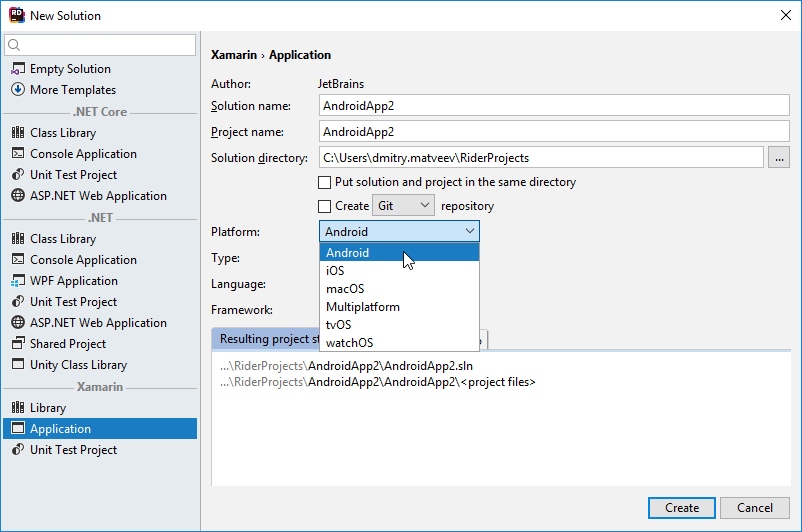
You can create a new Xamarin project in a new solution using File | New. or add a new Xamarin project to the existing solution by right-clicking the solution or solution folder node in the Solution Explorer, and choosing Add | New Project .
Xcode integration on macOS
When developing Xamarin applications on macOS, it is recommended to edit resource files and connect resources to code using Xcode.
You can use context menus of .storyboard , .xib , .plist files or of the Xamarin macios project node to open them in Xcode.
If the file or project has never been opened in Xcode before, JetBrains Rider will generate an Xcode project as follows:
xcodeproj project specifications (a project descriptor similar to csproj but for Xcode) is generated
Source files for all user types inherited NSObject (forms, delegates, views, controls, and so on) in Objective C are generated
All resources (images, designer files) are copied
When the project structure is ready, Xcode will start automatically and you can use it to edit resources. Every time Rider receives focus, it looks for changes (edits in existing files, new files, removed files) and integrates these changes into the Xamarin .NET project. It modifies .designer.cs parts of user types (inherited from NSObject ) and copies back all changed resources.
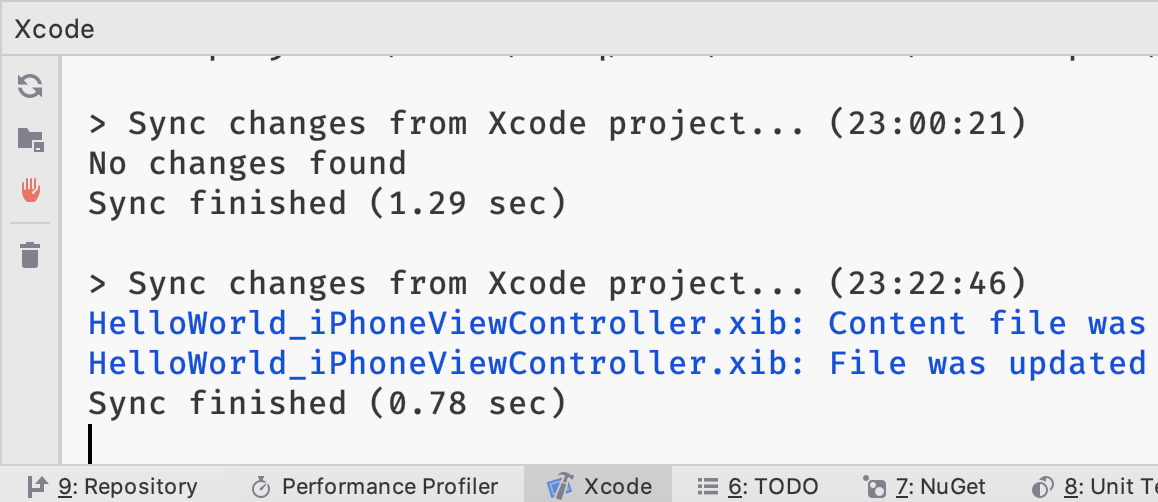
All Xcode-related events are printed in the Xcode console tool window, which appears when you open resources or projects in Xcode:
How it works under the hood
When you create a new Xamarin macios project
JetBrains Rider creates the corresponding xcodeproj project ( pbxproj and other necessary files) project in the obj\xcode subdirectory with all required settings and configurations.
Copies of all content files (views, plist files, images, and so on) are created in that directory.
For each ViewController type JetBrains Rider generates an objc class with actions and outlets.
The generated project is opened automatically in Xcode.
When you made changes in Xcode and then switch to Rider
All modified content files are copied back into .NET project.
Settings are updated.
objc files are parsed and *.designer.cs files are regenerated for view controllers. For all these files you will see a generated header:
Run and debug Xamarin applications
When you create or open a Xamarin project, JetBrains Rider automatically creates run/debug configurations for each Xamarin project in the solution.
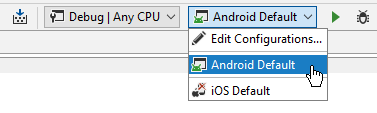
If you want to adjust something in the way your application starts and executes, you can edit and create new run/debug configurations. When you start a Xamarin application from the IDE, you can use the corresponding selector on the navigation bar to choose which configuration should be used:
Debug a Xamarin project, which was not created with JetBrains Rider
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Environment .
Enable Xamarin Android and Xamarin iOS & Mac support.
If you are on Windows and have Xamarin SDK installed via Visual Studio, it will be detected automatically. Otherwise, JetBrains Rider will suggest installing JetBrains Xamarin SDK.
JetBrains Xamarin SDK cannot be installed alongside with Visual Studio Xamarin SDK.
Once Xamarin SDK is installed, you can create Xamarin-specific run/debug configurations.
Open the Run/Debug Configuration dialog in one of the following ways:
Select Run | Edit Configurations from the main menu.
With the Navigation bar visible ( View | Appearance | Navigation Bar ), choose Edit Configurations from the run/debug configuration selector.
Press Alt+Shift+F10 and then press 0 .
In the Run/Debug Configuration dialog that opens, press Alt+Insert or click , then choose Xamarin.Android , Xamarin.iOS , or Xamarin.Mac from the list.
Specify the target project and other parameters if necessary, then click OK .
Use the newly created configuration to run and debug your Xamarin project.
Webinar recording: Better Xamarin Development with Rider for Mac
You can also watch this webinar recording where Dylan Berry explores the various ways Rider can help you improve your coding speed and quality when developing Xamarin apps.
Источник