- Running localhost on android
- Creating a local HTTP server on android
- Access local servers
- # Summary
- # Set up port forwarding
- # Map to custom local domains
- # Set up port forwarding to proxy server
- # Configure proxy settings on your device
- How to Run an Android App against a localhost API
- Moonshoot
- Case 1: If You Are Using the Emulator
- Case 2: You Are Using a Device
- Get Notified on New Future Studio Content and Platform Updates
- Connect Android App to Localhost Web Server Over Wi-Fi
- Connect Android App – is Local Server ready?
- Connect Android App to Localhost Over Wi-Fi
- Set up IP Pool Range in VDSL for Lasting Server Address
- Assign Fixed IP to Your Local Server and Access it in Mobile
Running localhost on android
Jan 29, 2017 · 1 min read
During a workshop on building notifications for web apps, I was introduced to the ability to debug directly from your mobile android phone. I’ve always tried to build my websites and applications as ‘mobile-first’, but up until this point I’ve only used the responsive developer tool in Chrome to simulate mobile screens. It works for the most part, but it doesn’t always accurately reflect how it will render on a mobile device.
So while you are in development, how do you test a localhost server on your android?
- The first part (and most likely my favorite) is unlocking the developer mode on your phone. Under the settings tab, go to ‘about this phone’, scroll down to the ‘build’ and tap it 7 times. When I read this I literally laughed out loud. It felt like instructions for a cheat into a videogame but I am serious that this is the way you unlock this feature.
- The next step is to set up remote debugging through chrome.
- Finally, set up a port forwarding to access local servers.
*One issue I had in adding a port was realizing that the phone and my computer can’t run off the same port number. So if you enter that the port is coming from ‘8080’ on the left-hand input, you need to say the phone’s local address is something like ‘localhost:8081’
Источник
Creating a local HTTP server on android
Some month back, I was trying to implement an app feature that allowed users to communicate(send texts and files) via a local HTTP connection, more like the way Xender works.
I searched for a lot of ways to do this, I found a few libraries but they didn’t offer the speed and simplicity I was looking for.
Eventually, after days of trying different libraries, I found Sun’s HttpServer.
This tutorial assumes you have basic knowledge of Kotlin and android development.
Let’s get started!!
The sun packages are not available on gradle so you’d have to include them in your project’s lib folder.
You can download the two jar files here . (Courtesy of @Oluwalekae)
Copy and paste the files as shown in this picture 👈
In your MainActivity.kt
- create a function to format our client’s inputStream to a string.
2. Declare a variable mHttpServer, data type HttpServer, which will be the instance of our server.
3. Create a method startServer, this is where we would start our server.
4. variable ‘rootHandler’ is an HttpHandler instance used to handle a request to the root path.
You can create as many handlers as you want based on the number of endpoints you want to have.
The mHttpServer.createContext() method allows us assign handlers to endpoints/routes.
We can add a messageHandler, in the end, our MainActivity.kt would look like this.
You can do most operations that you’d normally do on any http server, like Setting headers, handling file uploads, etc.
You can access the server from:
1. your browser from your phone’s browser using “http://127.0.0.1:5000”
2. or another device connected to your phone’s hotspot using “http://192.168.43.1:5000”
because is 5000 is our port number from the code.
Sun httpServer is the fastest server library you can get, trust me.
You can read more about the HttpServer here, and here.
Источник
Access local servers
Published on Monday, April 13, 2015
Technically, I’m a writer
Our latest news, updates, and stories by Meggin Kearney.
Host a site on a development machine web server, then access the content from an Android device.
With a USB cable and Chrome DevTools, you can run a site from a development machine and then view the site on an Android device.
# Summary
- Port forwarding enables you to view content from your development machine’s web server on your Android device.
- If your web server is using a custom domain, you can set up your Android device to access the content at that domain with custom domain mapping.
# Set up port forwarding
Port forwarding enables your Android device to access content that’s being hosted on your development machine’s web server. Port forwarding works by creating a listening TCP port on your Android device that maps to a TCP port on your development machine. Traffic between the ports travel through the USB connection between your Android device and development machine, so the connection doesn’t depend on your network configuration.
To enable port forwarding:
- Set up remote debugging between your development machine and your Android device. When you’re finished, you should see your Android device in the list.
- Click Port forwarding button. localhost:8080 is set up by default.
- Check Enable port forwarding. If you want to set up other ports, follow the steps 4 and 5. Otherwise skip to step 6.
- In the Port textfield on the left, enter the localhost port number from which you want to be able to access the site on your Android device. For example, if you wanted to access the site from localhost:5000 you would enter 5000 .
- In the IP address and port textfield on the right, enter the IP address or hostname on which your site is running on your development machine’s web server, followed by the port number. For example, if your site is running on localhost:7331 you would enter localhost:7331 .
- Click Done.
Port forwarding is now set up. You can see a status indicator of the port forward at the top as well as besides the device name.
To view the content, open up Chrome on your Android device and go to the localhost port that you specified in the Device port field. For example, if you entered 5000 in the field, then you would go to localhost:5000 .
# Map to custom local domains
Custom domain mapping enables you to view content on an Android device from a web server on your development machine that is using a custom domain.
For example, suppose that your site uses a third-party JavaScript library that only works on the allow-listed domain chrome.devtools . So, you create an entry in your hosts file on your development machine to map this domain to localhost (i.e. 127.0.0.1 chrome.devtools ). After setting up custom domain mapping and port forwarding, you’ll be able to view the site on your Android device at the URL chrome.devtools .
# Set up port forwarding to proxy server
To map a custom domain you must run a proxy server on your development machine. Examples of proxy servers are Charles, Squid, and Fiddler.
To set up port forwarding to a proxy:
- Run the proxy server and note the port that it’s using. Note: The proxy server and your web server must run on different ports.
- Set up port forwarding to your Android device. For the local address field, enter localhost: followed by the port that your proxy server is running on. For example, if it’s running on port 8000 , then you would enter localhost:8000 . In the device port field enter the number that you want your Android device to listen on, such as 3333 .
# Configure proxy settings on your device
Next, you need to configure your Android device to communicate with the proxy server.
- On your Android device go to Settings >Wi-Fi.
- Long-press the name of the network that you are currently connected to. Note: Proxy settings apply per network.
- Tap Modify network.
- Tap Advanced options. The proxy settings display.
- Tap the Proxy menu and select Manual.
- For the Proxy hostname field, enter localhost .
- For the Proxy port field, enter the port number that you entered for device port in the previous section.
- Tap Save.
With these settings, your device forwards all of its requests to the proxy on your development machine. The proxy makes requests on behalf of your device, so requests to your customized local domain are properly resolved.
Now you can access custom domains on your Android device Android just as you would on the development machine.
If your web server is running off of a non-standard port, remember to specify the port when requesting the content from your Android device. For example, if your web server is using the custom domain chrome.devtools on port 7331 , when you view the site from your Android device you should be using the URL chrome.devtools:7331 .
Tip: To resume normal browsing, remember to revert the proxy settings on your Android device after you disconnect from the development machine.
Last updated: Monday, April 13, 2015 • Improve article
Источник
How to Run an Android App against a localhost API
Moonshoot
Moonshoot is a
Student Feature.
Last week, when working on the new release of the eat foody Android app, I run into a significant issue. For some reason, my requests to our staging API were incomplete or somehow broken after updating to the newest version of our request library. After some rather clueless digging I knew I needed to run the broken requests against a debuggable server environment. This allows me to compare how the request leaves the Android app and arrives at the server. In my case, the local API endpoints were at http://localhost:3000/api .
Before googling the issue I attempted to change the code of eat foody’s Android app to run against http://localhost:3000/api . However, this rather obvious choice does not work, since localhost is the Android emulator or the device itself. The next two sections will describe solutions for making requests to your localhost server.
Case 1: If You Are Using the Emulator
The bad news first: this solution only work with the emulator and not with your actual devices. So start up your emulator (since it could take a while until it is ready). Start your server at localhost and attach the debugger. Next, change the API endpoints in your Android code to http://10.0.2.2 . This reroutes the requests from your emulator to your computer’s localhost. Run the Android app on the emulator and cause the requests you want to debug. This should enable you to catch the incoming request on the localhost server. In my case, this quickly resolved my issue.
Obviously, the use of this method is not limited to debugging. If you are on the train and have no Internet connection, you can use this approach to develop your app anyway. One last tip: if you use GenyMotion as your emulator, use http://10.0.3.2 as the localhost rerouting address.
Case 2: You Are Using a Device
A different approach is necessary when you want to avoid using the emulator. However, this solution requires you to be on the same Wi-Fi network. Change the API request endpoint to your computer’s local IP address, e.g. http://192.168.0.142 and run the app on your device. Once again, all requests should go against the localhost server running on your computer.
Let us know if you have any questions or issues: @futurestud_io
Get Notified on New Future Studio
Content and Platform Updates
Get your weekly push notification about new and trending
Future Studio content and recent platform enhancements
Источник
Connect Android App to Localhost Web Server Over Wi-Fi
DISCLOSURE: This article may contain affiliate links and any sales made through such links will reward us a small commission, at no extra cost for you. Read more about Affiliate Disclosure here.
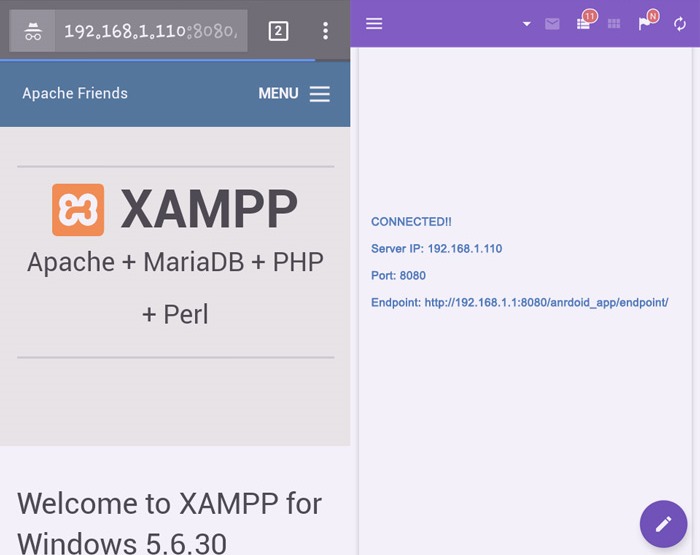
Connect android app to localhost over Wi-Fi and it gives a lot of flexibility to develop, run and test the app. My scenario was that I had created an android app which had a need to access my local web server (XAMPP) for faster testing and the application was running on the device as well as an emulator.
You might be using either PHP + MySQL or C# + MSSQL on Apache/IIS Server respectively. And you need to code and test your app before moving them to production. You can access or connect the android app to the local web server over Wi-Fi, without the need of internet connection. It saves you from waiting for the response from a remote host or your live server.
Check some excellent articles for easier PHP development.
Connect Android App – is Local Server ready?
I believe that you have already set up your localhost and files to serve the request being received from the device. Ensure that your local server is accessible (type http://localhost/ in your PC’s browser and get a response).
Just FYI, the article is intended to answer the following similar questions as well:
- Test local website on a mobile device
- Run android app against a localhost API
- How to access localhost from a mobile browser
- How to access localhost from Android over Wi-Fi
- Connecting android app to your WAMP/XAMPP server
- Connecting to localhost web server from android application
Connect Android App to Localhost Over Wi-Fi
Simply typing localhost or http://127.0.0.1 in your app code won’t work. You need to obtain the IPv4 address of your PC/server. If you’re using Windows PC, you can follow these steps to find the IPv4 address:
- On Start menu, type cmd to open Command Prompt.
- Run ipconfig command there.
- You will get the IPv4 address as highlighted in the image below.
As you can see my IPv4 address is 192.168.1.110. However, you might be worrying, do each time I need to check IP? No, absolutely not. Let me share you three facts.
- Generally, it’s needed to check only when your router gets reset.
- In my case, I had set IP address pool range in my VDSL modem and I’m getting the same address for my local server since years regardless of PC/router restart. I have mentioned how I did it to connect the android app to localhost running on my computer.
- The third is, routers/modems give you the option to reserve the IPv4 address for the specific device and you can assign fixed IP to your local server.
So fix once and always use that IP to access localhost from a mobile browser as well as your app.
Set up IP Pool Range in VDSL for Lasting Server Address
This step is optional and based on my personal experience. You generally don’t need it. Try only if your IPv4 address varies too much. Also, note that these are general instructions only and might vary from router to router.
- In your PC/laptop access http://192.168.1.1 and enter adequate credentials.
- You will have your router configuration page.
- Find the DHCP Server Settings page there.
On this page, set IP Pool Range and save changes. An IP Pool Range is a set of IP address range used by your router/modem to assign IPs to connected wired or wireless devices. Finally, don’t forget to restart the local server to take effect.
This page also shows you the list of connected devices along with their Mac Address. We will use it if this pool range setting doesn’t work for you.
Assign Fixed IP to Your Local Server and Access it in Mobile
Lastly, you can assign a permanent IP address to your local web server if above is not sufficient. Find DHCP Reserved or DHCP Static IP Configuration page in router configuration pages. You need to have Mac Address of localhost PC. Also, there is plenty of information available on the internet to find Mac Address of a device.
Give one desired IP address from range 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.255 (192.168.1.1 is normally the address of the router itself). Specify Mac Address (without colons if instructed) of local web server machine and save it. Restart your machine; confirm address using ipconfig command and you’re done.
Источник